5.0 KiB
How to use the Linux ftp command to up- and download files on the shell
In this tutorial, I will explain how to use the Linux ftp command on the shell. I will show you how to connect to an FTP server, up- and download files and create directories. While there are many nice desktops FTP clients available, the FTP command is still useful when you work remotely on a server over an SSH session and e.g. want to fetch a backup file from your FTP storage.
Step 1: Establishing an FTP connection
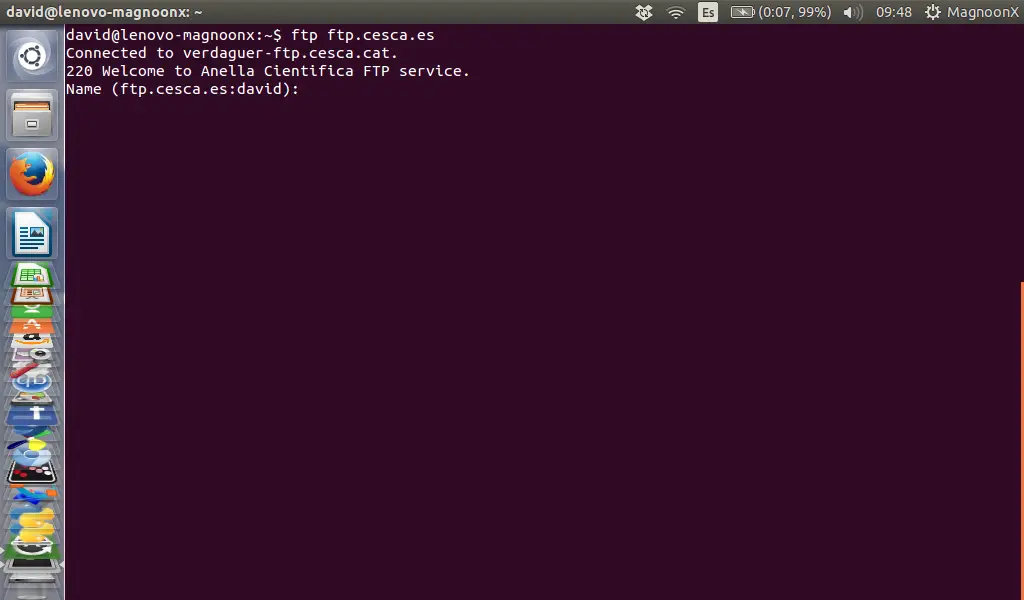
To connect to the FTP server, we have to type in the terminal window 'ftp' and then the domain name 'domain.com' or IP address of the FTP server.
Examples:
ftp domain.com
ftp 192.168.0.1
ftp user@ftpdomain.com
Note: for this example we used an anonymous server.
Replace the IP and domain in the above examples with the IP address or domain of your FTP server.
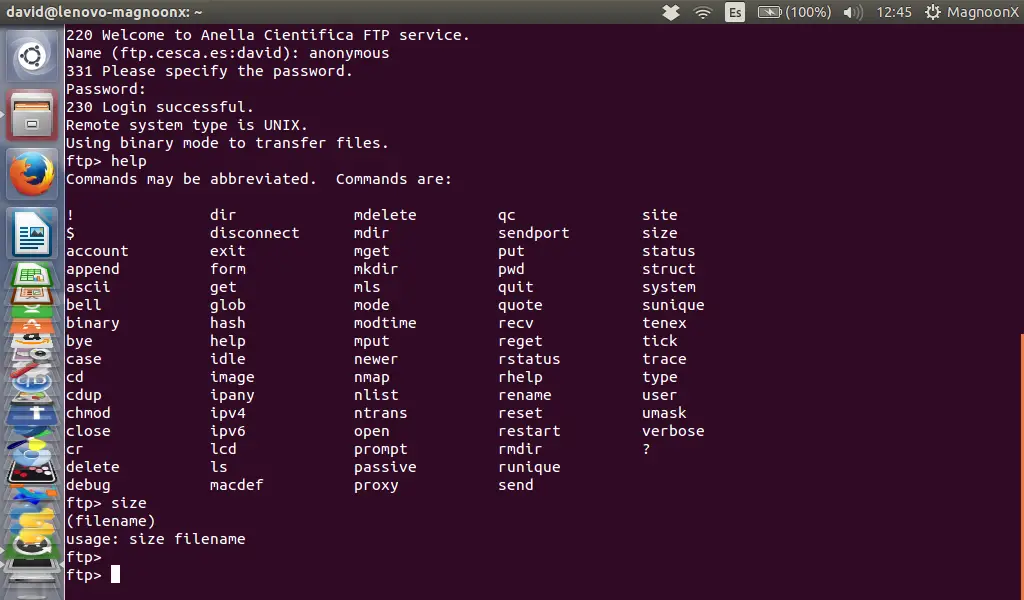
Step 2: Login with User and Password
Most FTP servers logins are password protected, so the server will ask us for a 'username' and a 'password'.
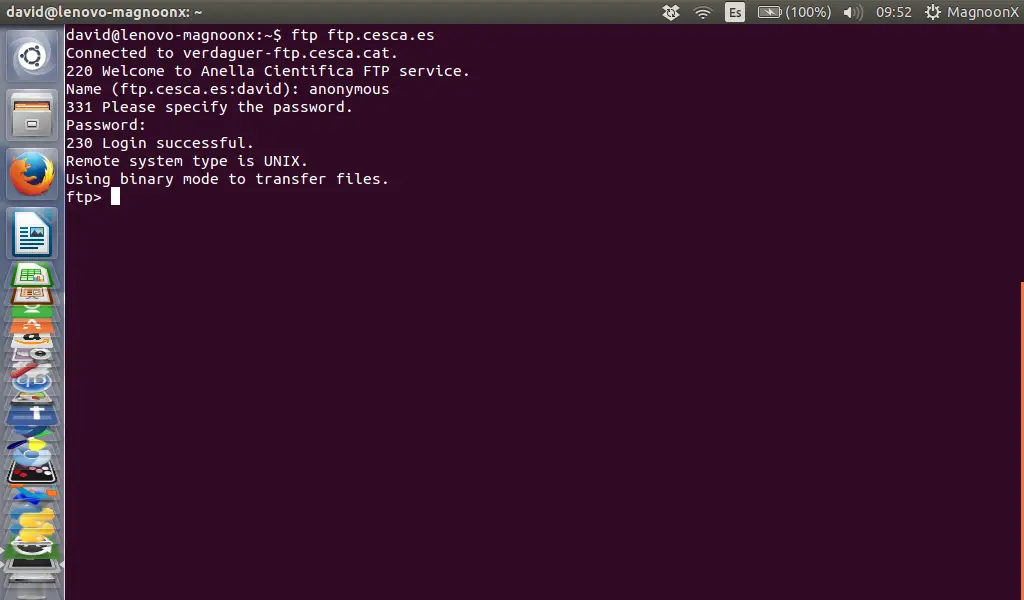
If you connect to a so-called anonymous FTP server, then try to use "anonymous" as user name and a nempty password:
Name: anonymous
Password:
The terminal will return a message like this:
230 Login successful.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
ftp>
When you are logged in successfully.
Step 3: Working with Directories
The commands to list, move and create folders on an FTP server are almost the same as we would use locally on our computer, ls for list, cd to change directories, mkdir to create directories...
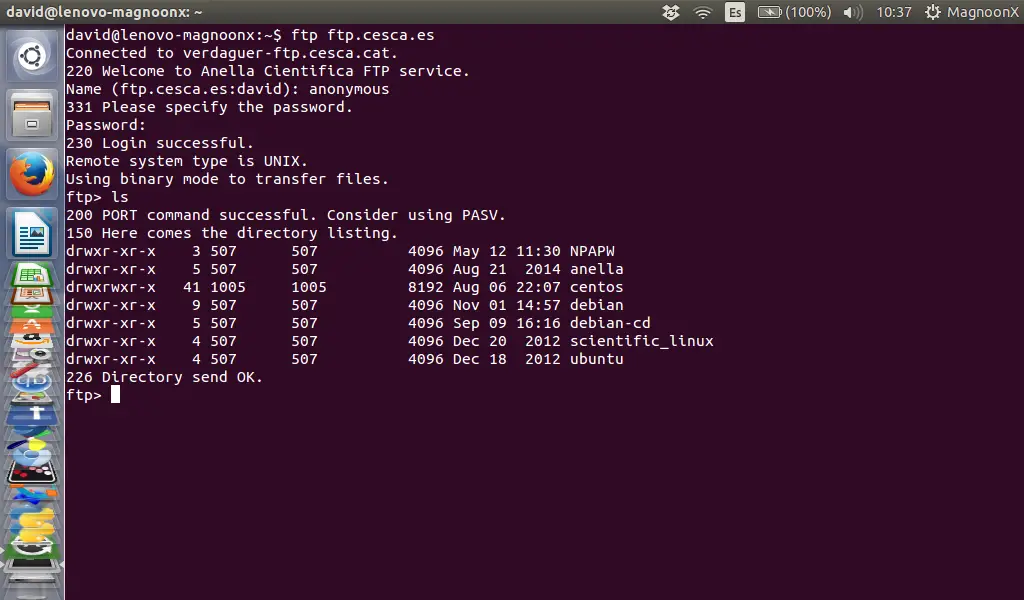
Listing directories with security settings:
ftp> ls
The server will return:
200 PORT command successful. Consider using PASV.
150 Here comes the directory listing.
directory list
....
....
226 Directory send OK.
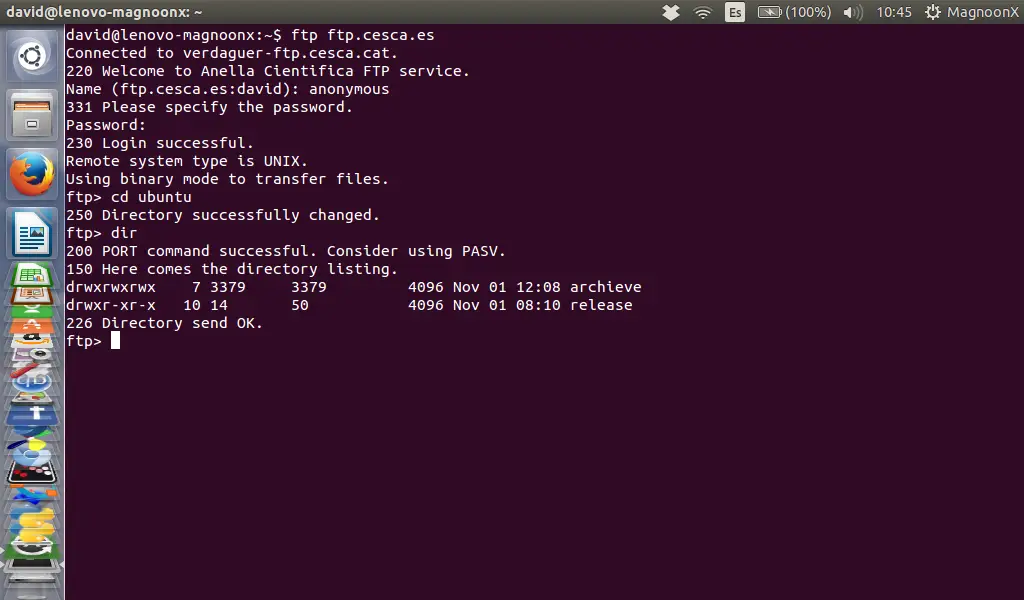
Changing Directories:
To change the directory we can type:
ftp> cd directory
The server will return:
250 Directory succesfully changed.
Step 4: Downloading files with FTP
Before downloading a file, we should set the local ftp file download directory by using 'lcd' command:
lcd /home/user/yourdirectoryname
If you dont specify the download directory, the file will be downloaded to the current directory where you were at the time you started the FTP session.
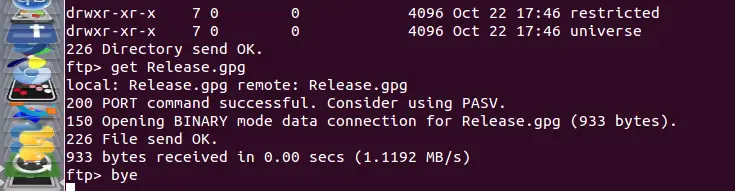
Now, we can use the command 'get' command to download a file, the usage is:
get file
The file will be downloaded to the directory previously set with the 'lcd' command.
The server will return the next message:
local: file remote: file
200 PORT command successful. Consider using PASV.
150 Opening BINARY mode data connection for file (xxx bytes).
226 File send OK.
XXX bytes received in x.xx secs (x.xxx MB/s).
To download several files we can use wildcards. In this example I will download all files with the .xls file extension.
mget *.xls
Step 5: Uploading Files with FTP
We can upload files that are in the local directory where we made the FTP connection.
To upload a file, we can use 'put' command.
put file
When the file that you want to upload is not in the local directory, you can use the absolute path starting with "/" as well:
put /path/file
To upload several files we can use the mput command similar to the mget example from above:
mput *.xls
Step 6: Closing the FTP connection
Once we have done the FTP work, we should close the connection for security reasons. There are three commands that we can use to close the connection:
bye
exit
quit
Any of them will disconnect our PC from the FTP server and will return:
221 Goodbye
If you need some additional help, once you are connected to the FTP server, type 'help' and this will show you all the available FTP commands.
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-use-ftp-on-the-linux-shell/