5.3 KiB
How to create a pull request in GitHub
Learn how to fork a repo, make changes, and ask the maintainers to
review and merge it.

So, you know how to use git. You have a GitHub repo and can push to it. All is well. But how the heck do you contribute to other people's GitHub projects? That is what I wanted to know after I learned git and GitHub. In this article, I will explain how to fork a git repo, make changes, and submit a pull request.
When you want to work on a GitHub project, the first step is to fork a repo.
Use my demo repo to try it out.
Once there, click on the Fork button in the top-right corner. This creates a new copy of my demo repo under your GitHub user account with a URL like:
`https://github.com/<YourUserName>/demo`
The copy includes all the code, branches, and commits from the original repo.
Next, clone the repo by opening the terminal on your computer and running the command:
`git clone https://github.com/<YourUserName>/demo`
Once the repo is cloned, you need to do two things:
- Create a new branch by issuing the command:
`git checkout -b new_branch`
- Create a new remote for the upstream repo with the command:
`git remote add upstream https://github.com/kedark3/demo`
In this case, "upstream repo" refers to the original repo you created your fork from.
Now you can make changes to the code. The following code creates a new branch, makes an arbitrary change, and pushes it to new_branch:
$ git checkout -b new_branch
Switched to a new branch ‘new_branch’
$ echo “some test file” > test
$ cat test
Some test file
$ git status
On branch new_branch
No commits yet
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
test
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
$ git add test
$ git commit -S -m "Adding a test file to new_branch"
[new_branch (root-commit) 4265ec8] Adding a test file to new_branch
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 test
$ git push -u origin new_branch
Enumerating objects: 3, done.
Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 918 bytes | 918.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Remote: Create a pull request for ‘new_branch’ on GitHub by visiting:
Remote: <http://github.com/example/Demo/pull/new/new\_branch>
Remote:
* [new branch] new_branch -> new_branch
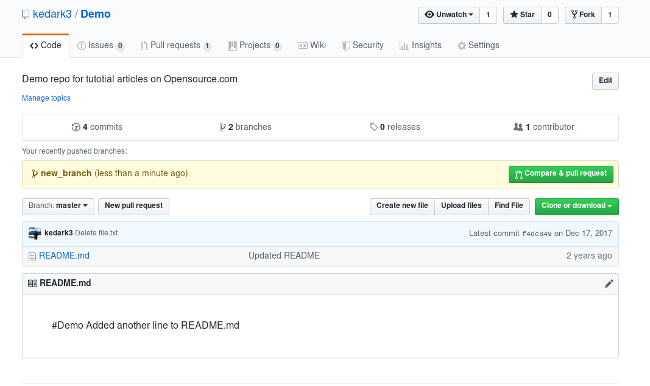
Once you push the changes to your repo, the Compare & pull request button will appear in GitHub.
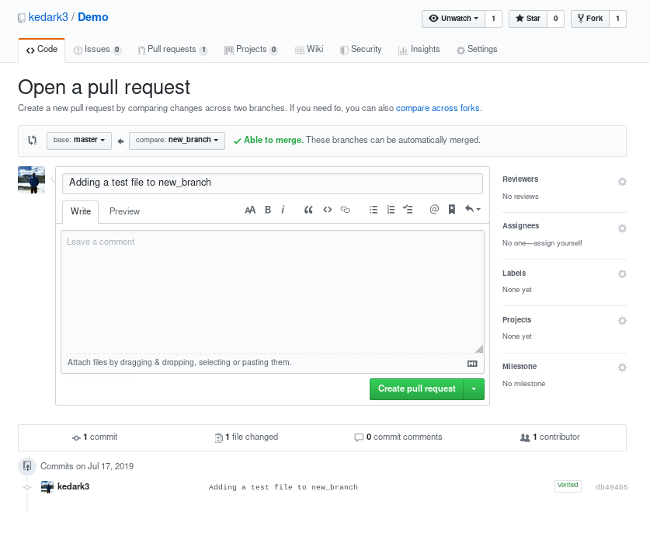
Click it and you'll be taken to this screen:
Open a pull request by clicking the Create pull request button. This allows the repo's maintainers to review your contribution. From here, they can merge it if it is good, or they may ask you to make some changes.
TLDR
In summary, if you want to contribute to a project, the simplest way is to:
- Find a project you want to contribute to
- Fork it
- Clone it to your local system
- Make a new branch
- Make your changes
- Push it back to your repo
- Click the Compare & pull request button
- Click Create pull request to open a new pull request
If the reviewers ask for changes, repeat steps 5 and 6 to add more commits to your pull request.
Happy coding!
In a previous article , I discussed the complaints that have been leveled against GitHub during the...
Arfon Smith works at GitHub and is involved in a number of activities at the intersection of open...
via: https://opensource.com/article/19/7/create-pull-request-github
作者:Kedar Vijay Kulkarni 选题:lujun9972 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID