8.7 KiB
如何在 Ubuntu 上设置时间同步
你可能设置过 cron 任务 来在特定时间备份重要文件或执行系统相关任务。也许你配置了一个日志服务器在特定时间间隔轮转日志。但如果你的时钟不同步,这些任务将无法按时执行。这就是要在 Linux 系统上设置正确的时区并保持时钟与互联网同步的原因。本指南介绍如何在 Ubuntu Linux 上设置时间同步。下面的步骤已经在 Ubuntu 18.04 上进行了测试,但是对于使用 systemd 的 timesyncd 服务的其他基于 Ubuntu 的系统它们是相同的。
在 Ubuntu 上设置时间同步
通常,我们在安装时设置时区。但是,你可以根据需要更改或设置不同的时区。
首先,让我们使用 date 命令查看 Ubuntu 系统中的当前时区:
$ date
示例输出:
Tue Jul 30 11:47:39 UTC 2019
如上所见,date 命令显示实际日期和当前时间。这里,我当前的时区是 UTC,代表协调世界时。
或者,你可以在 /etc/timezone 文件中查找当前时区。
$ cat /etc/timezone
UTC
现在,让我们看看时钟是否与互联网同步。只需运行:
$ timedatectl
示例输出:
Local time: Tue 2019-07-30 11:53:58 UTC
Universal time: Tue 2019-07-30 11:53:58 UTC
RTC time: Tue 2019-07-30 11:53:59
Time zone: Etc/UTC (UTC, +0000)
System clock synchronized: yes
systemd-timesyncd.service active: yes
RTC in local TZ: no
如你所见,timedatectl 命令显示本地时间、世界时、时区以及系统时钟是否与互联网服务器同步,以及 systemd-timesyncd.service 是处于活动状态还是非活动状态。就我而言,系统时钟已与互联网时间服务器同步。
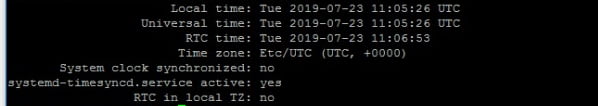
如果时钟不同步,你会看到下面截图中显示的 System clock synchronized: no。
时间同步已禁用。
注意:上面的截图是旧截图。这就是你看到不同日期的原因。
如果你看到 System clock synchronized: 值设置为 no,那么 timesyncd 服务可能处于非活动状态。因此,只需重启服务并看下是否正常。
$ sudo systemctl restart systemd-timesyncd.service
现在检查 timesyncd 服务状态:
$ sudo systemctl status systemd-timesyncd.service
● systemd-timesyncd.service - Network Time Synchronization
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/systemd-timesyncd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-07-30 10:50:18 UTC; 1h 11min ago
Docs: man:systemd-timesyncd.service(8)
Main PID: 498 (systemd-timesyn)
Status: "Synchronized to time server [2001:67c:1560:8003::c7]:123 (ntp.ubuntu.com)."
Tasks: 2 (limit: 2319)
CGroup: /system.slice/systemd-timesyncd.service
└─498 /lib/systemd/systemd-timesyncd
Jul 30 10:50:30 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:50:31 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:50:31 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:50:32 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:50:32 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:50:35 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:50:35 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:50:35 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:50:35 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Network configuration changed, trying to estab
Jul 30 10:51:06 ubuntuserver systemd-timesyncd[498]: Synchronized to time server [2001:67c:1560:800
如果此服务已启用并处于活动状态,那么系统时钟应与互联网时间服务器同步。
你可以使用命令验证是否启用了时间同步:
$ timedatectl
如果仍然不起作用,请运行以下命令以启用时间同步:
$ sudo timedatectl set-ntp true
现在,你的系统时钟将与互联网时间服务器同步。
使用 timedatectl 命令更改时区
如果我想使用 UTC 以外的其他时区怎么办?这很容易!
首先,使用命令列出可用时区:
$ timedatectl list-timezones
你将看到类似于下图的输出。
使用 timedatectl 命令列出时区
你可以使用以下命令设置所需的时区(例如,Asia/Shanghai):
(LCTT 译注:本文原文使用印度时区作为示例,这里为了便于使用,换为中国标准时区 CST。另外,在时区设置中,要注意 CST 这个缩写会代表四个不同的时区,因此建议使用城市和 UTC+8 来说设置。)
$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
使用 date 命令再次检查时区是否已真正更改:
$ date
Tue Jul 30 20:22:33 CST 2019
或者,如果需要详细输出,请使用 timedatectl 命令:
$ timedatectl
Local time: Tue 2019-07-30 20:22:35 CST
Universal time: Tue 2019-07-30 12:22:35 UTC
RTC time: Tue 2019-07-30 12:22:36
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
System clock synchronized: yes
systemd-timesyncd.service active: yes
RTC in local TZ: no
如你所见,我已将时区从 UTC 更改为 CST(中国标准时间)。
要切换回 UTC 时区,只需运行:
$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone UTC
使用 tzdata 更改时区
在较旧的 Ubuntu 版本中,没有 timedatectl 命令。这种情况下,你可以使用 tzdata(Time zone data)来设置时间同步。
$ sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
选择你居住的地理区域。对我而言,我选择 Asia。选择 OK,然后按回车键。
接下来,选择与你的时区对应的城市或地区。这里,我选择了 Kolkata(LCTT 译注:中国用户请相应使用 Shanghai 等城市)。
最后,你将在终端中看到类似下面的输出。
Current default time zone: 'Asia/Shanghai'
Local time is now: Tue Jul 30 21:59:25 CST 2019.
Universal Time is now: Tue Jul 30 13:59:25 UTC 2019.
在图形模式下配置时区
有些用户可能对命令行方式不太满意。如果你是其中之一,那么你可以轻松地在图形模式的系统设置面板中进行设置。
点击 Super 键(Windows 键),在 Ubuntu dash 中输入 settings,然后点击设置图标。
从 Ubuntu dash 启动系统的设置
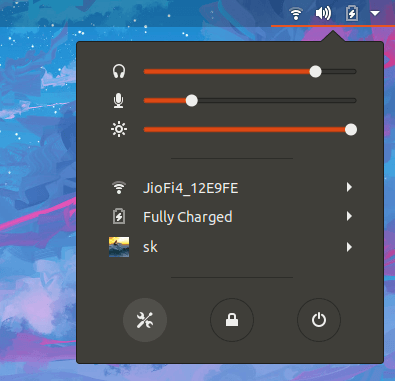
或者,单击位于 Ubuntu 桌面右上角的向下箭头,然后单击左上角的“设置”图标。
从顶部面板启动系统的设置
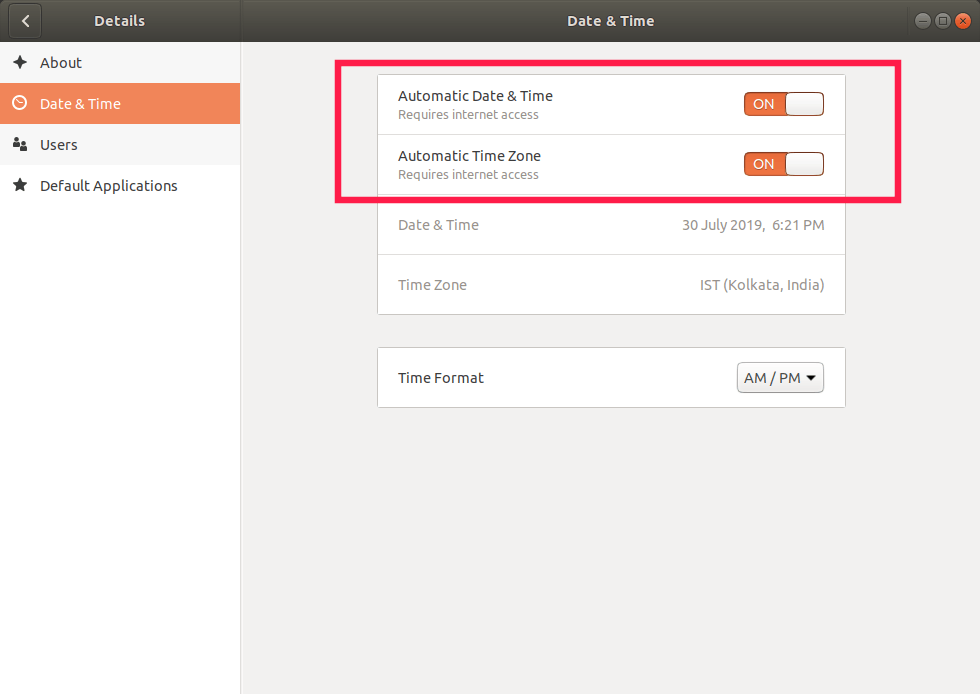
在下一个窗口中,选择“细节”,然后单击“日期与时间”选项。打开“自动的日期与时间”和“自动的时区”。
在 Ubuntu 中设置自动时区
关闭设置窗口就行了!你的系统始终应该与互联网时间服务器同步了。
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/how-to-set-up-time-synchronization-on-ubuntu/