4.0 KiB
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to access a NAT guest from host with VirtualBox
Question: I have a guest VM running on VirtualBox, which uses NAT networking. So the guest VM is getting a private IP address (10.x.x.x) assigned by VirtualBox. If I want to SSH to the guest VM from the host machine, how can I do that?
VirtualBox supports several networking options for guest VMs, one of them being NAT networking. When NAT networking is enabled for a guest VM, VirtualBox automatically performs network address translation between the guest VM and host's network stack, so that you do not have to configure anything on the host machine and local network for the guest VM's networking to work. The implication of such NAT, however, is that the guest VM is not reachable or visible from external networks as well as from the local host itself. This is a problem if you want to access the guest VM from the host machine for some reason (e.g., SSH).
If you want to access a NAT guest from the host on VirtualBox, you can enable port forwarding for VirtualBox NAT, either from the GUI or from the command line. This tutorial demonstrates how to SSH a NAT guest from the host by enabling port forwarding for port 22. If you want to access HTTP of a NAT guest instead, replace port 22 with port 80.
Configure VirtualBox Port Forwarding from the GUI
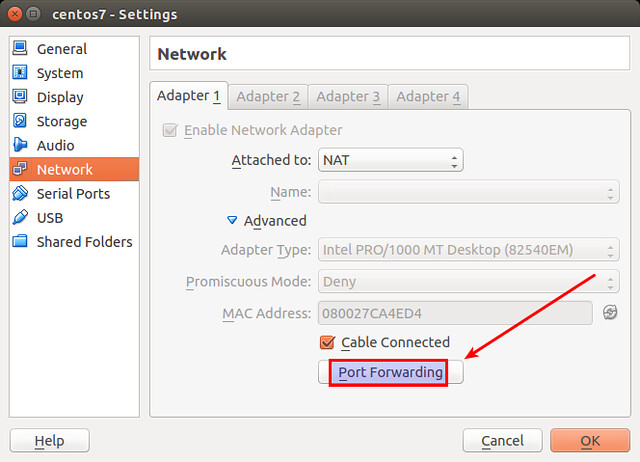
On VirtualBox, choose the guest VM you want to access, and open "Settings" window of the VM. Click on "Network" menu on the left, click on "Advanced" to show additional network adapter options.
Click on a button labeled "Port Forwarding."
You will see a window where you can configure port forwarding rules. Click on "Add" icon in the upper right corner.
Add a new port forwarding rule with the following detail.
- Name: SSH (any arbitrary unique name)
- Protocol: TCP
- Host IP: 127.0.0.1
- Host Port: 2222 (any unused port higher than 1024)
- Guest IP: IP address of the guest VM
- Guest Port: 22 (SSH port)
Port forwarding configured for the guest VM will be enabled automatically when you power on the guest VM. For verification, check that port 2222 is opened by VirtualBox after you launch the guest VM:
$ sudo netstat -nap | grep 2222
Now that port forwarding is in place, you can SSH to the guest VM bs follows.
$ ssh -p 2222 <login>@127.0.0.1
An SSH login request sent to 127.0.0.1:2222 will automatically be translated into 10.0.2.15:22 by VirtualBox, allowing you to SSH to the guest VM.
Configure VirtualBox Port Forwarding from the Command Line
VirtualBox comes with a command-line management interface called VBoxManage. Using this command-line tool, you can also set up port forwarding for your guest VM.
The following command creates a port forwarding rule for guest VM named "centos7" with IP address 10.0.2.15 and SSH port 22, mapped to local host at port 2222. The name of the rule ("SSH" in this example) must be unique.
$ VBoxManage modifyvm "centos7" --natpf1 "SSH,tcp,127.0.0.1,2222,10.0.2.15,22"
Once the rule is created, you can verify that by using the command below.
$ VBoxManage showvminfo "centos7" | grep NIC
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/access-nat-guest-from-host-virtualbox.html