mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-22 23:00:57 +08:00
259 lines
8.2 KiB
Markdown
259 lines
8.2 KiB
Markdown
如何用 Shell Tracing 跟踪 shell 脚本中命令的执行
|
||
============================================================
|
||
|
||
在[ shell 脚本调试系列][3] 中,本文将解释第三种 shell 脚本调试模式,即 shell tracing,并查看一些示例来演示它如何工作以及如何使用它。
|
||
|
||
本系列的前面部分清晰地阐明了另外两种 shell 脚本调试模式:verbose 模式和语法检查模式,以及如何在这些模式下启用 shell 脚本调试的易于理解的示例。
|
||
|
||
1. [如何在 Linux 中启用 shell 脚本调试模式 - 第1部分][1]
|
||
2. [如何在 shell 脚本中执行语法检查调试模式 - 第2部分][2]
|
||
|
||
shell tracing 只是跟踪 shell 脚本中的命令的执行。要打开 shell tracing,请使用 `-x` 调试选项。
|
||
|
||
这让 shell 在终端上执行时显示所有命令及其参数。
|
||
|
||
我们将使用下面的 `sys_info.sh` shell 脚本,它会简要地打印你的系统日期和时间、登录的用户数和系统的运行时间。脚本中包含我们需要查找和更正的语法错误。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
#script to print brief system info
|
||
ROOT_ID="0"
|
||
DATE=`date`
|
||
NO_USERS=`who | wc -l`
|
||
UPTIME=`uptime`
|
||
check_root(){
|
||
if [ "$UID" -ne "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
|
||
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
|
||
exit 1;
|
||
}
|
||
print_sys_info(){
|
||
echo "System Time : $DATE"
|
||
echo "Number of users: $NO_USERS"
|
||
echo "System Uptime : $UPTIME
|
||
}
|
||
check_root
|
||
print_sys_info
|
||
exit 0
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
保存文件并执行脚本。脚本只能用 root 用户运行,因此如下使用[ sudo 命令][4]运行:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ chmod +x sys_info.sh
|
||
$ sudo bash -x sys_info.sh
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][5]
|
||
|
||
*shell 跟踪 - 显示脚本中的错误*
|
||
|
||
从上面的输出我们可以观察到,首先执行命令,然后其输出做为一个变量的值。
|
||
|
||
例如,先执行 date,其输出做为变量 DATE 的值。
|
||
|
||
我们可以执行语法检查,只显示语法错误,如下所示:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo bash -n sys_info.sh
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][6]
|
||
|
||
*脚本中语法检查*
|
||
|
||
如果我们批判地看这个 shell 脚本,我们就会发现 `if 语句` 缺少了封闭条件的 `fi` 关键字。因此,让我们加上它,新的脚本应该看起来像这样:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
#script to print brief system info
|
||
ROOT_ID="0"
|
||
DATE=`date`
|
||
NO_USERS=`who | wc -l`
|
||
UPTIME=`uptime`
|
||
check_root(){
|
||
if [ "$UID" -ne "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
|
||
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
|
||
exit 1;
|
||
fi
|
||
}
|
||
print_sys_info(){
|
||
echo "System Time : $DATE"
|
||
echo "Number of users: $NO_USERS"
|
||
echo "System Uptime : $UPTIME
|
||
}
|
||
check_root
|
||
print_sys_info
|
||
exit 0
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
再次保存文件并以 root 执行,同时做语法检查:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo bash -n sys_info.sh
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][7]
|
||
|
||
*在 shell 脚本中执行语法检查*
|
||
|
||
上面的语法检查操作的结果仍然显示在脚本的第 21 行还有一个错误。所以,我们仍然要纠正一些语法。
|
||
|
||
再一次分析脚本,会发现第 21 行的错误是由于在 `print_sys_info` 函数内最后一个 [echo 命令][8]中没有闭合双引号`(”)`。
|
||
|
||
我们将在 echo 命令中添加闭合双引号并保存文件。修改过的脚本如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
#script to print brief system info
|
||
ROOT_ID="0"
|
||
DATE=`date`
|
||
NO_USERS=`who | wc -l`
|
||
UPTIME=`uptime`
|
||
check_root(){
|
||
if [ "$UID" -ne "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
|
||
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
|
||
exit 1;
|
||
fi
|
||
}
|
||
print_sys_info(){
|
||
echo "System Time : $DATE"
|
||
echo "Number of users: $NO_USERS"
|
||
echo "System Uptime : $UPTIME"
|
||
}
|
||
check_root
|
||
print_sys_info
|
||
exit 0
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
现在再一次检查语法。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo bash -n sys_info.sh
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
上面的命令不会产生任何输出,因为我们的脚本语法上正确。我们也可以再次跟踪脚本执行,它应该工作得很好:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo bash -x sys_info.sh
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][9]
|
||
|
||
*跟踪 shell 脚本执行*
|
||
|
||
现在运行脚本。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
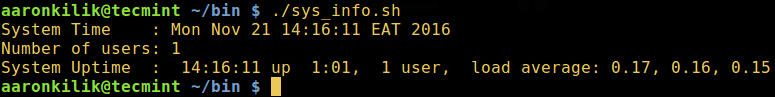
$ sudo ./sys_info.sh
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][10]
|
||
|
||
*用 shell 脚本显示日期、时间和运行时间*
|
||
|
||
### shell 跟踪执行的重要性
|
||
|
||
shell 脚本跟踪帮助我们识别语法错误,更重要的是识别逻辑错误。例如,在`sys_info.sh` shell 脚本中的 `check_root` 函数,它用于确定用户是否为 root,因为脚本只允许由超级用户执行。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
check_root(){
|
||
if [ "$UID" -ne "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
|
||
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
|
||
exit 1;
|
||
fi
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
这里的魔法是由 `if 语句` 表达式 `["$ UID" -ne "$ ROOT_ID"]` 控制的,一旦我们不使用合适的数字运算符(示例中为 `-ne`,这意味着不相等),我们最终可能会出一个逻辑错误。
|
||
|
||
假设我们使用 `-eq` (意思是等于),这将允许任何系统用户以及 root 用户运行脚本,因此是一个逻辑错误。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
check_root(){
|
||
if [ "$UID" -eq "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
|
||
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
|
||
exit 1;
|
||
fi
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
注意:我们在本系列开头介绍过,set 这个 shell 内置命令可以在 shell 脚本的特定部分激活调试。
|
||
|
||
因此,下面的行将帮助我们通过跟踪脚本的执行在其中找到这个逻辑错误:
|
||
|
||
具有逻辑错误的脚本:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
#script to print brief system info
|
||
ROOT_ID="0"
|
||
DATE=`date`
|
||
NO_USERS=`who | wc -l`
|
||
UPTIME=`uptime`
|
||
check_root(){
|
||
if [ "$UID" -eq "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
|
||
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
|
||
exit 1;
|
||
fi
|
||
}
|
||
print_sys_info(){
|
||
echo "System Time : $DATE"
|
||
echo "Number of users: $NO_USERS"
|
||
echo "System Uptime : $UPTIME"
|
||
}
|
||
#turning on and off debugging of check_root function
|
||
set -x ; check_root; set +x ;
|
||
print_sys_info
|
||
exit 0
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
保存文件并调用脚本,在输出中,我们可以看到一个普通系统用户可以在未 sudo 的情况下运行脚本。 这是因为 **USER_ID** 的值为 100,不等于 **ROOT_ID** 为 **0** 的 root。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ ./sys_info.sh
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][11]
|
||
|
||
**未 sudo 的情况下运行 shell 脚本**
|
||
|
||
那么,现在我们已经完成了[ shell 脚本调试系列][12],可以在下面的反馈栏里给我们关于本篇或者本系列提出问题或反馈。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
作者简介:
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin、web 开 发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/trace-shell-script-execution-in-linux/
|
||
|
||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||
校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/enable-shell-debug-mode-linux/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/check-syntax-in-shell-script/
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/enable-shell-debug-mode-linux/
|
||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/su-vs-sudo-and-how-to-configure-sudo-in-linux/
|
||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Shell-Tracing-Errors.png
|
||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Syntax-Checking-in-Script.png
|
||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Syntax-Check-in-Shell-Scripts.png
|
||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Trace-Shell-Execution.png
|
||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Script-to-Show-Date-and-Uptime.png
|
||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Run-Shell-Script-Without-Sudo.png
|
||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/enable-shell-debug-mode-linux/
|