5.7 KiB
基于 Hystrix 线程池技术实现资源隔离
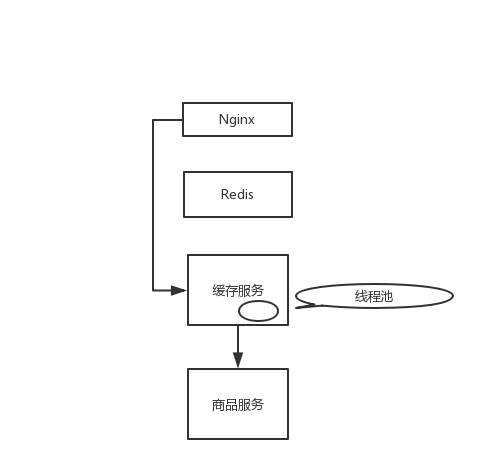
上一讲提到,如果从 Nginx 开始,缓存都失效了,Nginx 会直接通过缓存服务调用商品服务获取最新商品数据(我们基于电商项目做个讨论),有可能出现调用延时而把缓存服务资源耗尽的情况。这里,我们就来说说,怎么通过 Hystrix 线程池技术实现资源隔离。
资源隔离,就是说,你如果要把对某一个依赖服务的所有调用请求,全部隔离在同一份资源池内,不会去用其它资源了,这就叫资源隔离。哪怕对这个依赖服务,比如说商品服务,现在同时发起的调用量已经到了 1000,但是分配给商品服务线程池内就 10 个线程,最多就只会用这 10 个线程去执行。不会因为对商品服务调用的延迟,将 Tomcat 内部所有的线程资源全部耗尽。
Hystrix 进行资源隔离,其实是提供了一个抽象,叫做 Command。这也是 Hystrix 最最基本的资源隔离技术。
利用 HystrixCommand 获取单条数据
我们通过将调用商品服务的操作封装在 HystrixCommand 中,限定一个 key,比如下面的 GetProductInfoCommandGroup,在这里我们可以简单认为这是一个线程池,每次调用商品服务,就只会用该线程池中的资源,不会再去用其它线程资源了。
public class GetProductInfoCommand extends HystrixCommand<ProductInfo> {
private Long productId;
public GetProductInfoCommand(Long productId) {
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("GetProductInfoCommandGroup"));
this.productId = productId;
}
@Override
protected ProductInfo run() {
String url = "http://localhost:8081/getProductInfo?productId=" + productId;
// 调用商品服务接口
String response = HttpClientUtils.sendGetRequest(url);
return JSONObject.parseObject(response, ProductInfo.class);
}
}
我们在缓存服务接口中,根据 productId 创建 Command 并执行,获取到商品数据。
@RequestMapping("/getProductInfo")
@ResponseBody
public String getProductInfo(Long productId) {
HystrixCommand<ProductInfo> getProductInfoCommand = new GetProductInfoCommand(productId);
// 通过command执行,获取最新商品数据
ProductInfo productInfo = getProductInfoCommand.execute();
System.out.println(productInfo);
return "success";
}
上面执行的是 execute() 方法,其实是同步的。也可以对 command 调用 queue() 方法,它仅仅是将 command 放入线程池的一个等待队列,就立即返回,拿到一个 Future 对象,后面可以继续做其它一些事情,然后过一段时间对 Future 调用 get() 方法获取数据。这是异步的。
利用 HystrixObservableCommand 批量获取数据
只要是获取商品数据,全部都绑定到同一个线程池里面去,我们通过 HystrixObservableCommand 的一个线程去执行,而在这个线程里面,批量把多个 productId 的 productInfo 拉回来。
public class GetProductInfosCommand extends HystrixObservableCommand<ProductInfo> {
private String[] productIds;
public GetProductInfosCommand(String[] productIds) {
// 还是绑定在同一个线程池
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("GetProductInfoGroup"));
this.productIds = productIds;
}
@Override
protected Observable<ProductInfo> construct() {
return Observable.unsafeCreate((Observable.OnSubscribe<ProductInfo>) subscriber -> {
for (String productId : productIds) {
// 批量获取商品数据
String url = "http://localhost:8081/getProductInfo?productId=" + productId;
String response = HttpClientUtils.sendGetRequest(url);
ProductInfo productInfo = JSONObject.parseObject(response, ProductInfo.class);
subscriber.onNext(productInfo);
}
subscriber.onCompleted();
}).subscribeOn(Schedulers.io());
}
}
在缓存服务接口中,根据传来的 id 列表,比如是以 , 分隔的 id 串,通过上面的 HystrixObservableCommand,执行 Hystrix 的一些 API 方法,获取到所有商品数据。
public String getProductInfos(String productIds) {
String[] productIdArray = productIds.split(",");
HystrixObservableCommand<ProductInfo> getProductInfosCommand = new GetProductInfosCommand(productIdArray);
Observable<ProductInfo> observable = getProductInfosCommand.observe();
observable.subscribe(new Observer<ProductInfo>() {
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("获取完了所有的商品数据");
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* 获取完一条数据,就回调一次这个方法
* @param productInfo
*/
@Override
public void onNext(ProductInfo productInfo) {
System.out.println(productInfo);
}
});
return "success";
}
我们回过头来,看看 Hystrix 线程池技术是如何实现资源隔离的。
从 Nginx 开始,缓存都失效了,那么 Nginx 通过缓存服务去调用商品服务。缓存服务默认的线程大小是 10 个,最多就只有 10 个线程去调用商品服务的接口。即使商品服务接口故障了,最多就只有 10 个线程会 hang 死在调用商品服务接口的路上,缓存服务的 Tomcat 内其它的线程还是可以用来调用其它的服务,干其它的事情。