mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-10 22:21:11 +08:00
698 lines
21 KiB
Markdown
698 lines
21 KiB
Markdown
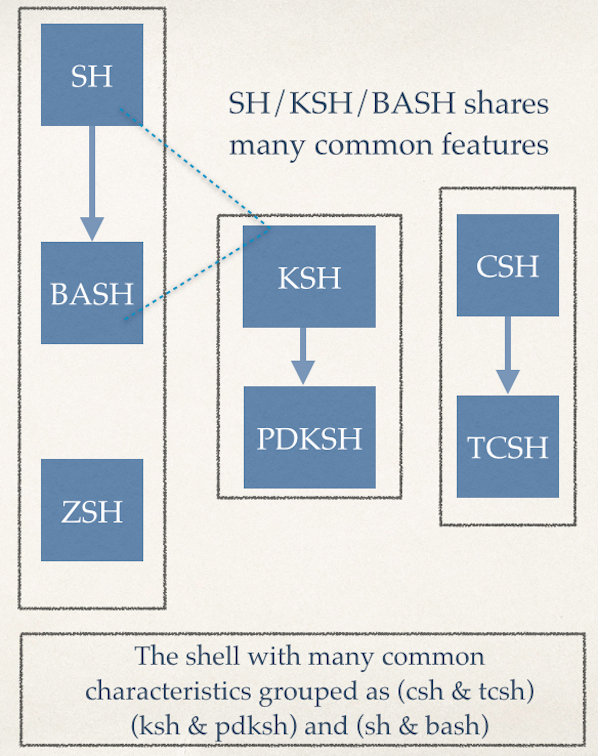
Shell入门:掌握Linux,OS X,Unix的Shell环境
|
||
================================================================================
|
||
在Linux或类Unix系统中,每个用户和进程都运行在一个特定环境中。这个环境包含了变量、设置、别名、函数以及更多的东西。下面是对Shell环境下一些常用命令的简单介绍,包括每个命令如何使用的例子,以及在命令行下设定你自己的环境来提高效率。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 找出你当前的shell ###
|
||
|
||
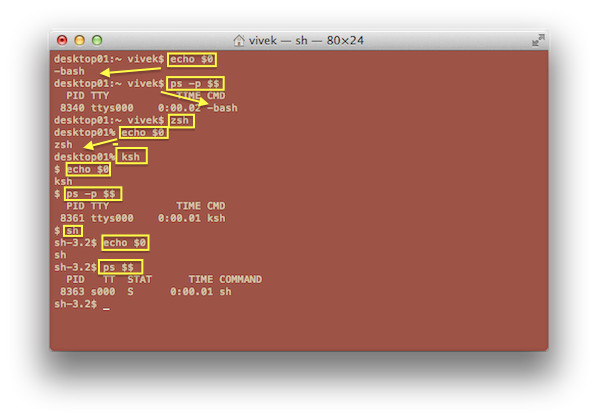
在终端应用中输入下面命令中的任意一个:
|
||
|
||
ps $$
|
||
ps -p $$
|
||
|
||
或者
|
||
|
||
echo "$0"
|
||
|
||
输出范例:
|
||
|
||
[][1]
|
||
|
||
*图1:找出当前的shell*
|
||
|
||
### 找出所有已安装的shell ###
|
||
|
||
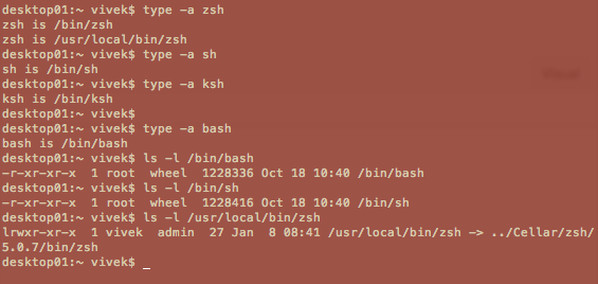
找到已安装shell的完整路径:
|
||
|
||
type -a zsh
|
||
type -a ksh
|
||
type -a sh
|
||
type -a bash
|
||
|
||
输出范例:
|
||
|
||
[][2]
|
||
|
||
*图2:找出shell的路径*
|
||
|
||
文件/etc/shells里包含了系统所支持的shell列表。每一行代表一个shell,是相对根目录的完整路径。用这个[cat命令][3]来查看这些数据:
|
||
|
||
cat /etc/shells
|
||
|
||
输出范例:
|
||
|
||
# List of acceptable shells for chpass(1).
|
||
# Ftpd will not allow users to connect who are not using
|
||
# one of these shells.
|
||
|
||
/bin/bash
|
||
/bin/csh
|
||
/bin/ksh
|
||
/bin/sh
|
||
/bin/tcsh
|
||
/bin/zsh
|
||
/usr/local/bin/fish
|
||
|
||
### 临时改变当前shell ###
|
||
|
||
只需要输入shell的名字。在下面的例子里,我从bash切换到了zsh:
|
||
|
||
zsh
|
||
|
||
这只是临时改变了系统shell。也叫做子shell。要从子/临时shell退出,输入下面的命令或者按下CTRL-D:
|
||
|
||
exit
|
||
|
||
### 找出子shell的层级或临时shell的嵌套层级 ###
|
||
|
||
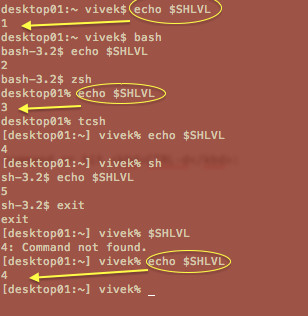
每个bash实例启动后,变量$SHLVL的值都会加一。输入下面的命令:
|
||
|
||
echo "$SHLVL"
|
||
|
||
示例输出:
|
||
|
||
[][4]
|
||
|
||
*图3:Bash shell嵌套层级(子shell数目)*
|
||
|
||
### 通过chsh命令永久变更系统shell ###
|
||
|
||
想要把当前系统shell从bash永久换成zsh?试试这个:
|
||
|
||
chsh -s /bin/zsh
|
||
|
||
想把其他用户的shell从bash永久换成ksh?试试这个:
|
||
|
||
sudo chsh -s /bin/ksh userNameHere
|
||
|
||
### 查看当前的环境变量 ###
|
||
|
||
你需要用到:
|
||
|
||
env
|
||
env | more
|
||
env | less
|
||
env | grep 'NAME'
|
||
|
||
示例输出:
|
||
|
||
TERM_PROGRAM=Apple_Terminal
|
||
SHELL=/bin/bash
|
||
TERM=xterm-256color
|
||
TMPDIR=/var/folders/6x/45252d6j1lqbtyy_xt62h40c0000gn/T/
|
||
Apple_PubSub_Socket_Render=/tmp/launch-djaOJg/Render
|
||
TERM_PROGRAM_VERSION=326
|
||
TERM_SESSION_ID=16F470E3-501C-498E-B315-D70E538DA825
|
||
USER=vivek
|
||
SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/launch-uQGJ2h/Listeners
|
||
__CF_USER_TEXT_ENCODING=0x1F5:0:0
|
||
PATH=/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/opt/X11/bin:/usr/local/go/bin:/usr/local/sbin/modemZapp:/Users/vivek/google-cloud-sdk/bin
|
||
__CHECKFIX1436934=1
|
||
PWD=/Users/vivek
|
||
SHLVL=2
|
||
HOME=/Users/vivek
|
||
LOGNAME=vivek
|
||
LC_CTYPE=UTF-8
|
||
DISPLAY=/tmp/launch-6hNAhh/org.macosforge.xquartz:0
|
||
_=/usr/bin/env
|
||
OLDPWD=/Users/vivek
|
||
|
||
下面是bash shell里一些常见变量的列表:
|
||
|
||
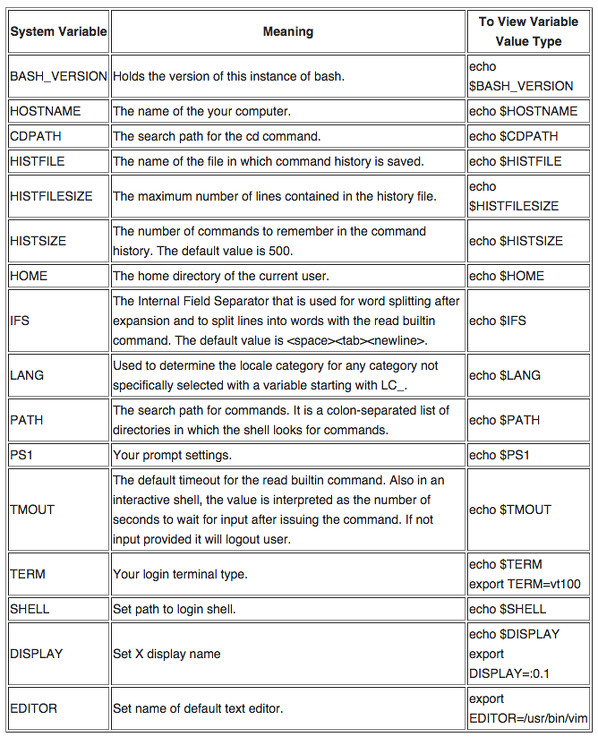
|
||
|
||
*图4:常见bash环境变量*
|
||
|
||
> **注意**:下面这些环境变量没事不要乱改。很可能会造成不稳定的shell会话:
|
||
>
|
||
> SHELL
|
||
>
|
||
> UID
|
||
>
|
||
> RANDOM
|
||
>
|
||
> PWD
|
||
>
|
||
> PPID
|
||
>
|
||
> SSH_AUTH_SOCK
|
||
>
|
||
> USER
|
||
>
|
||
> HOME
|
||
>
|
||
> LINENO
|
||
|
||
### 显示环境变量的值 ###
|
||
|
||
使用下面任意一条命令显示环境变量HOME的值:
|
||
|
||
## 使用printenv ##
|
||
printenv HOME
|
||
|
||
## 或者用echo ##
|
||
echo "$HOME"
|
||
|
||
# 考虑到可移植性,也可以用printf ##
|
||
printf "%s\n" "$HOME"
|
||
|
||
示例输出:
|
||
|
||
/home/vivek
|
||
|
||
### 增加或设定一个新环境变量 ###
|
||
|
||
下面是bash,zsh,sh和ksh的语法:
|
||
|
||
## 语法 ##
|
||
VAR=value
|
||
FOO=bar
|
||
|
||
## 设定vim为默认文本编辑器 ##
|
||
EDITOR=vim
|
||
export $EDITOR
|
||
|
||
## 考虑安全性,设定默认shell连接超时时间 ##
|
||
TMOUT=300
|
||
export TMOUT
|
||
|
||
## 你可以直接使用export命令设定命令的搜素路径 ##
|
||
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:/usr/local/bin:/path/to/mycoolapps
|
||
|
||
然后,使用printenv或者echo或printf命令查看环境变量PATH,EDITOR,和TMOUT的值:
|
||
|
||
printenv PATH
|
||
echo "$EDITOR"
|
||
printf "%s\n" $TMOUT
|
||
|
||
### 怎么修改一个现有的环境变量? ###
|
||
|
||
下面是语法:
|
||
|
||
export VAR=value
|
||
## 或者 ##
|
||
VAR=value
|
||
export $VAR
|
||
|
||
## 把默认文本编辑器从vim改为emacs ##
|
||
echo "$EDITOR" ## <--- 屏幕输出vim
|
||
EDITOR=emacs ## <--- 修改
|
||
export $EDITOR ## <--- 让修改在其他会话生效
|
||
echo "$EDITOR" ## <--- 屏幕输出emacs
|
||
|
||
**tcsh shell下增加和修改变量**的语法是下面这样的:
|
||
|
||
## 语法
|
||
setenv var value
|
||
printenv var
|
||
|
||
## 设置变量foo的值为bar ##
|
||
setenv foo bar
|
||
echo "$foo"
|
||
printenv foo
|
||
|
||
## 设置变量PATH ##
|
||
setenv PATH $PATH\:$HOME/bin
|
||
echo "$PATH"
|
||
|
||
## 设置变量PAGER ##
|
||
setenv PAGER most
|
||
printf "%s\n" $PAGER
|
||
|
||
### 找出bash shell的配置文件 ###
|
||
|
||
用下面的命令列出bash shell的文件:
|
||
|
||
ls -l ~/.bash* ~/.profile /etc/bash* /etc/profile
|
||
|
||
示例输出:
|
||
|
||
[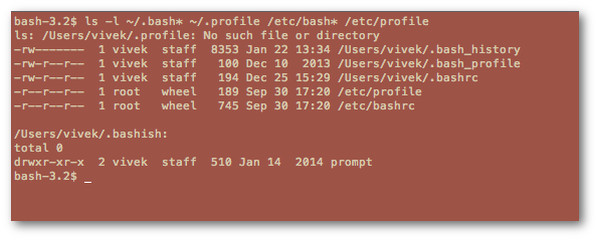][5]
|
||
|
||
*图5:列出bash的所有配置文件*
|
||
|
||
要查看所有的bash配置文件,输入:
|
||
|
||
less ~/.bash* ~/.profile /etc/bash* /etc/profile
|
||
|
||
可以使用文字编辑器比如vim或emacs来一个一个编辑bash配置文件:
|
||
|
||
vim ~/.bashrc
|
||
|
||
编辑/etc/目录下的文件,输入:
|
||
|
||
## 首先是备份,以防万一
|
||
sudo cp -v /etc/bashrc /etc/bashrc.bak.22_jan_15
|
||
|
||
########################################################################
|
||
## 然后,随心所欲随便改吧,好好玩玩shell环境或者提高一下效率:) ##
|
||
########################################################################
|
||
sudo vim /etc/bashrc
|
||
|
||
### 被Bash shell初始化过程中应用的文件搞糊涂了吗? ###
|
||
|
||
下面的"bash初始化文件"流程图应该有些帮助:
|
||
|
||
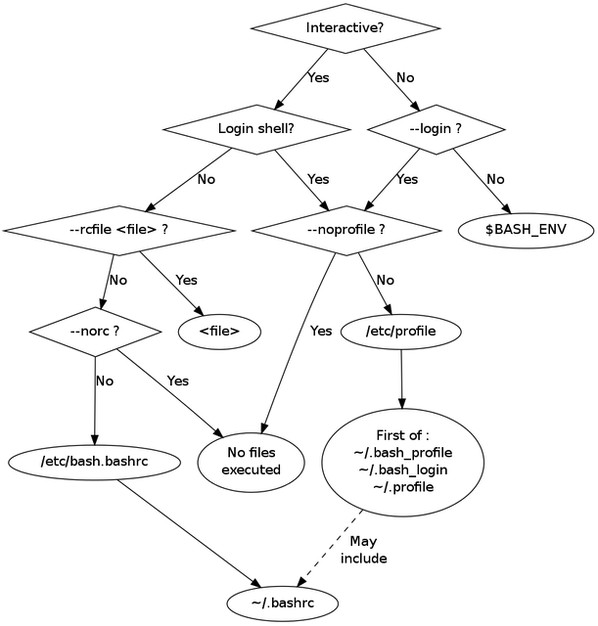
|
||
|
||
根据账户设定的默认shell,你的用户配置或系统配置可能是下面其中一种:
|
||
|
||
### 找出zsh shell配置文件 ###
|
||
|
||
zsh的[wiki][6]中建议用下面的命令:
|
||
|
||
strings =zsh | grep zshrc
|
||
|
||
示例输出:
|
||
|
||
/etc/zshrc
|
||
.zshrc
|
||
|
||
输入下面的命令列出你的zsh shell文件:
|
||
|
||
ls -l /etc/zsh/* /etc/profile ~/.z*
|
||
|
||
查看所有zsh配置文件:
|
||
|
||
less /etc/zsh/* /etc/profile ~/.z*
|
||
|
||
### 找出ksh shell配置文件 ###
|
||
|
||
1. 查看~/.profile或者/etc/profile文件。
|
||
|
||
### 找出tcsh shell配置文件 ###
|
||
|
||
1. C shell查看~/.login,~/.cshrc文件。
|
||
2. TC shell查看~/.tcshrc和~/.cshrc文件。
|
||
|
||
### 我可以写个类似这样每次登录时都自动执行的脚本吗? ###
|
||
|
||
是的,把你的命令或别名或其他设定添加到~/.bashrc(bash shell)或者~/.profile(sh/ksh/bash)或者~/.login(csh/tcsh)文件中。
|
||
|
||
### 我可以写个类似这样每次登出都自动执行的脚本吗? ###
|
||
|
||
是的,把你的命令或别名或其他设定添加到~/.bash_logout(bash)或者~/.logout(csh/tcsh)文件。
|
||
|
||
### history:获取关于shell会话的更多信息 ###
|
||
|
||
输入history命令来查看本次会话的历史:
|
||
|
||
history
|
||
|
||
示例输出:
|
||
|
||
9 ls
|
||
10 vi advanced-cache.php
|
||
11 cd ..
|
||
12 ls
|
||
13 w
|
||
14 cd ..
|
||
15 ls
|
||
16 pwd
|
||
17 ls
|
||
....
|
||
..
|
||
...
|
||
91 hddtemp /dev/sda
|
||
92 yum install hddtemp
|
||
93 hddtemp /dev/sda
|
||
94 hddtemp /dev/sg0
|
||
95 hddtemp /dev/sg1
|
||
96 smartctl -d ata -A /dev/sda | grep -i temperature
|
||
97 smartctl -d ata -A /dev/sg1 | grep -i temperature
|
||
98 smartctl -A /dev/sg1 | grep -i temperature
|
||
99 sensors
|
||
|
||
输入history 20来查看命令历史的后20条:
|
||
|
||
history 20
|
||
|
||
示例输出:
|
||
|
||
[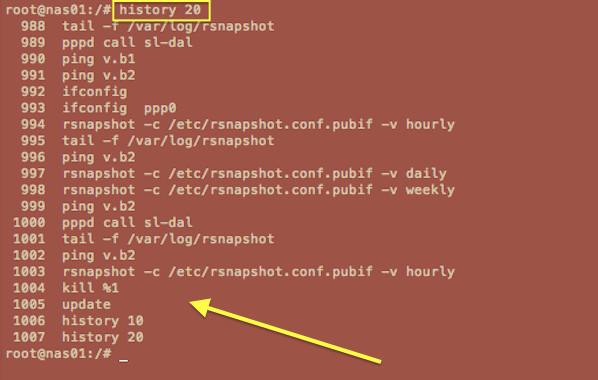][7]
|
||
|
||
*图6:在bash shell中使用history命令查看会话历史*
|
||
|
||
你可以重复使用之前的命令。简单地按下[上]或[下]方向键就可以查看之前的命令。在shell提示符下按下[CTRL-R]可以向后搜索历史缓存或文件来查找命令。重复最后一次命令,只需要在shell提示符下输入!!就好了:
|
||
|
||
ls -l /foo/bar
|
||
!!
|
||
|
||
在以上的历史记录中找到命令#93 (hddtemp /dev/sda),输入:
|
||
|
||
!93
|
||
|
||
### 使用sudo或su改变用户 ###
|
||
|
||
下面是语法:
|
||
|
||
su userName
|
||
|
||
## 登录为tom用户 ##
|
||
su tom
|
||
|
||
## 为用户tom打开一个新的shell会话 ##
|
||
su tom
|
||
|
||
## 登录为root用户 ##
|
||
su -
|
||
|
||
## sudo命令语法(必须在系统中配置有这个命令) ##
|
||
sudo -s
|
||
sudo tom
|
||
|
||
看看帖子"[Linux下使用其他用户身份运行命令][8]"更多地了解sudo,su和runuser命令。
|
||
|
||
### shell别名 ###
|
||
|
||
别名仅仅是命令的一个快捷方式。
|
||
|
||
### 列出所有的别名 ###
|
||
|
||
输入下面的命令:
|
||
|
||
alias
|
||
|
||
示例输出:
|
||
|
||
alias ..='cd ..'
|
||
alias ...='cd ../../../'
|
||
alias ....='cd ../../../../'
|
||
alias .....='cd ../../../../'
|
||
alias .4='cd ../../../../'
|
||
alias .5='cd ../../../../..'
|
||
alias bc='bc -l'
|
||
alias cd..='cd ..'
|
||
alias chgrp='chgrp --preserve-root'
|
||
alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root'
|
||
alias chown='chown --preserve-root'
|
||
alias cp='cp -i'
|
||
alias dnstop='dnstop -l 5 eth1'
|
||
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
|
||
alias ethtool='ethtool eth1'
|
||
|
||
### 设定一个别名 ###
|
||
|
||
bash/zsh语法:
|
||
|
||
alias c='clear'
|
||
alias down='sudo /sbin/shutdown -h now'
|
||
|
||
对于命令clear可以输入c别名,这样我们就可以输入c代替clear命令来清空屏幕:
|
||
|
||
c
|
||
|
||
或者输入down来关闭基于Linux的服务器:
|
||
|
||
down
|
||
|
||
你可以设定任意多的别名。看下"[Linux/Unix/Mac OS X系统中的30个方便的bash shell别名][9]"了解在类Unix系统中别名的实际应用。
|
||
|
||
### shell函数 ###
|
||
|
||
Bash/ksh/zsh函数允许你更进一步地配置shell环境。在这个例子中,我写了一个简单的名叫memcpu()的bash函数,用来显示前10个最占用CPU和内存的进程:
|
||
|
||
memcpu() { echo "*** Top 10 cpu eating process ***"; ps auxf | sort -nr -k 3 | head -10;
|
||
echo "*** Top 10 memory eating process ***"; ps auxf | sort -nr -k 4 | head -10; }
|
||
|
||
输入memcpu就可以在屏幕上看到下面的信息:
|
||
|
||
memcpu
|
||
|
||
*** Top 10 cpu eating process ***
|
||
nginx 39559 13.0 0.2 264020 35168 ? S 04:26 0:00 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nginx 39545 6.6 0.1 216484 13088 ? S 04:25 0:04 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nginx 39471 6.2 0.6 273352 81704 ? S 04:22 0:17 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nginx 39544 5.7 0.1 216484 13084 ? S 04:25 0:03 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nginx 39540 5.5 0.1 221260 19296 ? S 04:25 0:04 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nginx 39542 5.4 0.1 216484 13152 ? S 04:25 0:04 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nixcraft 39543 5.3 0.1 216484 14096 ? S 04:25 0:04 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nixcraft 39538 5.2 0.1 221248 18608 ? S 04:25 0:04 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nixcraft 39539 5.0 0.1 216484 16272 ? S 04:25 0:04 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nixcraft 39541 4.8 0.1 216484 14860 ? S 04:25 0:04 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
|
||
*** Top 10 memory eating process ***
|
||
498 63859 0.5 4.0 2429652 488084 ? Ssl 2014 177:41 memcached -d -p 11211 -u memcached -m 2048 -c 18288 -P /var/run/memcached/memcached.pid -l 10.10.29.68 -L
|
||
mysql 64221 4.2 3.4 4653600 419868 ? Sl 2014 1360:40 \_ /usr/libexec/mysqld --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --user=mysql --log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log --open-files-limit=65535 --pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid --socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
|
||
nixcraft 39418 0.4 1.1 295312 138624 ? S 04:17 0:02 | \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nixcraft 39419 0.5 0.9 290284 113036 ? S 04:18 0:02 | \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nixcraft 39464 0.7 0.8 294356 99200 ? S 04:20 0:02 | \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nixcraft 39469 0.3 0.7 288400 91256 ? S 04:20 0:01 | \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
nixcraft 39471 6.2 0.6 273352 81704 ? S 04:22 0:17 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
vivek 39261 2.2 0.6 253172 82812 ? S 04:05 0:28 \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
squid 9995 0.0 0.5 175152 72396 ? S 2014 27:00 \_ (squid) -f /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||
cybercit 3922 0.0 0.4 303380 56304 ? S Jan10 0:13 | \_ /usr/bin/php-cgi
|
||
|
||
看下"[如何编写和应用shell函数][10]"了解更多信息。
|
||
|
||
### 综合一下:定制你自己的Linux或Unix bash shell工作环境 ###
|
||
|
||
现在,你将使用bash shell配置自己的环境。我只介绍bash。但是理论上zsh,ksh和其他常用shell都差不多。让我们看看如何调整shell来适合我作为系统管理员的需求。编辑你的~/.bashrc文件来附加设定。下面是一些常用的配置选项。
|
||
|
||
#### #1: 设定bash路径和环境变量 ####
|
||
|
||
# 设定路径 ##
|
||
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin:/home/vivek/bin:/opt/firefox/bin:/opt/oraapp/bin
|
||
|
||
# 为cd命令设定路径
|
||
export CDPATH=.:$HOME:/var/www
|
||
|
||
使用less或more命令作为翻页器:
|
||
|
||
export PAGER=less
|
||
|
||
设定vim作为默认文本编辑器:
|
||
|
||
export EDITOR=vim
|
||
export VISUAL=vim
|
||
export SVN_EDITOR="$VISUAL"
|
||
|
||
设定Oracle数据库特别要求的参数:
|
||
|
||
export ORACLE_HOME=/usr/lib/oracle/xe/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/server
|
||
export ORACLE_SID=XE
|
||
export NLS_LANG=$($ORACLE_HOME/bin/nls_lang.sh)
|
||
|
||
设定JAVA_HOME和其他java路径,比如java版本:
|
||
|
||
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-6-sun/jre
|
||
|
||
# 把ORACLE和JAVA加入到PATH里
|
||
export PATH=$PATH:$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin
|
||
|
||
[使用密钥实现免密码登录][11]让ssh远程登录更安全:
|
||
|
||
# 再也不用输密码了
|
||
/usr/bin/keychain $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa
|
||
source $HOME/.keychain/$HOSTNAME-sh
|
||
|
||
最后,[打开bash命令补齐][12]
|
||
|
||
source /etc/bash_completion
|
||
|
||
#### #2: 设定bash命令提示符 ####
|
||
|
||
设定[定制的bash提示符(PS1)][13]:
|
||
|
||
PS1='{\u@\h:\w }\$ '
|
||
|
||
#### #3: 设定默认文件权限 ####
|
||
|
||
## 设定默认权限为644 ##
|
||
umask 022
|
||
|
||
#### #4: 调整shell命令历史设定 ####
|
||
|
||
# 不往命令历史里写入相同的行
|
||
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
|
||
|
||
# 忽略这些命令
|
||
HISTIGNORE="reboot:shutdown *:ls:pwd:exit:mount:man *:history"
|
||
|
||
# 通过HISTSIZE和HISTFILESIZE设定命令历史的长度
|
||
export HISTSIZE=10000
|
||
export HISTFILESIZE=10000
|
||
|
||
# 为命令历史文件增加时间戳
|
||
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T "
|
||
|
||
# 附加到命令历史文件,而不是覆盖
|
||
shopt -s histappend
|
||
|
||
#### #5: 设定shell会话的时区 ####
|
||
|
||
## 为我自己的shell会话设定IST(印度标准时间) ##
|
||
TZ=Asia/Kolkata
|
||
|
||
#### #6: 设定shell行编辑接口 ####
|
||
|
||
## 使用vi风格的行编辑接口,替代bash默认的emacs模式 ##
|
||
set -o vi
|
||
|
||
#### #7: 设定自己喜好的别名 ####
|
||
|
||
## 增加一些保护 ##
|
||
alias rm='rm -i'
|
||
alias cp='cp -i'
|
||
alias mv='mv -i'
|
||
|
||
## Memcached ##
|
||
alias mcdstats='/usr/bin/memcached-tool 10.10.29.68:11211 stats'
|
||
alias mcdshow='/usr/bin/memcached-tool 10.10.29.68:11211 display'
|
||
alias mcdflush='echo "flush_all" | nc 10.10.29.68 11211'
|
||
|
||
## 默认命令参数 ##
|
||
alias vi='vim'
|
||
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
|
||
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
|
||
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
|
||
alias bc='bc -l'
|
||
alias wget='wget -c'
|
||
alias chown='chown --preserve-root'
|
||
alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root'
|
||
alias chgrp='chgrp --preserve-root'
|
||
alias rm='rm -I --preserve-root'
|
||
alias ln='ln -i'
|
||
|
||
下面是一些额外的OS X Unix bash shell别名:
|
||
|
||
# 从bash打开桌面应用
|
||
alias preview="open -a '$PREVIEW'"
|
||
alias safari="open -a safari"
|
||
alias firefox="open -a firefox"
|
||
alias chrome="open -a google\ chrome"
|
||
alias f='open -a Finder '
|
||
|
||
# 清理那些.DS_Store文件
|
||
alias dsclean='find . -type f -name .DS_Store -delete'
|
||
|
||
#### #8: 寡人好色 ####
|
||
|
||
# 彩色的grep输出
|
||
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
|
||
export GREP_COLOR='1;33'
|
||
|
||
# 彩色的ls
|
||
export LSCOLORS='Gxfxcxdxdxegedabagacad'
|
||
# Gnu/linux的ls
|
||
ls='ls --color=auto'
|
||
|
||
# BSD/os x的ls命令
|
||
# alias ls='ls -G'
|
||
|
||
#### #9: 设定自己喜好的bash函数 ####
|
||
|
||
# 在屏幕上显示10个最近的历史命令
|
||
function ht {
|
||
history | awk '{a[$2]++}END{for(i in a){print a[i] " " i}}' | sort -rn | head
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
# host和ping命令的替代
|
||
# 接受http:// 或 https:// 或 ftps:// 名称用作域或主机名
|
||
_getdomainnameonly(){
|
||
local h="$1"
|
||
local f="${h,,}"
|
||
# remove protocol part of hostname
|
||
f="${f#http://}"
|
||
f="${f#https://}"
|
||
f="${f#ftp://}"
|
||
f="${f#scp://}"
|
||
f="${f#scp://}"
|
||
f="${f#sftp://}"
|
||
# remove username and/or username:password part of hostname
|
||
f="${f#*:*@}"
|
||
f="${f#*@}"
|
||
# remove all /foo/xyz.html*
|
||
f=${f%%/*}
|
||
# show domain name only
|
||
echo "$f"
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
ping(){
|
||
local array=( $@ ) # get all args in an array
|
||
local len=${#array[@]} # find the length of an array
|
||
local host=${array[$len-1]} # get the last arg
|
||
local args=${array[@]:0:$len-1} # get all args before the last arg in $@ in an array
|
||
local _ping="/bin/ping"
|
||
local c=$(_getdomainnameonly "$host")
|
||
[ "$t" != "$c" ] && echo "Sending ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to \"$c\"..."
|
||
# pass args and host
|
||
$_ping $args $c
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
host(){
|
||
local array=( $@ )
|
||
local len=${#array[@]}
|
||
local host=${array[$len-1]}
|
||
local args=${array[@]:0:$len-1}
|
||
local _host="/usr/bin/host"
|
||
local c=$(_getdomainnameonly "$host")
|
||
[ "$t" != "$c" ] && echo "Performing DNS lookups for \"$c\"..."
|
||
$_host $args $c
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#### #10: 通过shell shopt命令设定bash shell行为 ####
|
||
|
||
最后,你可以[使用set和shopt命令调整bash shell环境][14]:
|
||
|
||
# 目录拼写纠正
|
||
shopt -q -s cdspell
|
||
|
||
# 保证每次终端窗口改变大小后会更新显示
|
||
shopt -q -s checkwinsize
|
||
|
||
# 打开高级模式匹配功能
|
||
shopt -q -s extglob
|
||
|
||
# 退出时附加命令历史而不是覆盖
|
||
shopt -s histappend
|
||
|
||
# 在命令历史使用多行
|
||
shopt -q -s cmdhist
|
||
|
||
# 在后台任务结束时立刻通知
|
||
set -o notify
|
||
|
||
# 禁用[CTRL-D]来结束shell
|
||
set -o ignoreeof
|
||
|
||
### 总结 ###
|
||
|
||
这个帖子不难理解。它简短地将如何定制用户环境从头介绍了一下。要深入了解bash/ksh/zsh/csh/tcsh/的能力,我建议你用下面的命令阅读man文档:
|
||
|
||
man bash
|
||
man zsh
|
||
man tcsh
|
||
man ksh
|
||
|
||
> 这篇文章由Aadrika T. J.贡献;由admin编辑并增加了额外内容。你也可以[为nixCraft做出贡献][15]。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/howto/shell-primer-configuring-your-linux-unix-osx-environment/
|
||
|
||
作者:[nixCraft][a]
|
||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/about-us
|
||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/howto/shell-primer-configuring-your-linux-unix-osx-environment/attachment/finding-your-shell-like-a-pro/
|
||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/howto/shell-primer-configuring-your-linux-unix-osx-environment/attachment/finding-and-verifying-shell-path/
|
||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-unix-appleosx-bsd-cat-command-examples/
|
||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/howto/shell-primer-configuring-your-linux-unix-osx-environment/attachment/a-nested-shell-level-command/
|
||
[5]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/howto/shell-primer-configuring-your-linux-unix-osx-environment/attachment/list-bash-enviroment-variables/
|
||
[6]:http://zshwiki.org/home/config/files
|
||
[7]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/howto/shell-primer-configuring-your-linux-unix-osx-environment/attachment/history-outputs/
|
||
[8]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/open-source/command-line-hacks/linux-run-command-as-different-user/
|
||
[9]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/bash-aliases-mac-centos-linux-unix.html
|
||
[10]:http://bash.cyberciti.biz/guide/Chapter_9:_Functions
|
||
[11]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/ssh-passwordless-login-with-keychain-for-scripts/
|
||
[12]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-redhat-scientific-linuxenable-bash-completion/
|
||
[13]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-linux-unix-bash-shell-setup-prompt.html
|
||
[14]:http://bash.cyberciti.biz/guide/Setting_shell_options
|
||
[15]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/write-for-nixcraft/
|