3.8 KiB
translating---geekpi
Install and use Ansible (Automation Tool) in CentOS 7
Ansible is a free & open source Configuration and automation tool for UNIX like operating system. It is written in python and similar to Chef or Puppet but there is one difference and advantage of Ansible is that we don’t need to install any agent on the nodes. It uses SSH for making communication to its nodes.
In this article we will install and configure Ansible in CentOS 7 and will try to manage its two nodes.
Ansible Server – ansible.linuxtechi.com ( 192.168.1.15 )
Nodes – 192.168.1.9 , 192.168.1.10
Step :1 Set EPEL repository
Ansible package is not available in the default yum repositories, so we will enable epel repository for CentOS 7 using below commands
[root@ansible ~]# rpm -iUvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-5.noarch.rpm
Step:2 Install Anisble using yum command
[root@ansible ~]# yum install ansible
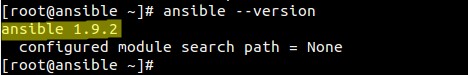
Once the installation is completed, check the ansible version :
[root@ansible ~]# ansible --version
Step:3 Setup keys based SSH authentication with Nodes.
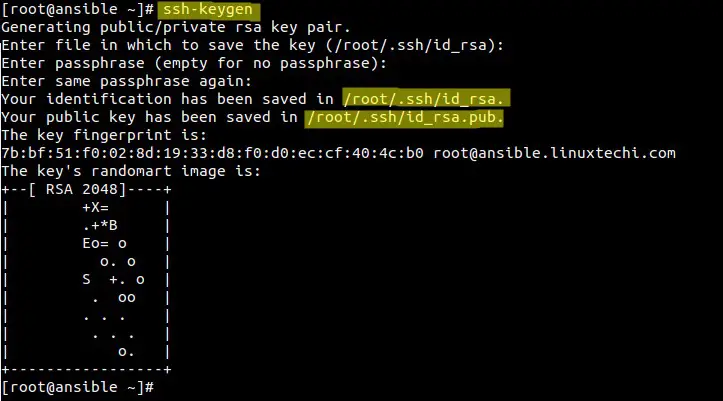
Generate keys on the Ansible server and copy public key to the nodes.
root@ansible ~]# ssh-keygen
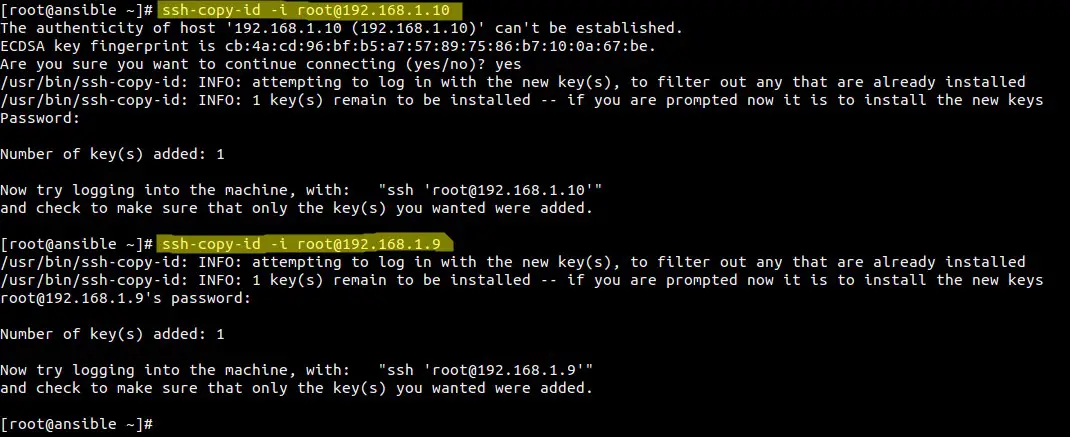
Use ssh-copy-id command to copy public key of Ansible server to its nodes.
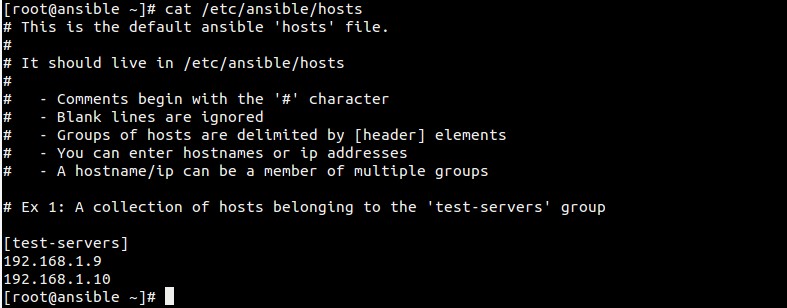
Step:4 Define the nodes or inventory of servers for Ansible.
File ‘/etc/ansible/hosts‘ maintains the inventory of servers for Ansible.
[root@ansible ~]# vi /etc/ansible/hosts
[test-servers]
192.168.1.9
192.168.1.10
Save and exit the file.
Sample output of hosts file.
Step:5 Now try to run the Commands from Ansible Server.
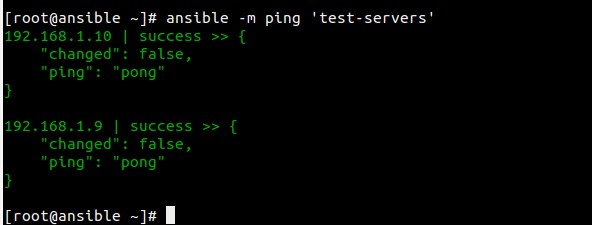
Check the connectivity of ‘test-servers’ or ansible nodes using ping
[root@ansible ~]# ansible -m ping 'test-servers'
Executing Shell commands :
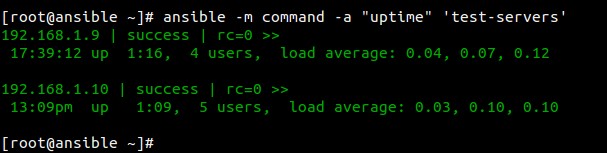
Example :1 Check the uptime of Ansible nodes
[root@ansible ~]# ansible -m command -a "uptime" 'test-servers'
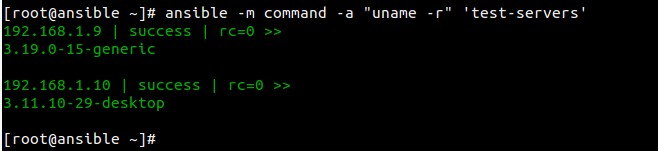
Example:2 Check Kernel Version of nodes
[root@ansible ~]# ansible -m command -a "uname -r" 'test-servers'
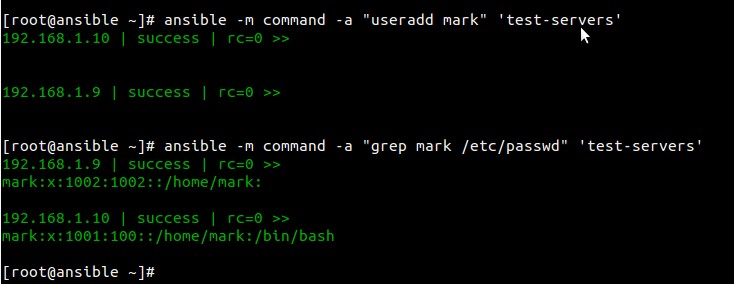
Example:3 Adding a user to the nodes
[root@ansible ~]# ansible -m command -a "useradd mark" 'test-servers'
[root@ansible ~]# ansible -m command -a "grep mark /etc/passwd" 'test-servers'
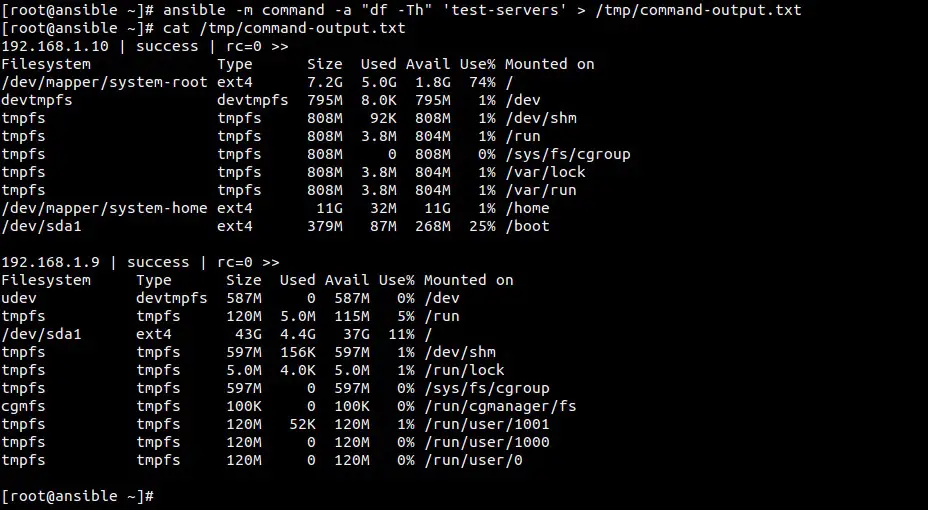
Example:4 Redirecting the output of command to a file
[root@ansible ~]# ansible -m command -a "df -Th" 'test-servers' > /tmp/command-output.txt
via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/install-and-use-ansible-in-centos-7/
作者:Pradeep Kumar 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID