23 KiB
Linux Desktop Setup
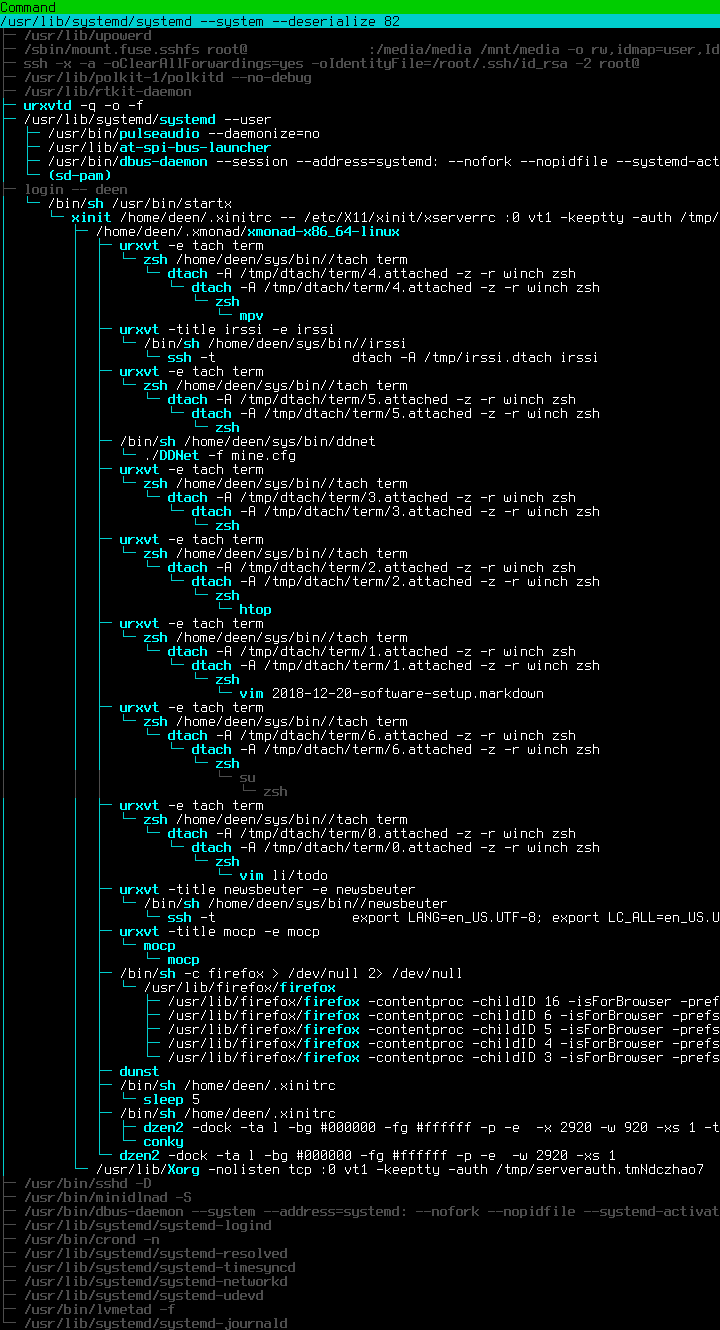
My software setup has been surprisingly constant over the last decade, after a few years of experimentation since I initially switched to Linux in 2006. It might be interesting to look back in another 10 years and see what changed. A quick overview of what’s running as I’m writing this post:
Motivation
My software priorities are, in no specific order:
- Programs should run on my local system so that I’m in control of them, this excludes cloud solutions.
- Programs should run in the terminal, so that they can be used consistently from anywhere, including weak computers or a phone.
- Keyboard focused is nearly automatic by using terminal software. I prefer to use the mouse where it makes sense only, reaching for the mouse all the time during typing feels like a waste of time. Occasionally it took me an hour to notice that the mouse wasn’t even plugged in.
- Ideally use fast and efficient software, I don’t like hearing the fan and feeling the room heat up. I can also keep running older hardware for much longer, my 10 year old Thinkpad x200s is still fine for all the software I use.
- Be composable. I don’t want to do every step manually, instead automate more when it makes sense. This naturally favors the shell.
Operating Systems
I had a hard start with Linux 12 years ago by removing Windows, armed with just the Gentoo Linux installation CD and a printed manual to get a functioning Linux system. It took me a few days of compiling and tinkering, but in the end I felt like I had learnt a lot.
I haven’t looked back to Windows since then, but I switched to Arch Linux on my laptop after having the fan fail from the constant compilation stress. Later I also switched all my other computers and private servers to Arch Linux. As a rolling release distribution you get package upgrades all the time, but the most important breakages are nicely reported in the Arch Linux News.
One annoyance though is that Arch Linux removes the old kernel modules once you upgrade it. I usually notice that once I try plugging in a USB flash drive and the kernel fails to load the relevant module. Instead you’re supposed to reboot after each kernel upgrade. There are a few hacks around to get around the problem, but I haven’t been bothered enough to actually use them.
Similar problems happen with other programs, commonly Firefox, cron or Samba requiring a restart after an upgrade, but annoyingly not warning you that that’s the case. SUSE, which I use at work, nicely warns about such cases.
For the DDNet production servers I prefer Debian over Arch Linux, so that I have a lower chance of breakage on each upgrade. For my firewall and router I used OpenBSD for its clean system, documentation and great pf firewall, but right now I don’t have a need for a separate router anymore.
Window Manager
Since I started out with Gentoo I quickly noticed the huge compile time of KDE, which made it a no-go for me. I looked around for more minimal solutions, and used Openbox and Fluxbox initially. At some point I jumped on the tiling window manager train in order to be more keyboard-focused and picked up dwm and awesome close to their initial releases.
In the end I settled on xmonad thanks to its flexibility, extendability and being written and configured in pure Haskell, a great functional programming language. One example of this is that at home I run a single 40” 4K screen, but often split it up into four virtual screens, each displaying a workspace on which my windows are automatically arranged. Of course xmonad has a module for that.
dzen and conky function as a simple enough status bar for me. My entire conky config looks like this:
out_to_console yes
update_interval 1
total_run_times 0
TEXT
${downspeed eth0} ${upspeed eth0} | $cpu% ${loadavg 1} ${loadavg 2} ${loadavg 3} $mem/$memmax | ${time %F %T}
And gets piped straight into dzen2 with conky | dzen2 -fn '-xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-12-*-*-*-*-*-*-*' -bg '#000000' -fg '#ffffff' -p -e '' -x 1000 -w 920 -xs 1 -ta r.
One important feature for me is to make the terminal emit a beep sound once a job is done. This is done simply by adding a \a character to the PR_TITLEBAR variable in zsh, which is shown whenever a job is done. Of course I disable the actual beep sound by blacklisting the pcspkr kernel module with echo "blacklist pcspkr" > /etc/modprobe.d/nobeep.conf. Instead the sound gets turned into an urgency by urxvt’s URxvt.urgentOnBell: true setting. Then xmonad has an urgency hook to capture this and I can automatically focus the currently urgent window with a key combination. In dzen I get the urgent windowspaces displayed with a nice and bright #ff0000.
The final result in all its glory on my Laptop:
I hear that i3 has become quite popular in the last years, but it requires more manual window alignment instead of specifying automated methods to do it.
I realize that there are also terminal multiplexers like tmux, but I still require a few graphical applications, so in the end I never used them productively.
Terminal Persistency
In order to keep terminals alive I use dtach, which is just the detach feature of screen. In order to make every terminal on my computer detachable I wrote a small wrapper script. This means that even if I had to restart my X server I could keep all my terminals running just fine, both local and remote.
Shell & Programming
Instead of bash I use zsh as my shell for its huge number of features.
As a terminal emulator I found urxvt to be simple enough, support Unicode and 256 colors and has great performance. Another great feature is being able to run the urxvt client and daemon separately, so that even a large number of terminals barely takes up any memory (except for the scrollback buffer).
There is only one font that looks absolutely clean and perfect to me: Terminus. Since i’s a bitmap font everything is pixel perfect and renders extremely fast and at low CPU usage. In order to switch fonts on-demand in each terminal with CTRL-WIN-[1-7] my ~/.Xdefaults contains:
URxvt.font: -xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-14-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
dzen2.font: -xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-14-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
URxvt.keysym.C-M-1: command:\033]50;-xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-12-*-*-*-*-*-*-*\007
URxvt.keysym.C-M-2: command:\033]50;-xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-14-*-*-*-*-*-*-*\007
URxvt.keysym.C-M-3: command:\033]50;-xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-18-*-*-*-*-*-*-*\007
URxvt.keysym.C-M-4: command:\033]50;-xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-22-*-*-*-*-*-*-*\007
URxvt.keysym.C-M-5: command:\033]50;-xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-24-*-*-*-*-*-*-*\007
URxvt.keysym.C-M-6: command:\033]50;-xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-28-*-*-*-*-*-*-*\007
URxvt.keysym.C-M-7: command:\033]50;-xos4-terminus-medium-r-normal-*-32-*-*-*-*-*-*-*\007
URxvt.keysym.C-M-n: command:\033]10;#ffffff\007\033]11;#000000\007\033]12;#ffffff\007\033]706;#00ffff\007\033]707;#ffff00\007
URxvt.keysym.C-M-b: command:\033]10;#000000\007\033]11;#ffffff\007\033]12;#000000\007\033]706;#0000ff\007\033]707;#ff0000\007
For programming and writing I use Vim with syntax highlighting and ctags for indexing, as well as a few terminal windows with grep, sed and the other usual suspects for search and manipulation. This is probably not at the same level of comfort as an IDE, but allows me more automation.
One problem with Vim is that you get so used to its key mappings that you’ll want to use them everywhere.
Python and Nim do well as scripting languages where the shell is not powerful enough.
System Monitoring
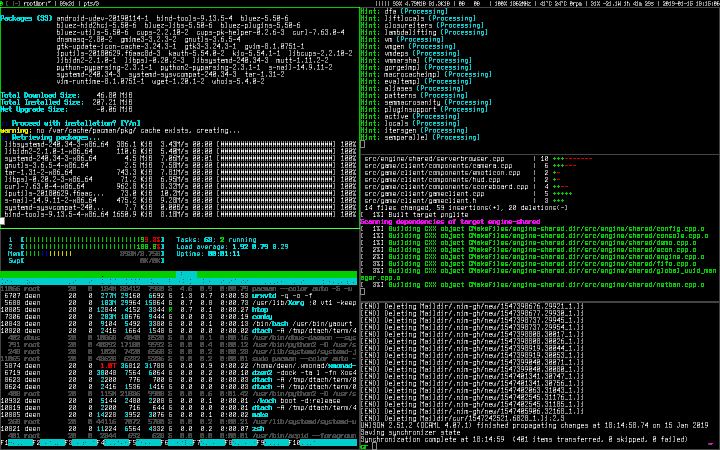
htop (look at the background of that site, it’s a live view of the server that’s hosting it) works great for getting a quick overview of what the software is currently doing. lm_sensors allows monitoring the hardware temperatures, fans and voltages. powertop is a great little tool by Intel to find power savings. ncdu lets you analyze disk usage interactively.
nmap, iptraf-ng, tcpdump and Wireshark are essential tools for analyzing network problems.
There are of course many more great tools.
Mails & Synchronization
On my home server I have a fetchmail daemon running for each email acccount that I have. Fetchmail just retrieves the incoming emails and invokes procmail:
#!/bin/sh
for i in /home/deen/.fetchmail/*; do
FETCHMAILHOME=$i /usr/bin/fetchmail -m 'procmail -d %T' -d 60
done
The configuration is as simple as it could be and waits for the server to inform us of fresh emails:
poll imap.1und1.de protocol imap timeout 120 user "dennis@felsin9.de" password "XXX" folders INBOX keep ssl idle
My .procmailrc config contains a few rules to backup all mails and sort them into the correct directories, for example based on the mailing list id or from field in the mail header:
MAILDIR=/home/deen/shared/Maildir
LOGFILE=$HOME/.procmaillog
LOGABSTRACT=no
VERBOSE=off
FORMAIL=/usr/bin/formail
NL="
"
:0wc
* ! ? test -d /media/mailarchive/`date +%Y`
| mkdir -p /media/mailarchive/`date +%Y`
# Make backups of all mail received in format YYYY/YYYY-MM
:0c
/media/mailarchive/`date +%Y`/`date +%Y-%m`
:0
* ^From: .*(.*@.*.kit.edu|.*@.*.uka.de|.*@.*.uni-karlsruhe.de)
$MAILDIR/.uni/
:0
* ^list-Id:.*lists.kit.edu
$MAILDIR/.uni-ml/
[...]
To send emails I use msmtp, which is also great to configure:
account default
host smtp.1und1.de
tls on
tls_trust_file /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
auth on
from dennis@felsin9.de
user dennis@felsin9.de
password XXX
[...]
But so far the emails are still on the server. My documents are all stored in a directory that I synchronize between all computers using Unison. Think of Unison as a bidirectional interactive rsync. My emails are part of this documents directory and thus they end up on my desktop computers.
This also means that while the emails reach my server immediately, I only fetch them on deman instead of getting instant notifications when an email comes in.
From there I read the mails with mutt, using the sidebar plugin to display my mail directories. The /etc/mailcap file is essential to display non-plaintext mails containing HTML, Word or PDF:
text/html;w3m -I %{charset} -T text/html; copiousoutput
application/msword; antiword %s; copiousoutput
application/pdf; pdftotext -layout /dev/stdin -; copiousoutput
News & Communication
Newsboat is a nice little RSS/Atom feed reader in the terminal. I have it running on the server in a tach session with about 150 feeds. Filtering feeds locally is also possible, for example:
ignore-article "https://forum.ddnet.tw/feed.php" "title =~ \"Map Testing •\" or title =~ \"Old maps •\" or title =~ \"Map Bugs •\" or title =~ \"Archive •\" or title =~ \"Waiting for mapper •\" or title =~ \"Other mods •\" or title =~ \"Fixes •\""
I use Irssi the same way for communication via IRC.
Calendar
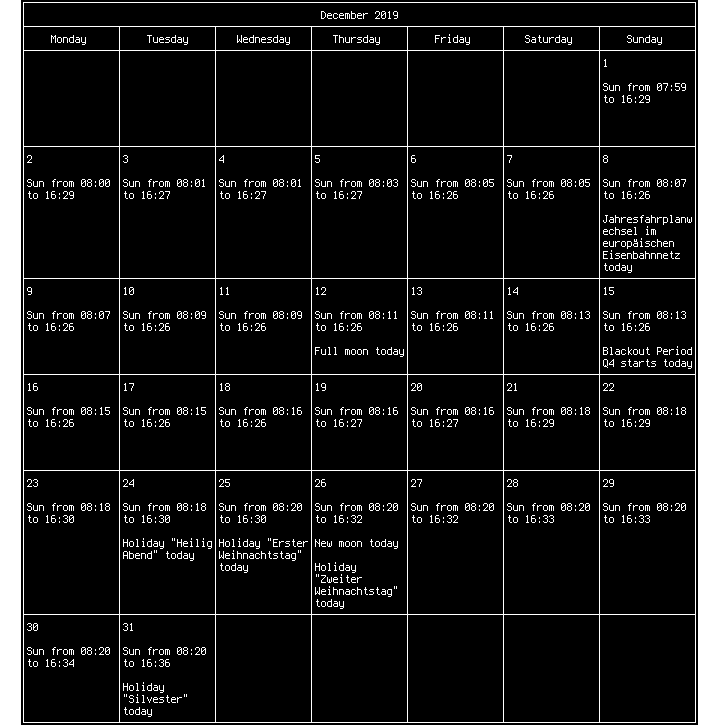
remind is a calendar that can be used from the command line. Setting new reminders is done by editing the rem files:
# One time events
REM 2019-01-20 +90 Flight to China %b
# Recurring Holidays
REM 1 May +90 Holiday "Tag der Arbeit" %b
REM [trigger(easterdate(year(today()))-2)] +90 Holiday "Karfreitag" %b
# Time Change
REM Nov Sunday 1 --7 +90 Time Change (03:00 -> 02:00) %b
REM Apr Sunday 1 --7 +90 Time Change (02:00 -> 03:00) %b
# Birthdays
FSET birthday(x) "'s " + ord(year(trigdate())-x) + " birthday is %b"
REM 16 Apr +90 MSG Andreas[birthday(1994)]
# Sun
SET $LatDeg 49
SET $LatMin 19
SET $LatSec 49
SET $LongDeg -8
SET $LongMin -40
SET $LongSec -24
MSG Sun from [sunrise(trigdate())] to [sunset(trigdate())]
[...]
Unfortunately there is no Chinese Lunar calendar function in remind yet, so Chinese holidays can’t be calculated easily.
I use two aliases for remind:
rem -m -b1 -q -g
to see a list of the next events in chronological order and
rem -m -b1 -q -cuc12 -w$(($(tput cols)+1)) | sed -e "s/\f//g" | less
to show a calendar fitting just the width of my terminal:
Dictionary
rdictcc is a little known dictionary tool that uses the excellent dictionary files from dict.cc and turns them into a local database:
$ rdictcc rasch
====================[ A => B ]====================
rasch:
- apace
- brisk [speedy]
- cursory
- in a timely manner
- quick
- quickly
- rapid
- rapidly
- sharpish [Br.] [coll.]
- speedily
- speedy
- swift
- swiftly
rasch [gehen]:
- smartly [quickly]
Rasch {n} [Zittergras-Segge]:
- Alpine grass [Carex brizoides]
- quaking grass sedge [Carex brizoides]
Rasch {m} [regional] [Putzrasch]:
- scouring pad
====================[ B => A ]====================
Rasch model:
- Rasch-Modell {n}
Writing and Reading
I have a simple todo file containing my tasks, that is basically always sitting open in a Vim session. For work I also use the todo file as a “done” file so that I can later check what tasks I finished on each day.
For writing documents, letters and presentations I use LaTeX for its superior typesetting. A simple letter in German format can be set like this for example:
\documentclass[paper = a4, fromalign = right]{scrlttr2}
\usepackage{german}
\usepackage{eurosym}
\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
\setlength{\parskip}{6pt}
\setlength{\parindent}{0pt}
\setkomavar{fromname}{Dennis Felsing}
\setkomavar{fromaddress}{Meine Str. 1\\69181 Leimen}
\setkomavar{subject}{Titel}
\setkomavar*{enclseparator}{Anlagen}
\makeatletter
\@setplength{refvpos}{89mm}
\makeatother
\begin{document}
\begin{letter} {Herr Soundso\\Deine Str. 2\\69121 Heidelberg}
\opening{Sehr geehrter Herr Soundso,}
Sie haben bei mir seit dem Bla Bla Bla.
Ich fordere Sie hiermit zu Bla Bla Bla auf.
\closing{Mit freundlichen Grüßen}
\end{letter}
\end{document}
Further example documents and presentations can be found over at my private site.
To read PDFs Zathura is fast, has Vim-like controls and even supports two different PDF backends: Poppler and MuPDF. Evince on the other hand is more full-featured for the cases where I encounter documents that Zathura doesn’t like.
Graphical Editing
GIMP and Inkscape are easy choices for photo editing and interactive vector graphics respectively.
In some cases Imagemagick is good enough though and can be used straight from the command line and thus automated to edit images. Similarly Graphviz and TikZ can be used to draw graphs and other diagrams.
Web Browsing
As a web browser I’ve always used Firefox for its extensibility and low resource usage compared to Chrome.
Unfortunately the Pentadactyl extension development stopped after Firefox switched to Chrome-style extensions entirely, so I don’t have satisfying Vim-like controls in my browser anymore.
Media Players
mpv with hardware decoding allows watching videos at 5% CPU load using the vo=gpu and hwdec=vaapi config settings. audio-channels=2 in mpv seems to give me clearer downmixing to my stereo speakers / headphones than what PulseAudio does by default. A great little feature is exiting with Shift-Q instead of just Q to save the playback location. When watching with someone with another native tongue you can use --secondary-sid= to show two subtitles at once, the primary at the bottom, the secondary at the top of the screen
My wirelss mouse can easily be made into a remote control with mpv with a small ~/.config/mpv/input.conf:
MOUSE_BTN5 run "mixer" "pcm" "-2"
MOUSE_BTN6 run "mixer" "pcm" "+2"
MOUSE_BTN1 cycle sub-visibility
MOUSE_BTN7 add chapter -1
MOUSE_BTN8 add chapter 1
youtube-dl works great for watching videos hosted online, best quality can be achieved with -f bestvideo+bestaudio/best --all-subs --embed-subs.
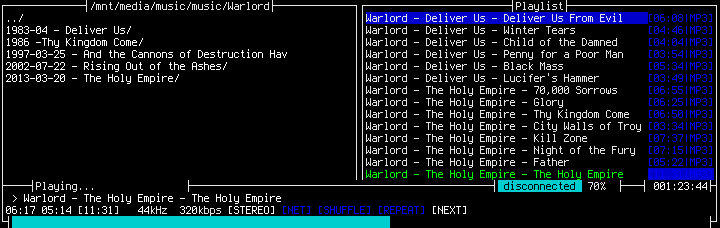
As a music player MOC hasn’t been actively developed for a while, but it’s still a simple player that plays every format conceivable, including the strangest Chiptune formats. In the AUR there is a patch adding PulseAudio support as well. Even with the CPU clocked down to 800 MHz MOC barely uses 1-2% of a single CPU core.
My music collection sits on my home server so that I can access it from anywhere. It is mounted using SSHFS and automount in the /etc/fstab/:
root@server:/media/media /mnt/media fuse.sshfs noauto,x-systemd.automount,idmap=user,IdentityFile=/root/.ssh/id_rsa,allow_other,reconnect 0 0
Cross-Platform Building
Linux is great to build packages for any major operating system except Linux itself! In the beginning I used QEMU to with an old Debian, Windows and Mac OS X VM to build for these platforms.
Nowadays I switched to using chroot for the old Debian distribution (for maximum Linux compatibility), MinGW to cross-compile for Windows and OSXCross to cross-compile for Mac OS X.
The script used to build DDNet as well as the instructions for updating library builds are based on this.
Backups
As usual, we nearly forgot about backups. Even if this is the last chapter, it should not be an afterthought.
I wrote rrb (reverse rsync backup) 10 years ago to wrap rsync so that I only need to give the backup server root SSH rights to the computers that it is backing up. Surprisingly rrb needed 0 changes in the last 10 years, even though I kept using it the entire time.
The backups are stored straight on the filesystem. Incremental backups are implemented using hard links (--link-dest). A simple config defines how long backups are kept, which defaults to:
KEEP_RULES=( \
7 7 \ # One backup a day for the last 7 days
31 8 \ # 8 more backups for the last month
365 11 \ # 11 more backups for the last year
1825 4 \ # 4 more backups for the last 5 years
)
Since some of my computers don’t have a static IP / DNS entry and I still want to back them up using rrb I use a reverse SSH tunnel (as a systemd service) for them:
[Unit]
Description=Reverse SSH Tunnel
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/ssh -N -R 27276:localhost:22 -o "ExitOnForwardFailure yes" server
KillMode=process
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Now the server can reach the client through ssh -p 27276 localhost while the tunnel is running to perform the backup, or in .ssh/config format:
Host cr-remote
HostName localhost
Port 27276
While talking about SSH hacks, sometimes a server is not easily reachable thanks to some bad routing. In that case you can route the SSH connection through another server to get better routing, in this case going through the USA to reach my Chinese server which had not been reliably reachable from Germany for a few weeks:
Host chn.ddnet.tw
ProxyCommand ssh -q usa.ddnet.tw nc -q0 chn.ddnet.tw 22
Port 22
Final Remarks
Thanks for reading my random collection of tools. I probably forgot many programs that I use so naturally every day that I don’t even think about them anymore. Let’s see how stable my software setup stays in the next years. If you have any questions, feel free to get in touch with me at dennis@felsin9.de.
Comments on Hacker News.
via: https://hookrace.net/blog/linux-desktop-setup/
作者:Dennis Felsing 选题:lujun9972 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID