mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
146 lines
4.4 KiB
Markdown
146 lines
4.4 KiB
Markdown
在 Linux/UNIX 终端下使用 nload 实时监控网络流量和带宽使用
|
||
=================================================================================
|
||
如果你想在命令行界面监控网络吞吐量,nload 应用程序是个不错的选择。它是一个实时监控网络流量和带宽使用的控制台应用程序,使用两个图表可视化地展示接收和发送的流量,并提供诸如数据交换总量、最小/最大网络带宽使用量等附加信息。
|
||
|
||
###安装###
|
||
|
||
#### 在 CentOS/RHEL/Red Hat/Fedora Linux 上安装 nload ####
|
||
|
||
首先在 CentOS 或者基于 RHEL 的操作系统上[启用 EPEL 仓库][1],然后键入 [yum 命令][2]安装 nload:
|
||
|
||
# yum install nload
|
||
|
||
#### 在 Debian 或者 Ubuntu Linux 上安装 nload ####
|
||
|
||
键入 [apt-get 命令][3]:
|
||
|
||
$ sudo apt-get install nload
|
||
|
||
#### 在 FreeBSD 操作系统上安装 nload ####
|
||
|
||
通过 port 安装 nload,键入:
|
||
|
||
# cd /usr/ports/net/nload/ && make install clean
|
||
|
||
或者添加包
|
||
|
||
# pkg install net/nload
|
||
|
||
#### 在 OpenBSD 操作系统上安装 nload ####
|
||
|
||
键入下列命令:
|
||
|
||
$ sudo pkg_add -i nload
|
||
|
||
#### 在类 Unix 操作系统上从源代码安装 nload ####
|
||
|
||
首先,使用 wget 或者 curl 命令获取源代码:
|
||
|
||
$ cd /tmp
|
||
$ wget http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||
|
||
[使用 tar 命令解压缩名为 nload-0.7.4.tar.gz 的 tar 包][4],键入:
|
||
|
||
$ tar xvf nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||
|
||
使用 cd 命令进入 nload 源代码所在目录:
|
||
|
||
$ cd nload*
|
||
|
||
然后键入 ./configure 为你的操作系统配置安装包:
|
||
|
||
$ sh ./configure
|
||
|
||
或者
|
||
|
||
$ ./configure
|
||
|
||
运行 configure 命令需要一点时间。完成后,使用 make 命令编译 nload:
|
||
|
||
$ make
|
||
|
||
最后,键入 make install 命令以 root 用户身份安装 nload 应用程序和相关文件:
|
||
|
||
$ sudo make install
|
||
|
||
或者
|
||
|
||
# make install
|
||
|
||
### 使用 ###
|
||
|
||
如何使用 nload 显示当前网络使用量呢?
|
||
|
||
基本语法是:
|
||
|
||
nload
|
||
nload device
|
||
nload [options] device1 device2
|
||
|
||
键入下列命令:
|
||
|
||
$ nload
|
||
$ nload eth0
|
||
$ nload em0 em2
|
||
|
||
会得到输出:
|
||
|
||
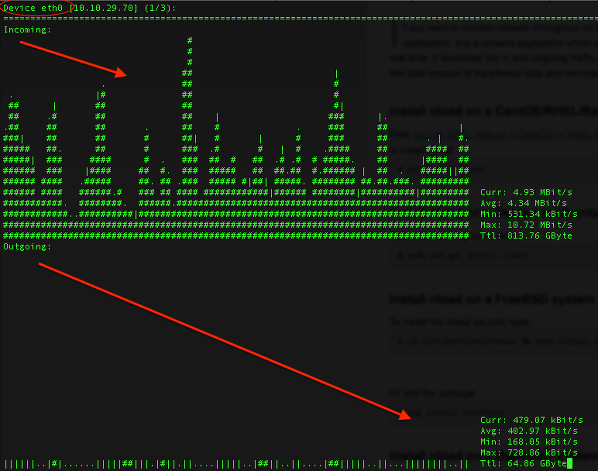
|
||
|
||
*图01: 使用 nload 命令*
|
||
|
||
#### 操控 nload 应用程序 ####
|
||
|
||
nload 命令一旦执行就会开始监控网络设备,你可以使用下列快捷键操控 nload 应用程序。
|
||
|
||
1. 你可以按键盘上的 ← → 或者 Enter/Tab 键在设备间切换。
|
||
2. 按 F2 显示选项窗口。
|
||
3. 按 F5 将当前设置保存到用户配置文件。
|
||
4. 按 F6 从配置文件重新加载设置。
|
||
5. 按 q 或者 Ctrl+C 退出 nload。
|
||
|
||
#### 设置显示刷新间隔 ####
|
||
|
||
默认每 100 毫秒刷新一次显示数值,下面的例子将时间间隔设置成 500 毫秒:
|
||
|
||
$ nload -t {interval_number_in_millisec}
|
||
$ nload -t 500
|
||
|
||
输出:
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
GIF 动画 01 - 使用 nload 命令
|
||
|
||
#### 设置流量数值显示的单位 ####
|
||
|
||
语法如下:
|
||
|
||
$ nload -u h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
||
$ nload -U h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
||
$ nload -u h
|
||
$ nload -u G
|
||
$ nload -U G
|
||
|
||
释义:
|
||
|
||
- 小写选项 -u: h 意为自动格式化为人类易读的单位,b 意为 Bit/s,k 意为 kBit/s,m 意为 MBit/s,g 意为 GBit/s。大写字母意为使用 Byte 替代 Bit。默认为 k。
|
||
- 大写选项 -U 与小写选项 -u 非常相似,不同之处在于它展示的是数据量,比如 Bit, kByte, GBit 等等。(没有 "/s")。默认值是 M。
|
||
|
||
### 结论 ###
|
||
|
||
我觉得 nload 是一个稳定可靠的应用程序,如果你喜欢 nload,你可能也想试试 Linux 和其他类 Unix 操作系统环境下的 vnstat 与 iftop 工具。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
译自: http://www.cyberciti.biz/networking/nload-linux-command-to-monitor-network-traffic-bandwidth-usage/
|
||
|
||
译者:[blueabysm](https://github.com/blueabysm) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-sl-centos-redhat6-enable-epel-repo/
|
||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-centos-fedora-linux-yum-command-howto/
|
||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-debian-package-management-cheat-sheet.html
|
||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/tar-extract-linux/
|