mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
118 lines
5.0 KiB
Markdown
118 lines
5.0 KiB
Markdown
在 Linux 上检测硬盘上的坏道和坏块
|
||
===
|
||
|
||
让我们从坏道和坏块的定义开始说起,它们是一块磁盘或闪存上不再能够被读写的部分,一般是由于磁盘表面特定的[物理损坏][7]或闪存晶体管失效导致的。
|
||
|
||
随着坏道的继续积累,它们会对你的磁盘或闪存容量产生令人不快或破坏性的影响,甚至可能会导致硬件失效。
|
||
|
||
同时还需要注意的是坏块的存在警示你应该开始考虑买块新磁盘了,或者简单地将坏块标记为不可用。
|
||
|
||
因此,在这篇文章中,我们通过几个必要的步骤,使用特定的[磁盘扫描工具][6]让你能够判断 Linux 磁盘或闪存是否存在坏道。
|
||
|
||
以下就是步骤:
|
||
|
||
### 在 Linux 上使用坏块工具检查坏道
|
||
|
||
坏块工具可以让用户扫描设备检查坏道或坏块。设备可以是一个磁盘或外置磁盘,由一个如 `/dev/sdc` 这样的文件代表。
|
||
|
||
首先,通过超级用户权限执行 [fdisk 命令][5]来显示你的所有磁盘或闪存的信息以及它们的分区信息:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo fdisk -l
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[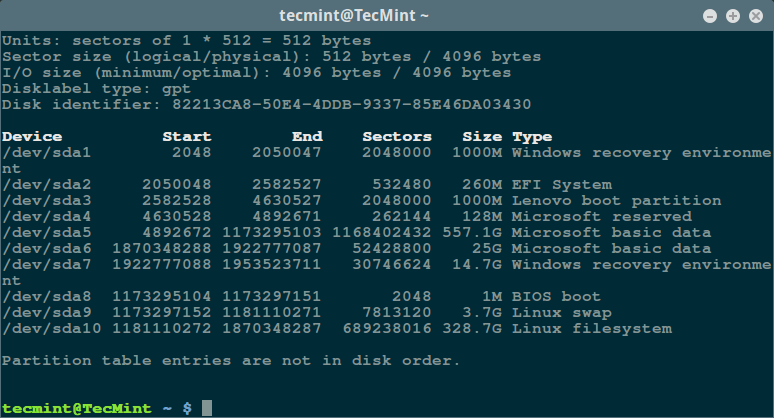][4]
|
||
|
||
*列出 Linux 文件系统分区*
|
||
|
||
然后用如下命令检查你的 Linux 硬盘上的坏道/坏块:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo badblocks -v /dev/sda10 > badsectors.txt
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[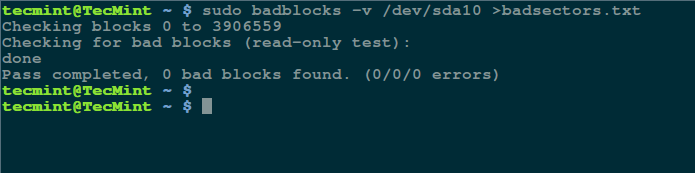][3]
|
||
|
||
*在 Linux 上扫描硬盘坏道*
|
||
|
||
上面的命令中,badblocks 扫描设备 `/dev/sda10`(记得指定你的实际设备),`-v` 选项让它显示操作的详情。另外,这里使用了输出重定向将操作结果重定向到了文件 `badsectors.txt`。
|
||
|
||
如果你在你的磁盘上发现任何坏道,卸载磁盘并像下面这样让系统不要将数据写入回报的扇区中。
|
||
|
||
你需要执行 `e2fsck`(针对 ext2/ext3/ext4 文件系统)或 `fsck` 命令,命令中还需要用到 `badsectors.txt` 文件和设备文件。
|
||
|
||
`-l` 选项告诉命令将在指定的文件 `badsectors.txt` 中列出的扇区号码加入坏块列表。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
------------ 针对 for ext2/ext3/ext4 文件系统 ------------
|
||
$ sudo e2fsck -l badsectors.txt /dev/sda10
|
||
|
||
或
|
||
|
||
------------ 针对其它文件系统 ------------
|
||
$ sudo fsck -l badsectors.txt /dev/sda10
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### 在 Linux 上使用 Smartmontools 工具扫描坏道
|
||
|
||
这个方法对带有 S.M.A.R.T(Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology,自我监控分析报告技术)系统的现代磁盘(ATA/SATA 和 SCSI/SAS 硬盘以及固态硬盘)更加的可靠和高效。S.M.A.R.T 系统能够帮助检测,报告,以及可能记录它们的健康状况,这样你就可以找出任何可能出现的硬件失效。
|
||
|
||
你可以使用以下命令安装 `smartmontools`:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
------------ 在基于 Debian/Ubuntu 的系统上 ------------
|
||
$ sudo apt-get install smartmontools
|
||
|
||
------------ 在基于 RHEL/CentOS 的系统上 ------------
|
||
$ sudo yum install smartmontools
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
安装完成之后,使用 `smartctl` 控制磁盘集成的 S.M.A.R.T 系统。你可以这样查看它的手册或帮助:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ man smartctl
|
||
$ smartctl -h
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
然后执行 `smartctrl` 命令并在命令中指定你的设备作为参数,以下命令包含了参数 `-H` 或 `--health` 以显示 SMART 整体健康自我评估测试结果。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo smartctl -H /dev/sda10
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[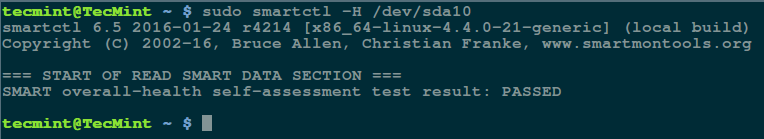][2]
|
||
|
||
*检查 Linux 硬盘健康*
|
||
|
||
上面的结果指出你的硬盘很健康,近期内不大可能发生硬件失效。
|
||
|
||
要获取磁盘信息总览,使用 `-a` 或 `--all` 选项来显示关于磁盘所有的 SMART 信息,`-x` 或 `--xall` 来显示所有关于磁盘的 SMART 信息以及非 SMART 信息。
|
||
|
||
在这个教程中,我们覆盖了有关[磁盘健康诊断][1]的重要话题,你可以下面的反馈区来分享你的想法或提问,并且记得多回来看看。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/check-linux-hard-disk-bad-sectors-bad-blocks/
|
||
|
||
|
||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/defragment-linux-system-partitions-and-directories/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Check-Linux-Hard-Disk-Health.png
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Scan-Hard-Disk-Bad-Sectors-in-Linux.png
|
||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/List-Linux-Filesystem-Partitions.png
|
||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/fdisk-commands-to-manage-linux-disk-partitions/
|
||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/ncdu-a-ncurses-based-disk-usage-analyzer-and-tracker/
|
||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/defragment-linux-system-partitions-and-directories/
|