12 KiB
磁盘写满或磁盘不可写?解决Linux和UNIX系统这些硬盘问题的8个小贴士
不能在Linux或者类UNIX系统的硬盘上写入数据?想解决服务器上磁盘损坏的问题吗?想知道你为什么总是在屏幕上看到“磁盘已满”的字眼吗?想学习处理这些问题的办法吗?试试一下这8个解决Linux及UNIX服务器硬盘问题的小贴士吧。
#1 - 错误: 设备上无剩余空间
当你的类UNIX系统磁盘写满了时你会在屏幕上看到这样的信息。在这种情况下,我运行fallocate命令然后我的系统就会提示磁盘空间已经耗尽:
$ fallocate -l 1G test4.img
fallocate: test4.img: fallocate failed: No space left on device
第一步是运行df命令来查看一个有分区的文件系统的总磁盘空间和可用空间的信息:
$ df
或者试试可读性比较强的输出格式:
$ df -h
部分输出内容:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda6 117G 54G 57G 49% /
udev 993M 4.0K 993M 1% /dev
tmpfs 201M 264K 200M 1% /run
none 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
none 1002M 0 1002M 0% /run/shm
/dev/sda1 1.8G 115M 1.6G 7% /boot
/dev/sda7 4.7G 145M 4.4G 4% /tmp
/dev/sda9 9.4G 628M 8.3G 7% /var
/dev/sda8 94G 579M 89G 1% /ftpusers
/dev/sda10 4.0G 4.0G 0 100% /ftpusers/tmp
使用df命令输出可以清楚地发现,在 /dev/sda10 分区下总共4.0Gb的空间被全部写满了。
修复磁盘写满的问题
1.用gzip,bzip2或tar命令压缩未压缩的日志和其它文件:
gzip /ftpusers/tmp/*.log
bzip2 /ftpusers/tmp/large.file.name
2.在类UNIX系统中用rm命令删除不想要的文件:
rm -rf /ftpusers/tmp/*.bmp
rsync --remove-source-files -azv /ftpusers/tmp/*.mov /mnt/usbdisk/
rsync --remove-source-files -azv /ftpusers/tmp/*.mov server2:/path/to/dest/dir/
4.在类UNIX系统中找出最占磁盘空间的目录或文件:
du -a /ftpusers/tmp | sort -n -r | head -n 10
du -cks * | sort -rn | head
5.清空指定文件。这招对日志文件很有效:
truncate -s 0 /ftpusers/ftp.upload.log
### bash/sh等 ##
>/ftpusers/ftp.upload.log
## perl ##
perl -e'truncate "filename", LENGTH'
6.在Linux和UNIX中找出并删除显示着但已经被删除的大文件:
## 基于Linux/Unix/OSX/BSD等系统 ##
lsof -nP | grep '(deleted)'
## 只基于Linux ##
find /proc/*/fd -ls | grep '(deleted)'
清空它:
## 基于Linux/Unix/OSX/BSD等所有系统 ##
> "/path/to/the/deleted/file.name"
## 只基于Linux ##
> "/proc/PID-HERE/fd/FD-HERE"
#2 - 文件系统是只读模式吗?
当你尝试新建或保存一个文件时,你可能最终得到诸如以下的错误:
$ cat > file
-bash: file: Read-only file system
运行mount命令来查看被挂载的文件系统是否处于只读状态:
$ mount
$ mount | grep '/ftpusers'
在基于Linux的系统中要修复这个问题,只需将这个处于只读状态的文件系统重新挂载即可:
# mount -o remount,rw /ftpusers/tmp
另外,我是这样用rw模式重新挂载FreeBSD 9.x服务器的根目录的:
# mount -o rw /dev/ad0s1a /
#3 - Am I running out of inodes?
有时候,df命令能显示出磁盘有空余的空间但是系统却声称文件系统已经写满了。此时你需要用以下命令来检查能在文件系统中识别文件及其属性的索引节点:
$ df -i
$ df -i /ftpusers/
部分输出内容:
Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
/dev/sda8 6250496 11568 6238928 1% /ftpusers
所以 /ftpusers 下有总计62,50,496KB大小的索引节点但是只有11,568KB被使用。你可以在 /ftpusers 位置下另外创建62,38,928KB大小的文件。如果你的索引节点100%被使用了,试试看以下的选项:
- 找出不想要的文件并删除它,或者把它移动到其它服务器上。
- 找出不想要的大文件并删除它,或者把它移动到其它服务器上。
#4 - 我的硬盘驱动器宕了吗?
日志文件中的输入/输出错误(例如 /var/log/messages)说明硬盘出了一些问题并且可能已经失效,你可以用smartctl命令来查看硬盘的错误,这是一个在类UNIX系统下控制和监控硬盘状态的一个命令。语法如下:
smartctl -a /dev/DEVICE
# check for /dev/sda on a Linux server
smartctl -a /dev/sda
你也可以用"Disk Utility"这个软件来获得同样的信息。
图 01: Gnome磁盘工具(Applications > System Tools > Disk Utility)
注意: 不要对SMART工具期望太高,它在某些状况下无法工作,我们要定期做备份。
#5 - 我的硬盘驱动器和服务器是不是太热了?
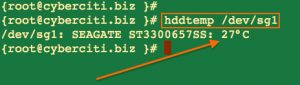
高温会引起服务器低效,所以你需要把服务器和磁盘维持在一个平稳适当的温度,高温甚至能导致服务器宕机或损坏文件系统和磁盘。用hddtemp或smartctl功能,通过从支持此特点的驱动上的SMART技术来读取数据的方式,从而查出你的Linux或基于UNIX系统上的硬件温度。只有现代硬驱动器有温度传感器。hddtemp功能也支持从SCSI驱动器读取SMART信息。hddtemp能作为一个简单的命令行工具或守护程序来从所有服务器中获取信息: hddtemp /dev/DISK hddtemp /dev/sg0
部分输出内容:
图 02: hddtemp正在运行
你也可以像下面显示的那样使用smartctl命令:
smartctl -d ata -A /dev/sda | grep -i temperature
我怎么获取CPU的温度
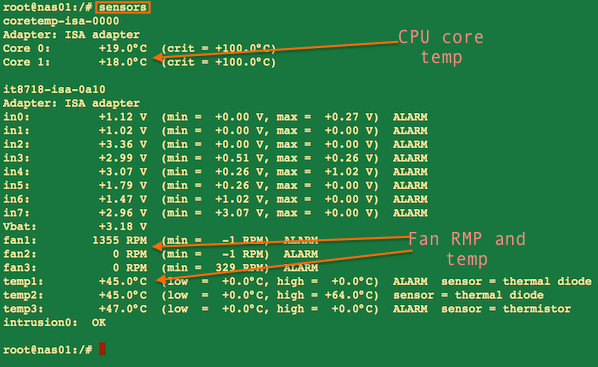
你可以使用Linux硬件监控工具例如像用基于Linux系统的lm_sensor功能来获取CPU温度:
sensors
Debian服务器的部分输出内容:
图 03: sensors命令提供了一台Linux计算机的CPU核心温度和其它信息
#6 - 处理损坏的文件系统
服务器上的文件系统可能会因为硬件重启或一些其它的错误比如坏区而损坏。你可以用fsck命令来修复损坏的文件系统:
umount /ftpusers
fsck -y /dev/sda8
来看看怎么应对Linux文件系统故障的更多信息。
#7 - 处理Linux中的软阵列
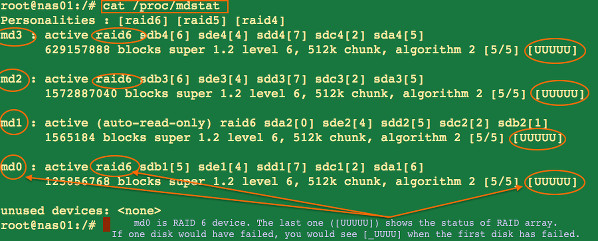
To find the current status of a Linux software raid type the following command:
## get detail on /dev/md0 raid ##
mdadm --detail /dev/md0
## Find status ##
cat /proc/mdstat
watch cat /proc/mdstat
Sample outputs:
图 04: Find the status of a Linux software raid command
You need to replace a failed hard drive. You must u remove the correct failed drive. In this example, I'm going to replace /dev/sdb (2nd hard drive of RAID 6). It is not necessary to take the storage offline to repair the RAID on Linux. This only works if your server support hot-swappable hard disk:
## remove disk from an array md0 ##
mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb1
mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --remove /dev/sdb1
# Do the same steps again for rest of /dev/sdbX ##
# Power down if not hot-swappable hard disk: ##
shutdown -h now
## copy partition table from /dev/sda to newly replaced /dev/sdb ##
sfdisk -d /dev/sda | sfdisk /dev/sdb
fdisk -l
## Add it ##
mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
# do the same steps again for rest of /dev/sdbX ##
# Now md0 will sync again. See it on screen ##
watch cat /proc/mdstat
See our tips on increasing RAID sync speed on Linux for more information.
#8 - 处理硬阵列
You can use the samrtctl command or vendor specific command to find out the status of RAID and disks in your controller:
## SCSI disk
smartctl -d scsi --all /dev/sgX
## Adaptec RAID array
/usr/StorMan/arcconf getconfig 1
## 3ware RAID Array
tw_cli /c0 show
See your vendor specific documentation to replace a failed disk.
Monitoring disk health
See our previous tutorials:
- Monitoring hard disk health with smartd under Linux or UNIX operating systems
- Shell script to watch the disk space
- UNIX get an alert when disk is full
- Monitor UNIX / Linux server disk space with a shell scrip
- Perl script to monitor disk space and send an email
- NAS backup server disk monitoring shell script
结论
I hope these tips will help you troubleshoot system disk issue on a Linux/Unix based server. I also recommend implementing a good backup plan in order to have the ability to recover from disk failure, accidental file deletion, file corruption, or complete server destruction:
- Debian / Ubuntu: Install Duplicity for encrypted backup in cloud
- HowTo: Backup MySQL databases, web server files to a FTP server automatically
- How To Set Red hat & CentOS Linux remote backup / snapshot server
- Debian / Ubuntu Linux install and configure remote filesystem snapshot with rsnapshot incremental backup utility
- Linux Tape backup with mt And tar command tutorial
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/datacenter/linux-unix-bsd-osx-cannot-write-to-hard-disk/