48 KiB
pinewall translating
Kubernetes distributed application deployment with sample Face Recognition App
Intro
Alright folks. Settle in. This is going to be a long, but hopefully, fun ride.
I’m going to deploy a distributed application with Kubernetes. I was trying to write an app which I thought is as close to real-world as possible. But obviously I cut some corners because of time and energy constraints.
My focus will be on Kubernetes and deployment.
Shall we?
The Application
TL;DR
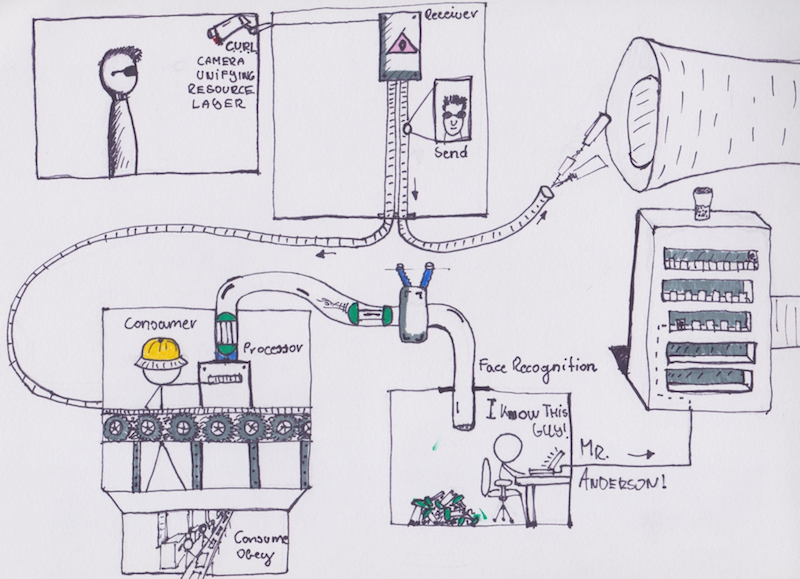
The application itself consists of six parts. The repository can be found here: Kube Cluster Sample.
It is a face recognition service which identifies images of people, comparing them to known individuals. A simple frontend displays a table of these images and whom they belong to. This happens by sending a request to a receiver. The request contains a path to an image. The image could be located anywhere. The receiver stores this path in the DB (MySQL) and sends a processing request to a queue. The queue uses NSQ. The request contains the ID of the saved image.
An Image Processing service is constantly monitoring the queue for jobs to do. The processing consists of the following steps: taking the ID, loading in the image and sending off the path of the image to a face recognition backend, written in Python, via gRPC. If the identification was successful, the backend returns the name of the image corresponding to that person. The image_processor then updates the image record with the person id and marks the image as processed successfully. If identification is unsuccessful the image is left as pending. If there was a failure during identification the image is flagged as failed.
Failed images can be re-tried with a cron job, for example.
So how does this all work? Let’s dive in.
Receiver
The receiver service is the starting point of the process. It’s an API which receives a request in the following format:
curl -d '{"path":"/unknown_images/unknown0001.jpg"}' http://127.0.0.1:8000/image/post
In this moment, receiver stores this path using a shared database cluster. The entity then will receive an ID from the database service. This application is based on the model where unique identification for Entity Objects is provided by the persistence layer. Once the ID is acquired, receiver will send a message to NSQ. The receiver’s job is done at this point.
Image Processor
Here is where the fun begins. When Image Processor first runs it creates two Go routines. These are…
Consume
This is an NSQ consumer. It has three jobs. First, it listens for messages on the queue. Second, when there is a message it appends the received ID to a thread safe slice of IDs that the second routine processes. Lastly it signals the second routine that there is work to do. It does that through sync.Condition.
ProcessImages
This routine processes a slice of IDs until the slice is drained completely. Once the slice is drained the routine goes into suspend instead of sleep-waiting on a channel. The processing of a single ID is through the following steps in order:
-
Establish a gRPC connection to the Face Recognition service (explained under Face Recognition)
-
Retrieve the image record from the database
-
Setup two functions for the Circuit Breaker
-
Function 1: The main function which does the RPC method call
-
Function 2: A health check for the Ping of the circuit breaker
-
-
Call Function 1 which sends the path of the image to the face recognition service. This path should be accessible by the face recognition service. Preferably something shared, like an NFS
-
If this call fails, update the image record as FAILEDPROCESSING
-
If it succeeds, an image name should come back which corresponds to a person in the db. It runs a joined SQL query which gets the corresponding person’s id
-
Update the Image record in the database with PROCESSED status and the ID of the person that image was identified as
This service can be replicated, meaning, more than one could run at the same time.
Circuit Breaker
In a system where replicating resources requires little to no effort, there still could be cases where, for example, the network goes down, or there are communication problems of any kind between two services. I implement a little circuit breaker around the gRPC calls for fun mostly.
This is how it works:
Once there are 5 unsuccessful calls to the service the circute breaker activates and doesn’t allow any more calls to go through. After a configured amount of time, it will send a health check to the service to see if it’s back up. If that still errors out, it increases the timeout. If not, it opens the circuit and allows traffic to proceed.
Front-End
This is only a simplistic table view with Go’s own html/template used to render a list of images.
Face Recognition
Here is where the identification magic is happening. I decided to make this a gRPC based service for the sole purpose of flexibility. I started writing it in Go, but decided that a Python implementation could be much sorter. In fact, not counting the gRPC code, the recognition part is about 7 lines of code. I’m using this fantastic library which has all the C bindings to OpenCV. Face Recognition. Having an API contract here means that I can change the implementation anytime as long as it adheres to the contract.
Note that there is a great Go library that I was about to use, but they have yet to write the needed C bindings. It’s called GoCV. Go, check them out. They have some pretty amazing things, like real time camera feed processing with only a couple of lines of code.
How the Python library works is simple in nature. Have a set of images about people you know and have a record for. In this case, I have a folder with a couple of images named, hannibal_1.jpg, hannibal_2.jpg, gergely_1.jpg, john_doe.jpg. In the database I have two tables named, person, person_images. They look like this:
+----+----------+
| id | name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | Gergely |
| 2 | John Doe |
| 3 | Hannibal |
+----+----------+
+----+----------------+-----------+
| id | image_name | person_id |
+----+----------------+-----------+
| 1 | hannibal_1.jpg | 3 |
| 2 | hannibal_2.jpg | 3 |
+----+----------------+-----------+
The face recognition library returns the name of the image the unknown image matches to. After that, a simple joined query like this will return the person in question.
select person.name, person.id from person inner join person_images as pi on person.id = pi.person_id where image_name = 'hannibal_2.jpg';
The gRPC call returns the id of the person which is than used to update the image’s person column.
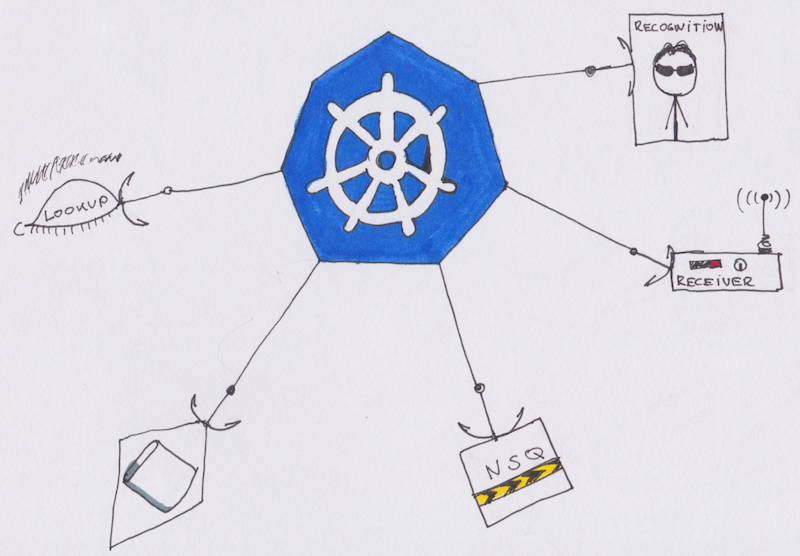
NSQ
NSQ is a little Go based queue. It can be scaled and has a minimal footprint on the system. It has a lookup service which consumers use to receive messages and a daemon that senders use to send messages.
NSQ’s philosophy is that the daemon should run with the sender application. That way, the sender sends to localhost only. But the daemon is connected to the lookup service and that’s how they achieve a global queue.
This means that there are as many NSQ daemons deployed as there are senders. Because the daemon has a minuscule resource requirement, it won’t interfere with the requirements of the main application.
Configuration
In order to be as flexible as possible and making use of Kubernetes’ ConfigSet, I’m using .env files in development to store configuration like the location of the database service or NSQ’s lookup address. In production, and that means the Kubernetes environment, I’ll use environment properties.
Conclusion for the Application
And that’s all there is to the architecture of the application we are about to deploy. All of its components are changeable and only coupled through the database, a queue and gRPC. This is imperative when deploying a distributed application because of how updating mechanics work. I will cover that part in the Deployment section.
Deployment with Kubernetes
Basics
What is Kubernetes?
I’ll cover some basics here, although I won’t go too much into details as that would require a whole book like this one: Kubernetes Up And Running. Also, you can look at the documentation if you are daring enough: Kubernetes Documentation.
Kubernetes is a containerized service and application manager. It scales easily, employs a swarm of containers but more importantly, it’s highly configurable via yaml based template files. People compare Kubernetes to Docker swarm, but Kubernetes does way more than that. For example, it’s container agnostic. You could use LXC with Kubernetes and it would work the same way you would use it with Docker. It provides a layer above managing a cluster of deployed services and applications. How? Let’s take a quick look at the building blocks of Kubernetes.
In Kubernetes you describe a desired state of the application and Kubernetes will do what it can to reach that state. States could be something like, deployed, paused, replicated 2 times and so and so forth.
One of the basics of Kubernetes is that it uses Labels and Annotations for all it’s components. Services, Deployments, ReplicaSets, DaemonSets, everyhting is labelled. Consider the following scenario. In order to identify what pod belongs to what application a labeled is used called app: myapp. Lets assume you have to containers of this application deployed. If you would remove the label app from one of the containers, Kubernetes would only detect one and thus would launch a new instance of myapp.
Kubernetes Cluster
For Kuberenetes to work, a Kubernetes cluster needs to be present. Setting that up one might be a bit painful, but luckily help is there. Minikube sets up a cluster for us locally with one Node. And AWS has a beta service running in the form of a Kubernetes cluster where the only thing you need to do is request nodes and define your deployments. The Kubernetes cluster components are documented here: Kubernetes Cluster Components.
Nodes
A Node is a worker machine. It can be anything from a vm to a physical machine, including all sorts of cloud provided vms.
Pods
Pods are a logically grouped collection of containers. That means, one Pod can potentially house a multitude of containers. A Pod gets its own DNS and virtual IP address after it has been created so Kubernetes can load balancer traffic to it. You rarely have to deal with containers directly. Even when debugging, like looking at logs, you usually invoke kubectl logs deployment/your-app -f instead of looking at a specific container. Although it is possible with -c container_name. The -f does a tail on the log.
Deployments
When creating any kind of resource in Kubernetes, it will use a Deployment in the background. A deployment describes a desired state of the current application. It’s an object you can use to update Pods or a Service to be in a different state; do an update, or rollout new version of your app. You don’t directly conrtol a ReplicaSet (described later) but control the deployment object which creates and manages a ReplicaSet.
Services
By default a Pod will get an IP address. However, since Pods are a volatile thing in Kubernetes you’ll need something more permanent. A queue, mysql, or an internal API, a frontend; these need to be long running and behind a static, unchanging IP or preferably a DNS record.
For this purpose, Kubernetes has Services for which you can define modes of accessibility. Load Balanced, simple IP or internal DNS.
How does Kubernetes know if a service is running correctly? You can configure Health Checks and Availability Checks. A HealtCheck will check if a container is running but that doesn’t mean that your service is running. For that, you have the availability check which pings a different endpoint in your application.
Since Services are pretty important, I recommend that you read up on them later here: Services. Fair warning, this is quiet dense. 24 A4 pages of networking, services and discovery. It’s also important to understand if you want to seriously use Kubernetes in production.
DNS / Service Discovery
If you create a service in the cluster that service will get a DNS record in Kubernetes provided by special Kubernetes deployments called kube-proxy and kube-dns. These two provid service discover inside a cluster. If you have a mysql service running and set clusterIP: none, than everyone in the cluster can reach that service by pinging mysql.default.svc.cluster.local. Where:
-
mysql– is the name of the service -
default– is the namespace name -
svc– is services -
cluster.local– is a local cluster domain
The domain can be changed by using a custom definition. To access a service outside the cluster, a DNS provider has to be used and Nginx (for example) to bind an IP address to a record. The public IP address of a service can be queried with the following commands:
-
NodePort –
kubectl get -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services mysql -
LoadBalancer –
kubectl get -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].LoadBalancer}" services mysql
Template Files
Like Docker Compose, or TerraForm or other service management tools, Kubernetes also provides infrastructure describing templates. What that means is that you rarely have to do anything by hand.
For example consider the following yaml template which describes an nginx Deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment #(1)
metadata: #(2)
name: nginx-deployment
labels: #(3)
app: nginx
spec: #(4)
replicas: 3 #(5)
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers: #(6)
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.7.9
ports:
- containerPort: 80
This is a simple deployment where we do the following:
-
(1) Define the type of the template with kind
-
(2) Add metadata that will identify this deployment and every resource that it would create with a label (3)
-
(4) Then comes the spec which describes the desired state
-
(5) For the nginx app have 3 replicas
-
(6) This is the template definition for the containers that this Pod will contain
-
nginx named container
-
nginx:1.7.9 image (docker in this case)
-
exposed ports
-
ReplicaSet
A ReplicaSet is a low level replication manager. It ensures that the correct number of replicates are running for a application. However, Deployments are higher level and should always manage ReplicaSets. You rarely have to use ReplicaSets directly. Unless you have a fringe case where you want to control the specifics of replication.
DaemonSet
Remember how I said Kubernetes is using Labels all the time? A DaemonSet is a controller that ensures that at daemonized application is always running on a node with a certain label.
For example, you want all the nodes labelled with logger or mission_critical to run an logger / auditing service daemon. Then you create a DaemonSet and give it a node selector called logger or mission_critical. Kubernetes will look for a node that has that label and always ensure that it will have an instance of that daemon running on it. Thus everyone running on that node will have access to that daemon locally.
In case of my application the NSQ daemon could be a DaemonSet. I would ensure it’s up on a node which has the receiver component running by labelling a node with receiver and specifying a DaemonSet with receiver application selector.
The DaemonSet has all the benefits of the ReplicaSet. It’s scalable and Kubernetes manages it; which means, all life cycle events are handled by Kube enusring it never dies or if it dies it gets immediately replaced.
Scaling
In Kubernetes it’s trivial to scale. The ReplicaSets take care of the number of instances of a Pod to run. Like you saw in the nginx deployment with the setting replicas:3. It’s up to us to write our application in a way that it allows Kubernetes to run multiple copies of it.
Of course the settings are vast. You can specify that the replicates must run on different Nodes, or various waiting times on how long to wait for an instance to come up. You can read up more on this subject here: Horizontal Scaling and here: Interactive Scaling with Kubernetes and of course the details of a ReplicaSet which controls all the scaling made possible in Kubernetes.
Conclusion for Kubernetes
It’s a convenient tool to handle container orchestration. Its unit of work are Pods and it has a layered architecture. The top level layer is Deployments through which you handle all other resources. It’s highly configurable. It provides an API for all calls you make, so potentionally, instead of running kubectl you can also write your own logic to send information to the Kubernetes API.
It provides support for all major cloud providers natively by now and it’s completely open source. Feel free to contribute, check the code if you would like to have a deeper understanding on how it works: Kubernetes on Github.
Minikube
I’m going to use Minikube. Minikube is a local kubernetes cluster simulator. It’s not great in simulating multiple nodes though, but for starting out and local play without any costs, it’s great. It uses a VM that can be fine tuned if necessary using VirtualBox and the likes.
All the kube template files that I’ll be using are located here: Kube files.
NOTE If, later on, you would like to play with scaling, but notice that the replicates are always in Pending state, remember, that minikube employs a single node only. It might not allow multiple replicas on the same node, or just plain ran out of resources to use. You can check available resources with the following command:
kubectl get nodes -o yaml
Building the containers
Kubernetes supports most of the containers out there. I’m going to use Docker. For all the services I’ve built, there is a Dockerfile included in the repository. I encourage you to study them. Most of them are simple. For the go services I’m using a multi stage build that got recently introduced. The Go services are Alpine Linux based. The Face Recognition service is Python. NSQ and MySQL are using their own containers.
Context
Kubernetes uses namespaces. If you don’t specify any it will use the default namespace. I’m going to permanently set a context to avoid polluting the default namespace. You do that like this:
❯ kubectl config set-context kube-face-cluster --namespace=face
Context "kube-face-cluster" created.
You have to also start using the context once it’s created like so:
❯ kubectl config use-context kube-face-cluster
Switched to context "kube-face-cluster".
After this, all kubectl commands will use the namespace face.
Deploying the Application
Overview of Pods and Services:
MySQL
The first Service I’m going to deploy is my database.
I’m using the Kubernetes example located here Kube MySQL which fits my needs. Note that this file is using a plain password for MYSQL_PASSWORD. I’m going to employ a vault described here Kubernetes Secrets.
I’ve created a secret locally as described in that document using a secret yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kube-face-secret
type: Opaque
data:
mysql_password: base64codehere
The base64 code I created with the following commands:
echo -n "ubersecurepassword" | base64
And this is what you’ll see in my deployment yaml file:
...
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kube-face-secret
key: mysql_password
...
One other thing worth mentioning. It’s using a volume to persist the database. The volume definition is as follows:
...
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
...
volumes:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mysql-pv-claim
...
presistentVolumeClain is the key here. This tells Kubernetes that this resource requires a persistent volume. How it’s provided is abstracted away from the user. You can be sure that Kubernetes will provide a volume that will always be there. Similar to Pods. To read up on the details check out this document: Kubernetes Persistent Volumes.
Deploying the mysql Service is done with the following command:
kubectl apply -f mysql.yaml
apply vs create. In short, apply is considered a declerative object configuration command while create is imperative. What that means for now is that create is usually for a one of task, like running something or creating a deployment. While, when using apply the user doesn’t define the action to be taken. That will be defined by Kubernetes based on the current status of the cluster. Thus, when there is no service called mysql and I’m calling apply -f mysql.yaml it will create the service. When running again, Kubernetes won’t do anything. But if I would run create again it would throw an error saying the service is already created.
For more information checkout the following docs: Kubernetes Object Management, Imperative Configuration, Declarative Configuration.
To see progress information, run:
# Describes the whole process
kubectl describe deployment mysql
# Shows only the pod
kubectl get pods -l app=mysql
Output should be similar to this:
...
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: mysql-55cd6b9f47 (1/1 replicas created)
...
Or in case of get pods:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
mysql-78dbbd9c49-k6sdv 1/1 Running 0 18s
To test the instance, run the following snippet:
kubectl run -it --rm --image=mysql:5.6 --restart=Never mysql-client -- mysql -h mysql -pyourpasswordhere
GOTCHA: If you change the password now, it’s not enough to re-apply your yaml file to update the container. Since the DB is persisted, the password will not be changed. You have to delete the whole deployment with kubectl delete -f mysql.yaml.
You should see the following when running a show databases.
If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter.
mysql>
mysql>
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| kube |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> exit
Bye
You’ll notice that I also mounted a file located here Database Setup SQL into the container. MySQL container automatically executed these. That file will bootstrap some data and the schema I’m going to use.
The volume definition is as follows:
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
- name: bootstrap-script
mountPath: /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/database_setup.sql
volumes:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mysql-pv-claim
- name: bootstrap-script
hostPath:
path: /Users/hannibal/golang/src/github.com/Skarlso/kube-cluster-sample/database_setup.sql
type: File
To check if the bootstrap script was successful run this:
~/golang/src/github.com/Skarlso/kube-cluster-sample/kube_files master*
❯ kubectl run -it --rm --image=mysql:5.6 --restart=Never mysql-client -- mysql -h mysql -uroot -pyourpasswordhere kube
If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter.
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_kube |
+----------------+
| images |
| person |
| person_images |
+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
This concludes the database service setup. Logs for this service can be viewed with the following command:
kubectl logs deployment/mysql -f
NSQ Lookup
The NSQ Lookup will run as an internal service. It doesn’t need access from the outside so I’m setting clusterIP: None which will tell Kubernetes that this service is a headless service. This means that it won’t be loadbalanced and it won’t be a single ip service. The DNS will be based upon service selectors.
Our NSQ Lookup selector is:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nsqlookup
Thus, the internal DNS will look like this: nsqlookup.default.svc.cluster.local.
Headless services are described in detail here: Headless Service.
Basically it’s the same as MySQL just with slight modifications. As stated earlier, I’m using NSQ’s own Docker Image called nsqio/nsq. All nsq commands are there, so nsqd will also use this image just with a different command. For nsqlookupd the command is as follows:
command: ["/nsqlookupd"]
args: ["--broadcast-address=nsqlookup.default.svc.cluster.local"]
What’s the --broadcast-address for, you might ask? By default, nsqlookup will use the hostname as broadcast address. Meaning, when the consumer runs a callback it will try to connect to something like http://nsqlookup-234kf-asdf:4161/lookup?topics=image which will not work of course. By setting the broadcast-address to the internal DNS that callback will be http://nsqlookup.default.svc.cluster.local:4161/lookup?topic=images. Which will work as expected.
NSQ Lookup also requires two ports forwarded. One for broadcasting and one for nsqd daemon callback. These are exposed in the Dockerfile and then utilized in the kubernetes template like this:
In the container template:
ports:
- containerPort: 4160
hostPort: 4160
- containerPort: 4161
hostPort: 4161
In the service template:
spec:
ports:
- name: tcp
protocol: TCP
port: 4160
targetPort: 4160
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 4161
targetPort: 4161
Names are required by kubernetes to distinguish between them.
To create this service, I’m using the following command as before:
kubectl apply -f nsqlookup.yaml
This concludes nsqlookupd. Two of the major players are in the sack.
Receiver
This is a more complex one. The receiver will do three things.
-
It will create some deployments
-
It will create the nsq daemon
-
It will be public facing
Deployments
The first deployment it creates is it’s own. The receiver container is skarlso/kube-receiver-alpine.
Nsq Daemon
The receiver starts an nsq daemon. Like said earlier, the receiver runs an nsq with it-self. It does that so talking to it can happen locally and not over the network. By making receiver do this, it will end up on the same node as the receiver.
NSQ daemon also needs some adjustments and parameters.
ports:
- containerPort: 4150
hostPort: 4150
- containerPort: 4151
hostPort: 4151
env:
- name: NSQLOOKUP_ADDRESS
value: nsqlookup.default.svc.cluster.local
- name: NSQ_BROADCAST_ADDRESS
value: nsqd.default.svc.cluster.local
command: ["/nsqd"]
args: ["--lookupd-tcp-address=$(NSQLOOKUP_ADDRESS):4160", "--broadcast-address=$(NSQ_BROADCAST_ADDRESS)"]
You can see the lookup-tcp-address and the broadcast-address are set. Lookup tcp address is the DNS for the nsqlookupd service. And the broadcast address is necessary just like with nsqlookupd so the callbacks are working properly.
Public facing
Now, this is the first time I’m deploying a public facing service. There are two options. I could use a LoadBalancer because this API will be under heavy load. And if this would be deployed anywhere in production, then it should be a LoadBalancer.
I’m doing this locally though with one node so something called a NodePort is enough. A NodePort exposes a service on each node’s IP at a static port. If not specified, it will assign a random port on the host between 30000-32767. But it can also be configured to be a specific port, using nodePort in the yaml. To reach this service I will have to use <NodeIP>:<NodePort>. If more than one node is configured a LoadBalancer can multiplex them to a single IP.
For further information check out this document: Publishing Services.
Putting this all together, we’ll get a receiver-service for which the template is as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: receiver-service
spec:
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8000
targetPort: 8000
selector:
app: receiver
type: NodePort
For a fixed nodePort on 8000 a definition of nodePort must be provided as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: receiver-service
spec:
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8000
targetPort: 8000
selector:
app: receiver
type: NodePort
nodePort: 8000
Image processor
The Image Processor is where I’m handling passing off images to be identified. It should have access to nsqlookupd, mysql and the gRPC endpoint of the face recognition service deployed later. This is actually a boring service. In fact, it’s not a service at all. It doesn’t expose anything and thus it’s the first deployment only component. For brevity, here is the whole template:
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: image-processor-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: image-processor
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: image-processor
spec:
containers:
- name: image-processor
image: skarlso/kube-processor-alpine:latest
env:
- name: MYSQL_CONNECTION
value: "mysql.default.svc.cluster.local"
- name: MYSQL_USERPASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kube-face-secret
key: mysql_userpassword
- name: MYSQL_PORT
# TIL: If this is 3306 without " kubectl throws an error.
value: "3306"
- name: MYSQL_DBNAME
value: kube
- name: NSQ_LOOKUP_ADDRESS
value: "nsqlookup.default.svc.cluster.local:4161"
- name: GRPC_ADDRESS
value: "face-recog.default.svc.cluster.local:50051"
The only interesting points in this file are the multitude of environment properties that are used to configure the application. Note the nsqlookupd address and the grpc address.
To create this deployment, run:
kubectl apply -f image_processor.yaml
Face - Recognition
The face recognition service does have a service. It’s a simple one, only needed by image-processor. It’s template is as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: face-recog
spec:
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 50051
targetPort: 50051
selector:
app: face-recog
clusterIP: None
The more interesting part is that it requires two volumes. The two volumes are known_people and unknown_people. Can you guess what they will contain? Yep, images. The known_people volume contains all the images associated to the known people in the database. The unknown_people volume will contain all the new images. And that’s the path we will need to use when sending images from the receiver. That is, where ever the mount points to. Which in my case is /unknown_people. Basically the path needs to be one that the face recognition service can access.
Now, with Kubernetes and Docker this is easy. It could be a mounted S3 or some kind of nfs or a local mount from host to guest. The possibilities are endless (around a dozen or so). I’m going to use a local mount for the sake of simplicity.
Mounting a volume has two parts. First, the Dockerfile has to specify volumes:
VOLUME [ "/unknown_people", "/known_people" ]
Second, the Kubernetes template as seen earlier with MySQL; the difference being hostPath instead of a claimed volume:
volumeMounts:
- name: known-people-storage
mountPath: /known_people
- name: unknown-people-storage
mountPath: /unknown_people
volumes:
- name: known-people-storage
hostPath:
path: /Users/hannibal/Temp/known_people
type: Directory
- name: unknown-people-storage
hostPath:
path: /Users/hannibal/Temp/
type: Directory
We also have to set the known_people folder config setting for face recognition. This is done via an environment property of course:
env:
- name: KNOWN_PEOPLE
value: "/known_people"
Then the Python code will look up images like this:
known_people = os.getenv('KNOWN_PEOPLE', 'known_people')
print("Known people images location is: %s" % known_people)
images = self.image_files_in_folder(known_people)
Where image_files_in_folder is:
def image_files_in_folder(self, folder):
return [os.path.join(folder, f) for f in os.listdir(folder) if re.match(r'.*\.(jpg|jpeg|png)', f, flags=re.I)]
Neat.
Now, if the receiver receives a request (and sends it off further the line) similar to the one below…
curl -d '{"path":"/unknown_people/unknown220.jpg"}' http://192.168.99.100:30251/image/post
…it will look for an image called unknown220.jpg under /unknown_people; locate an image in the known_folder that corresponds to the person on the unknown image and return the name of the image that matched.
Looking at logs you should see something like this:
# Receiver
❯ curl -d '{"path":"/unknown_people/unknown219.jpg"}' http://192.168.99.100:30251/image/post
got path: {Path:/unknown_people/unknown219.jpg}
image saved with id: 4
image sent to nsq
# Image Processor
2018/03/26 18:11:21 INF 1 [images/ch] querying nsqlookupd http://nsqlookup.default.svc.cluster.local:4161/lookup?topic=images
2018/03/26 18:11:59 Got a message: 4
2018/03/26 18:11:59 Processing image id: 4
2018/03/26 18:12:00 got person: Hannibal
2018/03/26 18:12:00 updating record with person id
2018/03/26 18:12:00 done
And that concludes all of the services that we need to deploy with Kubernetes to get this application to work.
Frontend
Last but not least, there is a small web-app which displays the information in the db for convenience. This is also a public facing service with the same parameters as the receiver’s service.
It looks like this:
Recap
So what is the situation so far? I deployed a bunch of services all over the place. A recap off the commands I used:
kubectl apply -f mysql.yaml
kubectl apply -f nsqlookup.yaml
kubectl apply -f receiver.yaml
kubectl apply -f image_processor.yaml
kubectl apply -f face_recognition.yaml
kubectl apply -f frontend.yaml
These could be in any order because the application does not allocate connections on start except for image_processor’s NSQ consumer. But that re-tries.
Query-ing kube for running pods with kubectl get pods should show something like this:
❯ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
face-recog-6bf449c6f-qg5tr 1/1 Running 0 1m
image-processor-deployment-6467468c9d-cvx6m 1/1 Running 0 31s
mysql-7d667c75f4-bwghw 1/1 Running 0 36s
nsqd-584954c44c-299dz 1/1 Running 0 26s
nsqlookup-7f5bdfcb87-jkdl7 1/1 Running 0 11s
receiver-deployment-5cb4797598-sf5ds 1/1 Running 0 26s
Running minikube service list:
❯ minikube service list
|-------------|----------------------|-----------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | URL |
|-------------|----------------------|-----------------------------|
| default | face-recog | No node port |
| default | kubernetes | No node port |
| default | mysql | No node port |
| default | nsqd | No node port |
| default | nsqlookup | No node port |
| default | receiver-service | http://192.168.99.100:30251 |
| kube-system | kube-dns | No node port |
| kube-system | kubernetes-dashboard | http://192.168.99.100:30000 |
|-------------|----------------------|-----------------------------|
Rolling update
What happens during a rolling update?
As it happens during software development, change is requested/needed to some parts of the application. What happens to our cluster if I would like to change one of it’s components without breaking the other? And also whilest maintaining backwards compatibility with no disruption to user experience. Thankfully Kubernetes can help with that.
What I don’t like is that the API only handles one image at a time. There is no option to bulk upload.
Code
Right now, we have the following code segment dealing with a single image:
// PostImage handles a post of an image. Saves it to the database
// and sends it to NSQ for further processing.
func PostImage(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
...
}
func main() {
router := mux.NewRouter()
router.HandleFunc("/image/post", PostImage).Methods("POST")
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8000", router))
}
We have two options. Add a new endpoint with /images/post and make the client use that, or modify the existing one.
The new client code has the advantage that it could fall back to submitting the old way if the new endpoint isn’t available. The old client code though doesn’t have this advantage so we can’t change the way our code works right now. Consider this. You have 90 servers. You do a slow paced rolling update. That will take out servers one step at a time doing an update. If an update lasts around a minute, that will take around one and a half hours to complete (not counting any parallel updates).
During that time, some of your servers will run the new code and some will run the old one. Calls are load balanced, thus you have no control over what server is hit. If a client is trying to do a call the new way but hits an old server the client would fail. The client could try a fallback, but since you eliminated the old version it will not succeed unless it, by chance, hits a server with the new code (assuming no sticky sessions are set).
Also, once all your servers are updated, an old client will not be able to use your service any longer at all.
Now, you could argue that you don’t want to keep around old versions of your code forever. And that is true in some sense. That’s why, what we are going to do, is modify the old code, to simply call the new code with some slight augmentations. This way, old code is not kept around. Once all clients have been migrated, the code can simply be deleted without any problems.
New Endpoint
Let’s add a new route method:
...
router.HandleFunc("/images/post", PostImages).Methods("POST")
...
And updating the old one to call the new one with a modified body like this:
// PostImage handles a post of an image. Saves it to the database
// and sends it to NSQ for further processing.
func PostImage(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var p Path
err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&p)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "got error while decoding body: %s", err)
return
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "got path: %+v\n", p)
var ps Paths
paths := make([]Path, 0)
paths = append(paths, p)
ps.Paths = paths
var pathsJSON bytes.Buffer
err = json.NewEncoder(&pathsJSON).Encode(ps)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "failed to encode paths: %s", err)
return
}
r.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(&pathsJSON)
r.ContentLength = int64(pathsJSON.Len())
PostImages(w, r)
}
Well, the naming could be better, but you should get the basic idea. I’m modifying the incoming single path by wrapping it into the new format and sending it over to the new end-point handler. And that’s it. There are a few more modifications, to check them out take a look at this PR: Rolling Update Bulk Image Path PR.
Now, we can call the receiver in two ways:
# Single Path:
curl -d '{"path":"unknown4456.jpg"}' http://127.0.0.1:8000/image/post
# Multiple Paths:
curl -d '{"paths":[{"path":"unknown4456.jpg"}]}' http://127.0.0.1:8000/images/post
Here, the client is curl. Normally, if the client would be a service, I would modify it that in case the new end-point throws a 404 it would try the old one next.
For brevity, I’m not modifying NSQ and the others to handle bulk image processing. They will still receive it one - by - one. I’ll leave that up to you as homework. ;)
New Image
To perform a rolling update, I must create a new image first from the receiver service. To do this, I’ll create a new image with a new tag, denoting a version v1.1.
docker build -t skarlso/kube-receiver-alpine:v1.1 .
Once this is complete, we can begin rolling out the change.
Rolling update
In Kubernetes, you can configure your rolling update in multiple ways.
Manual Update
If, say, I was using a container version in my config file called v1.0 than doing an update is simply calling:
kubectl rolling-update receiver --image:skarlso/kube-receiver-alpine:v1.1
If there is a problem during the rollout we can always rollback.
kubectl rolling-update receiver --rollback
It will set back the previous version no fuss, no muss.
Apply a new configuration file
The problem with by-hand updates is always that they aren’t in source control.
Consider this. Something changed, a couple of servers got updated, but nobody witnessed it. A new person comes along and does a change to the template and applys the template to the cluster. All the servers are updated, but suddenly, there is a service outage.
Long story sort, the servers which got updated are wacked over because the template didn’t reflect what has been done by hand. That is bad. Don’t do that.
The recommended way is to change the template to use the new version and than apply the template with the apply command.
Kubernetes recommends that the Deployment handles the rollout with ReplicaSets. This means however, that there must be at least two replicates present for a rolling update. Otherwise the update won’t work (unless maxUnavailable is set to 1). I’m increasing the replica count in the yaml and I set the new image version for the receiver container.
replicas: 2
...
spec:
containers:
- name: receiver
image: skarlso/kube-receiver-alpine:v1.1
...
Looking at the progress you should see something like this:
❯ kubectl rollout status deployment/receiver-deployment
Waiting for rollout to finish: 1 out of 2 new replicas have been updated...
You can add in additional rollout configuration settings by specifying the strategy part of the template like this:
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1
maxUnavailable: 0
Additional information on rolling update can be found in these documents: Deployment Rolling Update, Updating a Deployment, Manage Deployments, Rolling Update using ReplicaController.
NOTE MINIKUBE USERS: Since we are doing this on a local machine with one node and 1 replica of an application, we have to set maxUnavailable to 1. Otherwise, Kubernetes won’t allow the update to happen and the new version will always be in Pending state since we aren’t allowing that at any given point in time there is a situation where no containers are present for receiver app.
Scaling
Scaling is dead easy with Kubernetes. Since it’s managing the whole cluster, you basically, just have to put a number into the template of the desired replicas to use.
This has been a great post so far but it’s getting too long. I’m planning on writing a follow-up where I will be truly scaling things up on AWS with multiple nodes and replicas. Stay tuned.
Cleanup
kubectl delete deployments --all
kubectl delete services -all
Final Words
And that is it ladies and gentleman. We wrote, deployed, updated and scaled (well, not yet really) a distributed application with Kubernetes.
Any questions, please feel free to chat in the comments below, I’m happy to answer.
I hope you enjoyed reading this. I know, it’s quiet long and I was thinking of splitting it up, but having a cohesive, one page guide is sometimes useful and makes it easy to find something or save it for later read or even print as PDF.
Thank you for reading, Gergely.
via: https://skarlso.github.io/2018/03/15/kubernetes-distributed-application/