1.8 KiB
Use TestableMock In IDE
Use IntelliJ IDE
IntelliJ IDE supports the JSR-269 annotation processor and the maven-surefire-plugin arguments very well (both are techniques back the TestableMock). Usually you don't need any special configuration to make everything work, it's all out of the box.
Use Eclipse IDE
Since the built-in compilation feature of Eclipse is based on a self-made compiler, it is not compatible with the standard javac compilation process, which will cause the @EnablePrivateAccess annotation to be invalid when running test cases in the IDE. However, the function of accessing the private members of the class under test through the PrivateAccessor tool class will not be affected by differences in the compiler.
If the @EnablePrivateAccess annotation is used in the project, you can use mvn test -Dtest=<TestClassName> and mvn test -Dtest=<TestClassName>#<TestCaseName> in the command line of Eclipse to run a single test class or test case.
At the same time, because the built-in unit test executor of Eclipse completely ignores the configuration of the pom.xml file, additional configuration is required to use the Mock function.
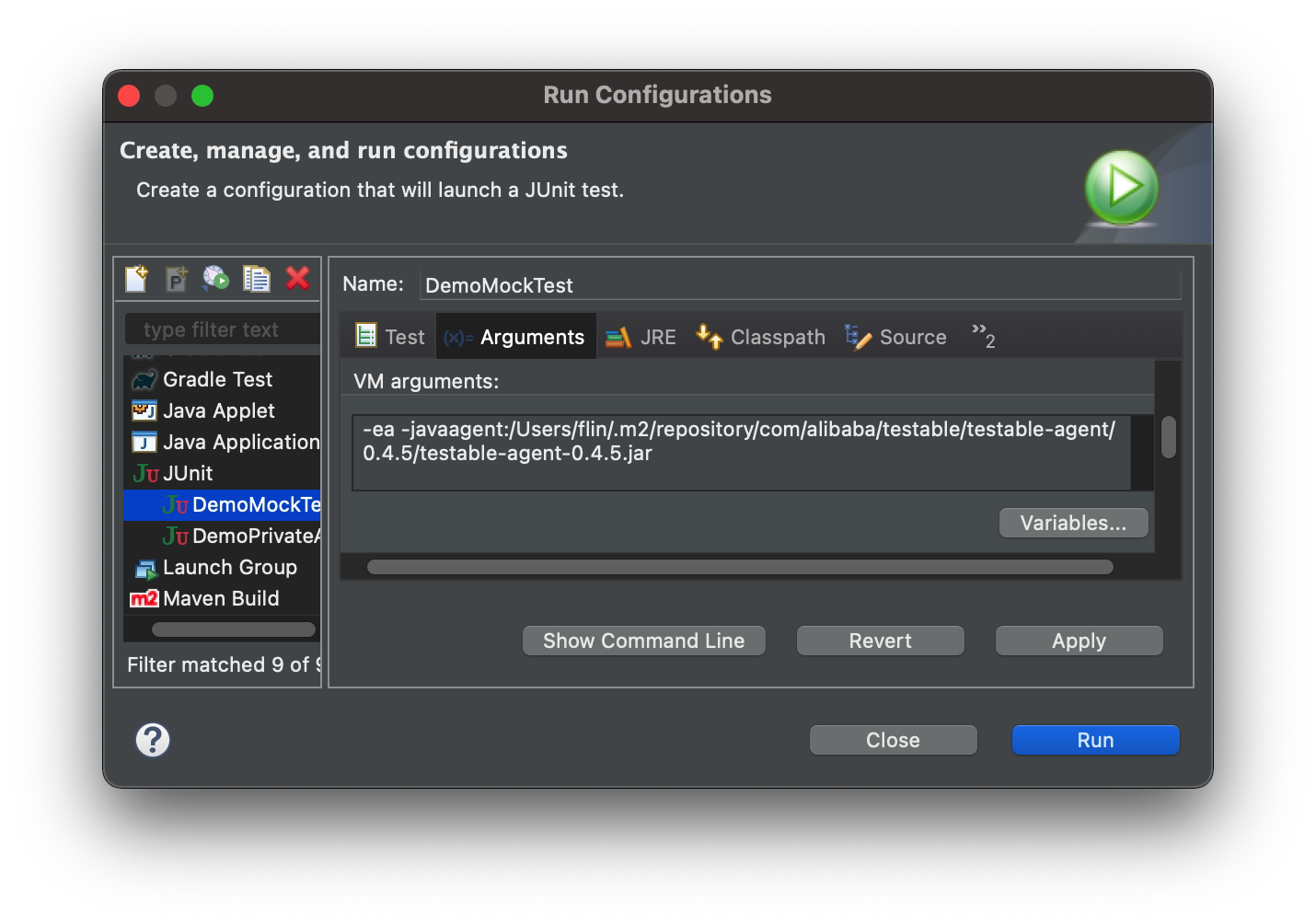
Take the use of JUnit as an example. You need to pull down from the small triangle next to the run button on the IDE toolbar, select "Run Configurations...", select the task to run the unit test on the left side, and switch to "arguments" Tab on the right side, append a -javaagent: parameter in the "VM Options", the following figure is an example, note that the testable-agent package should be modified to match the actual situation of the local Maven repository path.