mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
367 lines
14 KiB
Markdown
367 lines
14 KiB
Markdown
关于 Linux 进程你所需要知道的一切
|
||
============================================================
|
||
|
||
在这篇指南中,我们会逐步对进程做基本的了解,然后简要看看如何用特定命令[管理 Linux 进程][9]。
|
||
|
||
进程(process)是指正在执行的程序;是程序正在运行的一个实例。它由程序指令,和从文件、其它程序中读取的数据或系统用户的输入组成。
|
||
|
||
### 进程的类型
|
||
|
||
在 Linux 中主要有两种类型的进程:
|
||
|
||
* 前台进程(也称为交互式进程) - 这些进程由终端会话初始化和控制。换句话说,需要有一个连接到系统中的用户来启动这样的进程;它们不是作为系统功能/服务的一部分自动启动。
|
||
* 后台进程(也称为非交互式/自动进程) - 这些进程没有连接到终端;它们不需要任何用户输入。
|
||
|
||
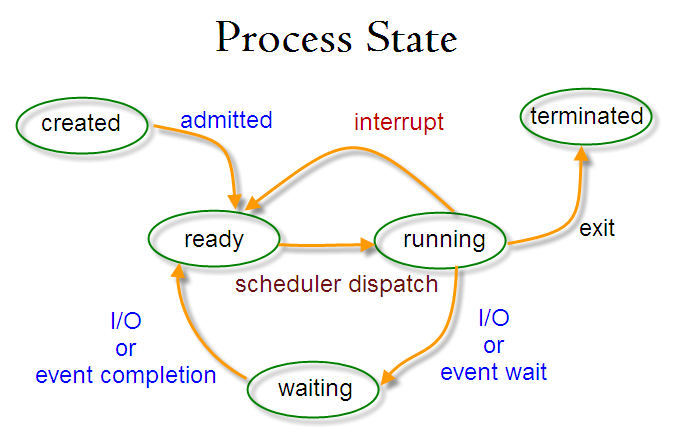
#### 什么是守护进程(daemon)
|
||
|
||
这是后台进程的特殊类型,它们在系统启动时启动,并作为服务一直运行;它们不会死亡。它们自发地作为系统任务启动(作为服务运行)。但是,它们能被用户通过 init 进程控制。
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][10]
|
||
|
||
*Linux 进程状态*
|
||
|
||
### 在 Linux 中创建进程
|
||
|
||
(LCTT 译注:此节原文不确,根据译者理解重新提供)
|
||
|
||
在 Linux 中创建进程有三种方式:
|
||
|
||
#### fork() 方式
|
||
|
||
使用 fork() 函数以父进程为蓝本复制一个进程,其 PID号与父进程 PID 号不同。在 Linux 环境下,fork() 是以写复制实现的,新的子进程的环境和父进程一样,只有内存与父进程不同,其他与父进程共享,只有在父进程或者子进程进行了修改后,才重新生成一份。
|
||
|
||
#### system() 方式
|
||
|
||
system() 函数会调用 `/bin/sh –c command` 来执行特定的命令,并且阻塞当前进程的执行,直到 command 命令执行完毕。新的子进程会有新的 PID。
|
||
|
||
#### exec() 方式
|
||
|
||
exec() 方式有若干种不同的函数,与之前的 fork() 和 system() 函数不同,exec() 方式会用新进程代替原有的进程,系统会从新的进程运行,新的进程的 PID 值会与原来的进程的 PID 值相同。
|
||
|
||
### Linux 如何识别进程?
|
||
|
||
由于 Linux 是一个多用户系统,意味着不同的用户可以在系统上运行各种各样的程序,内核必须唯一标识程序运行的每个实例。
|
||
|
||
程序由它的进程 ID(PID)和它父进程的进程 ID(PPID)识别,因此进程可以被分类为:
|
||
|
||
* 父进程 - 这些是在运行时创建其它进程的进程。
|
||
* 子进程 - 这些是在运行时由其它进程创建的进程。
|
||
|
||
#### init 进程
|
||
|
||
init 进程是系统中所有进程的父进程,它是[启动 Linux 系统][11]后第一个运行的程序;它管理着系统上的所有其它进程。它由内核自身启动,因此理论上说它没有父进程。
|
||
|
||
init 进程的进程 ID 总是为 1。它是所有孤儿进程的收养父母。(它会收养所有孤儿进程)。
|
||
|
||
#### 查找进程 ID
|
||
|
||
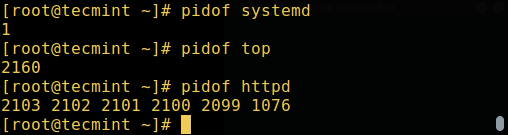
你可以用 pidof 命令查找某个进程的进程 ID:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# pidof systemd
|
||
# pidof top
|
||
# pidof httpd
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][12]
|
||
|
||
*查找 Linux 进程 ID*
|
||
|
||
要查找当前 shell 的进程 ID 以及它父进程的进程 ID,可以运行:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ echo $$
|
||
$ echo $PPID
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][13]
|
||
|
||
*查找 Linux 父进程 ID*
|
||
|
||
### 在 Linux 中启动进程
|
||
|
||
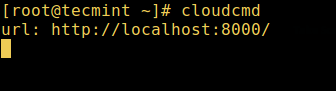
每次你运行一个命令或程序(例如 cloudcmd - CloudCommander),它就会在系统中启动一个进程。你可以按照下面的方式启动一个前台(交互式)进程,它会被连接到终端,用户可以发送输入给它:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# cloudcmd
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][14]
|
||
|
||
*启动 Linux 交互进程*
|
||
|
||
#### Linux 后台任务
|
||
|
||
要在后台(非交互式)启动一个进程,使用 `&` 符号,此时,该进程不会从用户中读取输入,直到它被移到前台。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# cloudcmd &
|
||
# jobs
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][15]
|
||
|
||
*在后台启动 Linux 进程*
|
||
|
||
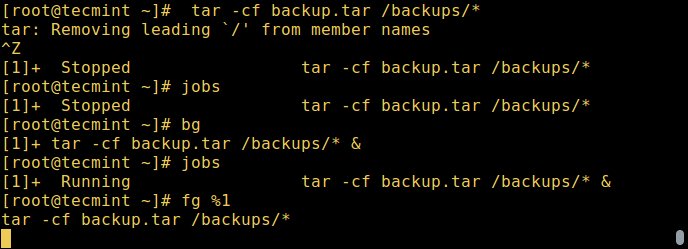
你也可以使用 `[Ctrl + Z]` 暂停执行一个程序并把它发送到后台,它会给进程发送 SIGSTOP 信号,从而暂停它的执行;它就会变为空闲:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# tar -cf backup.tar /backups/* #press Ctrl+Z
|
||
# jobs
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
要在后台继续运行上面被暂停的命令,使用 `bg` 命令:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# bg
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
要把后台进程发送到前台,使用 `fg` 命令以及任务的 ID,类似:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# jobs
|
||
# fg %1
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][16]
|
||
|
||
*Linux 后台进程任务*
|
||
|
||
你也可能想要阅读:[如何在后台启动 Linux 命令以及在终端分离(Detach)进程][17]
|
||
|
||
### Linux 中进程的状态
|
||
|
||
在执行过程中,取决于它的环境一个进程会从一个状态转变到另一个状态。在 Linux 中,一个进程有下面的可能状态:
|
||
|
||
* Running - 此时它正在运行(它是系统中的当前进程)或准备运行(它正在等待分配 CPU 单元)。
|
||
* Waiting - 在这个状态,进程正在等待某个事件的发生或者系统资源。另外,内核也会区分两种不同类型的等待进程;可中断等待进程(interruptible waiting processes) - 可以被信号中断,以及不可中断等待进程(uninterruptible waiting processes)- 正在等待硬件条件,不能被任何事件/信号中断。
|
||
* Stopped - 在这个状态,进程已经被停止了,通常是由于收到了一个信号。例如,正在被调试的进程。
|
||
* Zombie - 该进程已经死亡,它已经停止了但是进程表(process table)中仍然有它的条目。
|
||
|
||
### 如何在 Linux 中查看活跃进程
|
||
|
||
有很多 Linux 工具可以用于查看/列出系统中正在运行的进程,两个传统众所周知的是 [ps][18] 和 [top][19] 命令:
|
||
|
||
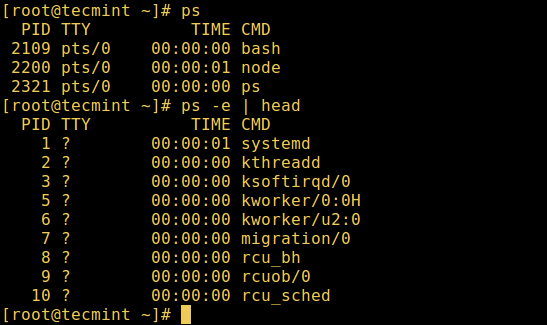
#### 1. ps 命令
|
||
|
||
它显示被选中的系统中活跃进程的信息,如下图所示:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# ps
|
||
# ps -e | head
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][20]
|
||
|
||
*列出 Linux 活跃进程*
|
||
|
||
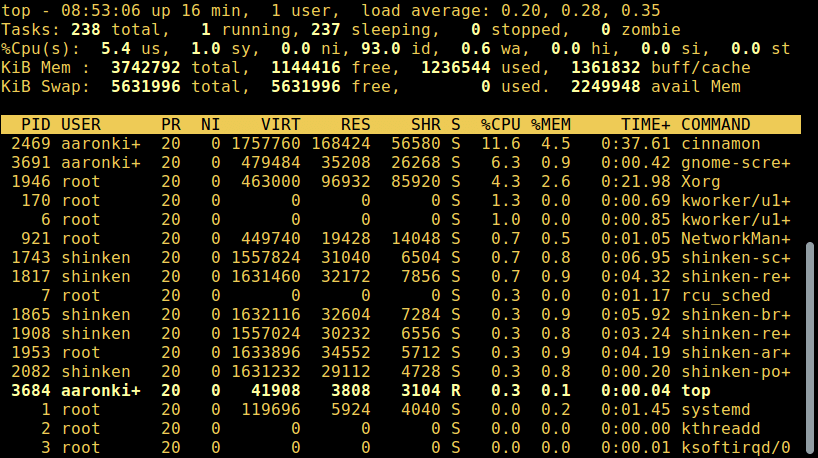
#### 2. top - 系统监控工具
|
||
|
||
[top 是一个强大的工具][21],它能给你提供 [运行系统的动态实时视图][22],如下面截图所示:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# top
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][23]
|
||
|
||
*列出 Linux 正在运行的程序*
|
||
|
||
阅读这篇文章获取更多 top 使用事例:[Linux 中 12 个 top 命令事例][24]
|
||
|
||
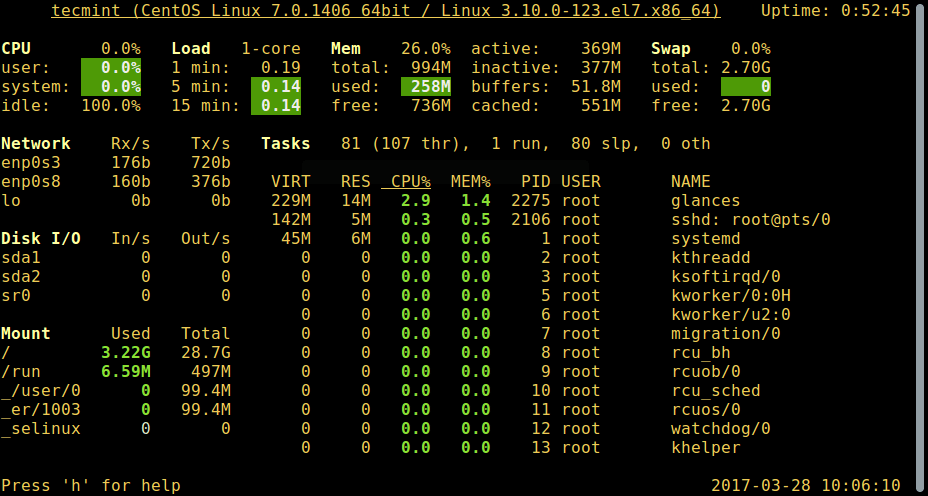
#### 3. glances - 系统监控工具
|
||
|
||
glances 是一个相对比较新的系统监控工具,它有一些比较高级的功能:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# glances
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][25]
|
||
|
||
*Glances – Linux 进程监控*
|
||
|
||
要获取完整使用指南,请阅读:[Glances - Linux 的一个高级实时系统监控工具][26]
|
||
|
||
还有很多你可以用来列出活跃进程的其它有用的 Linux 系统监视工具,打开下面的链接了解更多关于它们的信息:
|
||
|
||
1. [监控 Linux 性能的 20 个命令行工具][1]
|
||
2. [13 个有用的 Linux 监控工具][2]
|
||
|
||
### 如何在 Linux 中控制进程
|
||
|
||
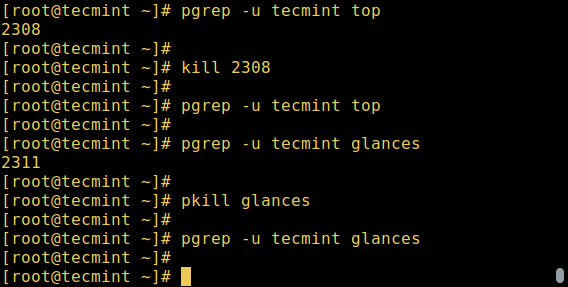
Linux 也有一些命令用于控制进程,例如 `kill`、`pkill`、`pgrep` 和 `killall`,下面是一些如何使用它们的基本事例:
|
||
|
||
````
|
||
$ pgrep -u tecmint top
|
||
$ kill 2308
|
||
$ pgrep -u tecmint top
|
||
$ pgrep -u tecmint glances
|
||
$ pkill glances
|
||
$ pgrep -u tecmint glances
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][27]
|
||
|
||
*控制 Linux 进程*
|
||
|
||
想要深入了解如何使用这些命令,在 Linux 中杀死/终止活跃进程,可以点击下面的链接:
|
||
|
||
1. [终止 Linux 进程的 Kill、Pkill 和 Killall 命令指南][3]
|
||
2. [如何在 Linux 中查找并杀死进程][4]
|
||
|
||
注意当你系统僵死(freeze)时你可以使用它们杀死 [Linux 中的不响应程序][28]。
|
||
|
||
#### 给进程发送信号
|
||
|
||
Linux 中控制进程的基本方法是给它们发送信号。你可以发送很多信号给一个进程,运行下面的命令可以查看所有信号:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ kill -l
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][29]
|
||
|
||
*列出所有 Linux 信号*
|
||
|
||
要给一个进程发送信号,可以使用我们之前提到的 `kill`、`pkill` 或 `pgrep` 命令。但只有被编程为能识别这些信号时程序才能响应这些信号。
|
||
|
||
大部分信号都是系统内部使用,或者给程序员编写代码时使用。下面是一些对系统用户非常有用的信号:
|
||
|
||
* SIGHUP 1 - 当控制它的终端被被关闭时给进程发送该信号。
|
||
* SIGINT 2 - 当用户使用 `[Ctrl+C]` 中断进程时控制它的终端给进程发送这个信号。
|
||
* SIGQUIT 3 - 当用户发送退出信号 `[Ctrl+D]` 时给进程发送该信号。
|
||
* SIGKILL 9 - 这个信号会马上中断(杀死)进程,进程不会进行清理操作。
|
||
* SIGTERM 15 - 这是一个程序终止信号(kill 默认发送这个信号)。
|
||
* SIGTSTP 20 - 它的控制终端发送这个信号给进程要求它停止(终端停止);通过用户按 `[Ctrl+Z]` 触发。
|
||
|
||
下面是当 Firefox 应用程序僵死时通过它的 PID 杀死它的 kill 命令事例:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ pidof firefox
|
||
$ kill 9 2687
|
||
或
|
||
$ kill -KILL 2687
|
||
或
|
||
$ kill -SIGKILL 2687
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
使用它的名称杀死应用,可以像下面这样使用 pkill 或 killall:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ pkill firefox
|
||
$ killall firefox
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
#### 更改 Linux 进程优先级
|
||
|
||
在 Linux 系统中,所有活跃进程都有一个优先级以及 nice 值。有比点优先级进程有更高优先级的进程一般会获得更多的 CPU 时间。
|
||
|
||
但是,有 root 权限的系统用户可以使用 `nice` 和 `renice` 命令影响(更改)优先级。
|
||
|
||
在 top 命令的输出中, NI 显示了进程的 nice 值:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ top
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][30]
|
||
|
||
*列出 Linux 正在运行的进程*
|
||
|
||
使用 `nice` 命令为一个进程设置 nice 值。记住一个普通用户可以给他拥有的进程设置 0 到 20 的 nice 值。
|
||
|
||
只有 root 用户可以使用负的 nice 值。
|
||
|
||
要重新设置一个进程的优先级,像下面这样使用 `renice` 命令:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ renice +8 2687
|
||
$ renice +8 2103
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
阅读我们其它如何管理和控制 Linux 进程的有用文章。
|
||
|
||
1. [Linux 进程管理:启动、停止以及中间过程][5]
|
||
2. [使用 ‘top’ 命令 Batch 模式查找内存使用最高的 15 个进程][6]
|
||
3. [在 Linux 中查找内存和 CPU 使用率最高的进程][7]
|
||
4. [在 Linux 中如何使用进程 ID 查找进程名称][8]
|
||
|
||
就是这些!如果你有任何问题或者想法,通过下面的反馈框和我们分享吧。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
|
||
作者简介:
|
||
|
||
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S(Free and Open-Source Software) 爱好者,一个 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,他相信知识共享。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-process-management/
|
||
|
||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||
|
||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-kill-a-process-in-linux/
|
||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-and-kill-running-processes-pid-in-linux/
|
||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-exam-boot-process-and-process-management/
|
||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-processes-by-memory-usage-top-batch-mode/
|
||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-processes-memory-ram-cpu-usage/
|
||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-process-name-pid-number-linux/
|
||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/dstat-monitor-linux-server-performance-process-memory-network/
|
||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/ProcessState.png
|
||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process/
|
||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Find-Linux-Process-ID.png
|
||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Find-Linux-Parent-Process-ID.png
|
||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Start-Linux-Interactive-Process.png
|
||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Start-Linux-Process-in-Background.png
|
||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Linux-Background-Process-Jobs.png
|
||
[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/run-linux-command-process-in-background-detach-process/
|
||
[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process-and-manage-services/
|
||
[19]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||
[20]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/ps-command.png
|
||
[21]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||
[22]:http://www.tecmint.com/bcc-best-linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||
[23]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/top-command.png
|
||
[24]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||
[25]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/glances.png
|
||
[26]:http://www.tecmint.com/glances-an-advanced-real-time-system-monitoring-tool-for-linux/
|
||
[27]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Control-Linux-Processes.png
|
||
[28]:http://www.tecmint.com/kill-processes-unresponsive-programs-in-ubuntu/
|
||
[29]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/list-all-signals.png
|
||
[30]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/top-command.png
|
||
[31]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||
[32]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||
[33]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|