10 KiB
Restrict SSH User Access to Certain Directory Using Chrooted Jail
There are several reasons to restrict a SSH user session to a particular directory, especially on web servers, but the obvious one is a system security. In order to lock SSH users in a certain directory, we can use chroot mechanism.
change root (chroot) in Unix-like systems such as Linux, is a means of separating specific user operations from the rest of the Linux system; changes the apparent root directory for the current running user process and its child process with new root directory called a chrooted jail.
In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to restrict a SSH user access to a given directory in Linux. Note that we’ll run the all the commands as root, use the sudo command if you are logged into server as a normal user.
Step 1: Create SSH Chroot Jail
1. Start by creating the chroot jail using the mkdir command below:
# mkdir -p /home/test
2. Next, identify required files, according to the sshd_config man page, the ChrootDirectory option specifies the pathname of the directory to chroot to after authentication. The directory must contain the necessary files and directories to support a user’s session.
For an interactive session, this requires at least a shell, commonly sh, and basic /dev nodes such as null, zero, stdin, stdout, stderr, and tty devices:
# ls -l /dev/{null,zero,stdin,stdout,stderr,random,tty}
Listing Required Files
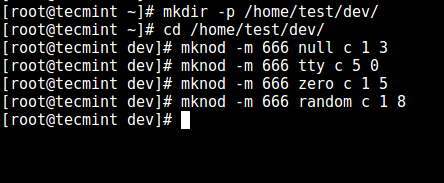
3. Now, create the /dev files as follows using the mknod command. In the command below, the -m flag is used to specify the file permissions bits, c means character file and the two numbers are major and minor numbers that the files point to.
# mkdir -p /home/test/dev/
# cd /home/test/dev/
# mknod -m 666 null c 1 3
# mknod -m 666 tty c 5 0
# mknod -m 666 zero c 1 5
# mknod -m 666 random c 1 8
Create /dev and Required Files
4. Afterwards, set the appropriate permission on the chroot jail. Note that the chroot jail and its subdirectories and subfiles must be owned by root user, and not writable by any normal user or group:
# chown root:root /home/test
# chmod 0755 /home/test
# ls -ld /home/test
Set Permissions on Directory
Step 2: Setup Interactive Shell for SSH Chroot Jail
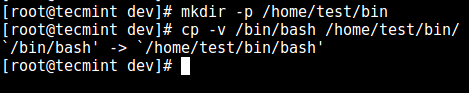
5. First, create the bin directory and then copy the /bin/bash files into the bin directory as follows:
# mkdir -p /home/test/bin
# cp -v /bin/bash /home/test/bin/
Copy Files to bin Directory
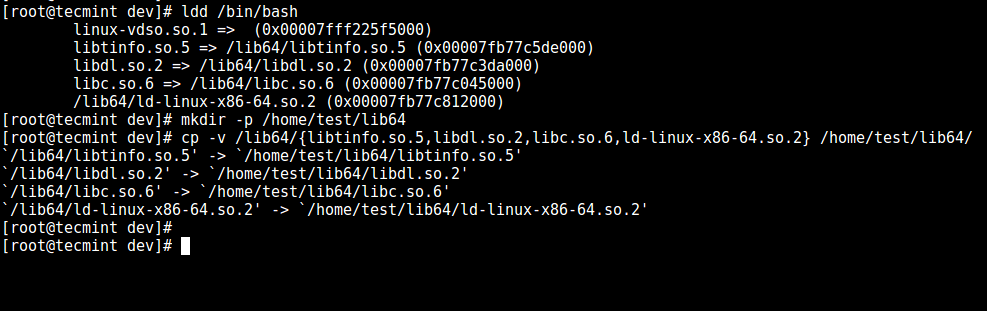
6. Now, identify bash required shared libs, as below and copy them into the lib directory:
# ldd /bin/bash
# mkdir -p /home/test/lib64
# cp -v /lib64/{libtinfo.so.5,libdl.so.2,libc.so.6,ld-linux-x86-64.so.2} /home/test/lib64/
Copy Shared Library Files
Step 3: Create and Configure SSH User
7. Now, create the SSH user with the useradd command and set a secure password for the user:
# useradd tecmint
# passwd tecmint
8. Create the chroot jail general configurations directory, /home/test/etc and copy the updated account files (/etc/passwd and /etc/group) into this directory as follows:
# mkdir /home/test/etc
# cp -vf /etc/{passwd,group} /home/test/etc/
Copy Password Files
Note: Each time you add more SSH users to the system, you will need to copy the updated account files into the /home/test/etc directory.
Step 4: Configure SSH to Use Chroot Jail
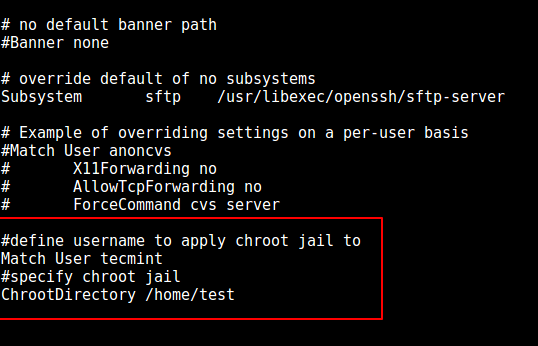
9. Now, open the sshd_config file.
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
and add/modify the lines below in the file.
#define username to apply chroot jail to
Match User tecmint
#specify chroot jail
ChrootDirectory /home/test
Configure SSH Chroot Jail
Save the file and exit, and restart the SSHD services:
# systemctl restart sshd
OR
# service sshd restart
Step 5: Testing SSH with Chroot Jail
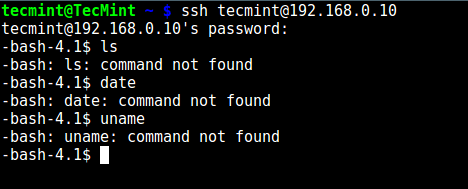
10. At this point, test if the chroot jail setup is working as expected:
# ssh tecmint@192.168.0.10
-bash-4.1$ ls
-bash-4.1$ date
-bash-4.1$ uname
Testing SSH User Chroot Jail
From the screenshot above, we can see that the SSH user is locked in the chrooted jail, and can’t run any external commands (ls, date, uname etc).
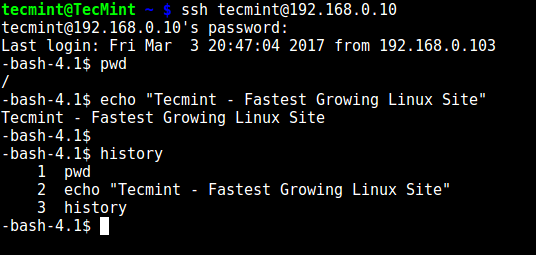
The user can only execute bash and its builtin commands such as(pwd, history, echo etc) as seen below:
# ssh tecmint@192.168.0.10
-bash-4.1$ pwd
-bash-4.1$ echo "Tecmint - Fastest Growing Linux Site"
-bash-4.1$ history
SSH Built-in Commands
Step 6. Create SSH User’s Home Directory and Add Linux Commands
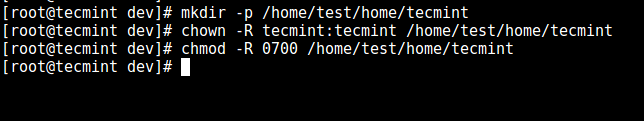
11. From the previous step, we can notice that the user is locked in the root directory, we can create a home directory for the the SSH user like so (do this for all future users):
# mkdir -p /home/test/home/tecmint
# chown -R tecmint:tecmint /home/test/home/tecmint
# chmod -R 0700 /home/test/home/tecmint
Create SSH User Home Directory
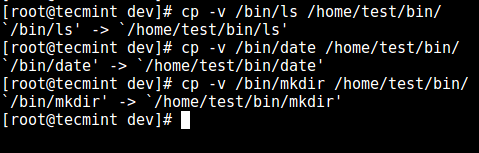
12. Next, install a few user commands such as ls, date, mkdir in the bin directory:
# cp -v /bin/ls /home/test/bin/
# cp -v /bin/date /home/test/bin/
# cp -v /bin/mkdir /home/test/bin/
Add Commands to SSH User
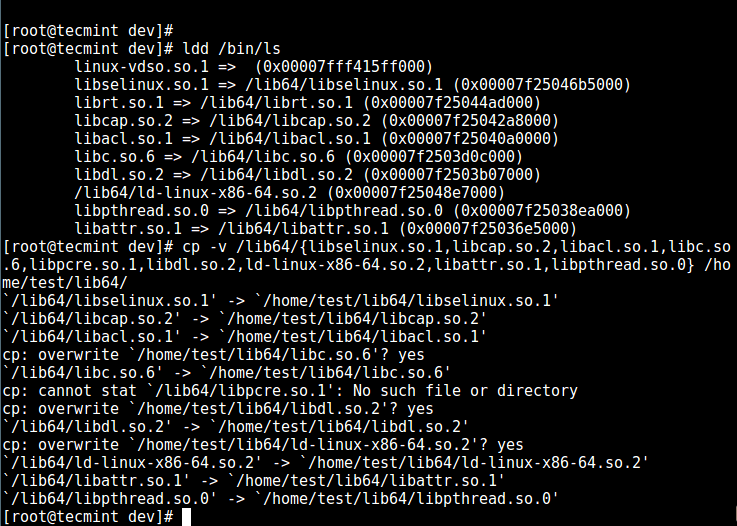
13. Next, check the shared libraries for the commands above and move them into the chrooted jail libraries directory:
# ldd /bin/ls
# cp -v /lib64/{libselinux.so.1,libcap.so.2,libacl.so.1,libc.so.6,libpcre.so.1,libdl.so.2,ld-linux-x86-64.so.2,libattr.so.1,libpthread.so.0} /home/test/lib64/
Copy Shared Libraries
Step 7. Testing SFTP with Chroot Jail
14. Do a final test using sftp; check if the commands you have just installed are working.
Add the line below in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file:
#Enable sftp to chrooted jail
ForceCommand internal-sftp
Save the file and exit. Then restart the SSHD services:
# systemctl restart sshd
OR
# service sshd restart
15. Now, test using SSH, you’ll get the following error:
# ssh tecmint@192.168.0.10
Test SSH Chroot Jail
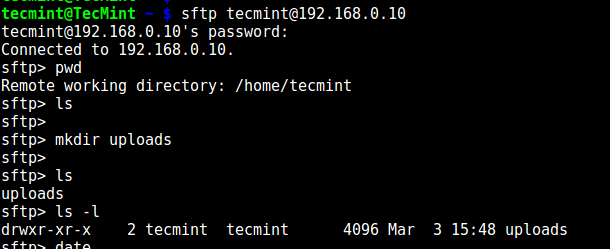
Try using SFTP as follows:
# sftp tecmint@192.168.0.10
Testing sFTP SSH User
Suggested Read: Restrict SFTP Users to Home Directories Using chroot Jail
That’s it for now!. In this article, we showed you how to restrict a SSH user in a given directory (chrooted jail) in Linux. Use the comment section below to offer us your thoughts about this guide.
作者简介:
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
via: http://www.tecmint.com/restrict-ssh-user-to-directory-using-chrooted-jail/
作者:Aaron Kili 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID