5.4 KiB
在命令行中管理 Wifi 连接
无论何时要安装一款新的 Linux 发行系统,一般的建议都是让您通过有线连接来接到互联网的。这主要的原因有两条:第一,您的无线网卡也许安装的驱动不正确而不能用;第二,如果您是从命令行中来安装系统的,管理 WiFi 就非常可怕。我总是试图避免在命令行中处理 WiFi 。但 Linux 的世界,应具有无所畏惧的精神。如果您不知道怎样操作,您需要继续往下来学习之,这就是写这篇文章的唯一原因。所以我强迫自己学习如何在命令行中管理 WiFi 连接。
There are of course multiple ways to connect to a WiFi from the command line. But for the sake of this post, and as an advice, I will try to use the most basic way: the one that uses programs and utilities included in the "default packages" of any distribution. Or at least I will try. An obvious reason for this choice is that the process can potentially be reproduced on any Linux computer. The downside is its relative complexity.通过命令行来设置连接到 WiFi 当然有很多种方法,但在这篇文章里,也是一个建议,我将会作用最基本的方法:那就是使用在任何发布版本中都有的包含在“默认包”里的程序和工具。
First, I will assume that you have the correct drivers loaded for your wireless LAN card. There is no way to start anything without that. And if you don't, you should take a look at the Wiki and documentation for your distribution.
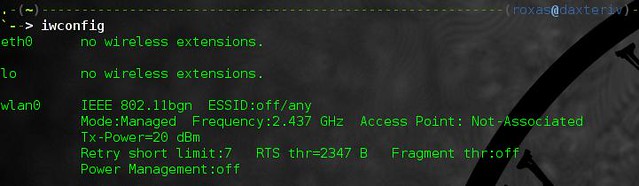
Then you can check which interface supports wireless connections with the command
$ iwconfig
In general, the wireless interface is called wlan0. There are of course exceptions, but for the rest of this tutorial, I will call it that way.
Just in case, you should make sure that the interface is up with:
$ sudo ip link set wlan0 up
Once you know that your interface is operational, you should scan for nearby wireless networks with:
$ sudo iw dev wlan0 scan | less
From the output, you can extract the name of the network (its SSID), its signal power, and which type of security it uses (e.g., WEP, WPA/WPA2). From there, the road splits into two: the nice and easy, and the slightly more complicated case.
If the network you want to connect to is not encrypted, you can connect straight to it with:
$ sudo iw dev wlan0 connect [network SSID]
If the network uses WEP encryption, it is also quite easy:
$ sudo iw dev wlan0 connect [network SSID] key 0:[WEP key]
But everything gets worse if the network uses WPA or WPA2 protocols. In this case, you have to use the utility called wpa_supplicant, which is not always included by default. You then have to modify the file at /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf to add the lines:
network={
ssid="[network ssid]"
psk="[the passphrase]"
priority=1
}
I recommend that you append it at the end of the file, and make sure that the other configurations are commented out. Be careful that both the ssid and the passphrase are case sensitive. You can also technically put the name of the access point as the ssid, and wpa_supplicant will replace it with the proper ssid.
Once the configuration file is completed, launch this command in the background:
$ sudo wpa_supplicant -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
Finally, whether you connected to an open or a secure network, you have to get an IP address. Simply use:
$ sudo dhcpcd wlan0
If everything goes well, you should get a brand new local IP via DHCP, and the process will fork in the background. If you want to be sure that you are connected, you can always check again with:
$ iwconfig
To conclude, I think that getting over the first step is completely worth it. You never know when your GUI will be down, or when you cannot access a wired connection, so getting ready now seems very important. Also, as mentioned before, there are a lot of ways (e.g., NetworkManager, wicd, netcfg, wifi) to manage a wireless connection. If I try to stick to the most basic way, I know that in some cases, the utilities that I used may not even be available to you, and that you would have to download them prior to that. On the other side of the balance, there are some more advanced programs, which are definitely not included in the "default packages," which will greatly simplify the whole process. But as a general advice, it is good to stick to the basics at first.
What other ways would you recommend to connect via WiFi from the command line? Please let us know in the comments.
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/manage-wifi-connection-command-line.html
作者:Adrien Brochard 译者:runningwater 校对:校对者ID