mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-10 22:21:11 +08:00
79 lines
7.9 KiB
Markdown
79 lines
7.9 KiB
Markdown
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
|
[#]: translator: ( )
|
|
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
|
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
|
[#]: url: ( )
|
|
[#]: subject: (6 tips and tricks for using KeePassX to secure your passwords)
|
|
[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/18/12/keepassx-security-best-practices)
|
|
[#]: author: (Michael McCune https://opensource.com/users/elmiko)
|
|
|
|
6 tips and tricks for using KeePassX to secure your passwords
|
|
======
|
|
Get more out of your password manager by following these best practices.
|
|

|
|
|
|
Our increasingly interconnected digital world makes security an essential and common discussion topic. We hear about [data breaches][1] with alarming regularity and are often on our own to make informed decisions about how to use technology securely. Although security is a deep and nuanced topic, there are some easy daily habits you can keep to reduce your attack surface.
|
|
|
|
Securing passwords and account information is something that affects anyone today. Technologies like [OAuth][2] help make our lives simpler by reducing the number of accounts we need to create, but we are still left with a staggering number of places where we need new, unique information to keep our records secure. An easy way to deal with the increased mental load of organizing all this sensitive information is to use a password manager like [KeePassX][3].
|
|
|
|
In this article, I will explain the importance of keeping your password information secure and offer suggestions for getting the most out of KeePassX. For an introduction to KeePassX and its features, I highly recommend Ricardo Frydman's article "[Managing passwords in Linux with KeePassX][4]."
|
|
|
|
### Why are unique passwords important?
|
|
|
|
Using a different password for each account is the first step in ensuring that your accounts are not vulnerable to shared information leaks. Generating new credentials for every account is time-consuming, and it is extremely common for people to fall into the trap of using the same password on several accounts. The main problem with reusing passwords is that you increase the number of accounts an attacker could access if one of them experiences a credential breach.
|
|
|
|
It may seem like a burden to create new credentials for each account, but the few minutes you spend creating and recording this information will pay for itself many times over in the event of a data breach. This is where password management tools like KeePassX are invaluable for providing convenience and reliability in securing your logins.
|
|
|
|
### 3 tips for getting the most out of KeePassX
|
|
|
|
I have been using KeePassX to manage my password information for many years, and it has become a primary resource in my digital toolbox. Overall, it's fairly simple to use, but there are a few best practices I've learned that I think are worth highlighting.
|
|
|
|
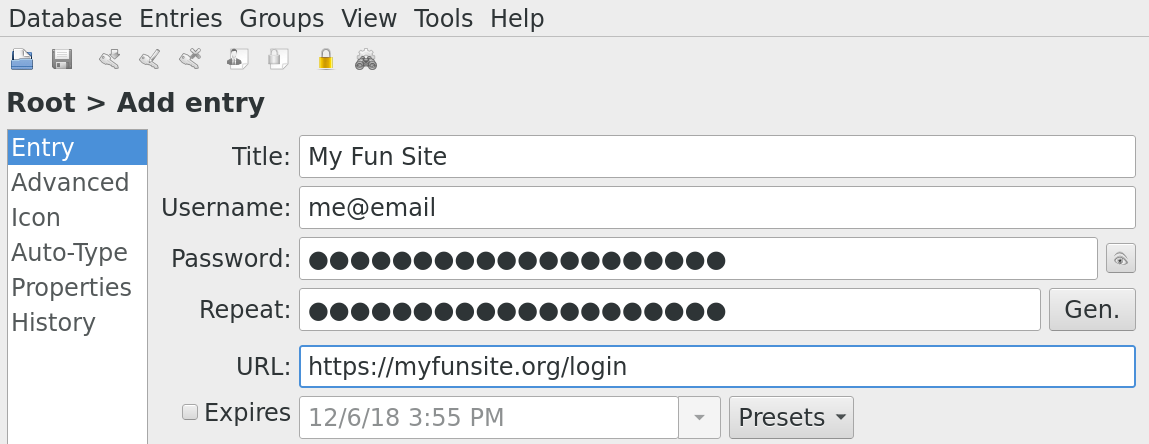
1. Add the direct login URL for each account entry. KeePassX has a very convenient shortcut to open the URL listed with an entry. (It's Control+Shift+U on Linux.) When creating a new account entry for a website, I spend some time to locate the site's direct login URL. Although most websites have a login widget in their navigation toolbars, they also usually have direct pages for login forms. By putting this URL into the URL field on the account entry setup form, I can use the shortcut to directly open the login page in my browser.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
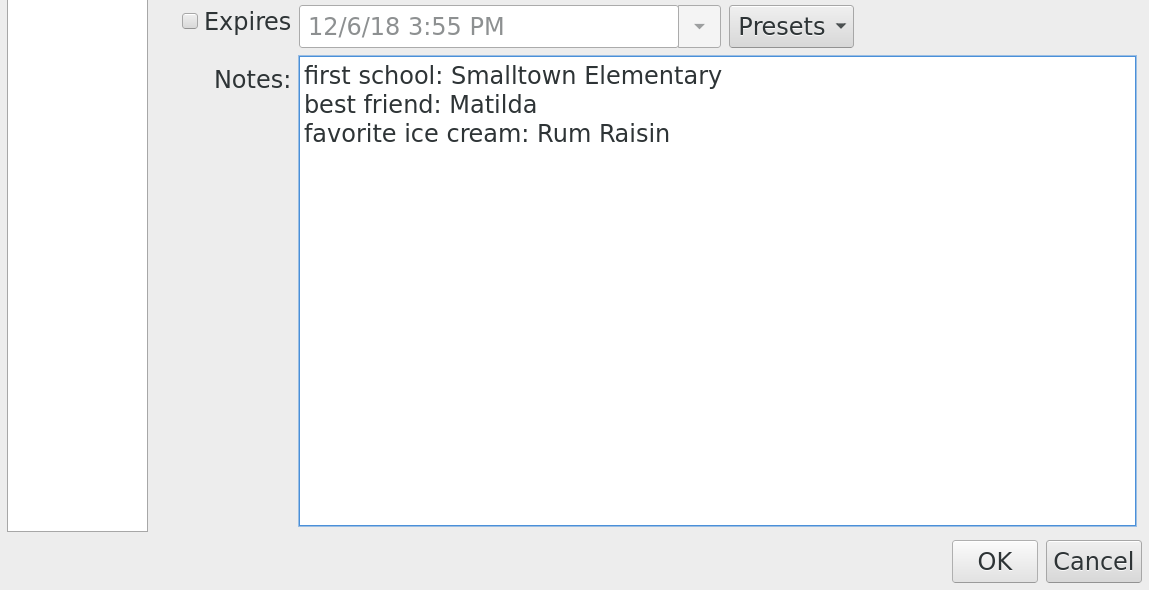
2. Use the Notes field to record extra security information. In addition to passwords, most websites will ask several questions to create additional authentication factors for an account. I use the Notes sections in my account entries to record these additional factors.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
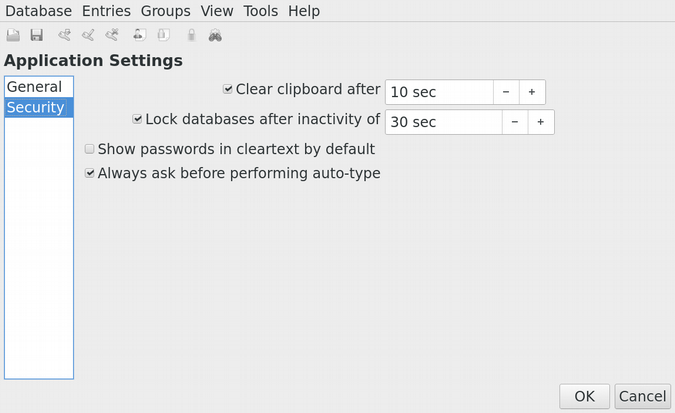
3. Turn on automatic database locking. In the **Application Settings** under the **Tools** menu, there is an option to lock the database after a period of inactivity. Enabling this option is a good common-sense measure, similar to enabling a password-protected screen lock, that will help ensure your password database is not left open and unprotected if someone else gains access to your computer.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Food for thought
|
|
|
|
Protecting your accounts with better password practices and daily habits is just the beginning. Once you start using a password manager, you need to consider issues like protecting the password database file and ensuring you don't forget or lose the master credentials.
|
|
|
|
The cloud-native world of disconnected devices and edge computing makes having a central password store essential. The practices and methodologies you adopt will help minimize your risk while you explore and work in the digital world.
|
|
|
|
1. Be aware of retention policies when storing your database in the cloud. KeePassX's database has an open format used by several tools on multiple platforms. Sooner or later, you will want to transfer your database to another device. As you do this, consider the medium you will use to transfer the file. The best option is to use some sort of direct transfer between devices, but this is not always convenient. Always think about where the database file might be stored as it winds its way through the information superhighway; an email may get cached on a server, an object store may move old files to a trash folder. Learn about these interactions for the platforms you are using before deciding where and how you will share your database file.
|
|
|
|
2. Consider the source of truth for your database while you're making edits. After you share your database file between devices, you might need to create accounts for new services or change information for existing services while using a device. To ensure your information is always correct across all your devices, you need to make sure any edits you make on one device end up in all copies of the database file. There is no easy solution to this problem, but you might think about making all edits from a single device or storing the master copy in a location where all your devices can make edits.
|
|
|
|
3. Do you really need to know your passwords? This is more of a philosophical question that touches on the nature of memorable passwords, convenience, and secrecy. I hardly look at passwords as I create them for new accounts; in most cases, I don't even click the "Show Password" checkbox. There is an idea that you can be more secure by not knowing your passwords, as it would be impossible to compel you to provide them. This may seem like a worrisome idea at first, but consider that you can recover or reset passwords for most accounts through alternate verification methods. When you consider that you might want to change your passwords on a semi-regular basis, it almost makes more sense to treat them as ephemeral information that can be regenerated or replaced.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Here are a few more ideas to consider as you develop your best practices.
|
|
|
|
I hope these tips and tricks have helped expand your knowledge of password management and KeePassX. You can find tools that support the KeePass database format on nearly every platform. If you are not currently using a password manager or have never tried KeePassX, I highly recommend doing so now!
|
|
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
|
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/12/keepassx-security-best-practices
|
|
|
|
作者:[Michael McCune][a]
|
|
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
|
|
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/elmiko
|
|
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
|
[1]: https://vigilante.pw/
|
|
[2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OAuth
|
|
[3]: https://www.keepassx.org/
|
|
[4]: https://opensource.com/business/16/5/keepassx
|