mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-29 21:41:00 +08:00
202 lines
9.8 KiB
Markdown
202 lines
9.8 KiB
Markdown
本地开发如何测试 Webhook
|
||
===================
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
[Webhook][10] 可用于外部系统通知你的系统发生了某个事件或更新。可能最知名的 [Webhook][10] 类型是支付服务提供商(PSP)通知你的系统支付状态有了更新。
|
||
|
||
它们通常以监听的预定义 URL 的形式出现,例如 `http://example.com/webhooks/payment-update`。同时,另一个系统向该 URL 发送具有特定有效载荷的 POST 请求(例如支付 ID)。一旦请求进入,你就会获得支付 ID,可以通过 PSP 的 API 用这个支付 ID 向它们询问最新状态,然后更新你的数据库。
|
||
|
||
其他例子可以在这个对 Webhook 的出色的解释中找到:[https://sendgrid.com/blog/whats-webhook/][12]。
|
||
|
||
只要系统可通过互联网公开访问(这可能是你的生产环境或可公开访问的临时环境),测试这些 webhook 就相当顺利。而当你在笔记本电脑上或虚拟机内部(例如,Vagrant 虚拟机)进行本地开发时,它就变得困难了。在这些情况下,发送 webhook 的一方无法公开访问你的本地 URL。此外,监视发送的请求也很困难,这可能使开发和调试变得困难。
|
||
|
||
因此,这个例子将解决:
|
||
|
||
* 测试来自本地开发环境的 webhook,该环境无法通过互联网访问。从服务器向 webhook 发送数据的服务无法访问它。
|
||
* 监控发送的请求和数据,以及应用程序生成的响应。这样可以更轻松地进行调试,从而缩短开发周期。
|
||
|
||
前置需求:
|
||
|
||
* *可选*:如果你使用虚拟机(VM)进行开发,请确保它正在运行,并确保在 VM 中完成后续步骤。
|
||
* 对于本教程,我们假设你定义了一个 vhost:`webhook.example.vagrant`。我在本教程中使用了 Vagrant VM,但你可以自由选择 vhost。
|
||
* 按照这个[安装说明][3]安装 `ngrok`。在 VM 中,我发现它的 Node 版本也很有用:[https://www.npmjs.com/package/ngrok][4],但你可以随意使用其他方法。
|
||
|
||
我假设你没有在你的环境中运行 SSL,但如果你使用了,请将在下面的示例中的端口 80 替换为端口 433,`http://` 替换为 `https://`。
|
||
|
||
### 使 webhook 可测试
|
||
|
||
我们假设以下示例代码。我将使用 PHP,但请将其视作伪代码,因为我留下了一些关键部分(例如 API 密钥、输入验证等)没有编写。
|
||
|
||
第一个文件:`payment.php`。此文件创建一个 `$payment` 对象,将其注册到 PSP。然后它获取客户需要访问的 URL,以便支付并将用户重定向到客户那里。
|
||
|
||
请注意,此示例中的 `webhook.example.vagrant` 是我们为开发设置定义的本地虚拟主机。它无法从外部世界进入。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
<?php
|
||
/*
|
||
* This file creates a payment and tells the PSP what webhook URL to use for updates
|
||
* After creating the payment, we get a URL to send the customer to in order to pay at the PSP
|
||
*/
|
||
$payment = [
|
||
'order_id' => 123,
|
||
'amount' => 25.00,
|
||
'description' => 'Test payment',
|
||
'redirect_url' => 'http://webhook.example.vagrant/redirect.php',
|
||
'webhook_url' => 'http://webhook.example.vagrant/webhook.php',
|
||
];
|
||
|
||
$payment = $paymentProvider->createPayment($payment);
|
||
header("Location: " . $payment->getPaymentUrl());
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
第二个文件:`webhook.php`。此文件等待 PSP 调用以获得有关更新的通知。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
<?php
|
||
/*
|
||
* This file gets called by the PSP and in the $_POST they submit an 'id'
|
||
* We can use this ID to get the latest status from the PSP and update our internal systems afterward
|
||
*/
|
||
|
||
$paymentId = $_POST['id'];
|
||
$paymentInfo = $paymentProvider->getPayment($paymentId);
|
||
$status = $paymentInfo->getStatus();
|
||
|
||
// Perform actions in here to update your system
|
||
if ($status === 'paid') {
|
||
..
|
||
}
|
||
elseif ($status === 'cancelled') {
|
||
..
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
我们的 webhook URL 无法通过互联网访问(请记住它:`webhook.example.vagrant`)。因此,PSP 永远不可能调用文件 `webhook.php`,你的系统将永远不会知道付款状态,这最终导致订单永远不会被运送给客户。
|
||
|
||
幸运的是,`ngrok` 可以解决这个问题。 [ngrok][13] 将自己描述为:
|
||
|
||
> ngrok 通过安全隧道将 NAT 和防火墙后面的本地服务器暴露给公共互联网。
|
||
|
||
让我们为我们的项目启动一个基本的隧道。在你的环境中(在你的系统上或在 VM 上)运行以下命令:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
ngrok http -host-header=rewrite webhook.example.vagrant:80
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 阅读其文档可以了解更多配置选项:[https://ngrok.com/docs][14]。
|
||
|
||
会出现这样的屏幕:
|
||
|
||
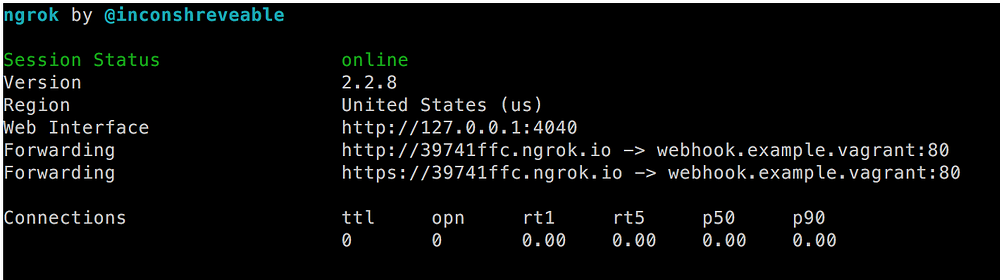
|
||
|
||
*ngrok 输出*
|
||
|
||
我们刚刚做了什么?基本上,我们指示 `ngrok` 在端口 80 建立了一个到 `http://webhook.example.vagrant` 的隧道。同一个 URL 也可以通过 `http://39741ffc.ngrok.io` 或 `https://39741ffc.ngrok.io` 访问,它们能被任何知道此 URL 的人通过互联网公开访问。
|
||
|
||
请注意,你可以同时获得 HTTP 和 HTTPS 两个服务。这个文档提供了如何将此限制为 HTTPS 的示例:[https://ngrok.com/docs#bind-tls][16]。
|
||
|
||
那么,我们如何让我们的 webhook 现在工作起来?将 `payment.php` 更新为以下代码:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
<?php
|
||
/*
|
||
* This file creates a payment and tells the PSP what webhook URL to use for updates
|
||
* After creating the payment, we get a URL to send the customer to in order to pay at the PSP
|
||
*/
|
||
$payment = [
|
||
'order_id' => 123,
|
||
'amount' => 25.00,
|
||
'description' => 'Test payment',
|
||
'redirect_url' => 'http://webhook.example.vagrant/redirect.php',
|
||
'webhook_url' => 'https://39741ffc.ngrok.io/webhook.php',
|
||
];
|
||
|
||
$payment = $paymentProvider->createPayment($payment);
|
||
header("Location: " . $payment->getPaymentUrl());
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
现在,我们告诉 PSP 通过 HTTPS 调用此隧道 URL。只要 PSP 通过隧道调用 webhook,`ngrok` 将确保使用未修改的有效负载调用内部 URL。
|
||
|
||
### 如何监控对 webhook 的调用?
|
||
|
||
你在上面看到的屏幕截图概述了对隧道主机的调用,这些数据相当有限。幸运的是,`ngrok` 提供了一个非常好的仪表板,允许你检查所有调用:
|
||
|
||
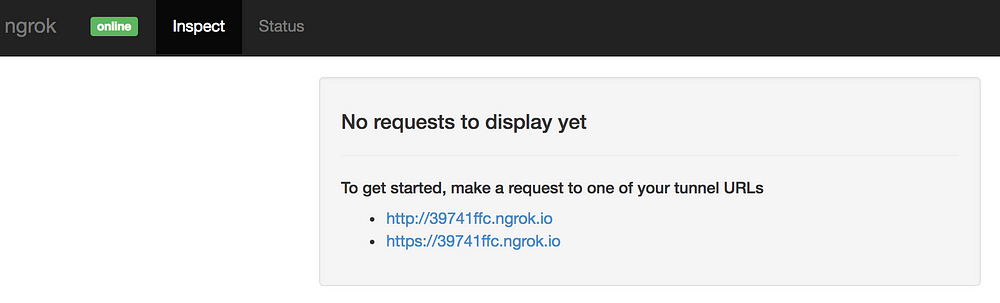
|
||
|
||
我不会深入研究这个问题,因为它是不言自明的,你只要运行它就行了。因此,我将解释如何在 Vagrant 虚拟机上访问它,因为它不是开箱即用的。
|
||
|
||
仪表板将允许你查看所有调用、其状态代码、标头和发送的数据。你将看到应用程序生成的响应。
|
||
|
||
仪表板的另一个优点是它允许你重放某个调用。假设你的 webhook 代码遇到了致命的错误,开始新的付款并等待 webhook 被调用将会很繁琐。重放上一个调用可以使你的开发过程更快。
|
||
|
||
默认情况下,仪表板可在 `http://localhost:4040` 访问。
|
||
|
||
### 虚拟机中的仪表盘
|
||
|
||
为了在 VM 中完成此工作,你必须执行一些额外的步骤:
|
||
|
||
首先,确保可以在端口 4040 上访问 VM。然后,在 VM 内创建一个文件已存放此配置:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
web_addr: 0.0.0.0:4040
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
现在,杀死仍在运行的 `ngrok` 进程,并使用稍微调整过的命令启动它:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
ngrok http -config=/path/to/config/ngrok.conf -host-header=rewrite webhook.example.vagrant:80
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
尽管 ID 已经更改,但你将看到类似于上一屏幕截图的屏幕。之前的网址不再有效,但你有了一个新网址。 此外,`Web Interface` URL 已更改:
|
||
|
||
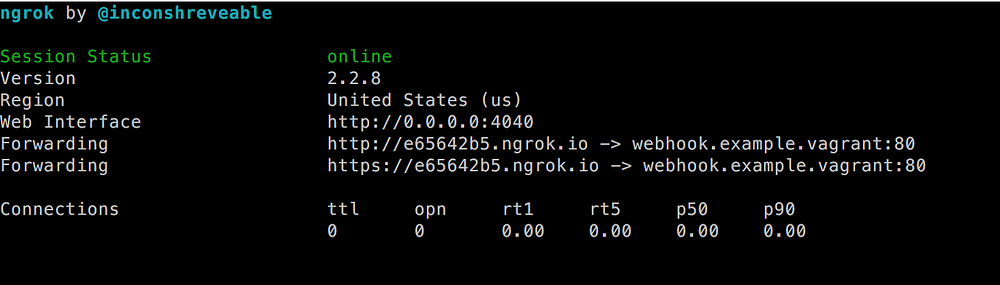
|
||
|
||
现在将浏览器指向 `http://webhook.example.vagrant:4040` 以访问仪表板。另外,对 `https://e65642b5.ngrok.io/webhook.php` 做个调用。这可能会导致你的浏览器出错,但仪表板应显示正有一个请求。
|
||
|
||
### 最后的备注
|
||
|
||
上面的例子是伪代码。原因是每个外部系统都以不同的方式使用 webhook。我试图基于一个虚构的 PSP 实现给出一个例子,因为可能很多开发人员在某个时刻肯定会处理付款。
|
||
|
||
请注意,你的 webhook 网址也可能被意图不好的其他人使用。确保验证发送给它的任何输入。
|
||
|
||
更好的的,可以向 URL 添加令牌,该令牌对于每个支付是唯一的。只有你的系统和发送 webhook 的系统才能知道此令牌。
|
||
|
||
祝你测试和调试你的 webhook 顺利!
|
||
|
||
注意:我没有在 Docker 上测试过本教程。但是,这个 Docker 容器看起来是一个很好的起点,并包含了明确的说明:[https://github.com/wernight/docker-ngrok][19] 。
|
||
|
||
--------
|
||
|
||
via: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/testing-webhooks-while-using-vagrant-for-development-98b5f3bedb1d
|
||
|
||
作者:[Stefan Doorn][a]
|
||
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:https://medium.freecodecamp.org/@stefandoorn
|
||
[1]:https://unsplash.com/photos/MYTyXb7fgG0?utm_source=unsplash&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=creditCopyText
|
||
[2]:https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=unsplash&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=creditCopyText
|
||
[3]:https://ngrok.com/download
|
||
[4]:https://www.npmjs.com/package/ngrok
|
||
[5]:http://webhook.example.vagrnat/
|
||
[6]:http://39741ffc.ngrok.io/
|
||
[7]:http://39741ffc.ngrok.io/
|
||
[8]:http://webhook.example.vagrant:4040/
|
||
[9]:https://e65642b5.ngrok.io/webhook.php.
|
||
[10]:https://sendgrid.com/blog/whats-webhook/
|
||
[11]:http://example.com/webhooks/payment-update%29
|
||
[12]:https://sendgrid.com/blog/whats-webhook/
|
||
[13]:https://ngrok.com/
|
||
[14]:https://ngrok.com/docs
|
||
[15]:http://39741ffc.ngrok.io%2C/
|
||
[16]:https://ngrok.com/docs#bind-tls
|
||
[17]:http://localhost:4040./
|
||
[18]:https://e65642b5.ngrok.io/webhook.php.
|
||
[19]:https://github.com/wernight/docker-ngrok
|
||
[20]:https://github.com/stefandoorn
|
||
[21]:https://twitter.com/stefan_doorn
|
||
[22]:https://www.linkedin.com/in/stefandoorn
|