mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
49 lines
2.1 KiB
Markdown
49 lines
2.1 KiB
Markdown
Linux有问必答:如何在脚本中获取进程ID(PID)
|
||
================================================================================
|
||
> **提问**: 我想要知道运行中脚本子shell的进程id。我该如何在shell脚本中得到PID。
|
||
|
||
当我在执行shell脚本时,它会启动一个叫子shell的进程。作为主shell的子进程,子shell将shell脚本中的命令作为批处理运行(因此称为“批处理进程”)。
|
||
|
||
在某些情况下,你也许想要知道运行中的子shell的PID。这个PID信息可以在不同的情况下使用。比如,你可以使用shell脚本的PID在/tmp下创建一个唯一的临时文件。有时侯脚本需要检测所有运行的进程,它可以从进程列表中排除自身的子shell。
|
||
|
||
在bash中,**子shell进程的PID**存储在一个特殊的变量‘$$’中。这个变量只读,你不可以在脚本中修改它。比如:
|
||
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
|
||
echo "PID of this script: $$"
|
||
|
||
上面的脚本会得到下面的输出:
|
||
|
||
PID of this script: 6583
|
||
|
||
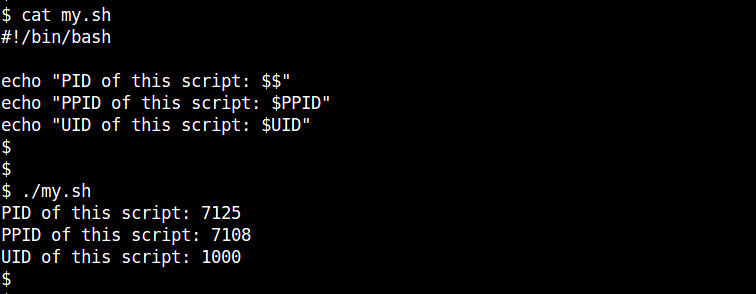
除了$$, bash shell还会导出其他的只读变量。比如,PPID存储子shell父进程的ID(也就是主shell)。UID存储了执行这个脚本的当前用户ID。比如:
|
||
|
||
#!/bin/bash
|
||
|
||
echo "PID of this script: $$"
|
||
echo "PPID of this script: $PPID"
|
||
echo "UID of this script: $UID"
|
||
|
||
输出是:
|
||
|
||
PID of this script: 6686
|
||
PPID of this script: 4656
|
||
UID of this script: 1000
|
||
|
||
上面输出中,PID每次执行都会变化。这个因为每次运行都会创建一个新的shell。另一方面,PPID每次都会一样只要你在同一个shell中运行。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
对于所有bash内置变量列表,参考man页。
|
||
|
||
$ man bash
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/process-id-pid-shell-script.html
|
||
|
||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|