mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-23 21:20:42 +08:00
107 lines
7.2 KiB
Markdown
107 lines
7.2 KiB
Markdown
Logreduce:用 Python 和机器学习去除日志噪音
|
||
======
|
||
|
||
> Logreduce 可以通过从大量日志数据中挑选出异常来节省调试时间。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
持续集成(CI)作业会生成大量数据。当一个作业失败时,弄清楚出了什么问题可能是一个繁琐的过程,它涉及到调查日志以发现根本原因 —— 这通常只能在全部的作业输出的一小部分中找到。为了更容易地将最相关的数据与其余数据分开,可以使用先前成功运行的作业结果来训练 [Logreduce][1] 机器学习模型,以从失败的运行日志中提取异常。
|
||
|
||
此方法也可以应用于其他用例,例如,从 [Journald][2] 或其他系统级的常规日志文件中提取异常。
|
||
|
||
### 使用机器学习来降低噪音
|
||
|
||
典型的日志文件包含许多标称事件(“基线”)以及与开发人员相关的一些例外事件。基线可能包含随机元素,例如难以检测和删除的时间戳或唯一标识符。要删除基线事件,我们可以使用 [k-最近邻模式识别算法][3](k-NN)。
|
||
|
||
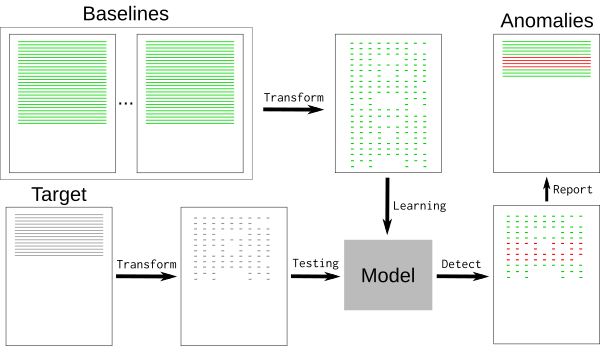
|
||
|
||
日志事件必须转换为可用于 k-NN 回归的数值。使用通用特征提取工具 [HashingVectorizer][4] 可以将该过程应用于任何类型的日志。它散列每个单词并在稀疏矩阵中对每个事件进行编码。为了进一步减少搜索空间,这个标记化过程删除了已知的随机单词,例如日期或 IP 地址。
|
||
|
||
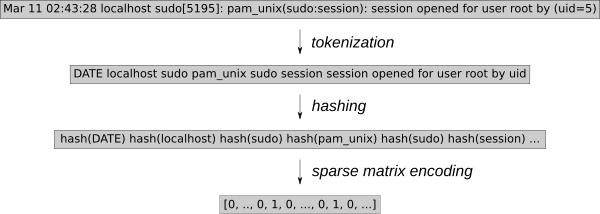
|
||
|
||
训练模型后,k-NN 搜索可以告诉我们每个新事件与基线的距离。
|
||
|
||
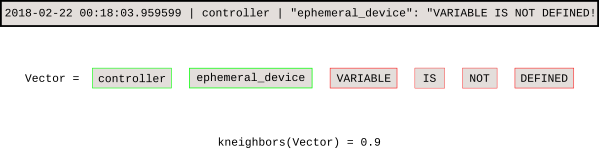
|
||
|
||
这个 [Jupyter 笔记本][5] 演示了该稀疏矩阵向量的处理和图形。
|
||
|
||
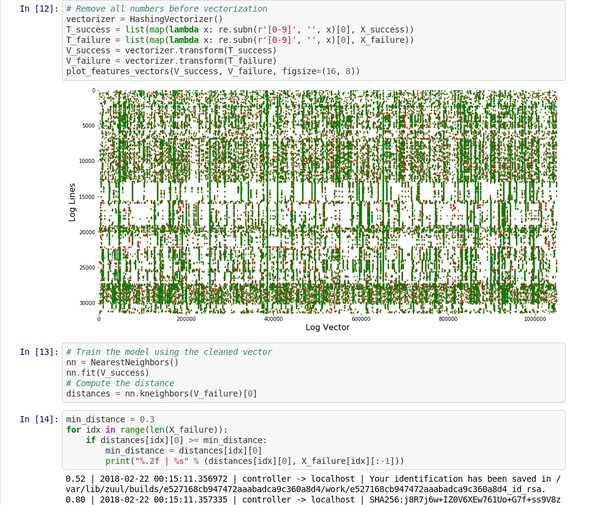
|
||
|
||
### Logreduce 介绍
|
||
|
||
Logreduce Python 软件透明地实现了这个过程。Logreduce 的最初目标是使用构建数据库来协助分析 [Zuul CI][6] 作业的失败问题,现在它已集成到 [Software Factory 开发车间][7]的作业日志处理中。
|
||
|
||
最简单的是,Logreduce 会比较文件或目录并删除相似的行。Logreduce 为每个源文件构建模型,并使用以下语法输出距离高于定义阈值的任何目标行:`distance | filename:line-number: line-content`。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ logreduce diff /var/log/audit/audit.log.1 /var/log/audit/audit.log
|
||
INFO logreduce.Classifier - Training took 21.982s at 0.364MB/s (1.314kl/s) (8.000 MB - 28.884 kilo-lines)
|
||
0.244 | audit.log:19963: type=USER_AUTH acct="root" exe="/usr/bin/su" hostname=managesf.sftests.com
|
||
INFO logreduce.Classifier - Testing took 18.297s at 0.306MB/s (1.094kl/s) (5.607 MB - 20.015 kilo-lines)
|
||
99.99% reduction (from 20015 lines to 1
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
更高级的 Logreduce 用法可以离线训练模型以便重复使用。可以使用基线的许多变体来拟合 k-NN 搜索树。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ logreduce dir-train audit.clf /var/log/audit/audit.log.*
|
||
INFO logreduce.Classifier - Training took 80.883s at 0.396MB/s (1.397kl/s) (32.001 MB - 112.977 kilo-lines)
|
||
DEBUG logreduce.Classifier - audit.clf: written
|
||
$ logreduce dir-run audit.clf /var/log/audit/audit.log
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Logreduce 还实现了接口,以发现 Journald 时间范围(天/周/月)和 Zuul CI 作业构建历史的基线。它还可以生成 HTML 报告,该报告在一个简单的界面中将在多个文件中发现的异常进行分组。
|
||
|
||
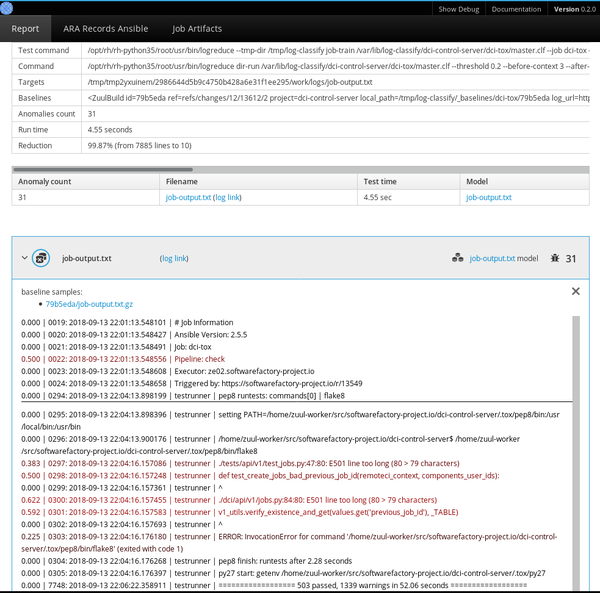
|
||
|
||
### 管理基线
|
||
|
||
使用 k-NN 回归进行异常检测的关键是拥有一个已知良好基线的数据库,该模型使用数据库来检测偏离太远的日志行。此方法依赖于包含所有标称事件的基线,因为基线中未找到的任何内容都将报告为异常。
|
||
|
||
CI 作业是 k-NN 回归的重要目标,因为作业的输出通常是确定性的,之前的运行结果可以自动用作基线。 Logreduce 具有 Zuul 作业角色,可以将其用作失败的作业发布任务的一部分,以便发布简明报告(而不是完整作业的日志)。只要可以提前构建基线,该原则就可以应用于其他情况。例如,标称系统的 [SoS 报告][8] 可用于查找缺陷部署中的问题。
|
||
|
||
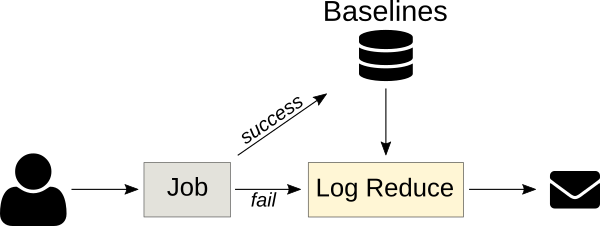
|
||
|
||
### 异常分类服务
|
||
|
||
下一版本的 Logreduce 引入了一种服务器模式,可以将日志处理卸载到外部服务,在外部服务中可以进一步分析该报告。它还支持导入现有报告和请求以分析 Zuul 构建。这些服务以异步方式运行分析,并具有 Web 界面以调整分数并消除误报。
|
||
|
||
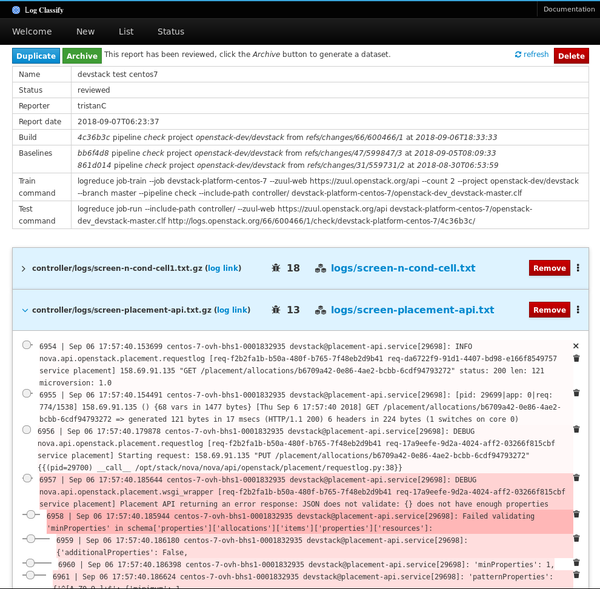
|
||
|
||
已审核的报告可以作为独立数据集存档,其中包含目标日志文件和记录在一个普通的 JSON 文件中的异常行的分数。
|
||
|
||
### 项目路线图
|
||
|
||
Logreduce 已经能有效使用,但是有很多机会来改进该工具。未来的计划包括:
|
||
|
||
* 策划在日志文件中发现的许多带注释的异常,并生成一个公共域数据集以进行进一步研究。日志文件中的异常检测是一个具有挑战性的主题,并且有一个用于测试新模型的通用数据集将有助于识别新的解决方案。
|
||
* 重复使用带注释的异常模型来优化所报告的距离。例如,当用户通过将距离设置为零来将日志行标记为误报时,模型可能会降低未来报告中这些日志行的得分。
|
||
* 对存档异常取指纹特征以检测新报告何时包含已知的异常。因此,该服务可以通知用户该作业遇到已知问题,而不是报告异常的内容。解决问题后,该服务可以自动重新启动该作业。
|
||
* 支持更多基准发现接口,用于 SOS 报告、Jenkins 构建、Travis CI 等目标。
|
||
|
||
如果你有兴趣参与此项目,请通过 #log-classify Freenode IRC 频道与我们联系。欢迎反馈!
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/quiet-log-noise-python-and-machine-learning
|
||
|
||
作者:[Tristan de Cacqueray][a]
|
||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/tristanc
|
||
[1]: https://pypi.org/project/logreduce/
|
||
[2]: http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/systemd-journald.service.8.html
|
||
[3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-nearest_neighbors_algorithm
|
||
[4]: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.feature_extraction.text.HashingVectorizer.html
|
||
[5]: https://github.com/TristanCacqueray/anomaly-detection-workshop-opendev/blob/master/datasets/notebook/anomaly-detection-with-scikit-learn.ipynb
|
||
[6]: https://zuul-ci.org
|
||
[7]: https://www.softwarefactory-project.io
|
||
[8]: https://sos.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
|
||
[9]: https://www.openstack.org/summit/berlin-2018/summit-schedule/speakers/4307
|
||
[10]: https://www.openstack.org/summit/berlin-2018/
|