4.9 KiB
XiatianSummer translating
Visualize Disk Usage On Your Linux System
Finding disk space usage is no big deal in Unix-like operating systems. We have a built-in command named du that can be used to calculate and summarize the disk space usage in minutes. And, we have some third-party tools like Ncdu and Agedu which can also be used to track down the disk usage. As you already know, these are all command line utilities and you will see the disk usage results in plain-text format. However, some of you’d like to view the results in visual or kind of image format. No worries! I know one such GUI tool to find out the disk usage details. Say hello to “Filelight” , a graphical utility to visualize disk usage on your Linux system and displays the disk usage results in a colored radial layout. Filelight is one of the oldest project and it has been around for a long time. It is completely free to use and open source.
Installing Filelight
Filelight is part of KDE applications and comes pre-installed with KDE-based Linux distributions.
If you’re using non-KDE distros, Filelight is available in the official repositories, so you can install it using the default package manager.
On Arch Linux and its variants such as Antergos, Manjaro Linux, Filelight can be installed as below.
$ sudo pacman -S filelight
On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:
$ sudo apt install filelight
On Fedora:
$ sudo dnf install filelight
On openSUSE:
$ sudo zypper install filelight
Visualize Disk Usage On Your Linux System
Once installed, launch Filelight from Menu or application launcher.
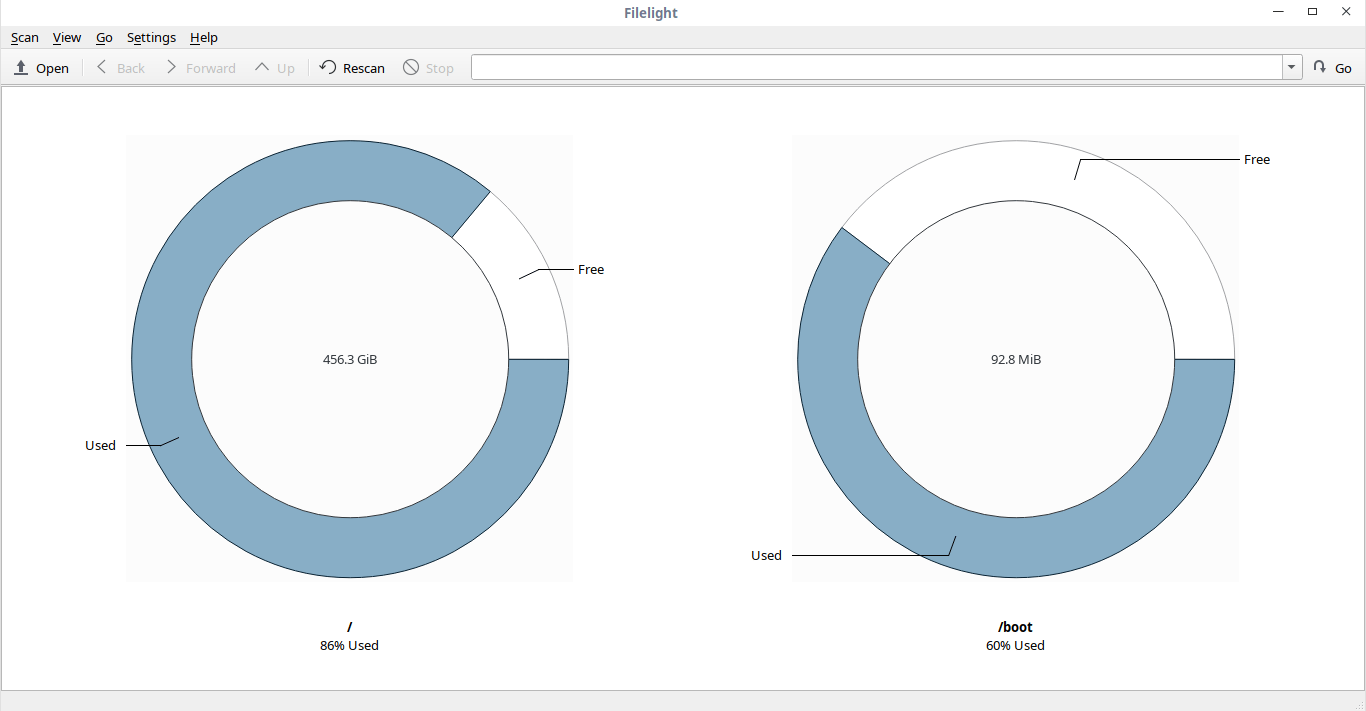
FIlelight graphically represents your filesystem as a set of concentric segmented-rings.
As you can see, Filelight displays the disk usage of the / and /boot filesystems by default.
You can also scan the individual folders of your choice to view the disk usage of that particular folder. To do so, go to Filelight - > Scan -> Scan Folder and choose the folder you want to scan.
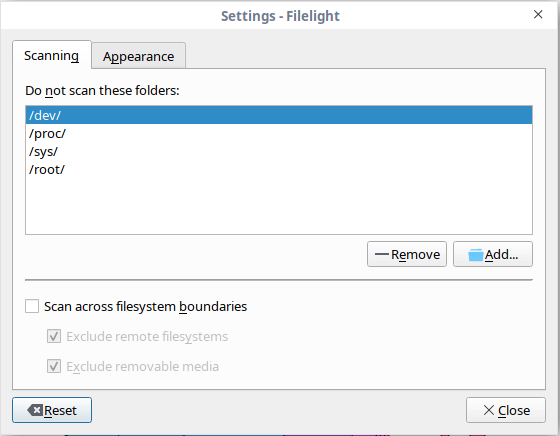
Filelight excludes the following directories from scanning:
- /dev
- /proc
- /sys
- /root
This option is helpful to skip the directories that you may not have permissions to read, or folders that are part of a virtual filesystem, such as /proc.
If you want to add any folder in this list, go to Filelight - > Settings -> Scanning and click “add” button and choose the folder you want to add in this list.
Similarly, to remove a folder from the list, choose the folder and click on “Remove”.
If you want to change the way filelight looks, go to Settings - > Appearance tab and change the color scheme as per your liking.
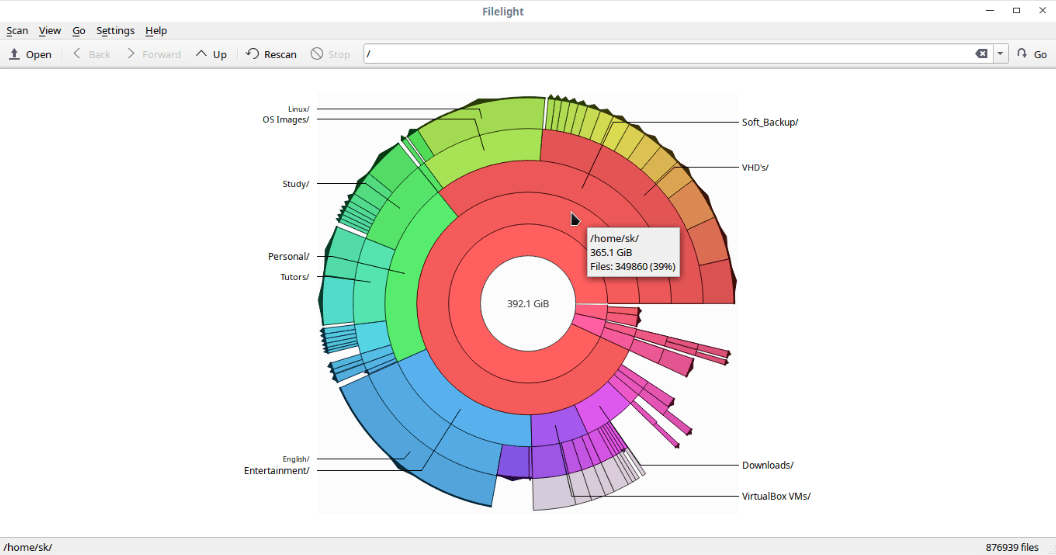
Each segment in the radial layout is represented with different colors. The following image represents the entire radial layout of / filesystem. To view the full information of files and folders, just hover the mouse pointer over them.
You can navigate around the the filesystem by simply clicking on the respective segment. To view the disk usage of any file or folder, just click on them and you will get the complete disk usage details of that particular folder/file.
Not just local filesystem, Filelight can able to scan your local, remote and removable disks. If you’re using any KDE-based Linux distribution, it can be integrated into file managers like Konqueror, Dolphin and Krusader.
Unlike the CLI utilities, you don’t have to use any extra arguments or options to view the results in human-readable format. Filelight will display the disk usage in human-readable format by default.
Conclusion
By using Filelight, you can quickly discover where exactly your diskspace is being used in your filesystem and free up the space wherever necessary by deleting the unwanted files or folders. If you are looking for some simple and user-learnedly graphical disk usage viewer, Filelight is worth trying.
And, that’s all for now. Hope this was useful. More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!
Cheers!
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/filelight-visualize-disk-usage-on-your-linux-system/