4.2 KiB
lnav: Advanced Log File Viewer for Linux Desktops and Servers
If you want to debug or troubleshoot any issues, you need an advanced log file viewer like lnav – which works wonders in the terminal for any Linux system.
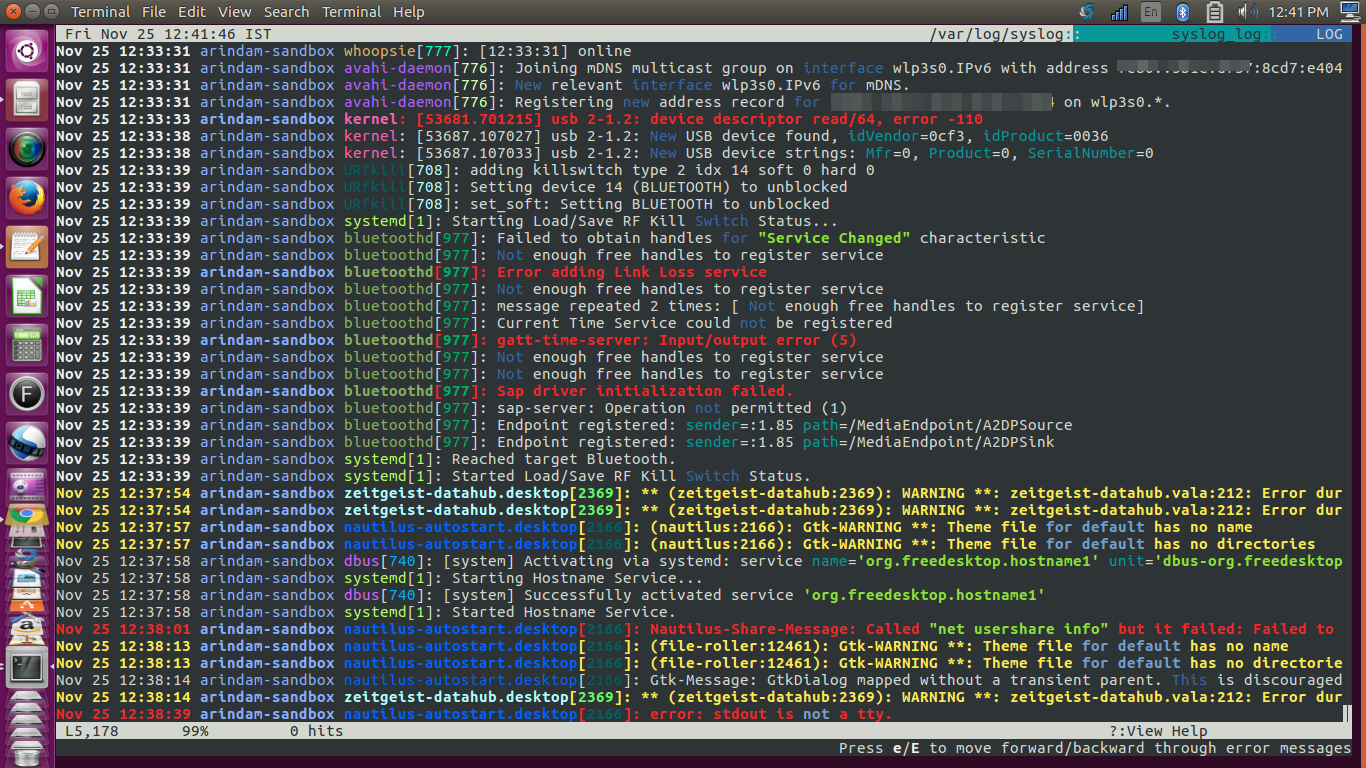
lnav: Log file viewer
lnav can unzip all the compressed log files on the fly and merge them together for a nice display. The display is parsed and formatted based on the types of errors/warnings – this helps to quickly glance through the thousands of logs, especially in servers.
While analysing the logs, timestamps are very important. So lnav merges multiple logs based on timestamps, which is very helpful for tracking down system issues.
Most of the important log file format detection is built-in; see below:
- Common Web Access Log format
- CUPS page_log
- Syslog
- Glog
- VMware ESXi/vCenter Logs
- dpkg.log
- uwsgi
- “Generic” – Any message that starts with a timestamp
- Strace
- sudo
- GZIP, BZIP
That is not all; lnav is also capable of the below features, making it an important app for Linux systems.
- Filter messages based on regular expression
- A timeline view of errors
- Pretty-Print view- helps to reformat
- Query Log using SQL
- A log is updated in real-time while being searched.
- Syntax highlight via regular expression (say you want to find out an IP address in the entire log)
- Tab completion of any word from the log which is displayed !!
To view the screenshots of the above features and learn more, visit this page.
How to Install
This program is available in official Ubuntu, Debian repo. Install it using the following command.
sudo apt install lnav
And for Fedora, RHEL users, use the below command:
sudo dnf install lnav
Also the developers provides an offline standalone executable which you don’t need to install. You can download the zip from the GitHub release page and execute as:
./lnav
Note: It’s also available for macOS which you can find in the above GitHub page.
lnav: How to use (Basics)
The simple command syntax is:
lnav [options] [logfile1 logfile2 …]
If you run just lnav from the command, it shows all the logs from your system (/var/log/messages and /var/log/syslog)
lnav
To view any specific log file, provide it via the command line:
lnav /var/log/syslog
Add timestamp in your log output using -t parameter
lnav -t /var/log/syslog
Here are some of the key switches of lnav
-d file Write debug messages to the given file.-a Load all of the most recent log file types.-r Load older rotated log files as well.-t Prepend timestamps to the lines of data being read inon the standard input.-w file Write the contents of the standard input to this file.-c cmd Execute a command after the files have been loaded.-f path Execute the commands in the given file.-n Run without the curses UI. (headless mode)
For further reading and exploration, visit the official documentation.
Next:How to Make LibreOffice Look Like Microsoft Office
via: https://www.debugpoint.com/advanced-log-file-viewer-lnav-ubuntu-linux/