8.7 KiB
idea2act translating
Turn your vi editor into a productivity powerhouse
A versatile and powerful editor, vi includes a rich set of potent commands that make it a popular choice for many users. This article specifically looks at commands that are not enabled by default in vi but are nevertheless useful. The commands recommended here are expected to be set in a vi configuration file. Though it is possible to enable commands individually from each vi session, the purpose of this article is to create a highly productive environment out of the box.
Before you begin
While "vim" is the technically correct name of the newer version of the vi editor, this article refers to it as "vi." vimrc is the configuration file used by vim.
The commands or configurations discussed here go into the vi startup configuration file, vimrc, located in the user home directory. Follow the instructions below to set the commands in vimrc:
(Note: The vimrc file is also used for system-wide configurations in Linux, such as /etc/vimrc or /etc/vim/vimrc. In this article, we'll consider only user-specific vimrc, present in user home folder.)
In Linux:
- Open the file with
vi $HOME/.vimrc - Type or copy/paste the commands in the cheat sheet at the end of this article
- Save and close (
:wq)
In Windows:
- First, install gvim
- Open gvim
- Click Edit --> Startup settings, which opens the _vimrc file
- Type or copy/paste the commands in the cheat sheet at the end of this article
- Click File --> Save
Let's delve into the individual vi productivity commands. These commands are classified into the following categories:
- Indentation & Tabs
- Display & Format
- Search
- Browse & Scroll
- Spell
- Miscellaneous
1. Indentation & Tabs
To automatically align the indentation of a line in a file:
set autoindent
Smart Indent uses the code syntax and style to align:
set smartindent
Tip: vi is language-aware and provides a default setting that works efficiently based on the programming language used in your file. There are many default configuration commands, including axs cindent, cinoptions, indentexpr, etc., which are not explained here. syn is a helpful command that shows or sets the file syntax.
To set the number of spaces to display for a tab:
set tabstop=4
To set the number of spaces to display for a “shift operation” (such as ‘>>’ or ‘<<’):
set shiftwidth=4
If you prefer to use spaces instead of tabs, this option inserts spaces when the Tab key is pressed. This may cause problems for languages such as Python that rely on tabs instead of spaces. In such cases, you may set this option based on the file type (see autocmd).
set expandtab
2. Display & Format
To show line numbers:
set number
To wrap text when it crosses the maximum line width:
set textwidth=80
To wrap text based on a number of columns from the right side:
set wrapmargin=2
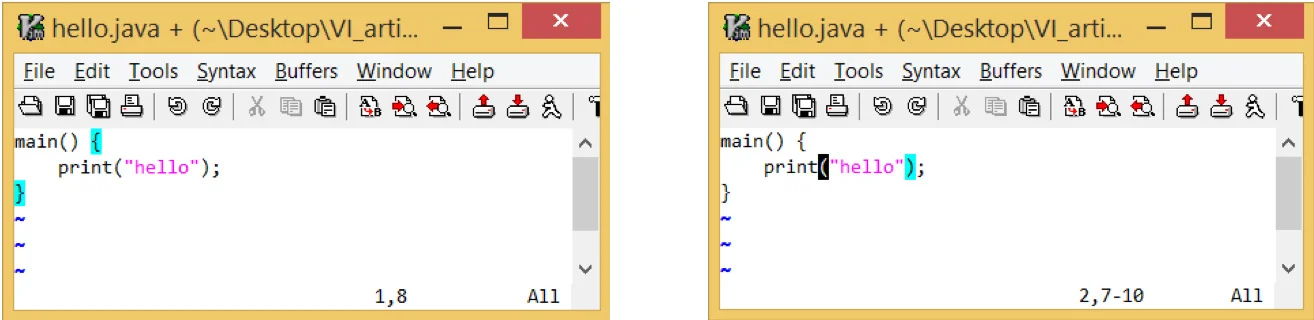
To identify open and close brace positions when you traverse through the file:
set showmatch
3. Search
To highlight the searched term in a file:
set hlsearch
To perform incremental searches as you type:
set incsearch
To search ignoring case (many users prefer not to use this command; set it only if you think it will be useful):
set ignorecase
To search without considering ignorecase when both ignorecase and smartcase are set and the search pattern contains uppercase:
set smartcase
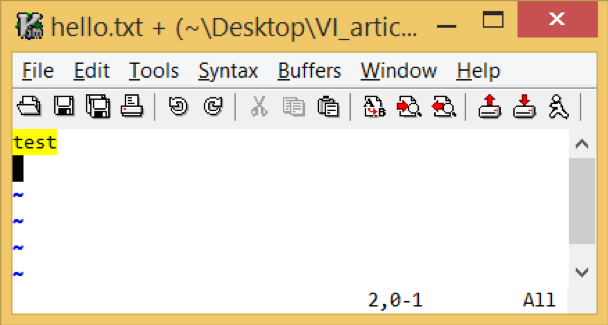
For example, if the file contains:
test Test
When both ignorecase and smartcase are set, a search for “test” finds and highlights both:
test Test
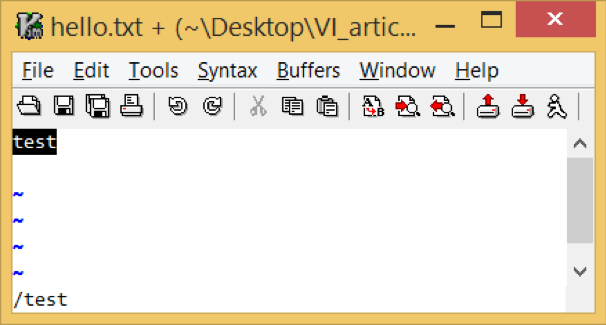
A search for “Test” highlights or finds only the second line:
test Test
4. Browse & Scroll
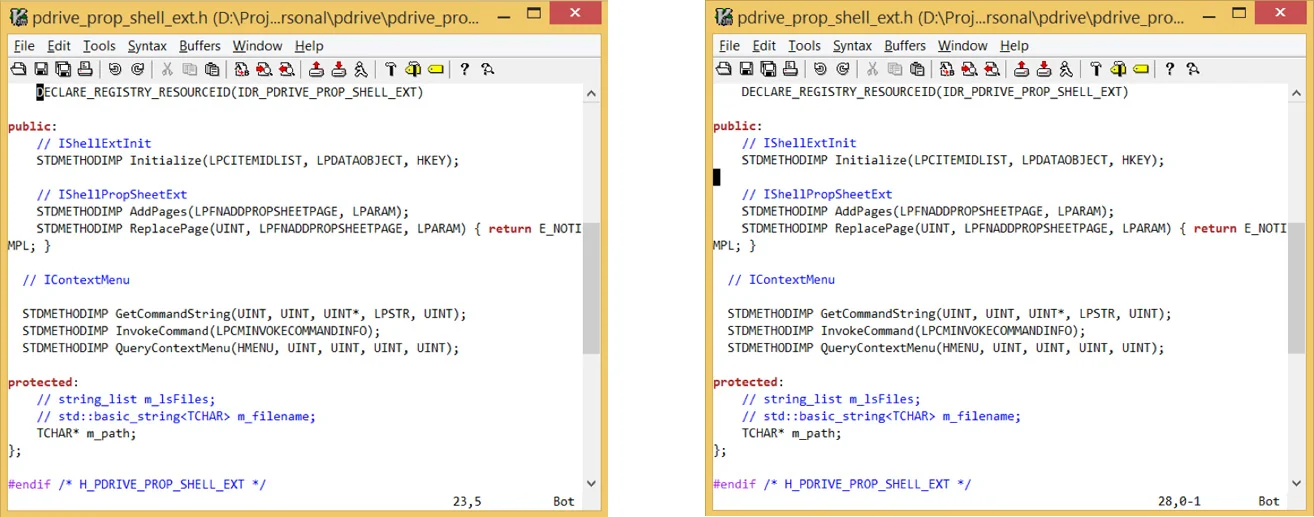
For a better visual experience, you may prefer to have the cursor somewhere in the middle rather than on the first line. The following option sets the cursor position to the 5th row.
set scrolloff=5
Example:
The first image is with scrolloff=0 and the second image is with scrolloff=5.
Tip: set sidescrolloff is useful if you also set nowrap.
To display a permanent status bar at the bottom of the vi screen showing the filename, row number, column number, etc.:
set laststatus=2
5. Spell
vi has a built-in spell-checker that is quite useful for text editing as well as coding. vi recognizes the file type and checks the spelling of comments only in code. Use the following command to turn on spell-check for the English language:
set spell spelllang=en_us
6. Miscellaneous
Disable creating backup file: When this option is on, vi creates a backup of the previous edit. If you do not want this feature, disable it as shown below. Backup files are named with a tilde (~) at the end of the filename.
set nobackup
Disable creating a swap file: When this option is on, vi creates a swap file that exists until you start editing the file. Swapfile is used to recover a file in the event of a crash or a use conflict. Swap files are hidden files that begin with . and end with .swp.
set noswapfile
Suppose you need to edit multiple files in the same vi session and switch between them. An annoying feature that's not readily apparent is that the working directory is the one from which you opened the first file. Often it is useful to automatically switch the working directory to that of the file being edited. To enable this option:
set autochdir
vi maintains an undo history that lets you undo changes. By default, this history is active only until the file is closed. vi includes a nifty feature that maintains the undo history even after the file is closed, which means you may undo your changes even after the file is saved, closed, and reopened. The undo file is a hidden file saved with the .un~ extension.
set undofile
To set audible alert bells (which sound a warning if you try to scroll beyond the end of a line):
set errorbells
If you prefer, you may set visual alert bells:
set visualbell
Bonus
vi provides long-format as well as short-format commands. Either format can be used to set or unset the configuration.
Long format for the autoindent command:
set autoindent
Short format for the autoindent command:
set ai
To see the current configuration setting of a command without changing its current value, use ? at the end:
set autoindent?
To unset or turn off a command, most commands take no as a prefix:
set noautoindent
It is possible to set a command for one file but not for the global configuration. To do this, open the file and type :, followed by the set command. This configuration is effective only for the current file editing session.
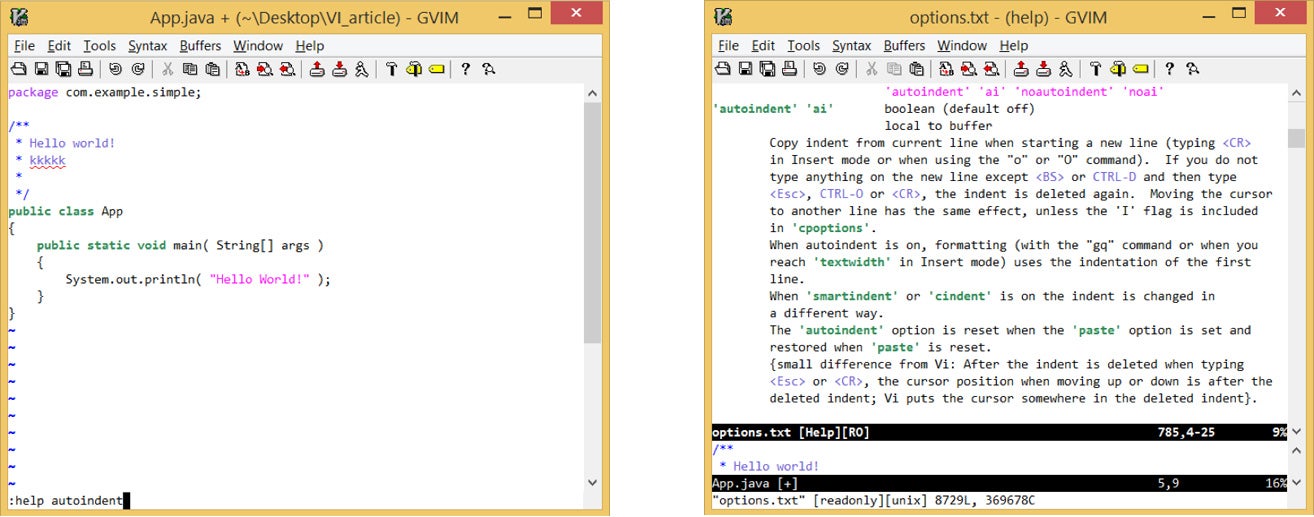
For help on a command:
:help autoindent
Note: The commands listed here were tested on Linux with Vim version 7.4 (2013 Aug 10) and Windows with Vim 8.0 (2016 Sep 12).
These useful commands are sure to enhance your vi experience. Which other commands do you recommend?
Cheat sheet
Copy/paste this list of commands in your vimrc file:
" Indentation & Tabs
set autoindent
set smartindent
set tabstop=4
set shiftwidth=4
set expandtab
set smarttab
" Display & format
set number
set textwidth=80
set wrapmargin=2
set showmatch
" Search
set hlsearch
set incsearch
set ignorecase
set smartcase
" Browse & Scroll
set scrolloff=5
set laststatus=2
" Spell
set spell spelllang=en_us
" Miscellaneous
set nobackup
set noswapfile
set autochdir
set undofile
set visualbell
set errorbells
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/vi-editor-productivity-powerhouse
作者:Girish Managoli 选题:lujun9972 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID