mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-07 22:11:09 +08:00
141 lines
11 KiB
Markdown
141 lines
11 KiB
Markdown
戴文的Linux内核专题:24 配置内核 (20)
|
||
================================================================================
|
||
|
||
|
||
欢迎进入Linux内核系列文章的下一篇!本篇我们就爱哪个会继续配置文件系统。
|
||
|
||
首先,我们启用"General filesystem local caching manager",它允许内核存储文件系统缓存。这可以增加在存储空间开销上的性能。
|
||
|
||
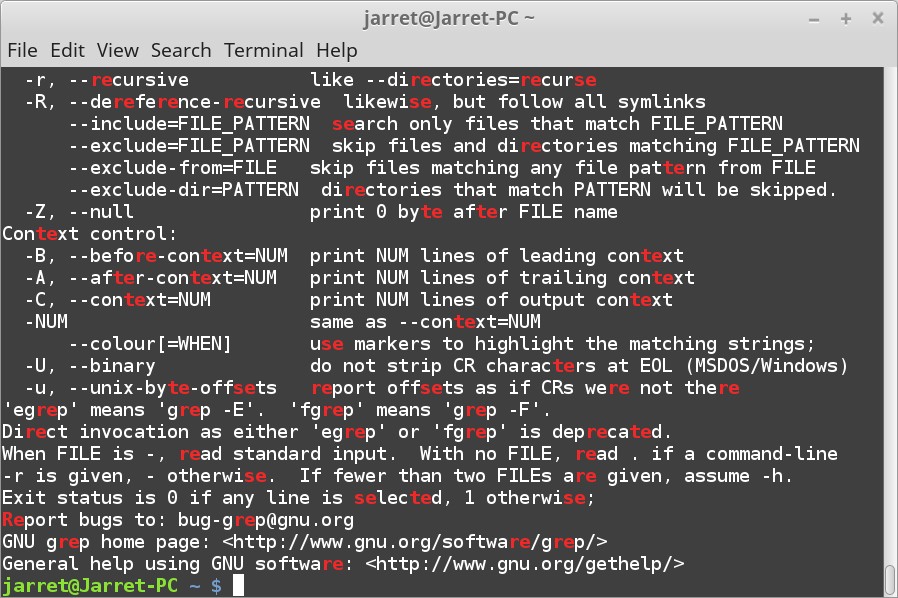
为了调试目的,缓存系统可以通过统计信息监控(Gather statistical information on local caching)。通常上,这个特性应该只在你计划调试的时候启用。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
下面的特性很像上面的,但是这个特性存储延迟信息(Gather latency information on local caching)。再说一次,这是个调试特性。
|
||
|
||
"Debug FS-Cache"提供了很多其他的缓存系统的调试功能。
|
||
|
||
下面的缓存调试工具会保存文件系统缓存对象的全局列表(任何进程可以访问这个列表)(Maintain global object list for debugging purposes)。
|
||
|
||
为了增强网络文件系统的速度,启用接下来的驱动(Filesystem caching on files)。这个特性允许整个本地文件系统被用于远程文件系统和存储单元的缓存。Linux内核会管理这个分区。
|
||
|
||
有两种不同的用于的调试驱动用于本地缓存系统和远程文件系统,它们是(Debug CacheFiles)和(Gather latency information on CacheFiles)。
|
||
|
||
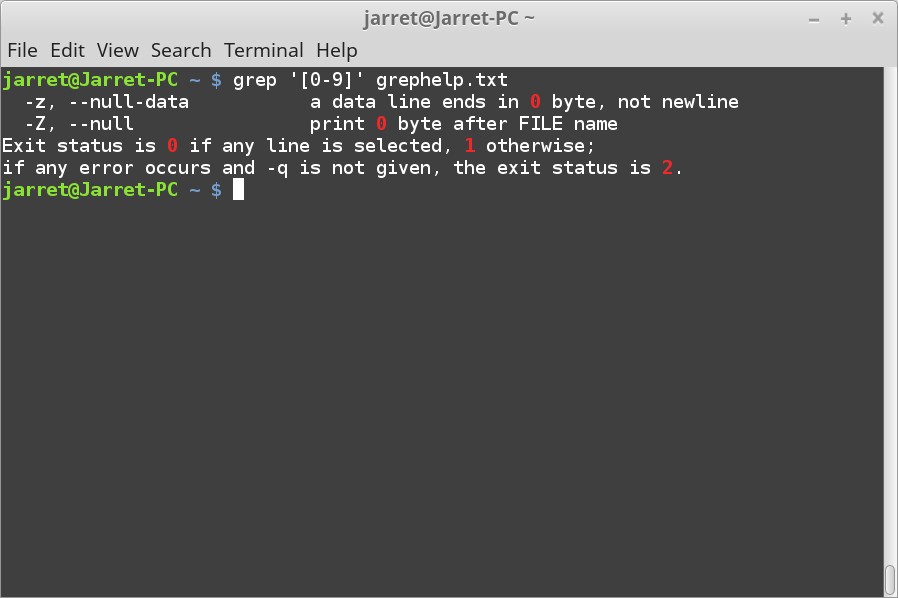
大多数通常的光盘文件系统是ISO 9660标准的ISO-9660,故名(ISO 9660 CDROM file system support)。这个驱动用于读/写主流的光盘。
|
||
|
||
当读取光盘中的长Unicode文件名或者这类文件时,需要这个驱动(Microsoft Joliet CDROM extensions)。这是ISO-9660文件系统的扩展。
|
||
|
||
"Transparent decompression extension"允许数据以压缩形式写入并以透明方式解压读出。这允许光盘上存放更多的数据。
|
||
|
||
"UDF file system support"允许内核读/写UDF文件系统的可重写光盘。UDF被设计用来管理增量写入。UDF允许光盘思想闪存盘那样使用。系统可以比常规ISO-9660文件系统写入的光盘更快地写入以及更新。然而,这并不比使用闪存快。
|
||
|
||
如你所知,Windows是一个很流行的系统。有很多存储器使用FAT文件系统。万幸的是,Linux支持这样的文件系统。这会明显地增加内核的大小,但是既然FAT文件系统是如此的通用,那么这点开销也是值得的。
|
||
|
||
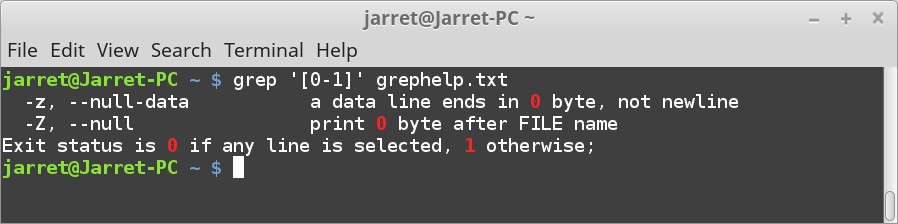
为了支持FAT文件系统,启用这个驱动(VFAT (Windows-95) fs support)。在写本篇的时候。驱动还不支持FAT64(通常成为exFAT)。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
代码页的大小可以在这里设置(Default codepage for FAT)。
|
||
|
||
在此之后,可以设置FAT文件系统的默认字符集(Default iocharset for FAT)。
|
||
|
||
NTFS文件系统在这个驱动提供支持(Default iocharset for FAT)。驱动提供了只读特性。为了写入NTFS,启用这个驱动(NTFS write support)。
|
||
|
||
Linux内核提供了NTFS文件系统的调试工具(NTFS debugging support)。
|
||
|
||
要在root根目录下有个proc目录,必须启用这个特性(/proc file system support)。一些其他相似的驱动依赖于这个,包括(/proc/kcore support)、(/proc/vmcore support)和 (Sysctl support (/proc/sys))。proc系统("process"的缩写)使用的proc文件系统有时称作procfds。这个文件系统在硬件的内存中,并在启用时创建。因此,当你在浏览proc中的文件时,用户仿佛像在其他存储单元上那样浏览内存。proc扮演一个用户空间和内核空间之间接口的角色。proc是在内核空间。
|
||
|
||
"Enable /proc page monitoring"提供了一些文件监视进程的内存利用。
|
||
|
||
"sysfs file system support"创建/sys文件加。sys文件系统在内存中并提供了内核对象的接口。
|
||
|
||
tmp目录被许多应用需要,包括Linux自己,因此强烈建议启用这个驱动(Tmpfs virtual memory file system support (former shm fs))。tmp文件系统可能存储在硬盘或者内存中,并只被用于存储临时文件。
|
||
|
||
Tmpfs POSIX Access Control Lists"驱动tmpfs虚拟文件系统额外的文件权限特性。
|
||
|
||
"Tmpfs extended attributes"提供了通常的tmpfs更多的属性。
|
||
|
||
"HugeTLB file system support"驱动提供了基于ramfs的hugetlbfs文件系统。这个虚拟文件系统包含了HugeTLB页。
|
||
|
||
|
||
configfs文件系统是一个以文件系统形式存在的内核对象管理器(Userspace-driven configuration filesystem)。强烈建议启用这个驱动。ConfigFS很像sysfs。然而,ConfigFS被用于创建和删除内核对象,而sysfs被用于浏览和修改内核对象。
|
||
|
||
下面,我们可以回到"真正"的文件系统了。那就是用户用来存放他们个人文件的文件系统。下面,内核能够读取ADFS文件系统(ADFS file system support)。
|
||
|
||
AFDFS文件系统写入被一个独立且不稳定的驱动提供 (ADFS write support (DANGEROUS))。ADFS代表Advanced Disc Filing System(高级光盘归档系统)。
|
||
|
||
Linux同样支持Amiga快速文件系统(Amiga FFS file system support)。 [http://www.linux.org/threads/amiga-fast-file-system-affs.4429/][2]
|
||
|
||
"eCrypt filesystem layer support"提供了POSIX兼容的加密文件系统层。这个eCrypt可以
|
||
用于任何文件系统无论驻留的文件系统分区表是什么。[http://www.linux.org/threads/intro-to-encryption.4376/][3]
|
||
|
||
eCrypt层可以有一个设备文件如果启用了这个驱动(Enable notifications for userspace key wrap/unwrap)。设备路径是/dev/ecryptfs。
|
||
|
||
Linux同样支持HFS和HFS+(Apple Macintosh file system support)和(Apple Extended HFS file system support)。[http://www.linux.org/threads/hierarchical-file-system-hfs.4480/][4] 与 [http://www.linux.org/threads/hierarchical-file-system-plus-hfs.4493/][5]
|
||
|
||
BeFS可以在Linux上作为只读文件系统使用(BeOS file system (BeFS) support (read only))。通常上,编写读取特性比编写写入能力简单。
|
||
|
||
特殊的BeFS调试特性(Debug BeFS)。
|
||
|
||
EFS是另外一个Linux只读不写的文件系统。 (EFS file system support (read only)). [http://www.linux.org/threads/extent-file-system-efs.4447/][5]
|
||
|
||
一些闪存可能使用JFFS2文件系统(Journalling Flash File System v2 (JFFS2) support)。下面,可以设置调试层 (JFFS2 debugging verbosity)。 [http://www.linux.org/threads/journaling-flash-file-system-version-2-jffs2.4495/][6]
|
||
|
||
为了在NAND和NOR闪存上使用JFFS2,需要这个驱动(JFFS2 write-buffering support)。
|
||
|
||
下面的驱动提供了更好的错误保护(Verify JFFS2 write-buffer reads)。
|
||
|
||
启用"JFFS2 summary support"可以更快挂载JFFS文件系统。这个驱动存储文件系统的信息。
|
||
|
||
像其他的文件系统的扩展/额外属性驱动一样,JFFS2也有这种驱动(JFFS2 XATTR support)。
|
||
|
||
JFFS2文件系统支持不同的透明压缩系统。这允许JFFS2系统上的文件更小,并且在读取时不需要用户任何特殊的操作。 (Advanced compression options for JFFS2)、 (JFFS2 ZLIB compression support)、(JFFS2 LZO compression support)、(JFFS2 RTIME compression support) 和 (JFFS2 RUBIN compression support)。默认的压缩格式定义在下面的选项中(JFFS2 default compression mode)。
|
||
|
||
JFFS2的继任者也被Linux内核支持(UBIFS file system support)。无排序块图像文件系统(Unsorted Block Image File System (UBIFS)) 同样与LogFS竞争。
|
||
|
||
Linux内核同样支持LogFS(LogFS file system)。
|
||
|
||
基于ROM的嵌入式系统需要CramFS的支持(Compressed ROM file system support (cramfs))。
|
||
|
||
此外,嵌入式系统可以使用SquashFS,这是一种只读压缩文件系统(SquashFS 4.0 - Squashed file system support)。Linux内核也支持SquashFS的扩展属性(Squashfs XATTR support)。
|
||
|
||
|
||
SquashFS支持三种不同的压缩格式 (Include support for ZLIB compressed file systems)、(Include support for LZO compressed file systems) 和 (Include support for XZ compressed file systems)。SquashFS的块大小可以设置为4KB (Use 4K device block size?)。同样,可以设置缓存大小(Additional option for memory-constrained systems)。
|
||
|
||
Linux内核支持 FreeVxFS (FreeVxFS file system support (VERITAS VxFS(TM) compatible))、 Minix (Minix file system support)、 MPEG filesystem (SonicBlue Optimized MPEG File System support)、 HPFS (OS/2 HPFS file system support)、 QNX4 (QNX4 file system support (read only))、 QNX6 (QNX6 file system support (read only)) 和 ROM 文件系统 (ROM file system support)。 [http://www.linux.org/threads/qnx-file-systems.4577/][8] and [http://www.linux.org/threads/minix-mini-unix-file-system.4545/][9]
|
||
|
||
"RomFS backing stores (Block device-backed ROM file system support)"提供了ROMfs不同额外的属性和能力的列表。
|
||
|
||
"Persistent store support"驱动提供对pstore文件系统的支持,这允许访问平台级的持久性存储。
|
||
|
||
pstore文件系统可以存储内核日志/消息(Log kernel console messages)。
|
||
|
||
当内核崩溃时(相当于Windows中的蓝屏死机),"Log panic/oops to a RAM buffer"会在RAM中存储日志。
|
||
|
||
下面一个驱动提供对Xenix、 Coherent、Version 7 和 System V 文件系统的支持(System V/Xenix/V7/Coherent file system support)。
|
||
|
||
Linux内核同样支持UFS(UFS file system support (read only))、 (UFS file system write support (DANGEROUS)) 和 (UFS debugging)。
|
||
|
||
内核也支持exofs(exofs: OSD based file system support)。
|
||
|
||
flash友好型文件系统(Flash-Friendly FileSystem)是一种对于闪存设备的特殊文件系统(F2FS filesystem support (EXPERIMENTAL))、 (F2FS Status Information )、 (F2FS extended attributes) 和 (F2FS Access Control Lists). [http://www.linux.org/threads/flash-friendly-file-system-f2fs.4477/][10]
|
||
|
||
下篇文章我们将配置网络文件系统。谢谢!
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-20.4957/
|
||
|
||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[1]:http://www.linux.org/threads/file-allocation-table-fat.4472/
|
||
[2]:http://www.linux.org/threads/amiga-fast-file-system-affs.4429/
|
||
[3]:http://www.linux.org/threads/intro-to-encryption.4376/
|
||
[4]:http://www.linux.org/threads/hierarchical-file-system-hfs.4480/
|
||
[5]:http://www.linux.org/threads/hierarchical-file-system-plus-hfs.4493/
|
||
[6]:http://www.linux.org/threads/extent-file-system-efs.4447/
|
||
[7]:http://www.linux.org/threads/journaling-flash-file-system-version-2-jffs2.4495/
|
||
[8]:http://www.linux.org/threads/qnx-file-systems.4577/
|
||
[9]:http://www.linux.org/threads/minix-mini-unix-file-system.4545/
|
||
[10]:http://www.linux.org/threads/flash-friendly-file-system-f2fs.4477/ |