mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-04 22:00:34 +08:00
267 lines
9.1 KiB
Markdown
267 lines
9.1 KiB
Markdown
如何用 Nagios 监控通用服务
|
||
================================================================================
|
||
Nagios内置了很多脚本来监控服务。本篇会使用其中一些来检查通用服务如MySql、Apache、DNS等等。
|
||
|
||
为了保证本篇集中在系统监控,我们不会在这里配置主机组或者模板,它们已经在 [前面的教程][1]中覆盖了,它们可以满足需要了。
|
||
|
||
### 在命令行中运行Nagios ###
|
||
|
||
通常建议在添加到Nagios前,先在命令行中运行Nagios服务检测脚本。它会给出执行是否成功以及脚本的输出将会看上去的样子。
|
||
|
||
这些脚本存储在 /etc/nagios-plugins/config/ ,可执行文件在 /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/。
|
||
|
||
下面就是该怎么做
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# cd /etc/nagios-plugins/config/
|
||
|
||
提供的脚本包含了语法帮助。示例包含了部分输出。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# cat /etc/nagios-plugins/config/tcp_udp.cfg
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
# 'check_tcp' command definition
|
||
define command{
|
||
command_name check_tcp
|
||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_tcp -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -p '$ARG1$'
|
||
|
||
了解了语法,TCP 80端口可以用下面的方法检查。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_tcp -H 10.10.10.1 -p 80
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
TCP OK - 0.000 second response time on port 80|time=0.000222s;;;0.000000;10.000000
|
||
|
||
### 示例拓扑 ###
|
||
|
||
本片中使用下面三台服务器。每台服务器运行多个通用服务。Nagios服务器现在运行的是Ubuntu。
|
||
|
||
- Server 1 (10.10.10.1) : MySQL, Apache2
|
||
- Server 2 (10.10.10.2) : Postfix, Apache2
|
||
- Server 3 (10.10.10.3) : DNS
|
||
|
||
首先,这些服务器被定义在了Nagios中。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/example.cfg
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
define host{
|
||
use generic-host
|
||
host_name test-server-1
|
||
alias test-server-1
|
||
address 10.10.10.1
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
define host{
|
||
use generic-host
|
||
host_name test-server-2
|
||
alias test-server-2
|
||
address 10.10.10.2
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
define host{
|
||
use generic-host
|
||
host_name test-server-3
|
||
alias test-server-3
|
||
address 10.10.10.3
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
### 监控MySQL服务 ###
|
||
|
||
#### MySQL 监控需要 ####
|
||
|
||
- 通过检查3306端口来检测MySQL是否运行中。
|
||
- 检测特定的数据库'testDB'是否可用。
|
||
|
||
#### MySQL 服务器设置 ####
|
||
|
||
开始检测MySQL时,需要记住MySQL默认只监听回环接口127.0.0.1。这增加了数据库的安全。手动调节需要告诉MySQL该监听什么其他接口。下面是该怎么做。
|
||
|
||
这个设置要在所有的MySQL服务器上完成。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# vim /etc/mysql/my.cnf
|
||
|
||
下面这行被注释掉以监听所有网络接口。
|
||
|
||
#bind-address = 127.0.0.1
|
||
|
||
同样,MySQL也不会让任意主机来连接它。需要为localhost和“任意”主机创建MySQL用户‘nagios’,接着在所有的数据库中为这个用户授予ALL权限,会这将在会用在监控中。
|
||
|
||
下面的设置对所有的MySQL服务器都已经设置。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# mysql -u root –p
|
||
## MySQL root 密码 ##
|
||
|
||
在MySQL服务器中创建'nagios@localhost'用户。
|
||
|
||
mysql> CREATE USER 'nagios'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'nagios-pass';
|
||
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'nagios'@'localhost';
|
||
|
||
创建'nagios@任意主机'用户。(LCTT 译注:实际上这两个是同一个用户,只是分别授权给localhost和任意主机的访问;因为它们所用的密码的同一个,修改任何一个,另外一个也相应变化。)
|
||
|
||
mysql> CREATE USER 'nagios'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'nagios-pass';
|
||
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'nagios'@'%';
|
||
|
||
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||
|
||
这使MySQL监听所有的网络接口,同样接受来自用户'nagios'的进入连接。
|
||
|
||
请注意,这种修改可能有安全隐患,所以需要提示几点:
|
||
|
||
- 这个设置将会暴露MySQL给所有的接口,包括外网。确保只有合法的网络访问是非常重要的。应该使用防火墙和TCP wrapper等过滤器。
|
||
- MySQL用户‘nagios’的密码应该非常强。如果只有几台Nagios服务器,那么应该创建'nagios@服务器名'用户而不是任意用户的'nagios@%'。
|
||
|
||
#### 对MySQL的Nagios配置 ####
|
||
|
||
按如下配置来做一些调整。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/services_nagios2.cfg
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
define service{
|
||
use generic-service
|
||
host_name test-server-1
|
||
;hostgroup can be used instead as well
|
||
|
||
service_description Check MYSQL via TCP port
|
||
check_command check_tcp!3306
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
define service{
|
||
use generic-service
|
||
host_name test-server-1
|
||
;hostgroup can be used instead as well
|
||
|
||
service_description Check availability of database 'testDB'
|
||
check_command check_mysql_database!nagios!nagios-pass!testDB
|
||
;check_mysql!userName!userPassword!databaseName
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
这样,Nagios就可以同时监控MySQL服务器及其数据库的可用性。
|
||
|
||
### 监控Apache服务器 ###
|
||
|
||
Nagios同样也可以监控Apache服务。
|
||
|
||
#### Apache监控需要 ####
|
||
|
||
- 监控apache服务是否可用
|
||
|
||
这个任务非常简单因为Nagios有一个内置命令。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/services_nagios2.cfg
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
define service{
|
||
use generic-service
|
||
host_name test-server-1, test-server-2
|
||
service_description Check Apache Web Server
|
||
check_command check_http
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
现在就非常简单了。
|
||
|
||
### 监控DNS服务 ###
|
||
|
||
Nagios通过向DNS服务器查询一个完全限定域名(FQDN),或者使用dig工具来查询。默认用于查询的FQDN的是www.google.com,但是这个可以按需改变。按照下面的文件修改来完成这个任务。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# vim /etc/nagios-plugins/config/dns.cfg
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
## The -H portion can be modified to replace Google ##
|
||
define command{
|
||
command_name check_dns
|
||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_dns -H www.google.com -s '$HOSTADDRESS$'
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
编辑下面的行。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/services_nagios2.cfg
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
## Nagios asks server-3 to resolve the IP for google.com ##
|
||
define service{
|
||
use generic-service
|
||
host_name test-server-3
|
||
service_description Check DNS
|
||
check_command check_dns
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
## Nagios asks server-3 to dig google.com ##
|
||
define service{
|
||
use generic-service
|
||
host_name test-server-3
|
||
service_description Check DNS via dig
|
||
check_command check_dig!www.google.com
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
### 监控邮件服务器 ###
|
||
|
||
Nagios可以监控不同的邮件服务组件如SMTP、POP、IMAP和mailq。之前提过,server-2设置了Postfix邮件服务。Nagios将被配置来监控SMTP和邮件队列。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/services_nagios2.cfg
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
define service{
|
||
use generic-service
|
||
host_name test-server-2
|
||
service_description Check SMTP
|
||
check_command check_smtp
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
define service{
|
||
use generic-service
|
||
host_name test-server-2
|
||
service_description Check Mail Queue
|
||
check_command check_mailq_postfix!50!100
|
||
;warning at 50, critical at 100
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
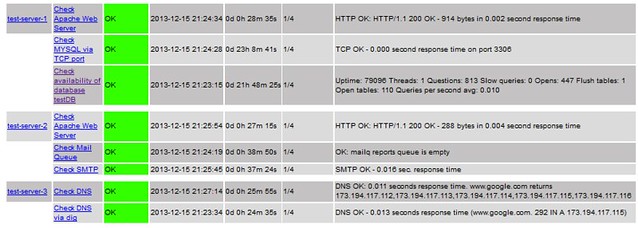
下面的截屏显示了目前配置监控服务的概览。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 基于端口自定义监控程序 ###
|
||
|
||
让我们假设如下定制程序同样运行在网络中,监听着一个特定的端口。
|
||
|
||
- 测试1号服务器:定制程序(TCP端口 12345)
|
||
|
||
做一些小的调整,Nagios也可以帮助我们监控这个程序。
|
||
|
||
root@nagios:~# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/services_nagios2.cfg
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
define service{
|
||
use generic-service
|
||
host_name test-server-1
|
||
service_description Check server 1 custom application
|
||
check_command check_tcp!12345
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
在结束之前的提示,Nagios可以监控网络很多其他的方面。存储在/etc/nagios-plugins/config/中的脚本为Nagios提供了很棒的能力。
|
||
|
||
一些Nagios提供的脚本被仅限于本地服务器,比如,服务器负载、进程并发数量、登录用户数量等。这些检查可以提供Nagios服务器内有用的信息。
|
||
|
||
希望这篇文章对你有用。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://xmodulo.com/monitor-common-services-nagios.html
|
||
|
||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-2436-1.html |