mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-04 22:00:34 +08:00
154 lines
8.2 KiB
Markdown
154 lines
8.2 KiB
Markdown
使用 Ansible 在树莓派上构建一个基于 Linux 的高性能计算系统
|
||
============================================================
|
||
|
||
### 使用低成本的硬件和开源软件设计一个高性能计算集群。
|
||
|
||

|
||
图片来源:opensource.com
|
||
|
||
在我的 [Opensource.com 上前面的文章中][14],我介绍了 [OpenHPC][15] 项目,它的目标是致力于加速高性能计算(HPC)的创新。这篇文章将更深入来介绍使用 OpenHPC 的特性来构建一个小型的 HPC 系统。将它称为 _HPC 系统_ 可能有点“扯虎皮拉大旗”的意思,因此,更确切的说法应该是,通过 OpenHPC 项目发布的 [方法构建集群][16] 系统。
|
||
|
||
这个集群由两台树莓派 3 系统作为活动计算节点,以及一台虚拟机作为主节点,结构示意如下:
|
||
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
我的主节点运行的是 x86_64 架构的 CentOS 操作系统,而计算节点运行了 aarch64 的轻度修改版的 CentOS 操作系统。
|
||
|
||
下图是真实的设备工作照:
|
||
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
去配置一台像上图这样的 HPC 系统,我是按照 OpenHPC 集群构建方法 —— [CentOS 7.4/aarch64 + Warewulf + Slurm 安装指南][17] (PDF) 的一些步骤来做的。这个方法包括 [Warewulf][18] 提供的使用说明;因为我的那三个系统是手动安装的,我跳过了 Warewulf 部分以及创建 [Ansible playbook][19] 的一些步骤。
|
||
|
||
|
||
在 [Ansible][26] playbooks 中设置完成我的集群之后,我就可以向资源管理器提交作业了。在我的这个案例中, [Slurm][27] 充当了资源管理器,它是集群中的一个实例,由它来决定我的作业什么时候在哪里运行。其中一种可做的事情是,在集群上启动一个简单的作业:
|
||
```
|
||
[ohpc@centos01 ~]$ srun hostname
|
||
calvin
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如果需要更多的资源,我可以去告诉 Slurm,我希望在 8 个 CPU 上去运行我的命令:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
[ohpc@centos01 ~]$ srun -n 8 hostname
|
||
hobbes
|
||
hobbes
|
||
hobbes
|
||
hobbes
|
||
calvin
|
||
calvin
|
||
calvin
|
||
calvin
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在第一个示例中,Slurm 在一个单个的 CPU 上运行了指定的命令(`hostname`),而在第二个示例中,Slurm 在 8 个 CPU 上运行了那个命令。我的计算节点一个命名为 `calvin`,而另一个命名为 `hobbes`;在上面的命令输出部分可以看到它们的名字。每个计算节点都是由 4 个 CPU 核心的树莓派 3 构成的。
|
||
|
||
在我的集群中提交作业的另一种方法是使用命令 `sbatch`,它可以用于运行脚本,将输出写入到一个文件,而不是我的终端上。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
[ohpc@centos01 ~]$ cat script1.sh
|
||
#!/bin/sh
|
||
date
|
||
hostname
|
||
sleep 10
|
||
date
|
||
[ohpc@centos01 ~]$ sbatch script1.sh
|
||
Submitted batch job 101
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
它将创建一个名为 `slurm-101.out` 的输出文件,这个输出文件包含下列的内容:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
Mon 11 Dec 16:42:31 UTC 2017
|
||
calvin
|
||
Mon 11 Dec 16:42:41 UTC 2017
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
为示范资源管理器的基本功能、简单的和一系列的命令行工具,这个集群系统是挺合适的,但是,去配置一个类似HPC 系统去做各种工作就有点无聊了。
|
||
|
||
一个更有趣的应用是在这个集群的所有可用 CPU 上运行一个 [Open MPI][20] 并行作业。我使用了一个基于 [Game of Life][21] 的应用,它被用于一个名为“使用 Red Hat 企业版 Linux 跨多种架构运行 `Game of Life`“的 [视频][22]。除了以前实现的基于 MPI 的 `Game of Life` 之外,在我的集群中现在运行的这个版本对每个涉及的主机的单元格颜色都是不同的。下面的脚本以图形输出的方式来交互式启动应用:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ cat life.mpi
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
|
||
module load gnu6 openmpi3
|
||
|
||
if [[ "$SLURM_PROCID" != "0" ]]; then
|
||
exit
|
||
fi
|
||
|
||
mpirun ./mpi_life -a -p -b
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
我使用下面的命令来启动作业,它告诉 Slurm,为这个作业分配 8 个 CPU:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ srun -n 8 --x11 life.mpi
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
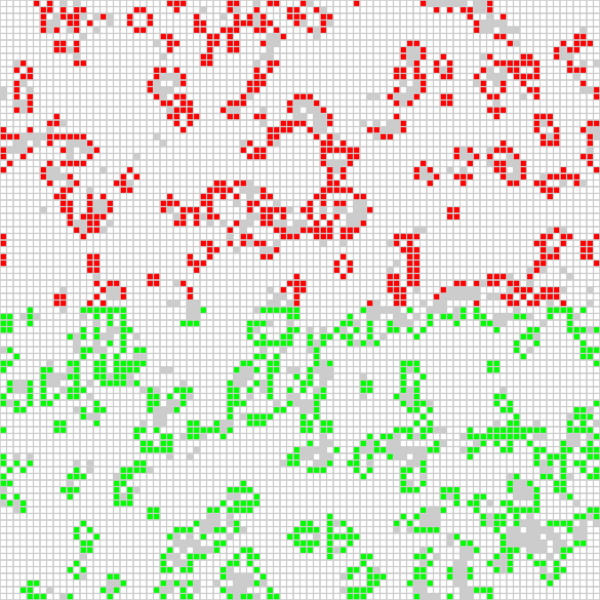
为了演示,这个作业有一个图形界面,它展示了当前计算的结果:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
红色单元格是由其中一个计算节点来计算的,而绿色单元格是由另外一个计算节点来计算的。我也可以让 `Game of Life` 程序为使用的每个 CPU 核心(这里的每个计算节点有四个核心)去生成不同的颜色,这样它的输出如下:
|
||
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
感谢 OpenHPC 提供的软件包和安装方法,因为它们我可以去配置一个由两个计算节点和一个主节点的 HPC 式的系统。我可以在资源管理器上提交作业,然后使用 OpenHPC 提供的软件在我的树莓派的 CPU 上去启动 MPI 应用程序。
|
||
|
||
* * *
|
||
|
||
_想学习更多的关于使用 OpenHPC 去构建树莓派集群,请参与 Adrian Reber 在 [DevConf.cz 2018][10] 的讨论,它于 1月 26-28 日在 Brno,Czech Republic 举行,以及在 [CentOS Dojo 2018][11] ,它于 2 月 2 日在 Brussels 举行。_
|
||
|
||
### 关于作者
|
||
|
||
[][23] Adrian Reber —— Adrian 是 Red Hat 的高级软件工程师,他早在 2010 年就开始了迁移的过程,迁移到高性能计算环境中,从那个时候起迁移了许多的程序,并因此获得了博士学位,然后加入了 Red Hat 公司并开始去迁移到容器。偶尔他仍然去迁移单个进程,并且它至今仍然对高性能计算非常感兴趣。[关于我的更多信息点这里][12]
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/1/how-build-hpc-system-raspberry-pi-and-openhpc
|
||
|
||
作者:[Adrian Reber ][a]
|
||
译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
|
||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/adrianreber
|
||
[1]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-are-linux-containers?utm_campaign=containers&intcmp=70160000000h1s6AAA
|
||
[2]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-docker?utm_campaign=containers&intcmp=70160000000h1s6AAA
|
||
[3]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-kubernetes?utm_campaign=containers&intcmp=70160000000h1s6AAA
|
||
[4]:https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2016/01/13/a-practical-introduction-to-docker-container-terminology/?utm_campaign=containers&intcmp=70160000000h1s6AAA
|
||
[5]:https://opensource.com/file/384031
|
||
[6]:https://opensource.com/file/384016
|
||
[7]:https://opensource.com/file/384021
|
||
[8]:https://opensource.com/file/384026
|
||
[9]:https://opensource.com/article/18/1/how-build-hpc-system-raspberry-pi-and-openhpc?rate=l9n6B6qRcR20LJyXEoUoWEZ4mb2nDc9sFZ1YSPc60vE
|
||
[10]:https://devconfcz2018.sched.com/event/DJYi/openhpc-introduction
|
||
[11]:https://wiki.centos.org/Events/Dojo/Brussels2018
|
||
[12]:https://opensource.com/users/adrianreber
|
||
[13]:https://opensource.com/user/188446/feed
|
||
[14]:https://opensource.com/article/17/11/openhpc
|
||
[15]:https://openhpc.community/
|
||
[16]:https://openhpc.community/downloads/
|
||
[17]:https://github.com/openhpc/ohpc/releases/download/v1.3.3.GA/Install_guide-CentOS7-Warewulf-SLURM-1.3.3-aarch64.pdf
|
||
[18]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warewulf
|
||
[19]:http://people.redhat.com/areber/openhpc/ansible/
|
||
[20]:https://www.open-mpi.org/
|
||
[21]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conway%27s_Game_of_Life
|
||
[22]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n8DvxMcOMXk
|
||
[23]:https://opensource.com/users/adrianreber
|
||
[24]:https://opensource.com/users/adrianreber
|
||
[25]:https://opensource.com/users/adrianreber
|
||
[26]:https://www.ansible.com/
|
||
[27]:https://slurm.schedmd.com/
|
||
[28]:https://opensource.com/tags/raspberry-pi
|
||
[29]:https://opensource.com/tags/programming
|
||
[30]:https://opensource.com/tags/linux
|
||
[31]:https://opensource.com/tags/ansible
|