8.1 KiB
How to check RPM package dependencies on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL 教你如何在Fedora,CentOS,RHEL中检查RPM包的依赖性
A typical RPM package on Red Hat-based systems requires all its dependent packages be installed to function properly. For end users, the complexity of such RPM dependency is hidden by package managers (e.g., yum or DNF) during package install/upgrade/removal process. However, if you are a sysadmin or a RPM maintainer, you need to be well-versed in RPM dependencies to maintain run-time environment for the system or roll out up-to-date RPM specs. 我们都知道,在基于红帽的Linux系统中,一个RPM包,需要把先将它依赖的其他包安装好才能正常的工作。对于终端用户,RPM的安装、更新、删除中存在的依赖关系已经被工具透明化了(如 yum或 DNF等)。但如果你是系统管理员或者RPM包的管理员,你需要对RPM包中存在的依赖关系以及时更新、删除适当的包来保证系统的正常运行。 In this tutorial, I am going to show how to check RPM package dependencies. Depending on whether a package is installed or not, there are several ways to identify its RPM dependencies. 在本教程中,我将教大家如何检查RPM包的依赖关系无论这个包是否已经安装进操作系统中,我们都有一些办法来检查它们的依赖性。
Method One
方法一
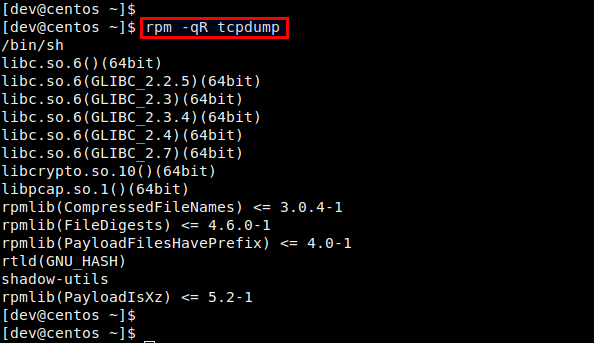
One way to find out RPM dependencies for a particular package is to use rpm command. The following command lists all dependent packages for a target package. 使用RPM命令可以列出目标包所依赖的所有包,如下: $ rpm -qR
Note that this command will work only if the target package is already installed. If you want to check package dependencies for any uninstalled package, you first need to download the RPM package locally (no need to install it).
注意,这种方法只适用于已安装的包。如果你需要检查一个未安装包的依赖关系,你需要把这个包先下载到本地来。
To download a RPM package without installing it, use a command-line utility called yumdownloader. Install yumdownloader as follows.
对于已在本地但未安装的包,可以使用叫做'yumdownloader'的工具,下面我们先安装yumdownloader:
$ sudo yum install yum-utils
Now let's check RPM depenencies of a uninstalled package (e.g., tcpdump). First download the package in the current folder with yumdownloader: 现在我们来检查一个未安装的RPM包的依赖关系(本列使用 tcpdump)。首先,我们使用yumdownloader把tcpdump的RPM包下载下来 $ yumdownloader --destdir=. tcpdump
Then use rpm command with "-qpR" options to list dependencies of the downloaded package. 然后再使用 "-qpR"参数显示该包的依赖关系。 # rpm -qpR tcpdump-4.4.0-2.fc19.i686.rpm
Method Two
方法二
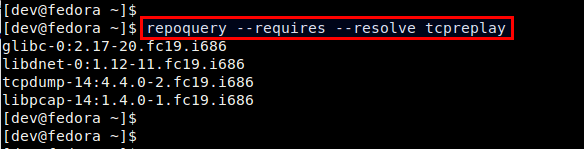
You can also get a list of dependencies for a RPM package using repoquery tool. repoquery works whether or not a target package is installed. This tool is included in yum-utils package. 你可以使用repoquery工具来罗列包的依赖关系,这个工具包含在yum-utils中。 $ sudo yum install yum-utils
To show all required packages for a particular package: 显示目标包所依赖的包: $ repoquery --requires --resolve
For repoquery to work, your computer needs network connectivity since repoquery pulls information from Yum repositories. 为让repoquery正常的工作,需要保持网络的畅通,应为repoquery需要在Yum库中查找信息。
Method Three
方法三
The third method to show RPM package dependencies is to use rpmreaper tool. Originally this tool is developed to clean up unnecessary packages and their dependencies on RPM-based systems. rpmreaper has an ncurses-based intuitive interface for browsing installed packages and their dependency trees. 第三个方法是使用rpmreaper工具。这个工具本来是用作清理系统中无用以及它们所依赖的包,rpmreaper有很直观的界面来展示已安装的包和它们依赖关系的树形图。 To install rpmrepater, use yum command. On CentOS, you need to set up EPEL repo first. 安装rpmrepater,在CentOS中,你需要先设置好EPEL库 $ sudo yum install rpmreaper
To browser RPM dependency trees, simply run: 只需运行rpmreaper就可以看到RPM包的依赖关系: $ rpmreaper
The rpmrepater interface will show you a list of all installed packages. You can navigate the list using up/down arrow keys. Press "r" on a highlighted package to show its dependencies. You can expand the whole dependency tree by recursively pressing "r" keys on individual dependent packages. The "L" flag indicates that a given package is a "leaf", meaning that no other package depends on this package. The "o" flag implies that a given package is in the middle of dependency chain. Pressing "b" on such a package will show you what other packages require the highlighted package. rpmrepater会向用户显示已安装包的列表,你可以使用上/下箭头来滚动屏幕。 你可以在指定包上使用"r"键来显示其依赖关系,循环在指定包上按下"r"键可以展示出余下的信息。 "L"标志的意思是说这个包是一片“孤叶”,意思说说没有任何包依赖它。 "o"标志是说这个包是整个依赖链的中间部分。 按下"b"键会显示其他依赖于该包的其他包。
Method Four
方法四
Another way to show package dependencies on RPM-based systems is to use rpmdep which is a command-line tool for generating a full package dependency graph of any installed RPM package. The tool analyzes RPM dependencies, and produce partially ordered package lists from topological sorting. The output of this tool can be fed into dotty graph visualization tool to generate a dependency graph image. 还有一个办法是使用rpmdep工具,rpmdep是一个命令行工具,可以显示已安装包的完整包依赖关系图。该工具会分析RPM包的依赖性,从完整的排完序 的拓扑图中摘取部分包的信息,形成列表展示给用户。该工具的输出结果可以直接使用到Dotty(可视化展示工具)中去。 To install rpmdep and dotty on Fedora: 在Fedora中安装rpmdep和dotty: $ sudo yum install rpmorphan graphviz
To install the same tools on CentOS: 在CentOs中安装: $ wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/rpmorphan/rpmorphan/1.14/rpmorphan-1.14-1.noarch.rpm $ sudo rpm -ivh rpmorphan-1.14-1.noarch.rpm $ sudo yum install graphviz
To generate and plot a dependency graph of a particular installed package (e.g., gzip): 生成包依赖的拓扑关系图: $ rpmdep.pl -dot gzip.dot gzip $ dot -Tpng -o output.png gzip.dot
So far in this tutorial, I demonstrate several ways to check what other packages a given RPM package relies on. If you want to know more about .deb package dependencies for Debian-based systems, you can refer to this guide instead. 教程到这个地方,我们用到了几种办法来检查包的依赖关系。如果您想知道如何在居于Debian的系统中检查.deb的包依赖关系,请阅读另外一篇文档
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/check-rpm-package-dependencies-fedora-centos-rhel.html