7.7 KiB
Add, Delete And Grant Sudo Privileges To Users In Fedora 36
Create sudo user in Fedora
Using sudo program, we can elevate the ability of a normal user to run administrative tasks, without giving away the root user's password in Linux operating systems. This guide explains how to add, delete and grant sudo privileges to users in Fedora 36 desktop and server editions.
I've divided this guide in three sections. The first section teaches you how to create a new user. In the second section, you'll learn how to give sudo access to the existing user. And in the last section, you will know how to remove sudo access from a user. I've also provided example commands in each section, so you can understand it better.
First, we will start with giving sudo access to a new user.
1. Create A New User In Fedora
Login to your Fedora system as root user or sudo user.
We can use either useradd or adduser commands to create users in Linux.
For the purpose of this guide, I am going to create a new user called "senthil" using adduser command.
To do so, I run the following command with sudo or root privilege:
$ sudo adduser senthil
Next, I am going to set a password to the newly created user "senthil" with passwd command:
$ sudo passwd senthil
We just created a normal user called "senthil". This user has not been given sudo access yet. So he can't perform any administrative tasks.
You can verify if an user has sudo access or not like below.
$ sudo -l -U senthil
Sample output:
User senthil is not allowed to run sudo on fedora.
As you can see, the user "senthil" is not yet allowed to run sudo. Let us go ahead and give him sudo access in the following steps.
2. Grant Sudo Privileges To Users In Fedora
To add a normal user to sudoers group, simply add him/her to the wheel group.
For those wondering, the wheel is a special group in some Unix-like operating systems (E.g. RHEL based systems). All the members of wheel group are allowed to perform administrative tasks. Wheel group is similar to sudo group in Debian-based systems.
We can add users to sudoers list in two ways. The first method is by using chmod command.
2.1. Add Users To Sudoers Using Usermod Command
Usermod
To grant sudo privileges to a user called "senthil", just add him to the wheel group using usermod command as shown below:
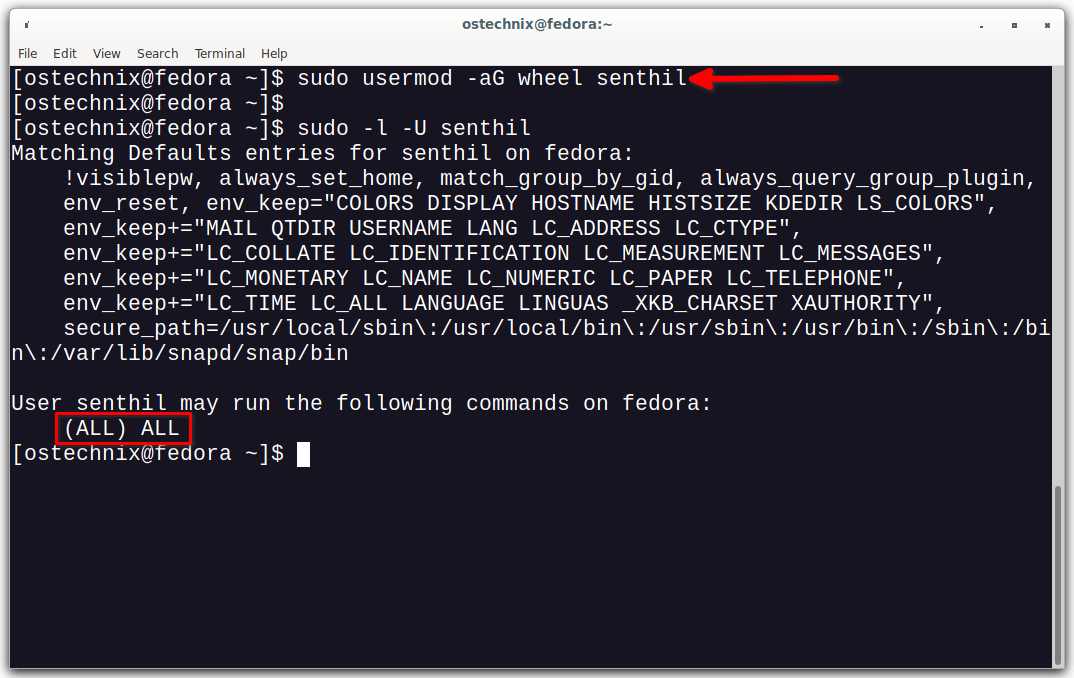
$ sudo usermod -aG wheel senthil
Here, -aG refers append to a supplementary group. In our case, it is wheel group.
Verify if the user is in the sudoers list with command:
$ sudo -l -U senthil
If you output something like below, it means the user has been given sudo access and he can able to perform all administrative tasks.
Matching Defaults entries for senthil on fedora:
!visiblepw, always_set_home, match_group_by_gid, always_query_group_plugin,
env_reset, env_keep="COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE KDEDIR LS_COLORS",
env_keep+="MAIL QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE",
env_keep+="LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES",
env_keep+="LC_MONETARY LC_NAME LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE",
env_keep+="LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY",
secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/var/lib/snapd/snap/bin
User senthil may run the following commands on fedora:
(ALL) ALL
As you see in the above output, the user "Senthil" can run ALL commands on any host.
2.2. Add Users To Sudoers By Editing Sudoers Configuration File
The another way to add users to sudoers list is by directly adding him/her to the sudoers configuration file.
Edit sudoers configuration file using command:
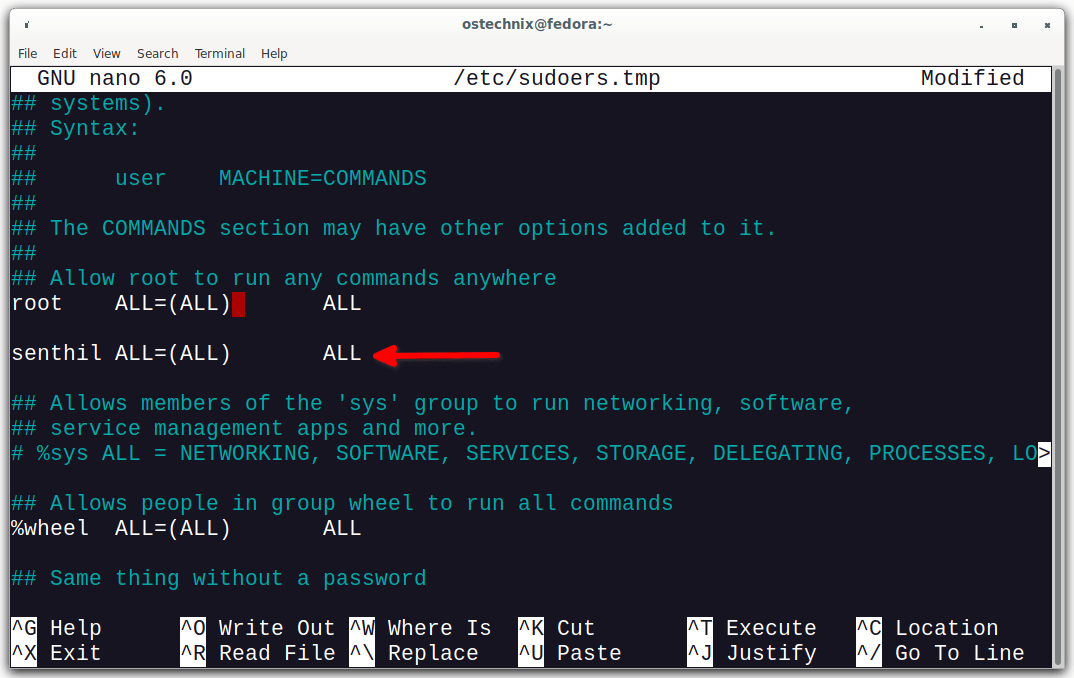
$ sudo visudo
This will open /etc/sudoers file in your Vi editor or whatever you have in your $PATH. Scroll down until you find following entry:
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
Right after the above entry, add the following line:
senthil ALL=(ALL) ALL
Here, the line ALL=(ALL) ALL refers the user "senthil" can perform any commands on any host. Replace "senthil" with your own username. Save the file and close it.
That's it. The user has been granted sudo access.
2.3. Verify Sudo Users
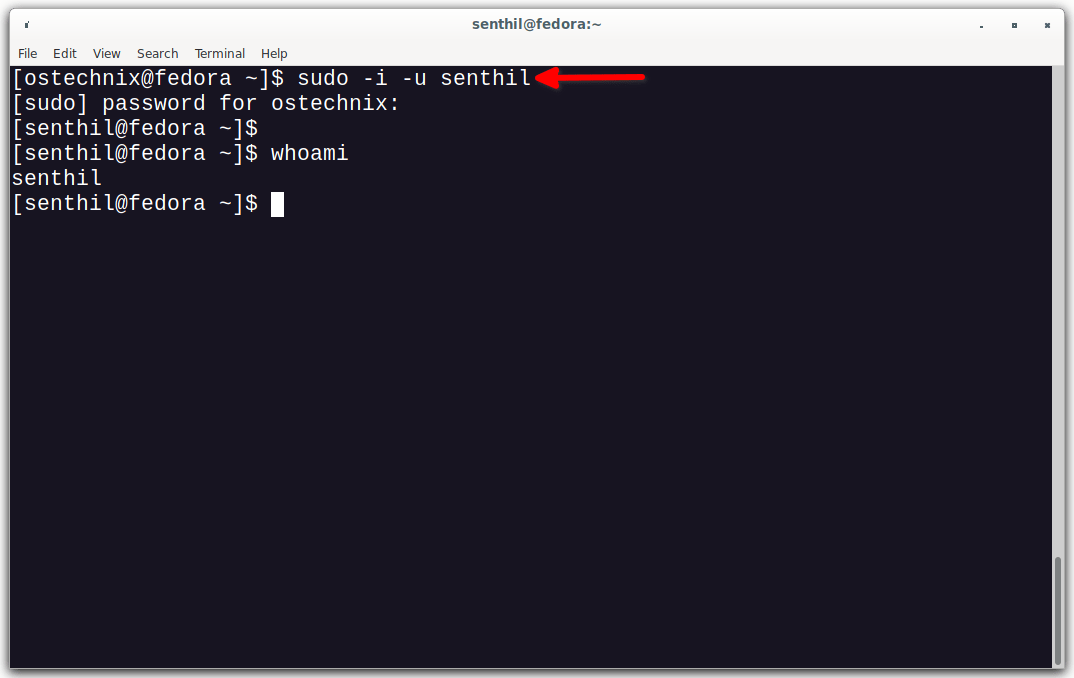
Log out from the current session and log back in as the newly created sudo user. Alternatively, you can directly switch to the other user, without having to log out from the current session, using the following command:
$ sudo -i -u senthil
Now, verify if the user can able to perform any administrative task with sudo permission:
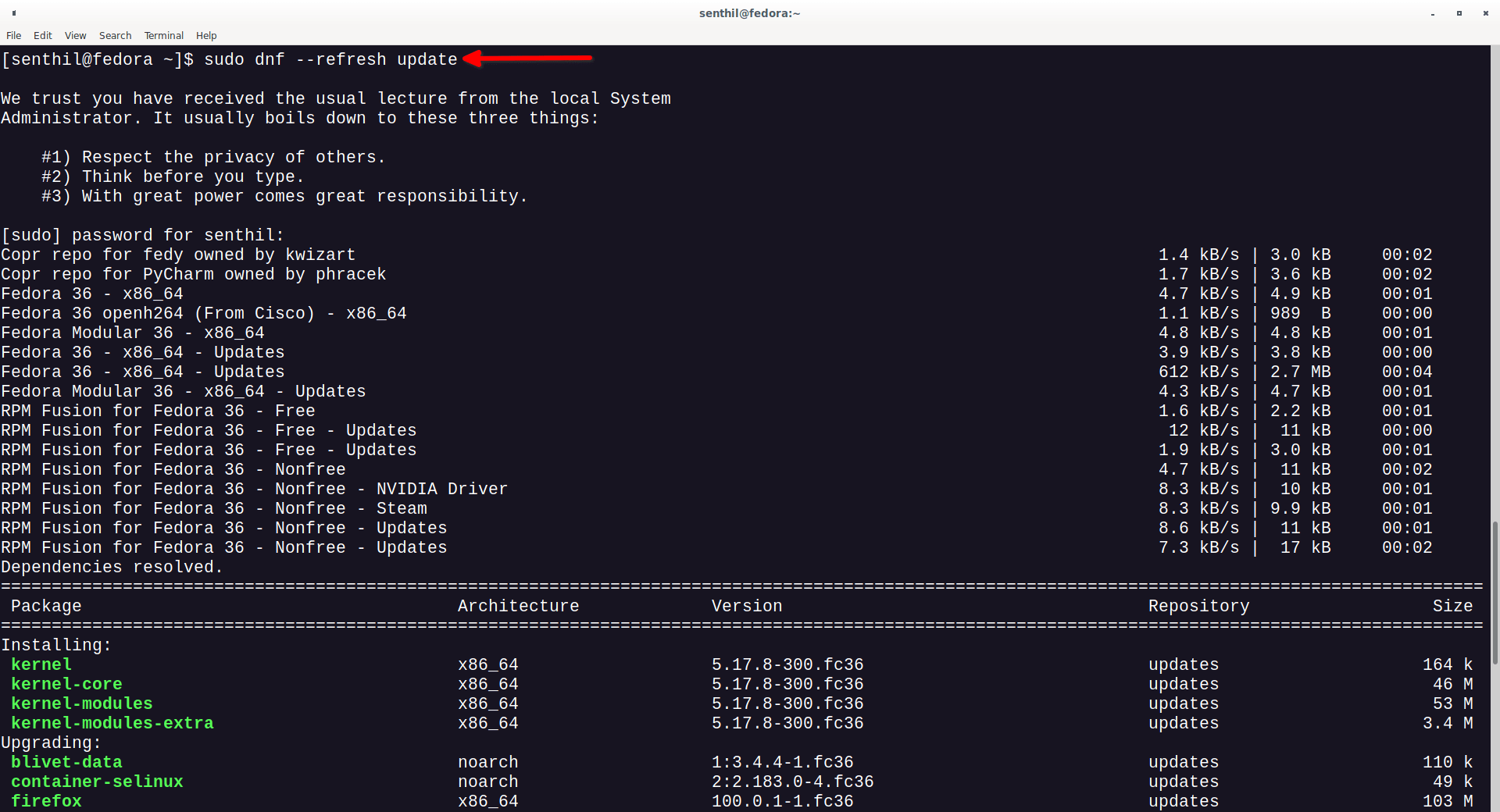
$ sudo dnf --refresh update
Great! The user can able to run the dnf update command with sudo privilege. From now on, the user can perform all commands prefixed with sudo.
3. Delete Sudo Access From A User
Make sure you logged out of the user's session and log back in as root or some other sudo user. Because you can't delete the sudo access of the currently logged in user.
We can remove sudo privileges from an user without having to entirely delete the user account.
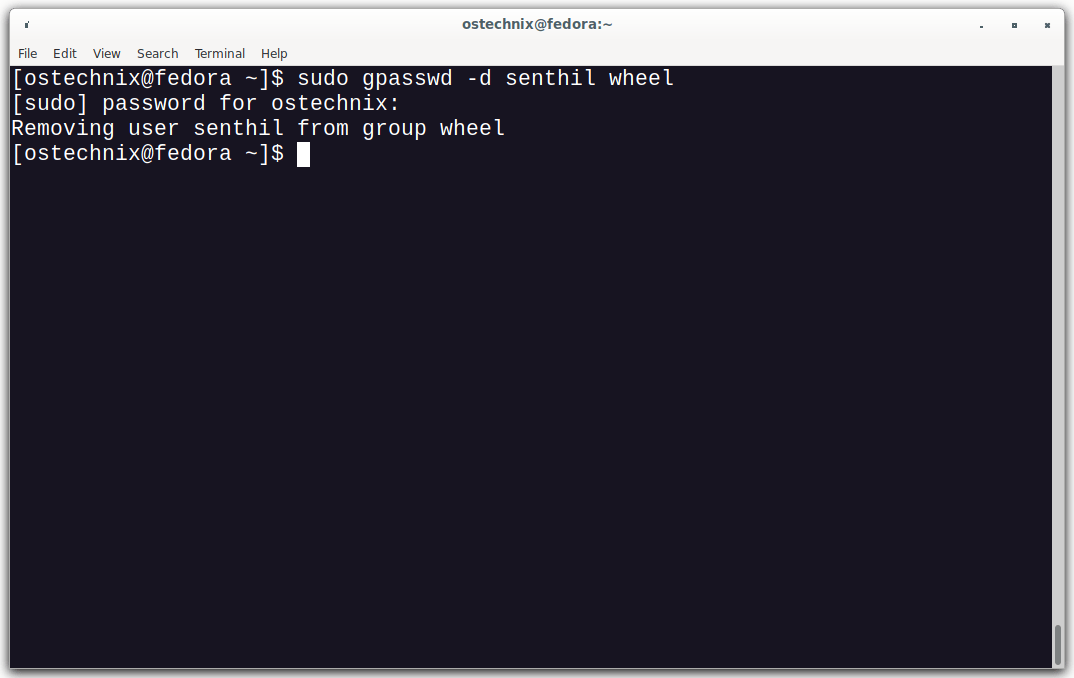
To do so, use gpasswd command to revoke sudo permissions from a user:
$ sudo gpasswd -d senthil wheel
Sample output:
Removing user senthil from group wheel
This will only remove sudo privilege of the given user. The user still exists in the system
Verify if the sudo access has been removed using command:
$ sudo -l -U senthil
User senthil is not allowed to run sudo on fedora35.
3.1. Permanently Delete User
If you don't need the user any more, you can permanently remove the user from the system using userdel command like below.
$ sudo userdel -r senthil
The above command will delete the user "senthil" along with his home directory and mail spool.
Conclusion
This concludes how to add, delete and grant sudo privileges to users in Fedora 36 operating system. This method is same for other RPM-based systems as well.
via: https://ostechnix.com/add-delete-and-grant-sudo-privileges-to-users-in-fedora/