mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-04 22:00:34 +08:00
157 lines
6.2 KiB
Markdown
157 lines
6.2 KiB
Markdown
如何编写与使用定制的 Shell 函数和功能库
|
||
============================================================
|
||
|
||
在 Linux 系统下,我们大量的使用 Shell 脚本来帮助我们完成许多事情,其中包括展示信息,甚至[自动化某些系统管理任务][1],制作简单的命令行工具等。
|
||
|
||
在本文中,我们将向新的 Linux 用户介绍在哪里存储他们定制的 shell 脚本,解释如何编写 shell 函数和功能库,如何在其它的脚本中使用那些功能库中的函数。
|
||
|
||
### 那么 Shell 脚本要存储在哪里呢
|
||
|
||
为了在执行脚本的时候避免指定脚本的绝对路径,脚本必须被存储在 $PATH 这个环境变量所指定路径的其中一个路径下。
|
||
|
||
使用下面的命令可以查看你系统中的 $PATH 环境变量:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ echo $PATH
|
||
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
通常来说,如果在用户主目录下有 bin 目录存在的话,你就可以将 shell 脚本存储在那个目录下,因为那个目录会自动的包含在用户的 $PATH 环境变量中(在Centos6/7下是这样的,在Debian8下不是这样的,在Ubuntu16.04下又是这样的)。
|
||
|
||
因此,在你的主目录下创建 bin 目录吧(当然也可以用来存储 Perl,[Awk][2],Python 脚本或者是其它程序):
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ mkdir ~/bin
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
接着,让我们来建立一个叫做 lib(libraries 的简写)的目录来存放你自己的功能库吧。你也可以在其中存放其它编程语言的功能库如 C 语言,Python 等等。在 lib 目录下建立另一个称为 sh 的目录;用这个目录来存放你的 shell 功能库:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ mkdir -p ~/lib/sh
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### 创建你自己的 Shell 函数和功能库
|
||
|
||
一个 shell 函数就是在一段脚本中能够一件特定任务的一组命令。它们使用起来和其它编程语言中的过程(可能指的是类似SQL中的存储过程之类的吧),子例程与函数十分相似。
|
||
|
||
编写函数的语法如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
[function] 函数名() { 命令 } (这里添加了原文中没有的[function],下文中没有使用这种形式的因此不确定是否合适)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
例如,你在脚本中写了一个用来显示日期的函数:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
showDATE() {date;}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
每当你需要显示日期时,只需要简单的调用函数的函数名即可:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ showDATE
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
简单来说 shell 功能库也是一个 shell 脚本,不过你也可以编写一个功能库来存储一些函数,以便你可以在其它的 shell 脚本中调用。
|
||
|
||
下面就是一个在我的 ~/lib/sh 目录下的功能库的实例其中包含了更多的函数示例:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
#Function to clearly list directories in PATH
|
||
showPATH() {
|
||
oldifs="$IFS" #store old internal field separator
|
||
IFS=: #specify a new internal field separator
|
||
for DIR in $PATH ; do echo $DIR ; done
|
||
IFS="$oldifs" #restore old internal field separator
|
||
}
|
||
#Function to show logged user
|
||
showUSERS() {
|
||
echo -e “Below are the user logged on the system:\n”
|
||
w
|
||
}
|
||
#Print a user’s details
|
||
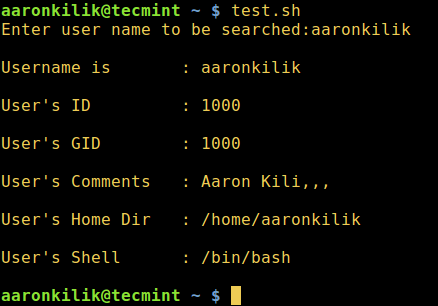
printUSERDETS() {
|
||
oldifs="$IFS" #store old internal field separator
|
||
IFS=: #specify a new internal field separator
|
||
read -p "Enter user name to be searched:" uname #read username
|
||
echo ""
|
||
#read and store from a here string values into variables using : as a field delimiter
|
||
read -r username pass uid gid comments homedir shell <<< "$(cat /etc/passwd | grep "^$uname")"
|
||
#print out captured values
|
||
echo -e "Username is : $username\n"
|
||
echo -e "User's ID : $uid\n"
|
||
echo -e "User's GID : $gid\n"
|
||
echo -e "User's Comments : $comments\n"
|
||
echo -e "User's Home Dir : $homedir\n"
|
||
echo -e "User's Shell : $shell\n"
|
||
IFS="$oldifs" #store old internal field separator
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
保存文件并且给脚本添加执行权限。
|
||
|
||
### 如何从功能库中调用函数呢?
|
||
|
||
要使用库里的某个函数,你首先需要使用下面列出的方式将包含改函数的功能库导入到需要执行的 shell 脚本中:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ . /path/to/lib (这里的. 和路径间应该是有空格的)
|
||
OR
|
||
$ source /path/to/lib
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
你可以像下面演示的方式一样,在其它的脚本中使用来自 ~/lib/sh/libMYFUNCS.sh 的 printUSERDETS 函数。
|
||
|
||
这样你就可以在这个脚本再写一遍相同的代码来输出指定的用户信息,而只需要简单的调用已存在的函数即可。
|
||
|
||
创建一个名为 test.sh 的新文件:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
#include lib
|
||
. ~/lib/sh/libMYFUNCS.sh
|
||
#use function from lib
|
||
printUSERDETS
|
||
#exit script
|
||
exit 0
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
保存,添加执行权限,执行:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ chmod 755 test.sh
|
||
$ ./test.sh
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][3]
|
||
|
||
编写 shell 函数
|
||
|
||
在本文中,我们介绍了在哪里存储 shell 脚本,解释如何编写自己的 shell 函数和功能库,如何在其它的脚本中使用那些功能库中的函数。
|
||
|
||
之后,我们还会介绍一种相当简单直接的方式来将 Vim 设置成为一个编写 Bash 脚本的 IDE(集成开发环境)。在那之前,记得要经常关注 TecMint ,如果能和我们分享你对这份指南的想法就更好了。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
作者简介:
|
||
|
||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/write-custom-shell-functions-and-libraries-in-linux/
|
||
|
||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||
译者:[wcnnbdk1](https://github.com/wcnnbdk1)
|
||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||
|
||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintenance-tasks/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/use-linux-awk-command-to-filter-text-string-in-files/
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Write-Shell-Functions.png
|