| images | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| mixed_tabs_and_spaces.py | ||
| README.md | ||

What the f*ck Python! 🐍
An interesting collection of surprising snippets and lesser-known Python features.
Python, being a beautifully designed high-level and interpreter-based programming language, provides us with many features for the programmer's comfort. But sometimes, the outcomes of a Python snippet may not seem obvious to a regular user at first sight.
Here is a fun project to collect such tricky & counter-intuitive examples and lesser-known features in Python, attempting to discuss what exactly is happening under the hood!
While some of the examples you see below may not be WTFs in the truest sense, but they'll reveal some of the interesting parts of Python that you might be unaware of. I find it a nice way to learn the internals of a programming language, and I think you'll find them interesting as well!
If you're an experienced Python programmer, you can take it as a challenge to get most of them right in first attempt. You may be already familiar with some of these examples, and I might be able to revive sweet old memories of yours being bitten by these gotchas 😅
PS: If you're a returning reader, you can learn about the new modifications here.
So, here we go...
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Structure of the Examples
- Usage
- 👀 Examples
- Section: Strain your brain!
- > Strings can be tricky sometimes/微妙的字符串 *
- > Time for some hash brownies!/是时候来点蛋糕了!
- > Return return everywhere!/到处返回!
- > Deep down, we're all the same./本质上,我们都一样. *
- > For what?/为什么?
- > Evaluation time discrepancy/执行时机差异
- >
isis not what it is!/出人意料的is! - > A tic-tac-toe where X wins in the first attempt!/一蹴即至!
- > The sticky output function/麻烦的输出
- >
is not ...is notis (not ...)/is not ...不是is (not ...) - > The surprising comma/意外的逗号
- > Backslashes at the end of string/字符串末尾的反斜杠
- > not knot!/别纠结!
- > Half triple-quoted strings/三个引号
- > Midnight time doesn't exist?/不存在的午夜?
- > What's wrong with booleans?/布尔你咋了?
- > Class attributes and instance attributes/类属性和实例属性
- > yielding None/生成 None
- > Mutating the immutable!/强人所难
- > The disappearing variable from outer scope/消失的外部变量
- > When True is actually False/真亦假
- > From filled to None in one instruction.../从有到无...
- > Subclass relationships/子类关系 *
- > The mysterious key type conversion/神秘的键型转换 *
- > Let's see if you can guess this?/看看你能否猜到这一点?
- Section: Appearances are deceptive!
- Section: Watch out for the landmines!
- > Modifying a dictionary while iterating over it/迭代字典时的修改
- > Stubborn
deloperator/坚强的del* - > Deleting a list item while iterating/迭代列表时删除元素
- > Loop variables leaking out!/循环变量泄漏!
- > Beware of default mutable arguments!/当心默认的可变参数!
- > Catching the Exceptions/捕获异常
- > Same operands, different story!/同人不同命!
- > The out of scope variable/外部作用域变量
- > Be careful with chained operations/小心链式操作
- > Name resolution ignoring class scope/忽略类作用域的名称解析
- > Needle in a Haystack/大海捞针
- Section: The Hidden treasures!
- Section: Miscellaneous
- Section: Strain your brain!
- Contributing
- Acknowledgements
- 🎓 License
Structure of the Examples
All the examples are structured like below:
> Some fancy Title *
The asterisk at the end of the title indicates the example was not present in the first release and has been recently added.
# Setting up the code. # Preparation for the magic...Output (Python version):
>>> triggering_statement Probably unexpected output(Optional): One line describing the unexpected output.
💡 Explanation:
- Brief explanation of what's happening and why is it happening.
Output:Setting up examples for clarification (if necessary)>>> trigger # some example that makes it easy to unveil the magic # some justified output
Note: All the examples are tested on Python 3.5.2 interactive interpreter, and they should work for all the Python versions unless explicitly specified in the description.
Usage
A nice way to get the most out of these examples, in my opinion, will be just to read the examples chronologically, and for every example:
- Carefully read the initial code for setting up the example. If you're an experienced Python programmer, most of the times you will successfully anticipate what's going to happen next.
- Read the output snippets and,
- Check if the outputs are the same as you'd expect.
- Make sure if you know the exact reason behind the output being the way it is.
- If no, take a deep breath, and read the explanation (and if you still don't understand, shout out! and create an issue here).
- If yes, give a gentle pat on your back, and you may skip to the next example.
PS: You can also read WTFpython at the command line. There's a pypi package and an npm package (supports colored formatting) for the same.
To install the npm package wtfpython
$ npm install -g wtfpython
Alternatively, to install the pypi package wtfpython
$ pip install wtfpython -U
Now, just run wtfpython at the command line which will open this collection in your selected $PAGER.
👀 Examples
Section: Strain your brain!
> Strings can be tricky sometimes/微妙的字符串 *
1.
>>> a = "some_string"
>>> id(a)
140420665652016
>>> id("some" + "_" + "string") # 注意两个的id值是相同的.
140420665652016
2.
>>> a = "wtf"
>>> b = "wtf"
>>> a is b
True
>>> a = "wtf!"
>>> b = "wtf!"
>>> a is b
False
>>> a, b = "wtf!", "wtf!"
>>> a is b
True # 3.7 版本返回结果为 False.
3.
>>> 'a' * 20 is 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa'
True
>>> 'a' * 21 is 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa'
False # 3.7 版本返回结果为 True
很好理解, 对吧?
💡 说明:
-
这些行为是由于 Cpython 在编译优化时, 某些情况下会尝试使用已经存在的不可变对象而不是每次都创建一个新对象. (这种行为被称作字符串的驻留[string interning])
-
发生驻留之后, 许多变量可能指向内存中的相同字符串对象. (从而节省内存)
-
在上面的代码中, 字符串是隐式驻留的. 何时发生隐式驻留则取决于具体的实现. 这里有一些方法可以用来猜测字符串是否会被驻留:
-
所有长度为 0 和长度为 1 的字符串都被驻留.
-
字符串在编译时被实现 (
'wtf'将被驻留, 但是''.join(['w', 't', 'f'])将不会被驻留) -
字符串中只包含字母,数字或下划线时将会驻留. 所以
'wtf!'由于包含!而未被驻留. 可以在这里找到 CPython 对此规则的实现.
-
-
当在同一行将
a和b的值设置为"wtf!"的时候, Python 解释器会创建一个新对象, 然后同时引用第二个变量(译: 仅适用于3.7以下, 详细情况请看这里). 如果你在不同的行上进行赋值操作, 它就不会“知道”已经有一个wtf!对象 (因为"wtf!"不是按照上面提到的方式被隐式驻留的). 它是一种编译器优化, 特别适用于交互式环境. -
常量折叠(constant folding) 是 Python 中的一种 窥孔优化(peephole optimization) 技术. 这意味着在编译时表达式
'a'*20会被替换为'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa'以减少运行时的时钟周期. 只有长度小于 20 的字符串才会发生常量折叠. (为啥? 想象一下由于表达式'a'*10**10而生成的.pyc文件的大小). 相关的源码实现在这里. -
如果你是使用 3.7 版本中运行上述示例代码, 会发现部分代码的运行结果与注释说明相同. 这是因为在 3.7 版本中, 常量折叠已经从窥孔优化器迁移至新的 AST 优化器, 后者可以以更高的一致性来执行优化. (由 Eugene Toder 和 INADA Naoki 在 bpo-29469 和 bpo-11549 中贡献.)
-
(译: 但是在最新的 3.8 版本中, 结果又变回去了. 虽然 3.8 版本和 3.7 版本一样, 都是使用 AST 优化器. 目前不确定官方对 3.8 版本的 AST 做了什么调整.)
> Time for some hash brownies!/是时候来点蛋糕了!
- hash brownie指一种含有大麻成分的蛋糕, 所以这里是句双关
1.
some_dict = {}
some_dict[5.5] = "Ruby"
some_dict[5.0] = "JavaScript"
some_dict[5] = "Python"
Output:
>>> some_dict[5.5]
"Ruby"
>>> some_dict[5.0]
"Python"
>>> some_dict[5]
"Python"
"Python" 消除了 "JavaScript" 的存在?
💡 说明:
- Python 字典通过检查键值是否相等和比较哈希值来确定两个键是否相同.
- 具有相同值的不可变对象在Python中始终具有相同的哈希值.
注意: 具有不同值的对象也可能具有相同的哈希值(哈希冲突).>>> 5 == 5.0 True >>> hash(5) == hash(5.0) True - 当执行
some_dict[5] = "Python"语句时, 因为Python将5和5.0识别为some_dict的同一个键, 所以已有值 "JavaScript" 就被 "Python" 覆盖了. - 这个 StackOverflow的 回答 漂亮地解释了这背后的基本原理.
> Return return everywhere!/到处返回!
def some_func():
try:
return 'from_try'
finally:
return 'from_finally'
Output:
>>> some_func()
'from_finally'
💡 说明:
- 当在 "try...finally" 语句的
try中执行return,break或continue后,finally子句依然会执行. - 函数的返回值由最后执行的
return语句决定. 由于finally子句一定会执行, 所以finally子句中的return将始终是最后执行的语句.
> Deep down, we're all the same./本质上,我们都一样. *
class WTF:
pass
Output:
>>> WTF() == WTF() # 两个不同的对象应该不相等
False
>>> WTF() is WTF() # 也不相同
False
>>> hash(WTF()) == hash(WTF()) # 哈希值也应该不同
True
>>> id(WTF()) == id(WTF())
True
💡 说明:
-
当调用
id函数时, Python 创建了一个WTF类的对象并传给id函数. 然后id函数获取其id值 (也就是内存地址), 然后丢弃该对象. 该对象就被销毁了. -
当我们连续两次进行这个操作时, Python会将相同的内存地址分配给第二个对象. 因为 (在CPython中)
id函数使用对象的内存地址作为对象的id值, 所以两个对象的id值是相同的. -
综上, 对象的id值仅仅在对象的生命周期内唯一. 在对象被销毁之后, 或被创建之前, 其他对象可以具有相同的id值.
-
那为什么
is操作的结果为False呢? 让我们看看这段代码.class WTF(object): def __init__(self): print("I") def __del__(self): print("D")Output:
>>> WTF() is WTF() I I D D False >>> id(WTF()) == id(WTF()) I D I D True正如你所看到的, 对象销毁的顺序是造成所有不同之处的原因.
> For what?/为什么?
some_string = "wtf"
some_dict = {}
for i, some_dict[i] in enumerate(some_string):
pass
Output:
>>> some_dict # 创建了索引字典.
{0: 'w', 1: 't', 2: 'f'}
💡 说明:
-
Python 语法 中对
for的定义是:for_stmt: 'for' exprlist 'in' testlist ':' suite ['else' ':' suite]其中
exprlist指分配目标. 这意味着对可迭代对象中的每一项都会执行类似{exprlist} = {next_value}的操作.一个有趣的例子说明了这一点:
for i in range(4): print(i) i = 10Output:
0 1 2 3你可曾觉得这个循环只会运行一次?
💡 说明:
- 由于循环在Python中工作方式, 赋值语句
i = 10并不会影响迭代循环, 在每次迭代开始之前, 迭代器(这里指range(4)) 生成的下一个元素就被解包并赋值给目标列表的变量(这里指i)了.
- 由于循环在Python中工作方式, 赋值语句
-
在每一次的迭代中,
enumerate(some_string)函数就生成一个新值i(计数器增加) 并从some_string中获取一个字符. 然后将字典some_dict键i(刚刚分配的) 的值设为该字符. 本例中循环的展开可以简化为:>>> i, some_dict[i] = (0, 'w') >>> i, some_dict[i] = (1, 't') >>> i, some_dict[i] = (2, 'f') >>> some_dict
> Evaluation time discrepancy/执行时机差异
1.
array = [1, 8, 15]
g = (x for x in array if array.count(x) > 0)
array = [2, 8, 22]
Output:
>>> print(list(g))
[8]
2.
array_1 = [1,2,3,4]
g1 = (x for x in array_1)
array_1 = [1,2,3,4,5]
array_2 = [1,2,3,4]
g2 = (x for x in array_2)
array_2[:] = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output:
>>> print(list(g1))
[1,2,3,4]
>>> print(list(g2))
[1,2,3,4,5]
💡 说明
- 在生成器表达式中,
in子句在声明时执行, 而条件子句则是在运行时执行. - 所以在运行前,
array已经被重新赋值为[2, 8, 22], 因此对于之前的1,8和15, 只有count(8)的结果是大于0的, 所以生成器只会生成8. - 第二部分中
g1和g2的输出差异则是由于变量array_1和array_2被重新赋值的方式导致的. - 在第一种情况下,
array_1被绑定到新对象[1,2,3,4,5], 因为in子句是在声明时被执行的, 所以它仍然引用旧对象[1,2,3,4](并没有被销毁). - 在第二种情况下, 对
array_2的切片赋值将相同的旧对象[1,2,3,4]原地更新为[1,2,3,4,5]. 因此g2和array_2仍然引用同一个对象(这个对象现在已经更新为[1,2,3,4,5]).
> is is not what it is!/出人意料的is!
下面是一个在互联网上非常有名的例子.
>>> a = 256
>>> b = 256
>>> a is b
True
>>> a = 257
>>> b = 257
>>> a is b
False
>>> a = 257; b = 257
>>> a is b
True
💡 说明:
is 和 == 的区别
is运算符检查两个运算对象是否引用自同一对象 (即, 它检查两个运算对象是否相同).==运算符比较两个运算对象的值是否相等.- 因此
is代表引用相同,==代表值相等. 下面的例子可以很好的说明这点,>>> [] == [] True >>> [] is [] # 这两个空列表位于不同的内存地址. False
256 是一个已经存在的对象, 而 257 不是
当你启动Python 的时候, 数值为 -5 到 256 的对象就已经被分配好了. 这些数字因为经常被使用, 所以会被提前准备好.
Python 通过这种创建小整数池的方式来避免小整数频繁的申请和销毁内存空间.
引用自 https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/long.html
当前的实现为-5到256之间的所有整数保留一个整数对象数组, 当你创建了一个该范围内的整数时, 你只需要返回现有对象的引用. 所以改变1的值是有可能的. 我怀疑这种行为在Python中是未定义行为. :-)
>>> id(256)
10922528
>>> a = 256
>>> b = 256
>>> id(a)
10922528
>>> id(b)
10922528
>>> id(257)
140084850247312
>>> x = 257
>>> y = 257
>>> id(x)
140084850247440
>>> id(y)
140084850247344
这里解释器并没有智能到能在执行 y = 257 时意识到我们已经创建了一个整数 257, 所以它在内存中又新建了另一个对象.
当 a 和 b 在同一行中使用相同的值初始化时,会指向同一个对象.
>>> a, b = 257, 257
>>> id(a)
140640774013296
>>> id(b)
140640774013296
>>> a = 257
>>> b = 257
>>> id(a)
140640774013392
>>> id(b)
140640774013488
- 当 a 和 b 在同一行中被设置为
257时, Python 解释器会创建一个新对象, 然后同时引用第二个变量. 如果你在不同的行上进行, 它就不会 "知道" 已经存在一个257对象了. - 这是一种特别为交互式环境做的编译器优化. 当你在实时解释器中输入两行的时候, 他们会单独编译, 因此也会单独进行优化. 如果你在
.py文件中尝试这个例子, 则不会看到相同的行为, 因为文件是一次性编译的.
> A tic-tac-toe where X wins in the first attempt!/一蹴即至!
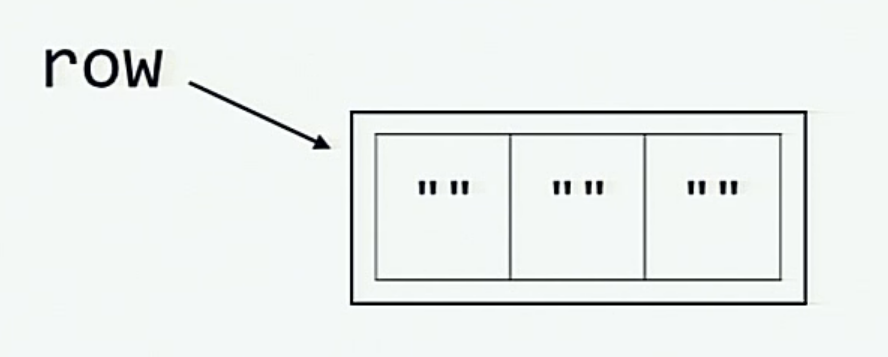
# 我们先初始化一个变量row
row = [""]*3 #row i['', '', '']
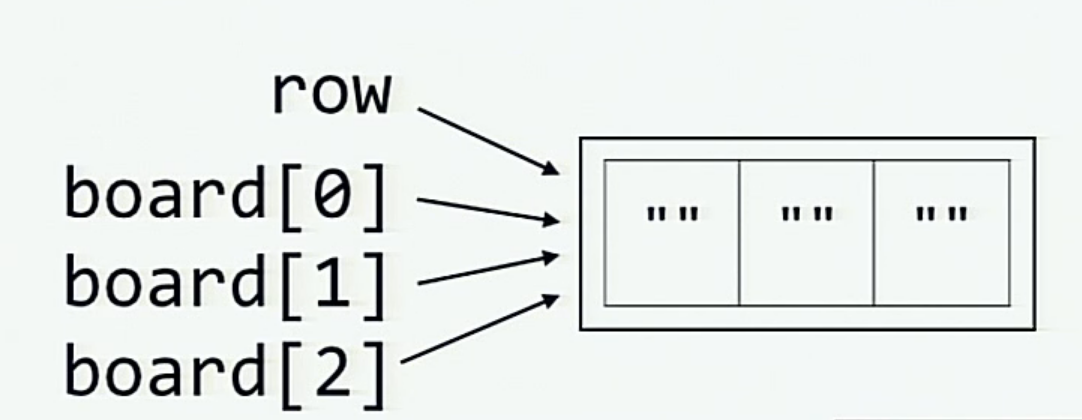
# 并创建一个变量board
board = [row]*3
Output:
>>> board
[['', '', ''], ['', '', ''], ['', '', '']]
>>> board[0]
['', '', '']
>>> board[0][0]
''
>>> board[0][0] = "X"
>>> board
[['X', '', ''], ['X', '', ''], ['X', '', '']]
我们有没有赋值过3个 "X" 呢?
💡 说明:
当我们初始化 row 变量时, 下面这张图展示了内存中的情况。
而当通过对 row 做乘法来初始化 board 时, 内存中的情况则如下图所示 (每个元素 board[0], board[1] 和 board[2] 都和 row 一样引用了同一列表.)
我们可以通过不使用变量 row 生成 board 来避免这种情况. (这个issue提出了这个需求.)
>>> board = [['']*3 for _ in range(3)]
>>> board[0][0] = "X"
>>> board
[['X', '', ''], ['', '', ''], ['', '', '']]
> The sticky output function/麻烦的输出
funcs = []
results = []
for x in range(7):
def some_func():
return x
funcs.append(some_func)
results.append(some_func()) # 注意这里函数被执行了
funcs_results = [func() for func in funcs]
Output:
>>> results
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> funcs_results
[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]
即使每次在迭代中将 some_func 加入 funcs 前的 x 值都不相同, 所有的函数还是都返回6.
// 再换个例子
>>> powers_of_x = [lambda x: x**i for i in range(10)]
>>> [f(2) for f in powers_of_x]
[512, 512, 512, 512, 512, 512, 512, 512, 512, 512]
💡 说明:
-
当在循环内部定义一个函数时, 如果该函数在其主体中使用了循环变量, 则闭包函数将与循环变量绑定, 而不是它的值. 因此, 所有的函数都是使用最后分配给变量的值来进行计算的.
-
可以通过将循环变量作为命名变量传递给函数来获得预期的结果. 为什么这样可行? 因为这会在函数内再次定义一个局部变量.
funcs = [] for x in range(7): def some_func(x=x): return x funcs.append(some_func)Output:
>>> funcs_results = [func() for func in funcs] >>> funcs_results [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
> is not ... is not is (not ...)/is not ... 不是 is (not ...)
>>> 'something' is not None
True
>>> 'something' is (not None)
False
💡 说明:
is not是个单独的二元运算符, 与分别使用is和not不同.- 如果操作符两侧的变量指向同一个对象, 则
is not的结果为False, 否则结果为True.
> The surprising comma/意外的逗号
Output:
>>> def f(x, y,):
... print(x, y)
...
>>> def g(x=4, y=5,):
... print(x, y)
...
>>> def h(x, **kwargs,):
File "<stdin>", line 1
def h(x, **kwargs,):
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
>>> def h(*args,):
File "<stdin>", line 1
def h(*args,):
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
💡 说明:
- 在Python函数的形式参数列表中, 尾随逗号并不一定是合法的.
- 在Python中, 参数列表部分用前置逗号定义, 部分用尾随逗号定义. 这种冲突导致逗号被夹在中间, 没有规则定义它.(译:这一句看得我也很懵逼,只能强翻了.详细解释看下面的讨论帖会一目了然.)
- 注意: 尾随逗号的问题已经在Python 3.6中被修复了. 而这篇帖子中则简要讨论了Python中尾随逗号的不同用法.
> Backslashes at the end of string/字符串末尾的反斜杠
Output:
>>> print("\\ C:\\")
\ C:\
>>> print(r"\ C:")
\ C:
>>> print(r"\ C:\")
File "<stdin>", line 1
print(r"\ C:\")
^
SyntaxError: EOL while scanning string literal
💡 说明:
- 在以
r开头的原始字符串中, 反斜杠并没有特殊含义.>>> print(repr(r"wt\"f")) 'wt\\"f' - 解释器所做的只是简单的改变了反斜杠的行为, 因此会直接放行反斜杠及后一个的字符. 这就是反斜杠在原始字符串末尾不起作用的原因.
> not knot!/别纠结!
x = True
y = False
Output:
>>> not x == y
True
>>> x == not y
File "<input>", line 1
x == not y
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
💡 说明:
- 运算符的优先级会影响表达式的求值顺序, 而在 Python 中
==运算符的优先级要高于not运算符. - 所以
not x == y相当于not (x == y), 同时等价于not (True == False), 最后的运算结果就是True. - 之所以
x == not y会抛一个SyntaxError异常, 是因为它会被认为等价于(x == not) y, 而不是你一开始期望的x == (not y). - 解释器期望
not标记是not in操作符的一部分 (因为==和not in操作符具有相同的优先级), 但是它在not标记后面找不到in标记, 所以会抛出SyntaxError异常.
> Half triple-quoted strings/三个引号
Output:
>>> print('wtfpython''')
wtfpython
>>> print("wtfpython""")
wtfpython
>>> # 下面的语句会抛出 `SyntaxError` 异常
>>> # print('''wtfpython')
>>> # print("""wtfpython")
💡 说明:
- Python 提供隐式的字符串连接, 例如,
>>> print("wtf" "python") wtfpython >>> print("wtf" "") # or "wtf""" wtf '''和"""在 Python中也是字符串定界符, Python 解释器在先遇到三个引号的的时候会尝试再寻找三个终止引号作为定界符, 如果不存在则会导致SyntaxError异常.
> Midnight time doesn't exist?/不存在的午夜?
from datetime import datetime
midnight = datetime(2018, 1, 1, 0, 0)
midnight_time = midnight.time()
noon = datetime(2018, 1, 1, 12, 0)
noon_time = noon.time()
if midnight_time:
print("Time at midnight is", midnight_time)
if noon_time:
print("Time at noon is", noon_time)
Output:
('Time at noon is', datetime.time(12, 0))
midnight_time 并没有被输出.
💡 说明:
在Python 3.5之前, 如果 datetime.time 对象存储的UTC的午夜时间(译: 就是 00:00), 那么它的布尔值会被认为是 False. 当使用 if obj: 语句来检查 obj 是否为 null 或者某些“空”值的时候, 很容易出错.
> What's wrong with booleans?/布尔你咋了?
1.
# 一个简单的例子, 统计下面可迭代对象中的布尔型值的个数和整型值的个数
mixed_list = [False, 1.0, "some_string", 3, True, [], False]
integers_found_so_far = 0
booleans_found_so_far = 0
for item in mixed_list:
if isinstance(item, int):
integers_found_so_far += 1
elif isinstance(item, bool):
booleans_found_so_far += 1
Output:
>>> integers_found_so_far
4
>>> booleans_found_so_far
0
2.
another_dict = {}
another_dict[True] = "JavaScript"
another_dict[1] = "Ruby"
another_dict[1.0] = "Python"
Output:
>>> another_dict[True]
"Python"
3.
>>> some_bool = True
>>> "wtf"*some_bool
'wtf'
>>> some_bool = False
>>> "wtf"*some_bool
''
💡 说明:
-
布尔值是
int的子类>>> isinstance(True, int) True >>> isinstance(False, int) True -
所以
True的整数值是1, 而False的整数值是0.>>> True == 1 == 1.0 and False == 0 == 0.0 True -
关于其背后的原理, 请看这个 StackOverflow 的回答.
> Class attributes and instance attributes/类属性和实例属性
1.
class A:
x = 1
class B(A):
pass
class C(A):
pass
Output:
>>> A.x, B.x, C.x
(1, 1, 1)
>>> B.x = 2
>>> A.x, B.x, C.x
(1, 2, 1)
>>> A.x = 3
>>> A.x, B.x, C.x
(3, 2, 3)
>>> a = A()
>>> a.x, A.x
(3, 3)
>>> a.x += 1
>>> a.x, A.x
(4, 3)
2.
class SomeClass:
some_var = 15
some_list = [5]
another_list = [5]
def __init__(self, x):
self.some_var = x + 1
self.some_list = self.some_list + [x]
self.another_list += [x]
Output:
>>> some_obj = SomeClass(420)
>>> some_obj.some_list
[5, 420]
>>> some_obj.another_list
[5, 420]
>>> another_obj = SomeClass(111)
>>> another_obj.some_list
[5, 111]
>>> another_obj.another_list
[5, 420, 111]
>>> another_obj.another_list is SomeClass.another_list
True
>>> another_obj.another_list is some_obj.another_list
True
💡 说明:
- 类变量和实例变量在内部是通过类对象的字典来处理(译: 就是
__dict__属性). 如果在当前类的字典中找不到的话就去它的父类中寻找. +=运算符会在原地修改可变对象, 而不是创建新对象. 因此, 在这种情况下, 修改一个实例的属性会影响其他实例和类属性.
> yielding None/生成 None
some_iterable = ('a', 'b')
def some_func(val):
return "something"
Output:
>>> [x for x in some_iterable]
['a', 'b']
>>> [(yield x) for x in some_iterable]
<generator object <listcomp> at 0x7f70b0a4ad58>
>>> list([(yield x) for x in some_iterable])
['a', 'b']
>>> list((yield x) for x in some_iterable)
['a', None, 'b', None]
>>> list(some_func((yield x)) for x in some_iterable)
['a', 'something', 'b', 'something']
💡 说明:
- 来源和解释可以在这里找到: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/32139885/yield-in-list-comprehensions-and-generator-expressions
- 相关错误报告: http://bugs.python.org/issue10544
- 这个bug在3.7以后的版本中不被推荐使用, 并在3.8中被修复. 因此在3.8中尝试在推导式中使用 yield, 只会得到一个 SyntaxError. 详细内容可以看3.7更新内容, 3.8更新内容.
> Mutating the immutable!/强人所难
some_tuple = ("A", "tuple", "with", "values")
another_tuple = ([1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6])
Output:
>>> some_tuple[2] = "change this"
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
>>> another_tuple[2].append(1000) # 这里不出现错误
>>> another_tuple
([1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6, 1000])
>>> another_tuple[2] += [99, 999]
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
>>> another_tuple
([1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6, 1000, 99, 999])
我还以为元组是不可变的呢...
💡 说明:
-
引用 https://docs.python.org/2/reference/datamodel.html
不可变序列 不可变序列的对象一旦创建就不能再改变. (如果对象包含对其他对象的引用,则这些其他对象可能是可变的并且可能会被修改; 但是,由不可变对象直接引用的对象集合不能更改.)
-
+=操作符在原地修改了列表. 元素赋值操作并不工作, 但是当异常抛出时, 元素已经在原地被修改了.
(译: 对于不可变对象, 这里指tuple, += 并不是原子操作, 而是 extend 和 = 两个动作, 这里 = 操作虽然会抛出异常, 但 extend 操作已经修改成功了. 详细解释可以看这里)
> The disappearing variable from outer scope/消失的外部变量
e = 7
try:
raise Exception()
except Exception as e:
pass
Output (Python 2.x):
>>> print(e)
# prints nothing
Output (Python 3.x):
>>> print(e)
NameError: name 'e' is not defined
💡 说明:
-
出处: https://docs.python.org/3/reference/compound_stmts.html#except
当使用
as为目标分配异常的时候, 将在except子句的末尾清除该异常.这就好像
except E as N: foo会被翻译成
except E as N: try: foo finally: del N这意味着异常必须在被赋值给其他变量才能在
except子句之后引用它. 而异常之所以会被清除, 则是由于上面附加的回溯信息(trackback)会和栈帧(stack frame)形成循环引用, 使得该栈帧中的所有本地变量在下一次垃圾回收发生之前都处于活动状态.(译: 也就是说不会被回收) -
子句在 Python 中并没有独立的作用域. 示例中的所有内容都处于同一作用域内, 所以变量
e会由于执行了except子句而被删除. 而对于有独立的内部作用域的函数来说情况就不一样了. 下面的例子说明了这一点:def f(x): del(x) print(x) x = 5 y = [5, 4, 3]Output:
>>>f(x) UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment >>>f(y) UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment >>> x 5 >>> y [5, 4, 3] -
在 Python 2.x 中,
Exception()实例被赋值给了变量e, 所以当你尝试打印结果的时候, 它的输出为空.(译: 正常的Exception实例打印出来就是空)Output (Python 2.x):
>>> e Exception() >>> print e # 没有打印任何内容!
> When True is actually False/真亦假
True = False
if True == False:
print("I've lost faith in truth!")
Output:
I've lost faith in truth!
💡 说明:
- 最初, Python 并没有
bool型 (人们用0表示假值, 用非零值比如1作为真值). 后来他们添加了True,False, 和bool型, 但是, 为了向后兼容, 他们没法把True和False设置为常量, 只是设置成了内置变量. - Python 3 由于不再需要向后兼容, 终于可以修复这个问题了, 所以这个例子无法在 Python 3.x 中执行!
> From filled to None in one instruction.../从有到无...
some_list = [1, 2, 3]
some_dict = {
"key_1": 1,
"key_2": 2,
"key_3": 3
}
some_list = some_list.append(4)
some_dict = some_dict.update({"key_4": 4})
Output:
>>> print(some_list)
None
>>> print(some_dict)
None
💡 说明:
大多数修改序列/映射对象的方法, 比如 list.append, dict.update, list.sort 等等. 都是原地修改对象并返回 None. 这样做的理由是, 如果操作可以原地完成, 就可以避免创建对象的副本来提高性能. (参考这里)
> Subclass relationships/子类关系 *
Output:
>>> from collections import Hashable
>>> issubclass(list, object)
True
>>> issubclass(object, Hashable)
True
>>> issubclass(list, Hashable)
False
子类关系应该是可传递的, 对吧? (即, 如果 A 是 B 的子类, B 是 C 的子类, 那么 A 应该 是 C 的子类.)
💡 说明:
- Python 中的子类关系并不一定是传递的. 任何人都可以在元类中随意定义
__subclasscheck__. - 当
issubclass(cls, Hashable)被调用时, 它只是在cls中寻找__hash__方法或者从继承的父类中寻找__hash__方法. - 由于
objectis 可散列的(hashable), 但是list是不可散列的, 所以它打破了这种传递关系. - 在这里可以找到更详细的解释.
> The mysterious key type conversion/神秘的键型转换 *
class SomeClass(str):
pass
some_dict = {'s':42}
Output:
>>> type(list(some_dict.keys())[0])
str
>>> s = SomeClass('s')
>>> some_dict[s] = 40
>>> some_dict # 预期: 两个不同的键值对
{'s': 40}
>>> type(list(some_dict.keys())[0])
str
💡 说明:
-
由于
SomeClass会从str自动继承__hash__方法, 所以s对象和"s"字符串的哈希值是相同的. -
而
SomeClass("s") == "s"为True是因为SomeClass也继承了str类__eq__方法. -
由于两者的哈希值相同且相等, 所以它们在字典中表示相同的键.
-
如果想要实现期望的功能, 我们可以重定义
SomeClass的__eq__方法.class SomeClass(str): def __eq__(self, other): return ( type(self) is SomeClass and type(other) is SomeClass and super().__eq__(other) ) # 当我们自定义 __eq__ 方法时, Python 不会再自动继承 __hash__ 方法 # 所以我们也需要定义它 __hash__ = str.__hash__ some_dict = {'s':42}Output:
>>> s = SomeClass('s') >>> some_dict[s] = 40 >>> some_dict {'s': 40, 's': 42} >>> keys = list(some_dict.keys()) >>> type(keys[0]), type(keys[1]) (__main__.SomeClass, str)
> Let's see if you can guess this?/看看你能否猜到这一点?
a, b = a[b] = {}, 5
Output:
>>> a
{5: ({...}, 5)}
💡 说明:
-
根据 Python 语言参考, 赋值语句的形式如下
(target_list "=")+ (expression_list | yield_expression)赋值语句计算表达式列表(expression list)(牢记 这可以是单个表达式或以逗号分隔的列表, 后者返回元组)并将单个结果对象从左到右分配给目标列表中的每一项.
-
(target_list "=")+中的+意味着可以有一个或多个目标列表. 在这个例子中, 目标列表是a, b和a[b](注意表达式列表只能有一个, 在我们的例子中是{}, 5). -
表达式列表计算结束后, 将其值自动解包后从左到右分配给目标列表(target list). 因此, 在我们的例子中, 首先将
{}, 5元组并赋值给a, b, 然后我们就可以得到a = {}且b = 5. -
a被赋值的{}是可变对象. -
第二个目标列表是
a[b](你可能觉得这里会报错, 因为在之前的语句中a和b都还没有被定义. 但是别忘了, 我们刚刚将a赋值{}且将b赋值为5). -
现在, 我们将通过将字典中键
5的值设置为元组({}, 5)来创建循环引用 (输出中的{...}指与a引用了相同的对象). 下面是一个更简单的循环引用的例子>>> some_list = some_list[0] = [0] >>> some_list [[...]] >>> some_list[0] [[...]] >>> some_list is some_list[0] True >>> some_list[0][0][0][0][0][0] == some_list True我们的例子就是这种情况 (
a[b][0]与a是相同的对象) -
总结一下, 你也可以把例子拆成
a, b = {}, 5 a[b] = a, b并且可以通过
a[b][0]与a是相同的对象来证明是循环引用>>> a[b][0] is a True
Section: Appearances are deceptive!
> Skipping lines?/跳过一行?
Output:
>>> value = 11
>>> valuе = 32
>>> value
11
什么鬼?
注意: 如果你想要重现的话最简单的方法是直接复制上面的代码片段到你的文件或命令行里.
💡 说明:
一些非西方字符虽然看起来和英语字母相同, 但会被解释器识别为不同的字母.
>>> ord('е') # 西里尔语的 'e' (Ye)
1077
>>> ord('e') # 拉丁语的 'e', 用于英文并使用标准键盘输入
101
>>> 'е' == 'e'
False
>>> value = 42 # 拉丁语 e
>>> valuе = 23 # 西里尔语 'e', Python 2.x 的解释器在这会抛出 `SyntaxError` 异常
>>> value
42
内置的 ord() 函数可以返回一个字符的 Unicode 代码点, 这里西里尔语 'e' 和拉丁语 'e' 的代码点不同证实了上述例子.
> Teleportation/空间移动 *
import numpy as np
def energy_send(x):
# 初始化一个 numpy 数组
np.array([float(x)])
def energy_receive():
# 返回一个空的 numpy 数组
return np.empty((), dtype=np.float).tolist()
Output:
>>> energy_send(123.456)
>>> energy_receive()
123.456
谁来给我发个诺贝尔奖?
💡 说明:
- 注意在
energy_send函数中创建的 numpy 数组并没有返回, 因此内存空间被释放并可以被重新分配. numpy.empty()直接返回下一段空闲内存,而不重新初始化. 而这个内存点恰好就是刚刚释放的那个(通常情况下, 并不绝对).
> Well, something is fishy.../嗯,有些可疑...
def square(x):
"""
一个通过加法计算平方的简单函数.
"""
sum_so_far = 0
for counter in range(x):
sum_so_far = sum_so_far + x
return sum_so_far
Output (Python 2.x):
>>> square(10)
10
难道不应该是100吗?
注意: 如果你无法重现, 可以尝试运行这个文件mixed_tabs_and_spaces.py.
💡 说明:
-
不要混用制表符(tab)和空格(space)! 在上面的例子中, return 的前面是"1个制表符", 而其他部分的代码前面是 "4个空格".
-
Python是这么处理制表符的:
首先, 制表符会从左到右依次被替换成8个空格, 直到被替换后的字符总数是八的倍数 <...>
-
因此,
square函数最后一行的制表符会被替换成8个空格, 导致return语句进入循环语句里面. -
Python 3 很友好, 在这种情况下会自动抛出错误.
Output (Python 3.x):
TabError: inconsistent use of tabs and spaces in indentation
Section: Watch out for the landmines!
> Modifying a dictionary while iterating over it/迭代字典时的修改
x = {0: None}
for i in x:
del x[i]
x[i+1] = None
print(i)
Output (Python 2.7- Python 3.5):
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
是的, 它运行了八次然后才停下来.
💡 说明:
- Python不支持对字典进行迭代的同时修改它.
- 它之所以运行8次, 是因为字典会自动扩容以容纳更多键值(我们有8次删除记录, 因此需要扩容). 这实际上是一个实现细节. (译: 应该是因为字典的初始最小值是8, 扩容会导致散列表地址发生变化而中断循环.)
- 在不同的Python实现中删除键的处理方式以及调整大小的时间可能会有所不同.(译: 就是说什么时候扩容在不同版本中可能是不同的, 在3.6及3.7的版本中到5就会自动扩容了. 以后也有可能再次发生变化. 这是为了避免散列冲突. 顺带一提, 后面两次扩容会扩展为32和256. 即
8->32->256.) - 更多的信息, 你可以参考这个StackOverflow的回答, 它详细的解释一个类似的例子.
> Stubborn del operator/坚强的 del *
class SomeClass:
def __del__(self):
print("Deleted!")
Output: 1.
>>> x = SomeClass()
>>> y = x
>>> del x # 这里应该会输出 "Deleted!"
>>> del y
Deleted!
唷, 终于删除了. 你可能已经猜到了在我们第一次尝试删除 x 时是什么让 __del__ 免于被调用的. 那让我们给这个例子增加点难度.
2.
>>> x = SomeClass()
>>> y = x
>>> del x
>>> y # 检查一下y是否存在
<__main__.SomeClass instance at 0x7f98a1a67fc8>
>>> del y # 像之前一样, 这里应该会输出 "Deleted!"
>>> globals() # 好吧, 并没有. 让我们看一下所有的全局变量
Deleted!
{'__builtins__': <module '__builtin__' (built-in)>, 'SomeClass': <class __main__.SomeClass at 0x7f98a1a5f668>, '__package__': None, '__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None}
好了,现在它被删除了 😕
💡 说明:
del x并不会立刻调用x.__del__().- 每当遇到
del x, Python 会将x的引用数减1, 当x的引用数减到0时就会调用x.__del__(). - 在第二个例子中,
y.__del__()之所以未被调用, 是因为前一条语句 (>>> y) 对同一对象创建了另一个引用, 从而防止在执行del y后对象的引用数变为0. - 调用
globals导致引用被销毁, 因此我们可以看到 "Deleted!" 终于被输出了. - (译: 这其实是 Python 交互解释器的特性, 它会自动让
_保存上一个表达式输出的值, 详细可以看这里.)
> Deleting a list item while iterating/迭代列表时删除元素
list_1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
list_2 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
list_3 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
list_4 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
for idx, item in enumerate(list_1):
del item
for idx, item in enumerate(list_2):
list_2.remove(item)
for idx, item in enumerate(list_3[:]):
list_3.remove(item)
for idx, item in enumerate(list_4):
list_4.pop(idx)
Output:
>>> list_1
[1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> list_2
[2, 4]
>>> list_3
[]
>>> list_4
[2, 4]
你能猜到为什么输出是 [2, 4] 吗?
💡 说明:
-
在迭代时修改对象是一个很愚蠢的主意. 正确的做法是迭代对象的副本,
list_3[:]就是这么做的.>>> some_list = [1, 2, 3, 4] >>> id(some_list) 139798789457608 >>> id(some_list[:]) # 注意python为切片列表创建了新对象. 139798779601192
del, remove 和 pop 的不同:
del var_name只是从本地或全局命名空间中删除了var_name(这就是为什么list_1没有受到影响).remove会删除第一个匹配到的指定值, 而不是特定的索引, 如果找不到值则抛出ValueError异常.pop则会删除指定索引处的元素并返回它, 如果指定了无效的索引则抛出IndexError异常.
为什么输出是 [2, 4]?
- 列表迭代是按索引进行的, 所以当我们从
list_2或list_4中删除1时, 列表的内容就变成了[2, 3, 4]. 剩余元素会依次位移, 也就是说,2的索引会变为 0,3会变为 1. 由于下一次迭代将获取索引为 1 的元素 (即3), 因此2将被彻底的跳过. 类似的情况会交替发生在列表中的每个元素上.
> Loop variables leaking out!/循环变量泄漏!
1.
for x in range(7):
if x == 6:
print(x, ': for x inside loop')
print(x, ': x in global')
Output:
6 : for x inside loop
6 : x in global
但是 x 从未在循环外被定义...
2.
# 这次我们先初始化x
x = -1
for x in range(7):
if x == 6:
print(x, ': for x inside loop')
print(x, ': x in global')
Output:
6 : for x inside loop
6 : x in global
3.
x = 1
print([x for x in range(5)])
print(x, ': x in global')
Output (on Python 2.x):
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
(4, ': x in global')
Output (on Python 3.x):
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
1 : x in global
💡 说明:
-
在 Python 中, for 循环使用所在作用域并在结束后保留定义的循环变量. 如果我们曾在全局命名空间中定义过循环变量. 在这种情况下, 它会重新绑定现有变量.
-
Python 2.x 和 Python 3.x 解释器在列表推导式示例中的输出差异, 在文档 What’s New In Python 3.0 中可以找到相关的解释:
"列表推导不再支持句法形式
[... for var in item1, item2, ...]. 取而代之的是[... for var in (item1, item2, ...)]. 另外, 注意列表推导具有不同的语义: 它们更接近于list()构造函数中生成器表达式的语法糖(译: 这一句我也不是很明白), 特别是循环控制变量不再泄漏到周围的作用域中."
> Beware of default mutable arguments!/当心默认的可变参数!
def some_func(default_arg=[]):
default_arg.append("some_string")
return default_arg
Output:
>>> some_func()
['some_string']
>>> some_func()
['some_string', 'some_string']
>>> some_func([])
['some_string']
>>> some_func()
['some_string', 'some_string', 'some_string']
💡 说明:
-
Python中函数的默认可变参数并不是每次调用该函数时都会被初始化. 相反, 它们会使用最近分配的值作为默认值. 当我们明确的将
[]作为参数传递给some_func的时候, 就不会使用default_arg的默认值, 所以函数会返回我们所期望的结果.def some_func(default_arg=[]): default_arg.append("some_string") return default_argOutput:
>>> some_func.__defaults__ # 这里会显示函数的默认参数的值 ([],) >>> some_func() >>> some_func.__defaults__ (['some_string'],) >>> some_func() >>> some_func.__defaults__ (['some_string', 'some_string'],) >>> some_func([]) >>> some_func.__defaults__ (['some_string', 'some_string'],) -
避免可变参数导致的错误的常见做法是将
None指定为参数的默认值, 然后检查是否有值传给对应的参数. 例:def some_func(default_arg=None): if not default_arg: default_arg = [] default_arg.append("some_string") return default_arg
> Catching the Exceptions/捕获异常
some_list = [1, 2, 3]
try:
# 这里会抛出异常 ``IndexError``
print(some_list[4])
except IndexError, ValueError:
print("Caught!")
try:
# 这里会抛出异常 ``ValueError``
some_list.remove(4)
except IndexError, ValueError:
print("Caught again!")
Output (Python 2.x):
Caught!
ValueError: list.remove(x): x not in list
Output (Python 3.x):
File "<input>", line 3
except IndexError, ValueError:
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
💡 说明:
-
如果你想要同时捕获多个不同类型的异常时, 你需要将它们用括号包成一个元组作为第一个参数传递. 第二个参数是可选名称, 如果你提供, 它将与被捕获的异常实例绑定. 例,
some_list = [1, 2, 3] try: # 这里会抛出异常 ``ValueError`` some_list.remove(4) except (IndexError, ValueError), e: print("Caught again!") print(e)Output (Python 2.x):
Caught again! list.remove(x): x not in listOutput (Python 3.x):
File "<input>", line 4 except (IndexError, ValueError), e: ^ IndentationError: unindent does not match any outer indentation level -
在 Python 3 中, 用逗号区分异常与可选名称是无效的; 正确的做法是使用
as关键字. 例,some_list = [1, 2, 3] try: some_list.remove(4) except (IndexError, ValueError) as e: print("Caught again!") print(e)Output:
Caught again! list.remove(x): x not in list
> Same operands, different story!/同人不同命!
1.
a = [1, 2, 3, 4]
b = a
a = a + [5, 6, 7, 8]
Output:
>>> a
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> b
[1, 2, 3, 4]
2.
a = [1, 2, 3, 4]
b = a
a += [5, 6, 7, 8]
Output:
>>> a
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> b
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
💡 说明:
-
a += b并不总是与a = a + b表现相同. 类实现op=运算符的方式 也许 是不同的, 列表就是这样做的. -
表达式
a = a + [5,6,7,8]会生成一个新列表, 并让a引用这个新列表, 同时保持b不变. -
表达式
a += [5,6,7,8]实际上是使用的是 "extend" 函数, 所以a和b仍然指向已被修改的同一列表.
> The out of scope variable/外部作用域变量
a = 1
def some_func():
return a
def another_func():
a += 1
return a
Output:
>>> some_func()
1
>>> another_func()
UnboundLocalError: local variable 'a' referenced before assignment
💡 说明:
-
当你在作用域中对变量进行赋值时, 变量会变成该作用域内的局部变量. 因此
a会变成another_func函数作用域中的局部变量, 但它在函数作用域中并没有被初始化, 所以会引发错误. -
可以阅读这个简短却很棒的指南, 了解更多关于 Python 中命名空间和作用域的工作原理.
-
想要在
another_func中修改外部作用域变量a的话, 可以使用global关键字.def another_func() global a a += 1 return aOutput:
>>> another_func() 2
> Be careful with chained operations/小心链式操作
>>> (False == False) in [False] # 可以理解
False
>>> False == (False in [False]) # 可以理解
False
>>> False == False in [False] # 为毛?
True
>>> True is False == False
False
>>> False is False is False
True
>>> 1 > 0 < 1
True
>>> (1 > 0) < 1
False
>>> 1 > (0 < 1)
False
💡 说明:
根据 https://docs.python.org/2/reference/expressions.html#not-in
形式上, 如果 a, b, c, ..., y, z 是表达式, 而 op1, op2, ..., opN 是比较运算符, 那么除了每个表达式最多只出现一次以外 a op1 b op2 c ... y opN z 就等于 a op1 b and b op2 c and ... y opN z.
虽然上面的例子似乎很愚蠢, 但是像 a == b == c 或 0 <= x <= 100 就很棒了.
False is False is False相当于(False is False) and (False is False)True is False == False相当于True is False and False == False, 由于语句的第一部分 (True is False) 等于False, 因此整个表达式的结果为False.1 > 0 < 1相当于1 > 0 and 0 < 1, 所以最终结果为True.- 表达式
(1 > 0) < 1相当于True < 1且
所以,>>> int(True) 1 >>> True + 1 # 与这个例子无关,只是好玩 21 < 1等于False
> Name resolution ignoring class scope/忽略类作用域的名称解析
1.
x = 5
class SomeClass:
x = 17
y = (x for i in range(10))
Output:
>>> list(SomeClass.y)[0]
5
2.
x = 5
class SomeClass:
x = 17
y = [x for i in range(10)]
Output (Python 2.x):
>>> SomeClass.y[0]
17
Output (Python 3.x):
>>> SomeClass.y[0]
5
💡 说明:
- 类定义中嵌套的作用域会忽略类内的名称绑定.
- 生成器表达式有它自己的作用域.
- 从 Python 3.X 开始, 列表推导式也有自己的作用域.
> Needle in a Haystack/大海捞针
1.
x, y = (0, 1) if True else None, None
Output:
>>> x, y # 期望的结果是 (0, 1)
((0, 1), None)
几乎每个 Python 程序员都遇到过类似的情况.
2.
t = ('one', 'two')
for i in t:
print(i)
t = ('one')
for i in t:
print(i)
t = ()
print(t)
Output:
one
two
o
n
e
tuple()
💡 说明:
- 对于 1, 正确的语句是
x, y = (0, 1) if True else (None, None). - 对于 2, 正确的语句是
t = ('one',)或者t = 'one',(缺少逗号) 否则解释器会认为t是一个字符串, 并逐个字符对其进行迭代. ()是一个特殊的标记,表示空元组.
Section: The Hidden treasures!
This section contains few of the lesser-known interesting things about Python that most beginners like me are unaware of (well, not anymore).
> Okay Python, Can you make me fly?/Python, 可否带我飞? *
好, 去吧.
import antigravity
Output: 嘘.. 这是个超级秘密.
💡 说明:
antigravity模块是 Python 开发人员发布的少数复活节彩蛋之一.import antigravity会打开一个 Python 的经典 XKCD 漫画页面.- 不止如此. 这个复活节彩蛋里还有一个复活节彩蛋. 如果你看一下代码, 就会发现还有一个函数实现了 XKCD's geohashing 算法.
> goto, but why?/goto, 但为什么? *
from goto import goto, label
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
for k in range(9):
print("I'm trapped, please rescue!")
if k == 2:
goto .breakout # 从多重循环中跳出
label .breakout
print("Freedom!")
Output (Python 2.3):
I'm trapped, please rescue!
I'm trapped, please rescue!
Freedom!
💡 说明:
- 2004年4月1日, Python 宣布 加入一个可用的
goto作为愚人节礼物. - 当前版本的 Python 并没有这个模块.
- 就算可以用, 也请不要使用它. 这里是为什么Python中没有
goto的原因.
> Brace yourself!/做好思想准备 *
如果你不喜欢在Python中使用空格来表示作用域, 你可以导入 C 风格的 {},
from __future__ import braces
Output:
File "some_file.py", line 1
from __future__ import braces
SyntaxError: not a chance
想用大括号? 没门! 觉得不爽, 请去用java.
💡 说明:
- 通常
__future__会提供 Python 未来版本的功能. 然而,这里的 “未来” 是一个讽刺. - 这是一个表达社区对此类问题态度的复活节彩蛋.
> Let's meet Friendly Language Uncle For Life/让生活更友好 *
Output (Python 3.x)
>>> from __future__ import barry_as_FLUFL
>>> "Ruby" != "Python" # 这里没什么疑问
File "some_file.py", line 1
"Ruby" != "Python"
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
>>> "Ruby" <> "Python"
True
这就对了.
💡 说明:
- 相关的 PEP-401 发布于 2009年4月1日 (所以你现在知道这意味着什么了吧).
- 引用 PEP-401
意识到 Python 3.0 里的 != 运算符是一个会引起手指疼痛的恐怖错误, FLUFL 将 <> 运算符恢复为唯一写法.
- Uncle Barry 在 PEP 中还分享了其他东西; 你可以在这里获得他们.
- (译: 虽然文档中没写,但应该是只能在交互解释器中使用.)
> Even Python understands that love is complicated/连Python也知道爱是难言的 *
import this
等等, this 是什么? this 是爱 ❤️
Output:
The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters
Beautiful is better than ugly.
优美胜于丑陋(Python 以编写优美的代码为目标)
Explicit is better than implicit.
明了胜于晦涩(优美的代码应当是明了的,命名规范,风格相似)
Simple is better than complex.
简洁胜于复杂(优美的代码应当是简洁的,不要有复杂的内部实现)
Complex is better than complicated.
复杂胜于凌乱(如果复杂不可避免,那代码间也不能有难懂的关系,要保持接口简洁)
Flat is better than nested.
扁平胜于嵌套(优美的代码应当是扁平的,不能有太多的嵌套)
Sparse is better than dense.
间隔胜于紧凑(优美的代码有适当的间隔,不要奢望一行代码解决问题)
Readability counts.
可读性很重要(优美的代码一定是可读的)
Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
没有特例特殊到需要违背这些规则(这些规则至高无上)
Although practicality beats purity.
尽管我们更倾向于实用性
Errors should never pass silently.
不要安静的包容所有错误
Unless explicitly silenced.
除非你确定需要这样做(精准地捕获异常,不写 except:pass 风格的代码)
In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
拒绝诱惑你去猜测的暧昧事物
There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.
而是尽量找一种,最好是唯一一种明显的解决方案(如果不确定,就用穷举法)
Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
虽然这并不容易,因为你不是 Python 之父(这里的 Dutch 是指 Guido )
Now is better than never.
现在行动好过永远不行动
Although never is often better than *right* now.
尽管不行动要好过鲁莽行动
If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
如果你无法向人描述你的方案,那肯定不是一个好方案;
If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
如果你能轻松向人描述你的方案,那也许会是一个好方案(方案测评标准)
Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
命名空间是一种绝妙的理念,我们应当多加利用(倡导与号召)
这是 Python 之禅!
>>> love = this
>>> this is love
True
>>> love is True
False
>>> love is False
False
>>> love is not True or False
True
>>> love is not True or False; love is love # 爱是难言的
True
💡 说明:
this模块是关于 Python 之禅的复活节彩蛋 (PEP 20).- 如果你认为这已经够有趣的了, 可以看看 this.py 的实现. 有趣的是, Python 之禅的实现代码违反了他自己 (这可能是唯一会发生这种情况的地方).
至于 love is not True or False; love is love, 意外却又不言而喻.
> Yes, it exists!/是的, 它存在!
循环的 else. 一个典型的例子:
def does_exists_num(l, to_find):
for num in l:
if num == to_find:
print("Exists!")
break
else:
print("Does not exist")
Output:
>>> some_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> does_exists_num(some_list, 4)
Exists!
>>> does_exists_num(some_list, -1)
Does not exist
异常的 else . 例,
try:
pass
except:
print("Exception occurred!!!")
else:
print("Try block executed successfully...")
Output:
Try block executed successfully...
💡 说明:
- 循环后的
else子句只会在循环没有触发break语句, 正常结束的情况下才会执行. - try 之后的
else子句也被称为 "完成子句", 因为在try语句中到达else子句意味着try块实际上已成功完成.
> Inpinity *
The spelling is intended. Please, don't submit a patch for this.
Output (Python 3.x):
>>> infinity = float('infinity')
>>> hash(infinity)
314159
>>> hash(float('-inf'))
-314159
💡 Explanation:
- Hash of infinity is 10⁵ x π.
- Interestingly, the hash of
float('-inf')is "-10⁵ x π" in Python 3, whereas "-10⁵ x e" in Python 2.
> Mangling time! *
class Yo(object):
def __init__(self):
self.__honey = True
self.bitch = True
Output:
>>> Yo().bitch
True
>>> Yo().__honey
AttributeError: 'Yo' object has no attribute '__honey'
>>> Yo()._Yo__honey
True
Why did Yo()._Yo__honey work? Only Indian readers would understand.
💡 Explanation:
- Name Mangling is used to avoid naming collisions between different namespaces.
- In Python, the interpreter modifies (mangles) the class member names starting with
__(double underscore) and not ending with more than one trailing underscore by adding_NameOfTheClassin front. - So, to access
__honeyattribute, we are required to append_Yoto the front which would prevent conflicts with the same name attribute defined in any other class.
Section: Miscellaneous
> += is faster
# using "+", three strings:
>>> timeit.timeit("s1 = s1 + s2 + s3", setup="s1 = ' ' * 100000; s2 = ' ' * 100000; s3 = ' ' * 100000", number=100)
0.25748300552368164
# using "+=", three strings:
>>> timeit.timeit("s1 += s2 + s3", setup="s1 = ' ' * 100000; s2 = ' ' * 100000; s3 = ' ' * 100000", number=100)
0.012188911437988281
💡 Explanation:
+=is faster than+for concatenating more than two strings because the first string (example,s1fors1 += s2 + s3) is not destroyed while calculating the complete string.
> Let's make a giant string!
def add_string_with_plus(iters):
s = ""
for i in range(iters):
s += "xyz"
assert len(s) == 3*iters
def add_bytes_with_plus(iters):
s = b""
for i in range(iters):
s += b"xyz"
assert len(s) == 3*iters
def add_string_with_format(iters):
fs = "{}"*iters
s = fs.format(*(["xyz"]*iters))
assert len(s) == 3*iters
def add_string_with_join(iters):
l = []
for i in range(iters):
l.append("xyz")
s = "".join(l)
assert len(s) == 3*iters
def convert_list_to_string(l, iters):
s = "".join(l)
assert len(s) == 3*iters
Output:
>>> timeit(add_string_with_plus(10000))
1000 loops, best of 3: 972 µs per loop
>>> timeit(add_bytes_with_plus(10000))
1000 loops, best of 3: 815 µs per loop
>>> timeit(add_string_with_format(10000))
1000 loops, best of 3: 508 µs per loop
>>> timeit(add_string_with_join(10000))
1000 loops, best of 3: 878 µs per loop
>>> l = ["xyz"]*10000
>>> timeit(convert_list_to_string(l, 10000))
10000 loops, best of 3: 80 µs per loop
Let's increase the number of iterations by a factor of 10.
>>> timeit(add_string_with_plus(100000)) # Linear increase in execution time
100 loops, best of 3: 9.75 ms per loop
>>> timeit(add_bytes_with_plus(100000)) # Quadratic increase
1000 loops, best of 3: 974 ms per loop
>>> timeit(add_string_with_format(100000)) # Linear increase
100 loops, best of 3: 5.25 ms per loop
>>> timeit(add_string_with_join(100000)) # Linear increase
100 loops, best of 3: 9.85 ms per loop
>>> l = ["xyz"]*100000
>>> timeit(convert_list_to_string(l, 100000)) # Linear increase
1000 loops, best of 3: 723 µs per loop
💡 Explanation
- You can read more about timeit from here. It is generally used to measure the execution time of snippets.
- Don't use
+for generating long strings — In Python,stris immutable, so the left and right strings have to be copied into the new string for every pair of concatenations. If you concatenate four strings of length 10, you'll be copying (10+10) + ((10+10)+10) + (((10+10)+10)+10) = 90 characters instead of just 40 characters. Things get quadratically worse as the number and size of the string increases (justified with the execution times ofadd_bytes_with_plusfunction) - Therefore, it's advised to use
.format.or%syntax (however, they are slightly slower than+for short strings). - Or better, if already you've contents available in the form of an iterable object, then use
''.join(iterable_object)which is much faster. add_string_with_plusdidn't show a quadratic increase in execution time unlikeadd_bytes_with_plusbecause of the+=optimizations discussed in the previous example. Had the statement beens = s + "x" + "y" + "z"instead ofs += "xyz", the increase would have been quadratic.def add_string_with_plus(iters): s = "" for i in range(iters): s = s + "x" + "y" + "z" assert len(s) == 3*iters >>> timeit(add_string_with_plus(10000)) 100 loops, best of 3: 9.87 ms per loop >>> timeit(add_string_with_plus(100000)) # Quadratic increase in execution time 1 loops, best of 3: 1.09 s per loop
> Explicit typecast of strings
a = float('inf')
b = float('nan')
c = float('-iNf') #These strings are case-insensitive
d = float('nan')
Output:
>>> a
inf
>>> b
nan
>>> c
-inf
>>> float('some_other_string')
ValueError: could not convert string to float: some_other_string
>>> a == -c #inf==inf
True
>>> None == None # None==None
True
>>> b == d #but nan!=nan
False
>>> 50/a
0.0
>>> a/a
nan
>>> 23 + b
nan
💡 Explanation:
'inf' and 'nan' are special strings (case-insensitive), which when explicitly typecasted to float type, are used to represent mathematical "infinity" and "not a number" respectively.
> Minor Ones
-
join()is a string operation instead of list operation. (sort of counter-intuitive at first usage)💡 Explanation: If
join()is a method on a string then it can operate on any iterable (list, tuple, iterators). If it were a method on a list, it'd have to be implemented separately by every type. Also, it doesn't make much sense to put a string-specific method on a genericlistobject API. -
Few weird looking but semantically correct statements:
[] = ()is a semantically correct statement (unpacking an emptytupleinto an emptylist)'a'[0][0][0][0][0]is also a semantically correct statement as strings are sequences(iterables supporting element access using integer indices) in Python.3 --0-- 5 == 8and--5 == 5are both semantically correct statements and evaluate toTrue.
-
Given that
ais a number,++aand--aare both valid Python statements but don't behave the same way as compared with similar statements in languages like C, C++ or Java.>>> a = 5 >>> a 5 >>> ++a 5 >>> --a 5💡 Explanation:
- There is no
++operator in Python grammar. It is actually two+operators. ++aparses as+(+a)which translates toa. Similarly, the output of the statement--acan be justified.- This StackOverflow thread discusses the rationale behind the absence of increment and decrement operators in Python.
- There is no
-
Python uses 2 bytes for local variable storage in functions. In theory, this means that only 65536 variables can be defined in a function. However, python has a handy solution built in that can be used to store more than 2^16 variable names. The following code demonstrates what happens in the stack when more than 65536 local variables are defined (Warning: This code prints around 2^18 lines of text, so be prepared!):
import dis exec(""" def f(): """ + """ """.join(["X"+str(x)+"=" + str(x) for x in range(65539)])) f() print(dis.dis(f)) -
Multiple Python threads won't run your Python code concurrently (yes you heard it right!). It may seem intuitive to spawn several threads and let them execute your Python code concurrently, but, because of the Global Interpreter Lock in Python, all you're doing is making your threads execute on the same core turn by turn. Python threads are good for IO-bound tasks, but to achieve actual parallelization in Python for CPU-bound tasks, you might want to use the Python multiprocessing module.
-
List slicing with out of the bounds indices throws no errors
>>> some_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] >>> some_list[111:] [] -
int('١٢٣٤٥٦٧٨٩')returns123456789in Python 3. In Python, Decimal characters include digit characters, and all characters that can be used to form decimal-radix numbers, e.g. U+0660, ARABIC-INDIC DIGIT ZERO. Here's an interesting story related to this behavior of Python. -
'abc'.count('') == 4. Here's an approximate implementation ofcountmethod, which would make the things more cleardef count(s, sub): result = 0 for i in range(len(s) + 1 - len(sub)): result += (s[i:i + len(sub)] == sub) return resultThe behavior is due to the matching of empty substring(
'') with slices of length 0 in the original string.
Contributing
All patches are Welcome! Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for further details.
For discussions, you can either create a new issue or ping on the Gitter channel
Acknowledgements
The idea and design for this collection were initially inspired by Denys Dovhan's awesome project wtfjs. The overwhelming support by the community gave it the shape it is in right now.
Some nice Links!
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sH4XF6pKKmk
- https://www.reddit.com/r/Python/comments/3cu6ej/what_are_some_wtf_things_about_python
- https://sopython.com/wiki/Common_Gotchas_In_Python
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/530530/python-2-x-gotchas-and-landmines
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1011431/common-pitfalls-in-python
- https://www.python.org/doc/humor/
- https://www.codementor.io/satwikkansal/python-practices-for-efficient-code-performance-memory-and-usability-aze6oiq65
🎓 License
Help
If you have any wtfs, ideas or suggestions, please share.
Surprise your geeky pythonist friends?
You can use these quick links to recommend wtfpython to your friends,
Need a pdf version?
I've received a few requests for the pdf version of wtfpython. You can add your details here to get the pdf as soon as it is finished.