mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-01 21:50:13 +08:00
73 lines
8.6 KiB
Markdown
73 lines
8.6 KiB
Markdown
The history of Android
|
||
================================================================================
|
||

|
||
The T-Mobile G1
|
||
Photo by T-Mobile
|
||
|
||
### Android 1.0—introducing Google Apps and actual hardware ###
|
||
|
||
By October 2008, Android 1.0 was ready for launch, and the OS debuted on the [T-Mobile G1][1] (AKA the HTC Dream). The G1 was released into a market dominated by the iPhone 3G and the [Nokia 1680 classic][2]. (Both of those phones went on to tie for the [best selling phone][3] of 2008, selling 35 million units each.) Hard numbers of G1 sales are tough to come by, but T-Mobile announced the device broke the one million units sold barrier in April 2009. It was way behind the competition by any measure.
|
||
|
||
The G1 was packing a single-core 528Mhz ARM 11 processor, an Adreno 130 GPU, 192MB of RAM, and a whopping 256MB of storage for the OS and Apps. It had a 3.2-inch, 320x480 display, which was mounted to a sliding mechanism that revealed a full hardware keyboard. So while Android software has certainly come a long way, the hardware has, too. Today, we can get much better specs than this in a watch form factor: the latest [Samsung smart watch][4] has 512MB of RAM and a 1GHz dual-core processor.
|
||
|
||
While the iPhone had a minimal amount of buttons, the G1 was the complete opposite, sporting almost every hardware control that was ever invented. It had call and end call buttons, home, back, and menu buttons, a shutter button for the camera, a volume rocker, a trackball, and, of course, about 50 keyboard buttons. Future Android devices would slowly back away from thousand-button interfaces, with nearly every new flagship lessening the number of buttons.
|
||
|
||
But for the first time, people saw Android running on actual hardware instead of a frustratingly slow emulator. Android 1.0 didn't have the smoothness, flare, or press coverage of the iPhone. It wasn't as capable as Windows Mobile 6.5. Still, it was a good start.
|
||
|
||

|
||
The default app selection of Android 1.0 and 0.9.
|
||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||
|
||
The core of Android 1.0 didn't look significantly different from the beta version released two months earlier, but the consumer product brought a ton more apps, including the full suite of Google apps. Calendar, Email, Gmail, IM, Market, Settings, Voice Dialer, and YouTube were all new. At the time, music was the dominant media type on smartphones, the king of which was the iTunes music store. Google didn't have an in-house music service of its own, so it tapped Amazon and bundled the Amazon MP3 store.
|
||
|
||
The most important addition to Android 1.0 was the debut of Google's store, called "Android Market Beta." While most companies were content with calling their app catalog some variant of "app store"—meaning a store that sold apps and only apps—Google had much wider ambitions. It went with the much more general name of "Android Market." The idea was that the Android Market would not just house apps, but everything you needed for your Android device.
|
||
|
||
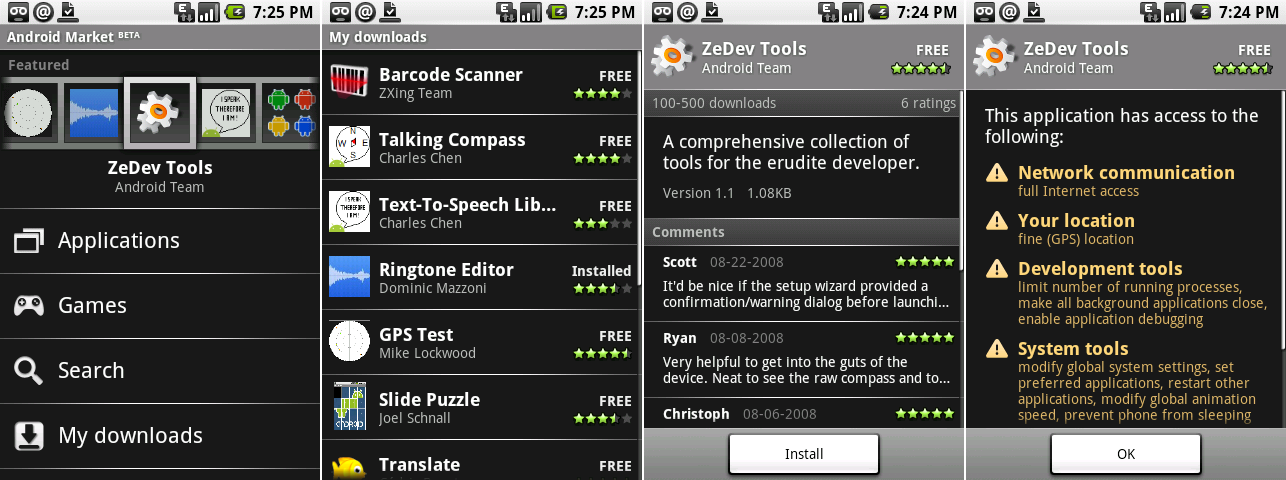
|
||
The first Android Market client. Screenshots show the main page, “my downloads," an app page, and an app permissions page.
|
||
Photo by [Google][5]
|
||
|
||
At the time, the Android Market only offered apps and games, and developers weren't even able to charge for them. Apple's App Store had a four-month head start on the Android Market, but Google's big differentiator was that Android's store was almost completely open. On the iPhone, apps were subject to review by Apple and had to meet design and technical guidelines. Potential apps also weren't allowed to duplicate the stock functionality. On the Android Market, developers were free to do whatever they wanted, including replacing the stock apps. The lack of control would turn out to be a blessing and a curse. It allowed developers to innovate on the existing functionality, but it also meant even the trashiest applications were allowed in.
|
||
|
||
Today, this client is another app that can no longer communicate with Google's servers. Luckily, it's one of the few early Android apps [actually documented][6] on the Internet. The main screen provided links to the common areas like Apps, Games, Search, and Downloads, and the top section had horizontally scrolling icons for featured apps. Search results and the "My Downloads" page displayed apps in a scrolling list, showing the name, developers, cost (at this point, always free), and rating. Individual app pages showed a brief description, install count, comments and ratings from users, and the all-important install button. This early Android Market didn’t support pictures, and the only field for developers was a description box with a 500-character limit. This made things like maintaining a changelog very difficult, as the only spot to put it was in the description.
|
||
|
||
Right out of the gate, the Android Market showed permissions that an app required before installing. This is something Apple wouldn't get around to implementing until 2012, after an iOS app was caught [uploading entire address books][7] to the cloud without the user's knowledge. The permissions display gave a full rundown of what permissions an app was using, although this version railroaded users into agreeing. There was an “OK" button, but no way to cancel other than the back button.
|
||
|
||
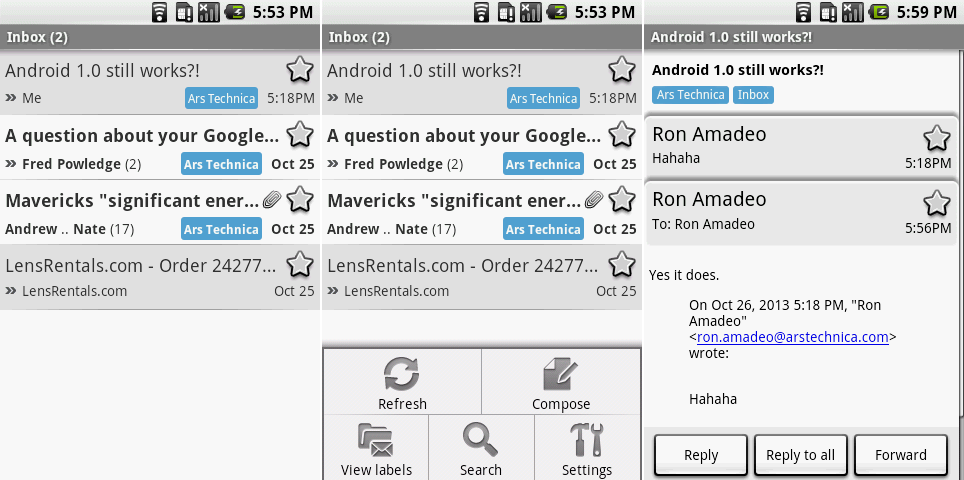
|
||
Gmail showing the inbox, the inbox with the menu open.
|
||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||
|
||
The next most important app was probably Gmail. Most of the base functionality was here already. Unviewed messages showed up in bold, and labels displayed as colored tags. Individual messages in the Inbox showed the subject, author(s), and number of replies in a conversation. The trademark Gmail star was here—a quick tap would star or unstar something. As usual for early versions of Android, the Menu housed all the buttons on the main inbox view. Once inside a message, though, things got a little more modern, with "reply" and "forward" buttons as permanent fixtures at the bottom of the screen. Individual replies could be expanded and collapsed just by tapping on them.
|
||
|
||
The rounded corners, shadows, and bubbly icons gave the whole app a "cartoonish" look, but it was a good start. Android's function-first philosophy was really coming through here: Gmail supported labels, threaded messaging, searching, and push e-mail.
|
||
|
||
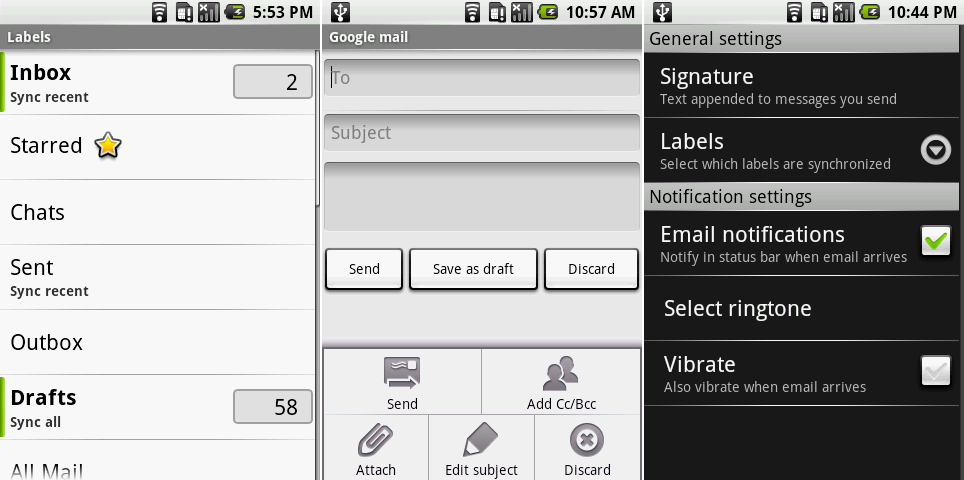
|
||
Gmail’s label view, compose screen, and settings on Android 1.0.
|
||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||
|
||
But if you thought Gmail was ugly, the Email app took it to another level. There was no separate inbox or folder view—everything was mashed into a single screen. The app presented you with a list of folders and tapping on one would expand the contents in-line. Unread messages were denoted with a green line on the left, and that was about it for the e-mail interface. The app supported IMAP and POP3 but not Exchange.
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
|
||
|
||
[@RonAmadeo][t]
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/6/
|
||
|
||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2008/10/android-g1-review/
|
||
[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nokia_1680_classic
|
||
[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_best-selling_mobile_phones#2008
|
||
[4]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/04/review-we-wear-samsungs-galaxy-gear-and-galaxy-fit-so-you-dont-have-to/
|
||
[5]:http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2008/08/android-market-user-driven-content.html
|
||
[6]:http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2008/08/android-market-user-driven-content.html
|
||
[7]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2012/02/path-addresses-privacy-controversy-but-social-apps-remain-a-risk-to-users/
|
||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo |