5.3 KiB
Linux security: Cmd provides visibility, control over user activity
There's a new Linux security tool you should be aware of — Cmd (pronounced "see em dee") dramatically modifies the kind of control that can be exercised over Linux users. It reaches way beyond the traditional configuration of user privileges and takes an active role in monitoring and controlling the commands that users are able to run on Linux systems.
Provided by a company of the same name, Cmd focuses on cloud usage. Given the increasing number of applications being migrated into cloud environments that rely on Linux, gaps in the available tools make it difficult to adequately enforce required security. However, Cmd can also be used to manage and protect on-premises systems.
How Cmd differs from traditional Linux security controls
The leaders at Cmd — Milun Tesovic and Jake King — say organizations cannot confidently predict or control user behavior until they understand how users work routinely and what is considered “normal.” They seek to provide a tool that will granularly control, monitor, and authenticate user activity.
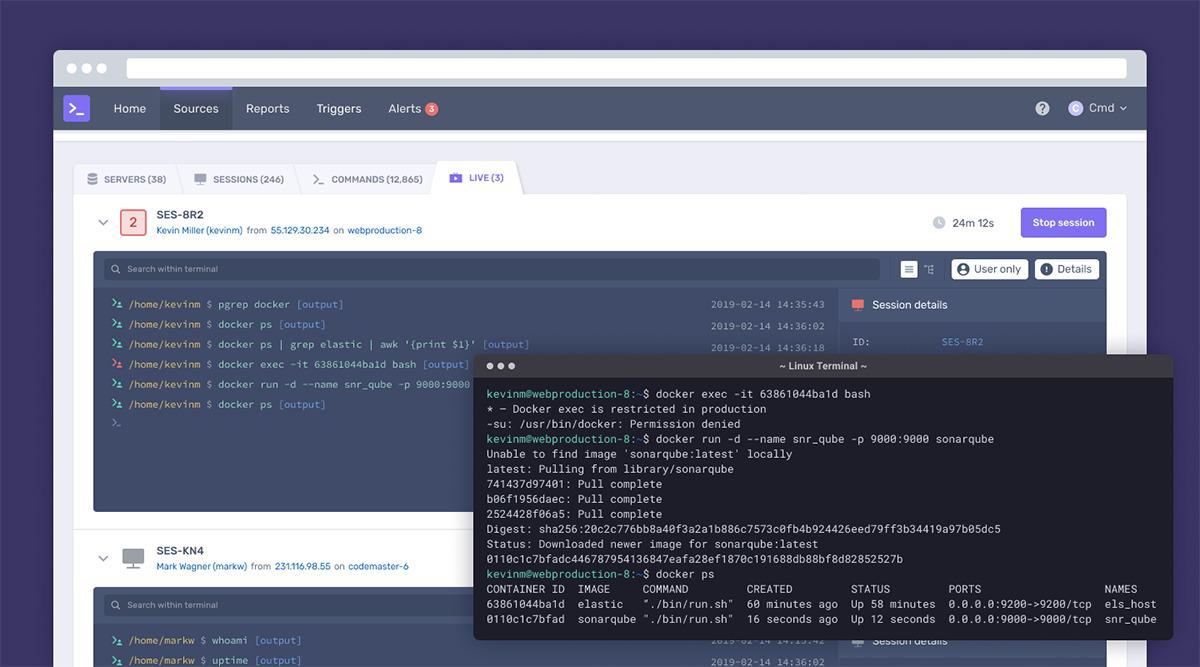
Cmd monitors user activity by forming user activity profiles (characterizing the activities these users generally perform), noticing abnormalities in their online behavior (login times, commands used, user locations, etc.), and preventing and reporting certain activities (e.g., downloading or modifying files and running privileged commands) that suggest some kind of system compromise might be underway. The product's behaviors are configurable and changes can be made rapidly.
The kind of tools most of us are using today to detect threats, identify vulnerabilities, and control user privileges have taken us a long way, but we are still fighting the battle to keep our systems and data safe. Cmd brings us a lot closer to identifying the intentions of hostile users whether those users are people who have managed to break into accounts or represent insider threats.
View live Linux sessions
How does Cmd work?
In monitoring and managing user activity, Cmd:
- Collects information that profiles user activity
- Uses the baseline to determine what is considered normal
- Detects and proactively prevents threats using specific indicators
- Sends alerts to responsible people
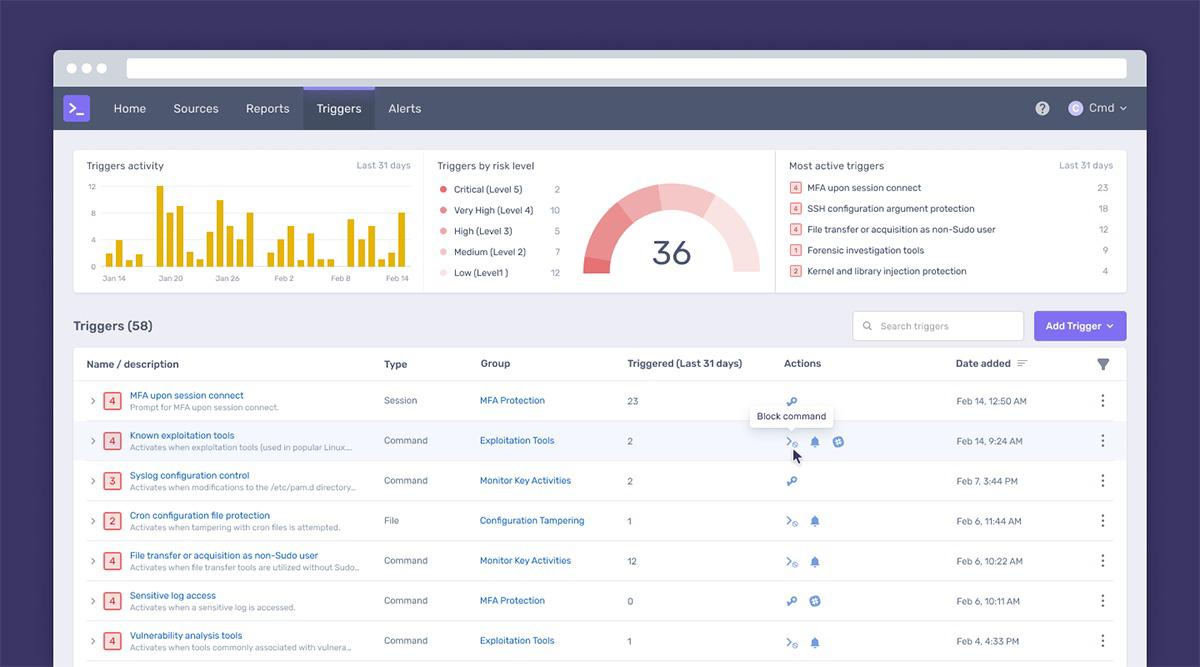
Building custom policies in Cmd
Cmd goes beyond defining what sysadmins can control through traditional methods, such as configuring sudo privileges, providing much more granular and situation-specific controls.
Administrators can select escalation policies that can be managed separately from the user privilege controls managed by Linux sysadmins.
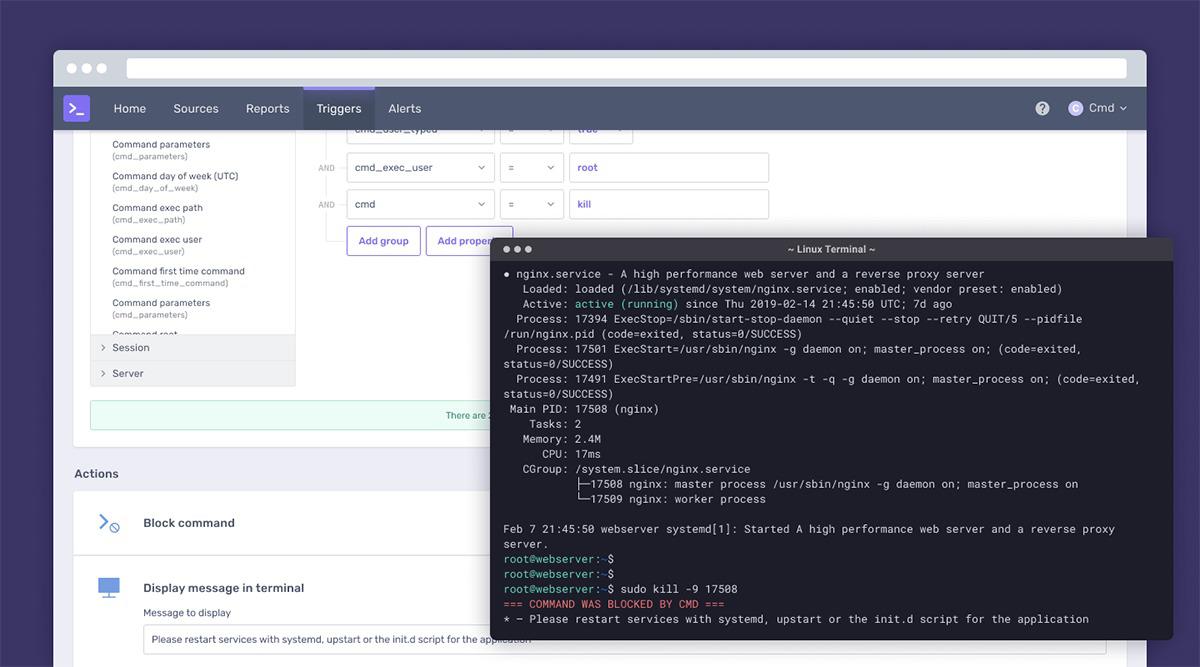
The Cmd agent provides real-time visibility (not after-the-fact log analysis) and can block actions, require additional authentication, or negotiate authorization as needed.
Also, Cmd supports custom rules based on geolocation if user locations are available. And new policies can be pushed to agents deployed on hosts within minutes.
Building a trigger query in Cmd
Funding news for Cmd
Cmd recently got a financial boost, having completed of a $15 million round of funding led by GV (formerly Google Ventures) with participation from Expa, Amplify Partners, and additional strategic investors. This brings the company's raised funding to $21.6 million and will help it continue to add new defensive capabilities to the product and grow its engineering teams.
In addition, the company appointed Karim Faris, general partner at GV, to its board of directors.
Join the Network World communities on Facebook and LinkedIn to comment on topics that are top of mind.
作者:Sandra Henry-Stocker 选题:lujun9972 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID