mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-01 21:50:13 +08:00
101 lines
4.6 KiB
Markdown
101 lines
4.6 KiB
Markdown
4 Useful Way to Know Plugged USB Device Name in Linux
|
||
============================================================
|
||
|
||
As a newbie, one of the many [things you should master in Linux][1] is identification of devices attached to your system. It may be your computer’s hard disk, an external hard drive or removable media such USB drive or SD Memory card.
|
||
|
||
Using USB drives for file transfer is so common today, and for those (new Linux users) who prefer to use the command line, learning the different ways to identify a USB device name is very important, when you need to format it.
|
||
|
||
Once you attach a device to your system such as a USB, especially on a desktop, it is automatically mounted to a given directory, normally under /media/username/device-label and you can then access the files in it from that directory. However, this is not the case with a server where you have to[ manually mount a device][2] and specify its mount point.
|
||
|
||
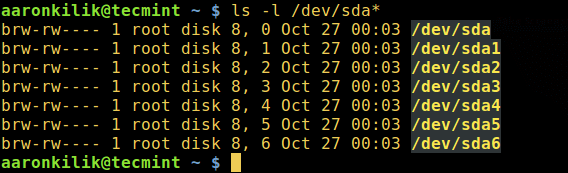
Linux identifies devices using special device files stored in `/dev` directory. Some of the files you will find in this directory include `/dev/sda` or `/dev/hda` which represents your first master drive, each partition will be represented by a number such as `/dev/sda1` or `/dev/hda1` for the first partition and so on.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ ls /dev/sda*
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][3]
|
||
|
||
List All Linux Device Names
|
||
|
||
Now let’s find out device names using some different command-line tools as shown:
|
||
|
||
### Find Out Plugged USB Device Name Using df Command
|
||
|
||
To view each device attached to your system as well as its mount point, you can use the [df command][4](checks Linux disk space utilization) as shown in the image below:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ df -h
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][5]
|
||
|
||
Find USB Device Name Using df Command
|
||
|
||
### Use lsblk Command to Find USB Device Name
|
||
|
||
You can also use the [lsblk command (list block devices)][6] which lists all block devices attached to your system like so:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ lsblk
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][7]
|
||
|
||
List Linux Block Devices
|
||
|
||
### Identify USB Device Name with fdisk Utility
|
||
|
||
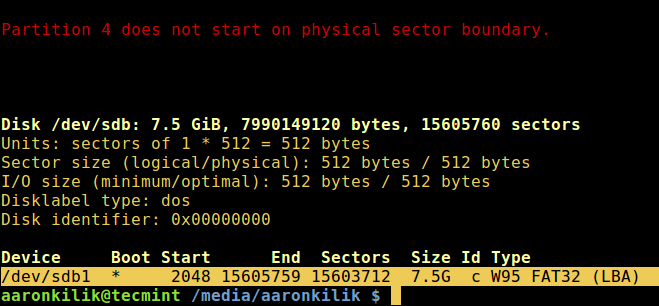
[fdisk is a powerful utility][8] which prints out the partition table on all your block devices, a USB drive inclusive, you can run it will root privileges as follows:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ sudo fdisk -l
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][9]
|
||
|
||
List Partition Table of Block Devices
|
||
|
||
### Determine USB Device Name with dmesg Command
|
||
|
||
dmesg is an important command that prints or controls the kernel ring buffer, a data structure which [stores information about the kernel’s operations][10].
|
||
|
||
Run the command below to view kernel operation messages which will as well print information about your USB device:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ dmesg
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][11]
|
||
|
||
dmesg – Prints USB Device Name
|
||
|
||
That is all for now, in this article, we have covered different approaches of how to find out a USB device name from the command line. You can also share with us any other methods for the same purpose or perhaps offer us your thoughts about the article via the response section below.
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/find-usb-device-name-in-linux
|
||
|
||
作者:[Aaron Kili ][a]
|
||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/tag/linux-tricks/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/mount-filesystem-in-linux/
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/List-All-Linux-Device-Names.png
|
||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-check-disk-space-in-linux/
|
||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Find-USB-Device-Name.png
|
||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/commands-to-collect-system-and-hardware-information-in-linux/
|
||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/List-Linux-Block-Devices.png
|
||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/fdisk-commands-to-manage-linux-disk-partitions/
|
||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/List-Partition-Table.png
|
||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/dmesg-commands/
|
||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/dmesg-shows-kernel-information.png
|