6.8 KiB
How To Restore Sudo Privileges To A User
The other day I was testing how to add a regular user to sudo group and remove the given privileges to make him as a normal user again on Ubuntu. While testing, I removed my administrative user from the ‘sudo’ group. As you already know, a user should be in sudo group to do any administrative tasks. But, I had only one super user and I already took out his sudo privileges. Whenever I run a command with sudo prefix, I encountered an error – “ sk is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported “. I can’t do any administrative tasks. I couldn’t switch to root user using ‘sudo su’ command. As you know already, root user is disabled by default in Ubuntu, so I can’t log in as root user either. Have you ever been in a situation like this? No worries! This brief tutorial explains how to restore sudo privileges to a user on Linux. I tested this on Ubuntu 18.04 system, but it might work on other Linux distributions as well.
Restore Sudo Privileges
Boot your Linux system into recovery mode.
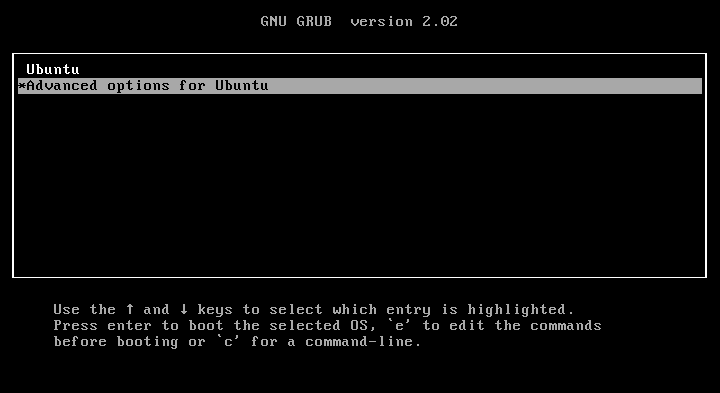
To do so, restart your system and press and hold the SHIFT key while booting. You will see the grub boot menu. Choose “Advanced options for Ubuntu” from the boot menu list.
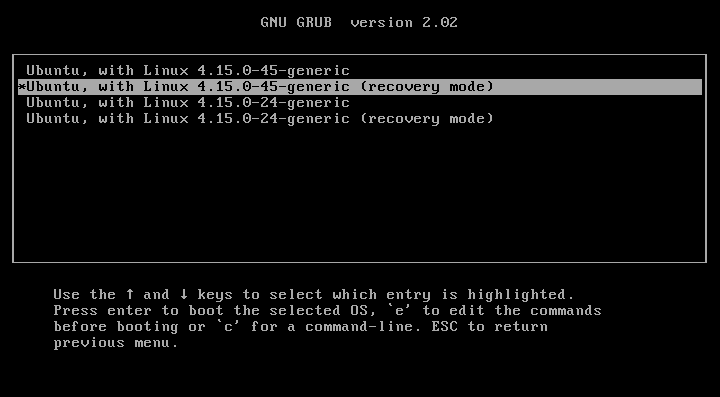
In the next screen, choose “recovery mode” option and hit ENTER:
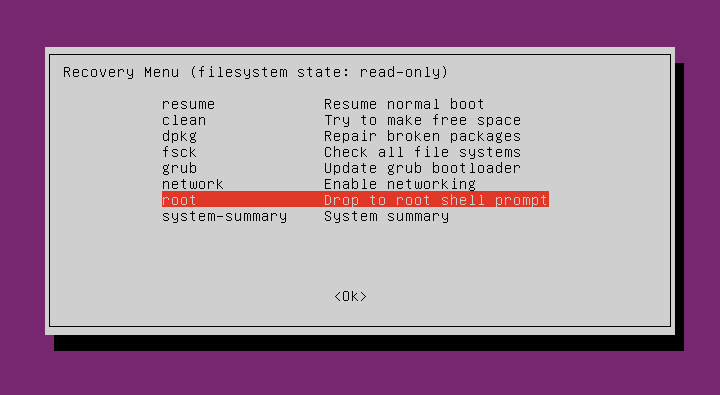
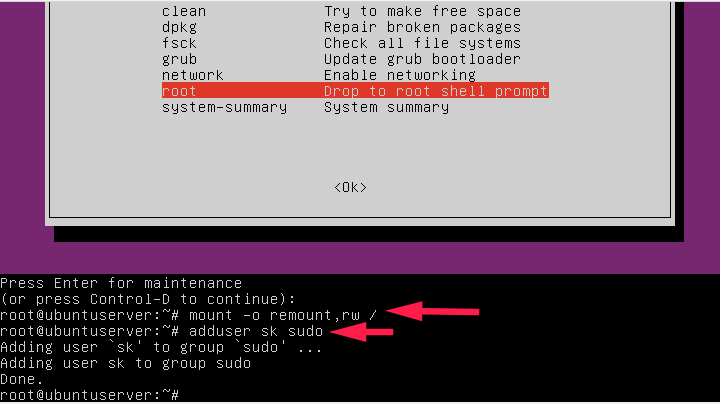
Next, choose “Drop to root shell prompt” option and hit ENTER key:
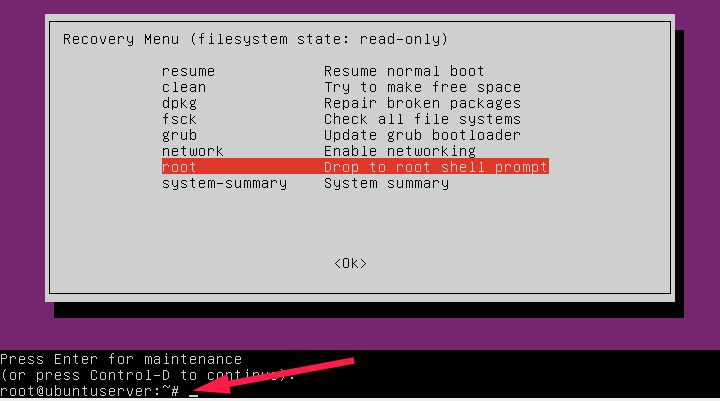
You’re now in recovery mode as root user.
Type the following command to mount root (/) file system in read/write mode.
mount -o remount,rw /
Now, add the user that you removed from the sudo group.
In my case, I am adding the user called ‘sk’ to the sudo group using the following command:
adduser sk sudo
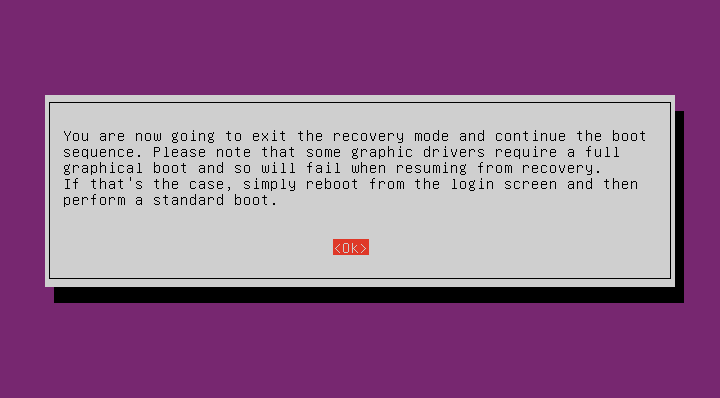
Then, type exit to return back to the recovery menu. Select Resume to start your Ubuntu system.
Press ENTER to continue to log-in normal mode:
Now check if the sudo privileges have been restored.
To do so, type the following command from the Terminal.
$ sudo -l -U sk
Sample output:
[sudo] password for sk:
Matching Defaults entries for sk on ubuntuserver:
env_reset, mail_badpass,
secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin
User sk may run the following commands on ubuntuserver:
(ALL : ALL) ALL
As you see in the above message, the user sk can run all commands with sudo prefix. Congratulations! You have successfully restored the sudo privileges to the user.
There are also other possibilities for causing broken sudo
Please note that I actually did it on purpose. I removed myself from the sudo group and fixed the broken sudo privileges as described above. Don’t do this if you have only one sudo user. And, this method will work only on systems that you have physical access. If it is remote server or vps, it is very difficult to fix it. You might require your hosting provider’s help.
Also, there are two other possibilities for causing broken sudo.
- The /etc/sudoers file might have been altered.
- You or someone might have changed the permission of /etc/sudoers file.
If you have done any one or all of the above mentioned things and ended up with broken sudo, try the following solutions.
Solution 1:
If you have altered the contents of /etc/sudoers file, go to the recovery mode as described earlier.
Backup the existing /etc/sudoers file before making any changes.
cp /etc/sudoers /etc/sudoers.bak
Then, open /etc/sudoers file:
visudo
Make the changes in the file to look like this:
#
# This file MUST be edited with the 'visudo' command as root.
#
# Please consider adding local content in /etc/sudoers.d/ instead of
# directly modifying this file.
#
# See the man page for details on how to write a sudoers file.
#
Defaults env_reset
Defaults mail_badpass
Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin"
# Host alias specification
# User alias specification
# Cmnd alias specification
# User privilege specification
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
# Members of the admin group may gain root privileges
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
# Allow members of group sudo to execute any command
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
# See sudoers(5) for more information on "#include" directives:
#includedir /etc/sudoers.d
Once you modified the contents to reflect like this, press CTRL+X and y save and close the file.
Finally, type ‘exit’ and select Resume to start your Ubuntu system to exit from the recovery mode and continue booting as normal user.
Now, try to use run any command with sudo prefix to verify if the sudo privileges are restored.
Solution 2:
If you changed the permission of the /etc/sudoers file, this method will fix the broken sudo issue.
From the recovery mode, run the following command to set the correct permission to /etc/sudoers file:
chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers
Once you set the proper permission to the file, type ‘exit’ and select Resume to start your Ubuntu system in normal mode. Finally, verify if you can able to run any sudo command.
Suggested read:
And, that’s all for now. Hope this was useful . More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!
Cheers!
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/how-to-restore-sudo-privileges-to-a-user/