9.2 KiB
Translating by filefi
How to Install and Use Wireshark on Debian 9 / Ubuntu 16.04 / 17.10
by Pradeep Kumar · Published November 29, 2017 · Updated November 29, 2017
Wireshark is free and open source, cross platform, GUI based Network packet analyzer that is available for Linux, Windows, MacOS, Solaris etc. It captures network packets in real time & presents them in human readable format. Wireshark allows us to monitor the network packets up to microscopic level. Wireshark also has a command line utility called ‘tshark‘ that performs the same functions as Wireshark but through terminal & not through GUI.
Wireshark can be used for network troubleshooting, analyzing, software & communication protocol development & also for education purposed. Wireshark uses a library called ‘pcap‘ for capturing the network packets.
Wireshark comes with a lot of features & some those features are;
-
Support for a hundreds of protocols for inspection,
-
Ability to capture packets in real time & save them for later offline analysis,
-
A number of filters to analyzing data,
-
Data captured can be compressed & uncompressed on the fly,
-
Various file formats for data analysis supported, output can also be saved to XML, CSV, plain text formats,
-
data can be captured from a number of interfaces like ethernet, wifi, bluetooth, USB, Frame relay , token rings etc.
In this article, we will discuss how to install Wireshark on Ubuntu/Debain machines & will also learn to use Wireshark for capturing network packets.
Installation of Wireshark on Ubuntu 16.04 / 17.10
Wireshark is available with default Ubuntu repositories & can be simply installed using the following command. But there might be chances that you will not get the latest version of wireshark.
linuxtechi@nixworld:~$ sudo apt-get update
linuxtechi@nixworld:~$ sudo apt-get install wireshark -y
So to install latest version of wireshark we have to enable or configure official wireshark repository.
Use the beneath commands one after the another to configure repository and to install latest version of Wireshark utility
linuxtechi@nixworld:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:wireshark-dev/stable
linuxtechi@nixworld:~$ sudo apt-get update
linuxtechi@nixworld:~$ sudo apt-get install wireshark -y
Once the Wireshark is installed execute the below command so that non-root users can capture live packets of interfaces,
linuxtechi@nixworld:~$ sudo setcap 'CAP_NET_RAW+eip CAP_NET_ADMIN+eip' /usr/bin/dumpcap
Installation of Wireshark on Debian 9
Wireshark package and its dependencies are already present in the default debian 9 repositories, so to install latest and stable version of Wireshark on Debian 9, use the following command:
linuxtechi@nixhome:~$ sudo apt-get update
linuxtechi@nixhome:~$ sudo apt-get install wireshark -y
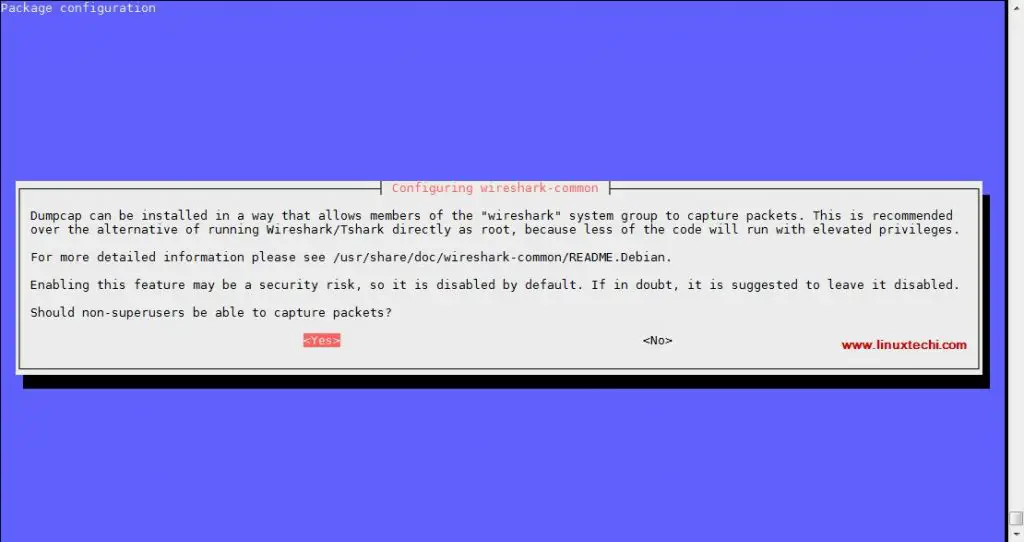
During the installation, it will prompt us to configure dumpcap for non-superusers,
Select ‘yes’ and then hit enter.
Once the Installation is completed, execute the below command so that non-root users can also capture the live packets of the interfaces.
linuxtechi@nixhome:~$ sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/dumpcap
We can also use the latest source package to install the wireshark on Ubuntu/Debain & many other Linux distributions.
Installing Wireshark using source code on Debian / Ubuntu Systems
Firstly download the latest source package (which is 2.4.2 at the time for writing this article), use the following command,
linuxtechi@nixhome:~$ wget https://1.as.dl.wireshark.org/src/wireshark-2.4.2.tar.xz
Next extract the package & enter into the extracted directory,
linuxtechi@nixhome:~$ tar -xf wireshark-2.4.2.tar.xz -C /tmp
linuxtechi@nixhome:~$ cd /tmp/wireshark-2.4.2
Now we will compile the code with the following commands,
linuxtechi@nixhome:/tmp/wireshark-2.4.2$ ./configure --enable-setcap-install
linuxtechi@nixhome:/tmp/wireshark-2.4.2$ make
Lastly install the compiled packages to install Wireshark on the system,
linuxtechi@nixhome:/tmp/wireshark-2.4.2$ sudo make install
linuxtechi@nixhome:/tmp/wireshark-2.4.2$ sudo ldconfig
Upon installation a separate group for Wireshark will also be created, we will now add our user to the group so that it can work with wireshark otherwise you might get ‘permission denied‘ error when starting wireshark.
To add the user to the wireshark group, execute the following command,
linuxtechi@nixhome:~$ sudo usermod -a -G wireshark linuxtechi
Now we can start wireshark either from GUI Menu or from terminal with this command,
linuxtechi@nixhome:~$ wireshark
Access Wireshark on Debian 9 System
Click on Wireshark icon
Access Wireshark on Ubuntu 16.04 / 17.10
Click on Wireshark icon
Capturing and Analyzing packets
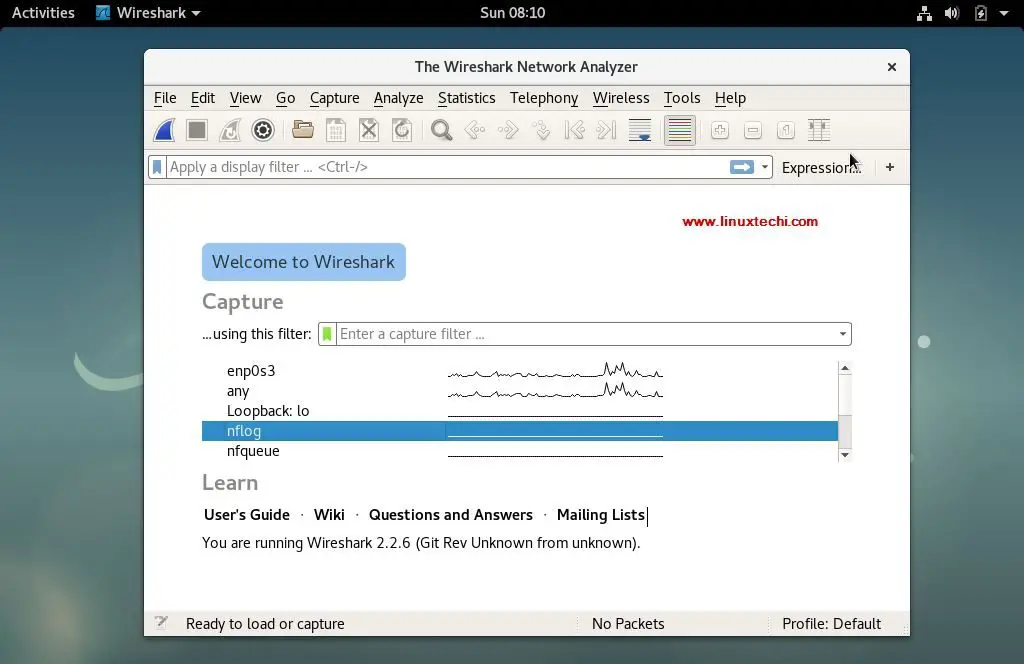
Once the wireshark has been started, we should be presented with the wireshark window, example is shown above for Ubuntu and Debian system.
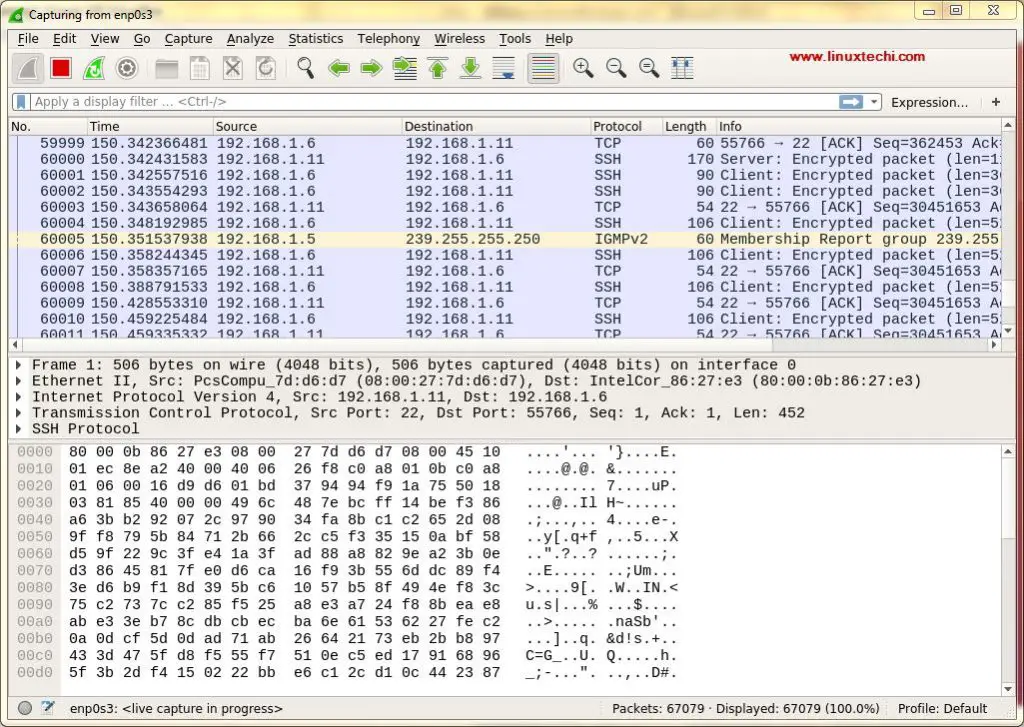
All these are the interfaces from where we can capture the network packets. Based on the interfaces you have on your system, this screen might be different for you.
We are selecting ‘enp0s3’ for capturing the network traffic for that inteface. After selecting the inteface, network packets for all the devices on our network start to populate (refer to screenshot below)
First time we see this screen we might get overwhelmed by the data that is presented in this screen & might have thought how to sort out this data but worry not, one the best features of Wireshark is its filters.
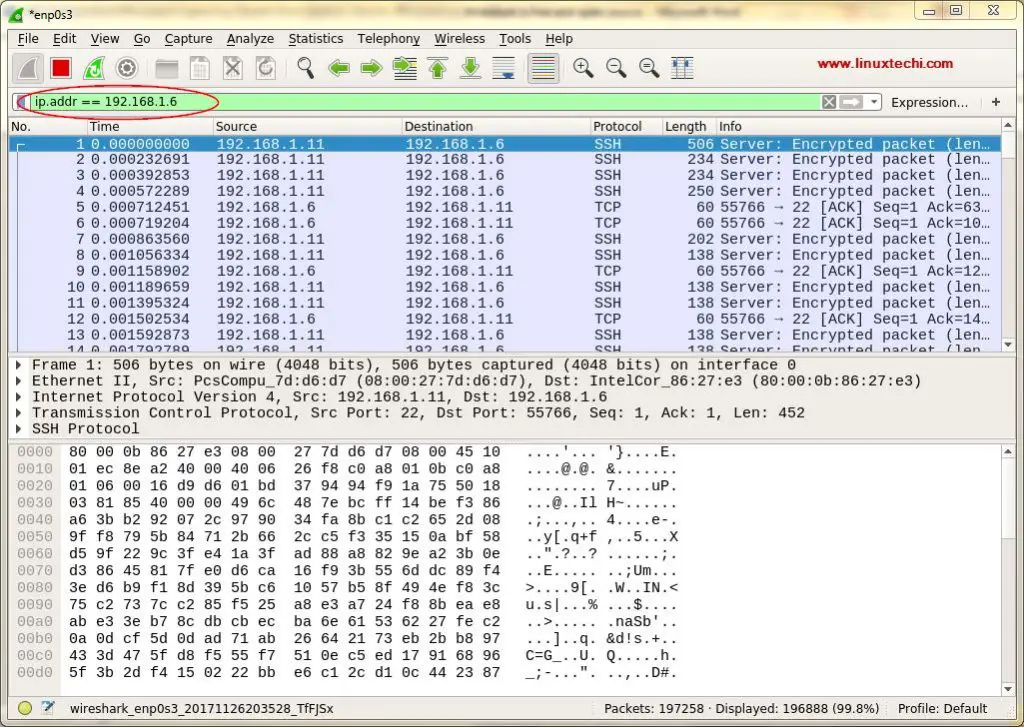
We can sort/filter out the data based on IP address, Port number, can also used source & destination filters, packet size etc & can also combine 2 or more filters together to create more comprehensive searches. We can either write our filters in ‘Apply a Display Filter‘ tab , or we can also select one of already created rules. To select pre-built filter, click on ‘flag‘ icon , next to ‘Apply a Display Filter‘ tab,
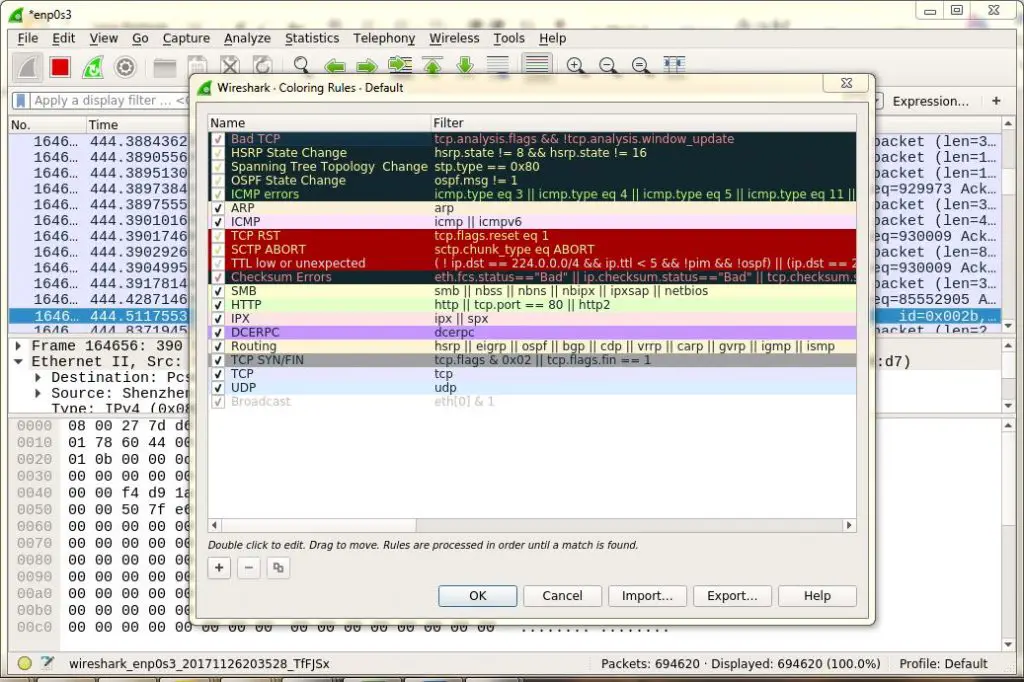
We can also filter data based on the color coding, By default, light purple is TCP traffic, light blue is UDP traffic, and black identifies packets with errors , to see what these codes mean, click View -> Coloring Rules, also we can change these codes.
After we have the results that we need, we can then click on any of the captured packets to get more details about that packet, this will show all the data about that network packet.
Wireshark is an extremely powerful tool takes some time to getting used to & make a command over it, this tutorial will help you get started. Please feel free to drop in your queries or suggestions in the comment box below.
via: https://www.linuxtechi.com
作者:Pradeep Kumar 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID