14 KiB
Audit your sharding database algorithm
This demonstration of ShardingSphere 5.2.0 elaborates on the implementation logic for auditing data sharding with specific SQL examples.
Thanks to the ShardingSphere community's continuous review and feedback to develop features such as data sharding and read/write splitting, our team found that some users create many shards when using the data sharding feature.
In such cases, there can be 1,000 physical tables corresponding to a sharding logical table, which disturbs users.
For instance, a SELECT * FROM t_order statement will lead to a full-route, which is obviously not the case for OLTP. This SQL can be placed in another Proxy to avoid blocking other requests.
However, if users are not familiar with Proxy or how to write a where condition and don't know that sharding is not supported in this condition, a full-route is still required.
A full-route can lower the performance of Proxy and even result in the failure of a reasonable request. Imagine that there are 1,000 shards in a physical database. If they are executed in parallel, 1,000 connections are needed, and if in serial, the request can lead to a timeout. For this reason, community users asked whether the unreasonable request could be intercepted directly.
Our team considered the issue for a while. One option is to simply block the full-route operation. Doing so requires a check in the code and adding a switch to the configuration file. On the other hand, if the user later needs to set a table to read-only or requires the update operation to carry a limit, does that mean the code and configuration change again? This approach obviously goes against the pluggable logic of Proxy.
In response to the above problems, the recently released Apache ShardingSphere 5.2.0 provides users with auditing for the SQL sharding function. The audit can either be an interception operation or a statistical operation. Similar to the sharding and unique key generation algorithms, the audit algorithm is plugin-oriented, user-defined, and configurable.
Next, I will elaborate on the implementation logic for auditing data sharding with specific SQL examples.
Audit for sharding interface
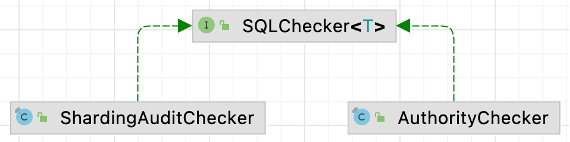
The entrance to Apache ShardingSphere's audit is in the org.apache.shardingsphere.infra.executor.check.SQLCheckEngine class, which will invoke the check method of the SQLChecker interface. Currently, the ShardingSphere audit contains an audit for permission (verify username and password) and an audit for sharding.
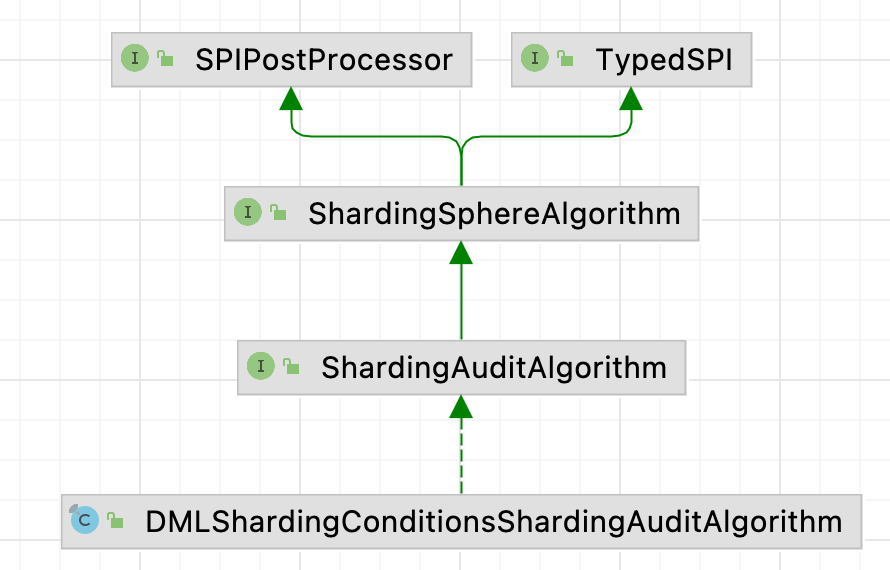
This example focuses on the parent interface implemented in the ShardingAuditChecker of audit for sharding.
You can learn its working principles quickly by viewing the check code of org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.checker.audit.ShardingAuditChecker.
public interface ShardingAuditAlgorithm extends ShardingSphereAlgorithm {/**
* Sharding audit algorithm SQL check.
*
* @param sqlStatementContext SQL statement context
* @param parameters SQL parameters
* @param grantee grantee
* @param database database
* @return SQL check result
*/
SQLCheckResult CHECK(SQLStatementContext<?> sqlStatementContext, List<Object> parameters, Grantee grantee, ShardingSphereDatabase DATABASE);
}
This method obtains the audit strategies of all the sharding tables involved and invokes the audit algorithms configured in each sharding table audit strategy. An exception is displayed to the user if an audit algorithm fails to pass.
Some users may wonder what disableAuditNames does here. The sharding audit also allows users to skip this process. In some cases, users may need to execute SQL that should have been blocked by the audit, and they are aware of the impact of this SQL.
Users can utilize the Hint: disableAuditNames to skip audit interception, which will be described with practical examples later. The Proxy Administrators can configure allowHintDisable to control whether to allow users to skip this process. The default value is true, indicating that a Hint-based skip is permitted.
Audit for sharding algorithm
The audit for sharding algorithm interface org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.spi.ShardingAuditAlgorithm is inherited from SPI class ShardingSphereAlgorithm. It inherits type and props properties and defines its own check method. If you want to customize your audit algorithm, just implement the interface and add it to INF.services.
public interface ShardingAuditAlgorithm extends ShardingSphereAlgorithm {/**
* Sharding audit algorithm SQL check.
*
* @param sqlStatementContext SQL statement context
* @param parameters SQL parameters
* @param grantee grantee
* @param database database
* @return SQL check result
*/
SQLCheckResult CHECK(SQLStatementContext<?> sqlStatementContext, List<Object> parameters, Grantee grantee, ShardingSphereDatabase DATABASE);
}
Apache ShardingSphere implements a general audit for sharding algorithm org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.algorithm.audit.DMLShardingConditionsShardingAuditAlgorithm, namely the above-mentioned SQL statement that intercepts the full-route.
The algorithm makes decisions by determining whether the sharding condition is null. Of course, it won't intercept broadcast tables and non-sharding tables.
public final class DMLShardingConditionsShardingAuditAlgorithm implements ShardingAuditAlgorithm {
@Getter
private Properties props;
@Override
public void init(final Properties props){
this.props = props;}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
@Override
public SQLCheckResult CHECK(final SQLStatementContext<?> sqlStatementContext, final List<Object> parameters, final Grantee grantee, final ShardingSphereDatabase DATABASE){IF(sqlStatementContext.getSqlStatement() instanceof DMLStatement){
ShardingRule rule =DATABASE.getRuleMetaData().getSingleRule(ShardingRule.class);IF(rule.isAllBroadcastTables(sqlStatementContext.getTablesContext().getTableNames())|| sqlStatementContext.getTablesContext().getTableNames().stream().noneMatch(rule::isShardingTable)){RETURNNEW SQLCheckResult(TRUE,"");}
ShardingConditionEngine shardingConditionEngine = ShardingConditionEngineFactory.createShardingConditionEngine(sqlStatementContext,DATABASE, rule);IF(shardingConditionEngine.createShardingConditions(sqlStatementContext, parameters).isEmpty()){RETURNNEW SQLCheckResult(FALSE,"Not allow DML operation without sharding conditions");}}RETURNNEW SQLCheckResult(TRUE,"");}
@Override
public String getType(){RETURN"DML_SHARDING_CONDITIONS";}}
I'd like to introduce another audit for the sharding algorithm: LimitRequiredShardingAuditAlgorithm. This algorithm can intercept SQL without carrying a limit in the update and delete operations.
As this algorithm is less universal, it is not currently integrated into Apache ShardingSphere. As you can see, it is very easy to implement a custom algorithm, which is why the audit for sharding framework is needed. Thanks to its plugin-oriented architecture, ShardingSphere boasts great scalability.
public final class LimitRequiredShardingAuditAlgorithm implements ShardingAuditAlgorithm {
@Getter
private Properties props;
@Override
public void init(final Properties props){
this.props = props;}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
@Override
public SQLCheckResult CHECK(final SQLStatementContext<?> sqlStatementContext, final List<Object> parameters, final Grantee grantee, final ShardingSphereDatabase DATABASE){IF(sqlStatementContext instanceof UpdateStatementContext && !((MySQLUpdateStatement) sqlStatementContext.getSqlStatement()).getLimit().isPresent()){RETURNNEW SQLCheckResult(FALSE,"Not allow update without limit");}IF(sqlStatementContext instanceof DeleteStatementContext && !((MySQLDeleteStatement) sqlStatementContext.getSqlStatement()).getLimit().isPresent()){RETURNNEW SQLCheckResult(FALSE,"Not allow delete without limit");}RETURNNEW SQLCheckResult(TRUE,"");}
@Override
public String getType(){RETURN"LIMIT_REQUIRED";}}
Use audit for sharding
Audit for sharding requires you to configure an audit strategy for logical tables. To help you get started quickly, its configuration is the same as that of the sharding algorithm and the sharding key value generator.
There is an algorithm definition and strategy definition, and a default audit strategy is also supported. If the audit strategy is configured in the logical table, it affects only that logical table.
If defaultAuditStrategy is configured in the logical table, it takes effect for all the logical tables under the sharding rule. Auditors are similar to ShardingAlgorithms, auditStrategy to databaseStrategy, and defaultAuditStrategy to defaultDatabaseStrategy or defaultTableStrategy.
Please refer to the following example. Only the configuration of the audit for sharding is displayed. You must configure the sharding algorithm and data source yourself.
rules:- !SHARDINGTABLES:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}
auditStrategy:
auditorNames:- sharding_key_required_auditor
allowHintDisable: TRUE
defaultAuditStrategy:
auditorNames:- sharding_key_required_auditor
allowHintDisable: TRUE
auditors:
sharding_key_required_auditor:TYPE: DML_SHARDING_CONDITIONS
Step 1: Execute a query operation. An error is displayed as the audit strategy for intercepting the full-database route is configured.
mysql>SELECT*FROM t_order;
ERROR 13000(44000): SQLCHECK failed, error message: NOT allow DML operation WITHOUT sharding conditions
Step 2: Add HINT. The name of the HINT is /* ShardingSphere hint: disableAuditNames */,and disableAuditNames is followed by the auditorsNames configured in the preceding command.
If multiple names exist, separate them with spaces such as/* ShardingSphere hint: disableAuditNames=auditName1 auditName2*/. After using HINT, you can see that the SQL operation is successfully executed.
mysql>/* ShardingSphere hint: disableAuditNames=sharding_key_required_auditor */SELECT*FROM t_order;
+----------+---------+------------+--------+| order_id | user_id | address_id |STATUS|+----------+---------+------------+--------+|30|20|10|20||32|22|10|20|+----------+---------+------------+--------+2ROWSINSET(0.01 sec)
Note: HINT requires you to modify the server.yaml configuration of Proxy. In addition, if you are using MySQL terminal to connect to Proxy directly, you need to add the -c property—otherwise, HINT comments will be filtered out of the MySQL terminal and will not be parsed by Proxy on the backend.
rules:- !SQL_PARSER
sqlCommentParseEnabled: TRUE
sqlStatementCache:
initialCapacity: 2000
maximumSize: 65535
parseTreeCache:
initialCapacity: 128
maximumSize: 1024
props:
proxy-hint-enabled: TRUE
mysql -uroot -proot -h127.0.0.1 -P3307 -c
DistSQL with audit for sharding
As you can see from the release notes, Apache ShardingSphere 5.2.0 supports the following DistSQL with audit for sharding function:
CREATE SHARDING AUDITOR
ALTER SHARDING AUDITOR
SHOW SHARDING AUDIT ALGORITHMS
The following DistSQL will be supported IN future releases:
DROP SHARDING AUDITOR
SHOW UNUSED SHARDING AUDIT ALGORITHMS
CREATE SHARDING TABLE RULE # including AUDIT_STRATEGY
This post introduced how audit for sharding works with specific examples. I believe you already have a basic understanding of this function and can use it whenever you need or use a custom algorithm.
You are also welcome to submit general algorithms to the community. If you have any ideas to contribute or encounter issues with your ShardingSphere, feel free to post them on GitHub.
This article originally appeared on ShardingSphere 5.2.0: Audit for sharding intercepts unreasonable requests in multi-shards scenarios and is republished with permission.
via: https://opensource.com/article/22/11/audit-sharding-database
作者:Yacine Si Tayeb, PhD 选题:lkxed 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID