mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
222 lines
11 KiB
Markdown
222 lines
11 KiB
Markdown
# Kali Linux – Fresh Installation Guide
|
||
|
||
Kali Linux is arguably one of the best out of the box [Linux distributions available for security testing][18]. While many of the tools in Kali can be installed in most Linux distributions, the Offensive Security team developing Kali has put countless hours into perfecting their ready to boot security distribution.
|
||
|
||
Kali Linux is a Debian based, security distribution. The distribution comes pre-loaded with hundreds of well known security tools and has gained quite a name for itself.
|
||
|
||
Kali even has an industry respected certification available called “Pentesting with Kali”. The certification is a rigorous 24 hour challenge in which applicants must successfully compromise a number of computers with another 24 hours to write up a professional penetration test report that is sent to and graded by the personnel at Offensive Security. Successfully passing this exam will allow the test taker to obtain the OSCP credential.
|
||
|
||
The focus of this guide and future articles is to help individuals become more familiar with Kali Linux and several of the tools available within the distribution.
|
||
|
||
Please be sure to use extreme caution with the tools included with Kali as many of them can accidentally be used in a manner that will break computer systems. The information contained within all of these Kali articles is intended for legal usages.
|
||
|
||
#### System Requirements
|
||
|
||
Kali has some minimum suggested specifications for hardware. Depending upon the intended use, more may be desired. This guide will be assuming that the reader will want to install Kali as the only operating system on the computer.
|
||
|
||
1. At least 10GB of disk space; strongly encouraged to have more
|
||
2. At least 512MB of ram; more is encouraged especially for graphical environments
|
||
3. USB or CD/DVD boot support
|
||
4. Kali Linux ISO available from [https://www.kali.org/downloads/][1]
|
||
|
||
#### Create a Bootable USB Using dd Command
|
||
|
||
This guide will be assuming that a USB drive is available to use as the installation media. Take note that the USB drive should be as close to 4/8GB as possible and ALL DATA WILL BE REMOVED!
|
||
|
||
The author has had issues with larger USB drives but some may still work. Regardless, following the next few steps WILL RESULT IN DATA LOSS ON THE USB DRIVE.
|
||
|
||
Please be sure to backup all data before proceeding. This bootable Kali Linux USB drive is going to be created from another Linux machine.
|
||
|
||
Step 1 is to obtain the Kali Linux ISO. This guide is going to use the current newest version of Kali with the Enlightenment [Linu desktop environment][17].
|
||
|
||
To obtain this version, type the following into a terminal.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ cd ~/Downloads
|
||
$ wget -c http://cdimage.kali.org/kali-2016.2/kali-linux-e17-2016.2-amd64.iso
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
The two commands above will download the Kali Linux ISO into the current user’s ‘Downloads’ folder.
|
||
|
||
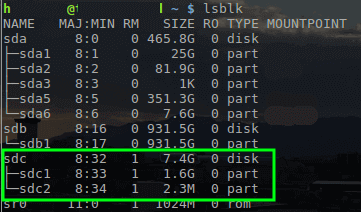
The next process is to write the ISO to a USB drive to boot the installer. To accomplish this we can use the ‘dd’tool within Linux. First, the disk name needs to be located with lsblk command though.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ lsblk
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][16]
|
||
|
||
Find Out USB Device Name in Linux
|
||
|
||
With the name of the USB drive determined as `/dev/sdc`, the Kali ISO can be written to the drive with the ‘dd’tool.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo dd if=~/Downloads/kali-linux-e17-2016.2-amd64.iso of=/dev/sdc
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Important: The above command requires root privileges so utilize sudo or login as the root user to run the command. Also this command will REMOVE EVERYTHING on the USB drive. Be sure to backup needed data.
|
||
|
||
Once the ISO is copied over to the USB drive, proceed further to install Kali Linux.
|
||
|
||
### Installation of Kali Linux Distribution
|
||
|
||
1. First, plug the USB drive into the respective computer that Kali should be installed upon and proceed to boot to the USB drive. Upon successful booting to the USB drive, the user will be presented with the following screen and should proceed with the ‘Install’ or ‘Graphical Install’ options.
|
||
|
||
This guide will be using the ‘Graphical Install’ method.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][15]
|
||
|
||
Kali Linux Boot Menu
|
||
|
||
2. The next couple of screens will ask the user to select locale information such as language, country, and keyboard layout.
|
||
|
||
Once through the locale information, the installer will prompt for a hostname and domain for this install. Provide the appropriate information for the environment and continue installing.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][14]
|
||
|
||
Set Hostname for Kali Linux
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][13]
|
||
|
||
Set Domain for Kali Linux
|
||
|
||
3. After setting up the hostname and domain name, the root user’s password needs to be set. DO NOT FORGET THIS PASSWORD.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][12]
|
||
|
||
Set Root User Password for Kali Linux
|
||
|
||
4. After setting the password is set, the installer will prompt for time zone data and then pause at the disk partitioning.
|
||
|
||
If Kali will be the only operating on the machine, the easiest option is to use ‘Guided – Use Entire Disk’ and then select the storage device you wish to install Kali.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][11]
|
||
|
||
Select Kali Linux Installation Type
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][10]
|
||
|
||
Select Kali Linux Installation Disk
|
||
|
||
5. The next question will prompt the user to determine the partitioning on the storage device. Most installs can simply put all data on one partition though.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][9]
|
||
|
||
Install Kali Linux Files in Partition
|
||
|
||
6. The final step with ask the user to confirm all changes to be made to the disk on the host machine. Be aware that continuing will ERASE DATA ON THE DISK.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][8]
|
||
|
||
Confirm Disk Partition Write Changes
|
||
|
||
7. Once confirming the partition changes, the installer will run through the process of installing the files. Once it is completed, the system will want to setup a network mirror to obtain future pieces of software and updates. Be sure to enable this functionality if you wish to use the Kali repositories.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][7]
|
||
|
||
Configure Kali Linux Package Manager
|
||
|
||
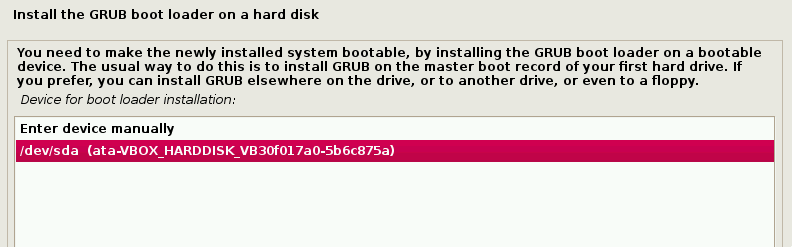
8. After selecting a network mirror, the system will ask to install grub. Again this guide is assuming that Kali is to be the only operating system on this computer.
|
||
|
||
Selecting ‘Yes’ on this screen will allow the user to pick the device to write the necessary boot loader information to the hard drive to boot Kali.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][6]
|
||
|
||
Install GRUB Boot Loader
|
||
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][5]
|
||
|
||
Select Partition to Install GRUB Boot Loader
|
||
|
||
9. Once the installer finishes installing GRUB to the disk, it will alert the user to reboot the machine to boot into the newly installed Kali machine.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][4]
|
||
|
||
Kali Linux Installation Completed
|
||
|
||
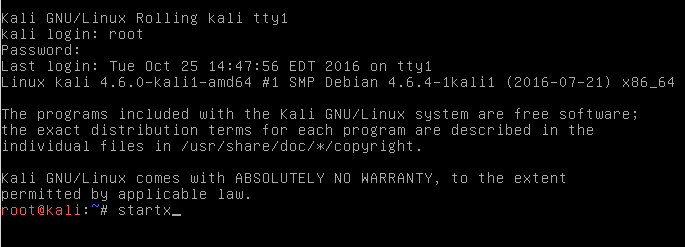
10. Since this guide installed Enlightenment as the Kali desktop environment, it will likely default boot into a shell.
|
||
|
||
In order to launch Enlightenment, log in as the user ‘root‘ with the password created earlier in the installation process.
|
||
|
||
Once logged in all that needs to be issued to start Enlightenment is the command ‘startx‘.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# startx
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][3]
|
||
|
||
Start Enlightenment Desktop in Kali Linux
|
||
|
||
The first time that Enlightenment is run, it will ask the user for some configuration preferences and then launch the Desktop Environment.
|
||
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][2]
|
||
|
||
Kali Linux Enlightenment Desktop
|
||
|
||
At this point, Kali is successfully installed and ready to be used! Upcoming articles will walk through the tools available within Kali and how the can be utilized to test the security posture of hosts and networks. Please feel free to post any comments or questions below.
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/kali-linux-installation-guide/
|
||
|
||
作者:[Rob Turner][a]
|
||
|
||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||
|
||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/robturner/
|
||
[1]:https://www.kali.org/downloads/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Kali-Linux-Enlightenment-Desktop.png
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Start-Enlightenment-Desktop-in-Kali-Linux.png
|
||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Kali-Linux-Installation-Completed.png
|
||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Select-Partition-to-Install-GRUB-Boot-Loader.png
|
||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Install-GRUB-Boot-Loader.png
|
||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Configure-Kali-Linux-Package-Manager.png
|
||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Confirm-Disk-Partition-Write-Changes.png
|
||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Install-Kali-Linux-Files-in-Partition.png
|
||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Select-Kali-Linux-Installation-Disk.png
|
||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Select-Kali-Linux-Installation-Type.png
|
||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Set-Root-User-Password-for-Kali-Linux.png
|
||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Set-Domain-for-Kali-Linux.png
|
||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Set-Hostname-for-Kali-Linux.png
|
||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Kali-Linux-Boot-Menu.png
|
||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Find-USB-Device-Name-in-Linux.png
|
||
[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/
|
||
[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/best-security-centric-linux-distributions-of-2016/
|