mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-04 22:00:34 +08:00
73 lines
4.1 KiB
Markdown
73 lines
4.1 KiB
Markdown
在 Linux 命令行中使用 ls 列出文件的技巧
|
||
======
|
||
|
||
> 学习一些 Linux `ls` 命令最有用的变化。
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
我在 Linux 中最先学到的命令之一就是 `ls`。了解系统中文件所在目录中的内容非常重要。能够查看和修改不仅仅是一些文件还有所有文件也很重要。
|
||
|
||
我的第一个 Linux 备忘录是[单页 Linux 手册][1],它于 1999 年发布,成了我的首选参考资料。当我开始探索 Linux 时,我把它贴在桌子上并经常参考它。它在第一页第一列的底部介绍了 `ls -l` 列出文件的命令。
|
||
|
||
之后,我将学习这个最基本命令的其它迭代。通过 `ls` 命令,我开始了解 Linux 文件权限的复杂性,以及哪些是我的文件,哪些需要 root 或者 sudo 权限来修改。随着时间的推移,我习惯了使用命令行,虽然我仍然使用 `ls -l` 来查找目录中的文件,但我经常使用 `ls -al`,这样我就可以看到可能需要更改的隐藏文件,比如那些配置文件。
|
||
|
||
根据 Eric Fischer 在 [Linux 文档项目][2]中关于 `ls` 命令的文章,该命令的起源可以追溯到 1961 年 MIT 的<ruby>相容分时系统<rt>Compatible Time-Sharing System</rt></ruby>(CTSS)上的 `listf` 命令。当 CTSS 被 [Multics][3] 代替时,命令变为 `list`,并有像 `list -all` 的开关。根据[维基百科][4],`ls` 出现在 AT&T Unix 的原始版本中。我们今天在 Linux 系统上使用的 `ls` 命令来自 [GNU Core Utilities][5]。
|
||
|
||
大多数时候,我只使用几个迭代的命令。我通常用 `ls` 或 `ls -al` 查看目录内容,但是你还应该熟悉许多其它选项。
|
||
|
||
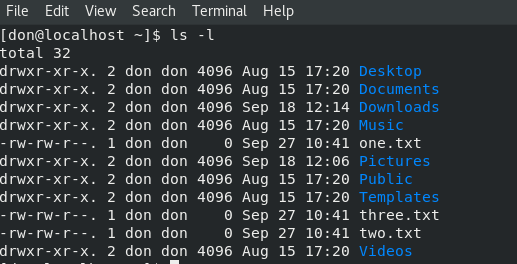
`ls -l` 提供了一个简单的目录列表:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
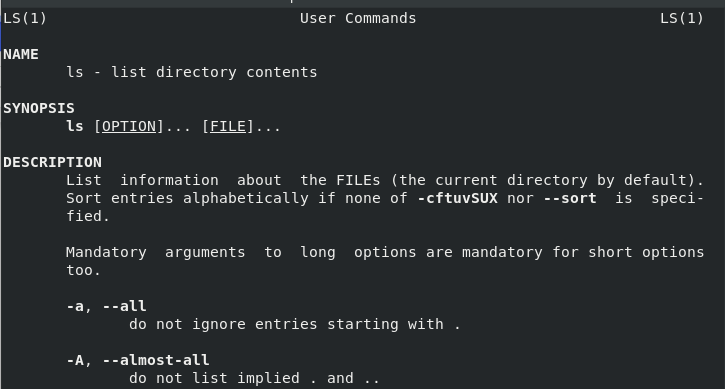
在我的 Fedora 28 系统的手册页中,我发现 `ls` 还有许多其它选项,所有这些选项都提供了有关 Linux 文件系统的有趣且有用的信息。通过在命令提示符下输入 `man ls`,我们可以开始探索其它一些选项:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
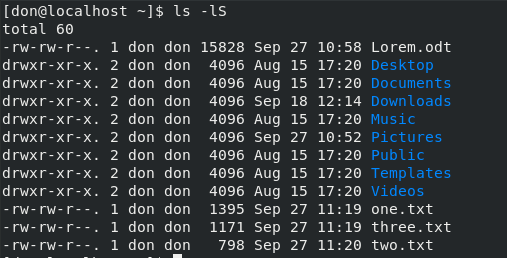
要按文件大小对目录进行排序,请使用 `ls -lS`:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
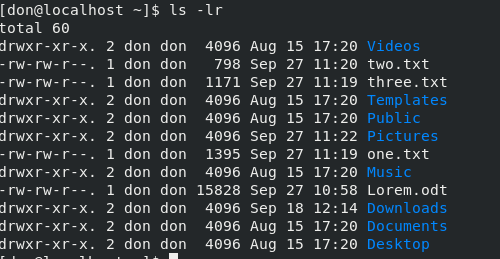
要以相反的顺序列出内容,请使用 `ls -lr`:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
要按列列出内容,请使用 `ls -c`:
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
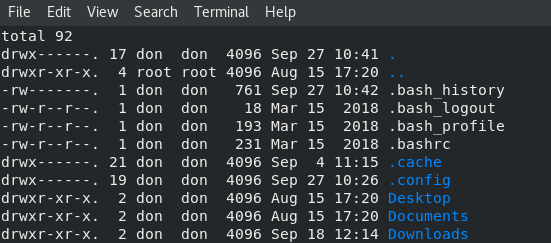
`ls -al` 提供了同一目录中所有文件的列表:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
以下是我认为有用且有趣的一些其它选项:
|
||
|
||
* 仅列出目录中的 .txt 文件:`ls *.txt`
|
||
* 按文件大小列出:`ls -s`
|
||
* 按时间和日期排序:`ls -t`
|
||
* 按扩展名排序:`ls -X`
|
||
* 按文件大小排序:`ls -S`
|
||
* 带有文件大小的长格式:`ls -ls`
|
||
|
||
要生成指定格式的目录列表并将其定向到文件供以后查看,请输入 `ls -al > mydirectorylist`。最后,我找到的一个更奇特的命令是 `ls -R`,它提供了计算机上所有目录及其内容的递归列表。
|
||
|
||
有关 `ls` 命令的所有迭代的完整列表,请参阅 [GNU Core Utilities][6]。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/10/ls-command
|
||
|
||
作者:[Don Watkins][a]
|
||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||
校对:[pityonline](https://github.com/pityonline)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins
|
||
[1]: http://hackerspace.cs.rutgers.edu/library/General/One_Page_Linux_Manual.pdf
|
||
[2]: http://www.tldp.org/LDP/LG/issue48/fischer.html
|
||
[3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multics
|
||
[4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ls
|
||
[5]: http://www.gnu.org/s/coreutils/
|
||
[6]: https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/manual/html_node/ls-invocation.html#ls-invocation
|