mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-10 22:21:11 +08:00
320 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
320 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
LFCS 第十讲:学习简单的 Shell 脚本编程和文件系统故障排除
|
||
|
||
================================================================================
|
||
Linux 基金会发起了 LFCS 认证 (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin, Linux 基金会认证系统管理员),这是一个全新的认证体系,主要目标是让全世界任何人都有机会考取认证。认证内容为 Linux 中间系统的管理,主要包括:系统运行和服务的维护、全面监控和分析的能力以及问题来临时何时想上游团队请求帮助的决策能力
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
LFCS 系列第十讲
|
||
|
||
请看以下视频,这里边介绍了 Linux 基金会认证程序。
|
||
|
||
注:youtube 视频
|
||
|
||
<video src="https://dn-linuxcn.qbox.me/static%2Fvideo%2FIntroducing%20The%20Linux%20Foundation%20Certification%20Program-Y29qZ71Kicg.mp4" controls="controls" width="100%">
|
||
</video>
|
||
|
||
本讲是系列教程中的第十讲,主要集中讲解简单的 Shell 脚本编程和文件系统故障排除。这两块内容都是 LFCS 认证中的必备考点。
|
||
|
||
### 理解终端 (Terminals) 和 Shell ###
|
||
|
||
首先要声明一些概念。
|
||
|
||
- Shell 是一个程序,它将命令传递给操作系统来执行。
|
||
- Terminal 也是一个程序,作为最终用户,我们需要使用它与 Shell 来交互。比如,下边的图片是 GNOME Terminal。
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
Gnome Terminal
|
||
|
||
启动 Shell 之后,会呈现一个命令提示符 (也称为命令行) 提示我们 Shell 已经做好了准备,接受标准输入设备输入的命令,这个标准输入设备通常是键盘。
|
||
|
||
你可以参考该系列文章的 [第一讲 使用命令创建、编辑和操作文件][1] 来温习一些常用的命令。
|
||
|
||
Linux 为提供了许多可以选用的 Shell,下面列出一些常用的:
|
||
|
||
**bash Shell**
|
||
|
||
Bash 代表 Bourne Again Shell,它是 GNU 项目默认的 Shell。它借鉴了 Korn shell (ksh) 和 C shell (csh) 中有用的特性,并同时对性能进行了提升。它同时也是 LFCS 认证中所涵盖的风发行版中默认 Shell,也是本系列教程将使用的 Shell。
|
||
|
||
**sh Shell**
|
||
|
||
Bash Shell 是一个比较古老的 shell,一次多年来都是多数类 Unix 系统的默认 shell。
|
||
|
||
**ksh Shell**
|
||
|
||
Korn SHell (ksh shell) 也是一个 Unix shell,是贝尔实验室 (Bell Labs) 的 David Korn 在 19 世纪 80 年代初的时候开发的。它兼容 Bourne shell ,并同时包含了 C shell 中的多数特性。
|
||
|
||
|
||
一个 shell 脚本仅仅只是一个可执行的文本文件,里边包含一条条可执行命令。
|
||
|
||
### 简单的 Shell 脚本编程 ###
|
||
|
||
As mentioned earlier, a shell script is born as a plain text file. Thus, can be created and edited using our preferred text editor. You may want to consider using vi/m (refer to [Usage of vi Editor – Part 2][2] of this series), which features syntax highlighting for your convenience.
|
||
|
||
Type the following command to create a file named myscript.sh and press Enter.
|
||
|
||
# vim myscript.sh
|
||
|
||
The very first line of a shell script must be as follows (also known as a shebang).
|
||
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
|
||
It “tells” the operating system the name of the interpreter that should be used to run the text that follows.
|
||
|
||
Now it’s time to add our commands. We can clarify the purpose of each command, or the entire script, by adding comments as well. Note that the shell ignores those lines beginning with a pound sign # (explanatory comments).
|
||
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
echo This is Part 10 of the 10-article series about the LFCS certification
|
||
echo Today is $(date +%Y-%m-%d)
|
||
|
||
Once the script has been written and saved, we need to make it executable.
|
||
|
||
# chmod 755 myscript.sh
|
||
|
||
Before running our script, we need to say a few words about the $PATH environment variable. If we run,
|
||
|
||
echo $PATH
|
||
|
||
from the command line, we will see the contents of $PATH: a colon-separated list of directories that are searched when we enter the name of a executable program. It is called an environment variable because it is part of the shell environment – a set of information that becomes available for the shell and its child processes when the shell is first started.
|
||
|
||
When we type a command and press Enter, the shell searches in all the directories listed in the $PATH variable and executes the first instance that is found. Let’s see an example,
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
Environment Variables
|
||
|
||
If there are two executable files with the same name, one in /usr/local/bin and another in /usr/bin, the one in the first directory will be executed first, whereas the other will be disregarded.
|
||
|
||
If we haven’t saved our script inside one of the directories listed in the $PATH variable, we need to append ./ to the file name in order to execute it. Otherwise, we can run it just as we would do with a regular command.
|
||
|
||
# pwd
|
||
# ./myscript.sh
|
||
# cp myscript.sh ../bin
|
||
# cd ../bin
|
||
# pwd
|
||
# myscript.sh
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
Execute Script
|
||
|
||
#### Conditionals ####
|
||
|
||
Whenever you need to specify different courses of action to be taken in a shell script, as result of the success or failure of a command, you will use the if construct to define such conditions. Its basic syntax is:
|
||
|
||
if CONDITION; then
|
||
COMMANDS;
|
||
else
|
||
OTHER-COMMANDS
|
||
fi
|
||
|
||
Where CONDITION can be one of the following (only the most frequent conditions are cited here) and evaluates to true when:
|
||
|
||
- [ -a file ] → file exists.
|
||
- [ -d file ] → file exists and is a directory.
|
||
- [ -f file ] →file exists and is a regular file.
|
||
- [ -u file ] →file exists and its SUID (set user ID) bit is set.
|
||
- [ -g file ] →file exists and its SGID bit is set.
|
||
- [ -k file ] →file exists and its sticky bit is set.
|
||
- [ -r file ] →file exists and is readable.
|
||
- [ -s file ]→ file exists and is not empty.
|
||
- [ -w file ]→file exists and is writable.
|
||
- [ -x file ] is true if file exists and is executable.
|
||
- [ string1 = string2 ] → the strings are equal.
|
||
- [ string1 != string2 ] →the strings are not equal.
|
||
|
||
[ int1 op int2 ] should be part of the preceding list, while the items that follow (for example, -eq –> is true if int1 is equal to int2.) should be a “children” list of [ int1 op int2 ] where op is one of the following comparison operators.
|
||
|
||
- -eq –> is true if int1 is equal to int2.
|
||
- -ne –> true if int1 is not equal to int2.
|
||
- -lt –> true if int1 is less than int2.
|
||
- -le –> true if int1 is less than or equal to int2.
|
||
- -gt –> true if int1 is greater than int2.
|
||
- -ge –> true if int1 is greater than or equal to int2.
|
||
|
||
#### For Loops ####
|
||
|
||
This loop allows to execute one or more commands for each value in a list of values. Its basic syntax is:
|
||
|
||
for item in SEQUENCE; do
|
||
COMMANDS;
|
||
done
|
||
|
||
Where item is a generic variable that represents each value in SEQUENCE during each iteration.
|
||
|
||
#### While Loops ####
|
||
|
||
This loop allows to execute a series of repetitive commands as long as the control command executes with an exit status equal to zero (successfully). Its basic syntax is:
|
||
|
||
while EVALUATION_COMMAND; do
|
||
EXECUTE_COMMANDS;
|
||
done
|
||
|
||
Where EVALUATION_COMMAND can be any command(s) that can exit with a success (0) or failure (other than 0) status, and EXECUTE_COMMANDS can be any program, script or shell construct, including other nested loops.
|
||
|
||
#### Putting It All Together ####
|
||
|
||
We will demonstrate the use of the if construct and the for loop with the following example.
|
||
|
||
**Determining if a service is running in a systemd-based distro**
|
||
|
||
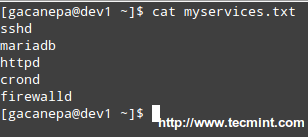
Let’s create a file with a list of services that we want to monitor at a glance.
|
||
|
||
# cat myservices.txt
|
||
|
||
sshd
|
||
mariadb
|
||
httpd
|
||
crond
|
||
firewalld
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
Script to Monitor Linux Services
|
||
|
||
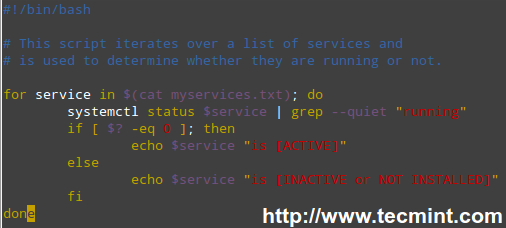
Our shell script should look like.
|
||
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
|
||
# This script iterates over a list of services and
|
||
# is used to determine whether they are running or not.
|
||
|
||
for service in $(cat myservices.txt); do
|
||
systemctl status $service | grep --quiet "running"
|
||
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
|
||
echo $service "is [ACTIVE]"
|
||
else
|
||
echo $service "is [INACTIVE or NOT INSTALLED]"
|
||
fi
|
||
done
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
Linux Service Monitoring Script
|
||
|
||
**Let’s explain how the script works.**
|
||
|
||
1). The for loop reads the myservices.txt file one element of LIST at a time. That single element is denoted by the generic variable named service. The LIST is populated with the output of,
|
||
|
||
# cat myservices.txt
|
||
|
||
2). The above command is enclosed in parentheses and preceded by a dollar sign to indicate that it should be evaluated to populate the LIST that we will iterate over.
|
||
|
||
3). For each element of LIST (meaning every instance of the service variable), the following command will be executed.
|
||
|
||
# systemctl status $service | grep --quiet "running"
|
||
|
||
This time we need to precede our generic variable (which represents each element in LIST) with a dollar sign to indicate it’s a variable and thus its value in each iteration should be used. The output is then piped to grep.
|
||
|
||
The –quiet flag is used to prevent grep from displaying to the screen the lines where the word running appears. When that happens, the above command returns an exit status of 0 (represented by $? in the if construct), thus verifying that the service is running.
|
||
|
||
An exit status different than 0 (meaning the word running was not found in the output of systemctl status $service) indicates that the service is not running.
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
Services Monitoring Script
|
||
|
||
We could go one step further and check for the existence of myservices.txt before even attempting to enter the for loop.
|
||
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
|
||
# This script iterates over a list of services and
|
||
# is used to determine whether they are running or not.
|
||
|
||
if [ -f myservices.txt ]; then
|
||
for service in $(cat myservices.txt); do
|
||
systemctl status $service | grep --quiet "running"
|
||
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
|
||
echo $service "is [ACTIVE]"
|
||
else
|
||
echo $service "is [INACTIVE or NOT INSTALLED]"
|
||
fi
|
||
done
|
||
else
|
||
echo "myservices.txt is missing"
|
||
fi
|
||
|
||
**Pinging a series of network or internet hosts for reply statistics**
|
||
|
||
You may want to maintain a list of hosts in a text file and use a script to determine every now and then whether they’re pingable or not (feel free to replace the contents of myhosts and try for yourself).
|
||
|
||
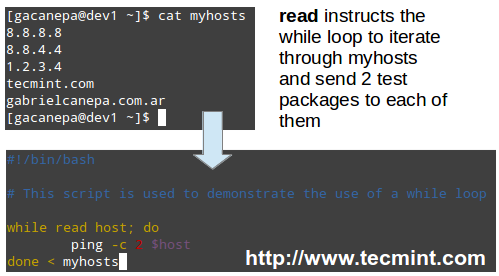
The read shell built-in command tells the while loop to read myhosts line by line and assigns the content of each line to variable host, which is then passed to the ping command.
|
||
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
|
||
# This script is used to demonstrate the use of a while loop
|
||
|
||
while read host; do
|
||
ping -c 2 $host
|
||
done < myhosts
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
Script to Ping Servers
|
||
|
||
Read Also:
|
||
|
||
- [Learn Shell Scripting: A Guide from Newbies to System Administrator][3]
|
||
- [5 Shell Scripts to Learn Shell Programming][4]
|
||
|
||
### Filesystem Troubleshooting ###
|
||
|
||
Although Linux is a very stable operating system, if it crashes for some reason (for example, due to a power outage), one (or more) of your file systems will not be unmounted properly and thus will be automatically checked for errors when Linux is restarted.
|
||
|
||
In addition, each time the system boots during a normal boot, it always checks the integrity of the filesystems before mounting them. In both cases this is performed using a tool named fsck (“file system check”).
|
||
|
||
fsck will not only check the integrity of file systems, but also attempt to repair corrupt file systems if instructed to do so. Depending on the severity of damage, fsck may succeed or not; when it does, recovered portions of files are placed in the lost+found directory, located in the root of each file system.
|
||
|
||
Last but not least, we must note that inconsistencies may also happen if we try to remove an USB drive when the operating system is still writing to it, and may even result in hardware damage.
|
||
|
||
The basic syntax of fsck is as follows:
|
||
|
||
# fsck [options] filesystem
|
||
|
||
**Checking a filesystem for errors and attempting to repair automatically**
|
||
|
||
In order to check a filesystem with fsck, we must first unmount it.
|
||
|
||
# mount | grep sdg1
|
||
# umount /mnt
|
||
# fsck -y /dev/sdg1
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
Check Filesystem Errors
|
||
|
||
Besides the -y flag, we can use the -a option to automatically repair the file systems without asking any questions, and force the check even when the filesystem looks clean.
|
||
|
||
# fsck -af /dev/sdg1
|
||
|
||
If we’re only interested in finding out what’s wrong (without trying to fix anything for the time being) we can run fsck with the -n option, which will output the filesystem issues to standard output.
|
||
|
||
# fsck -n /dev/sdg1
|
||
|
||
Depending on the error messages in the output of fsck, we will know whether we can try to solve the issue ourselves or escalate it to engineering teams to perform further checks on the hardware.
|
||
|
||
### 总结 ###
|
||
|
||
We have arrived at the end of this 10-article series where have tried to cover the basic domain competencies required to pass the LFCS exam.
|
||
|
||
For obvious reasons, it is not possible to cover every single aspect of these topics in any single tutorial, and that’s why we hope that these articles have put you on the right track to try new stuff yourself and continue learning.
|
||
|
||
If you have any questions or comments, they are always welcome – so don’t hesitate to drop us a line via the form below!
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-basic-shell-scripting-and-linux-filesystem-troubleshooting/
|
||
|
||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||
译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
|
||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/sed-command-to-create-edit-and-manipulate-files-in-linux/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/learning-shell-scripting-language-a-guide-from-newbies-to-system-administrator/
|
||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/basic-shell-programming-part-ii/
|