mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
169 lines
6.5 KiB
Markdown
169 lines
6.5 KiB
Markdown
5 Ways to Find a ‘Binary Command’ Description and Location on File System
|
||
============================================================
|
||
|
||
With the thousands of [commands/programs available in Linux systems][1], knowing the type and purpose of a given command as well as its location (absolute path) on the system can be a little challenge for newbies.
|
||
|
||
Knowing a few details of commands/programs not only helps a [Linux user master the numerous commands][2], but it also enables a user understand what operations on the system to use them for, either from the command line or a script.
|
||
|
||
Therefore, in this article we will explain to you five useful commands for showing a short description and the location of a given command.
|
||
|
||
To discover new commands on your system look into all the directories in your PATH environmental variable. These directories store all the installed commands/programs on the system.
|
||
|
||
Once you find an interesting command name, before you proceed to read more about it probably in the man page, try to gather some shallow information about it as follows.
|
||
|
||
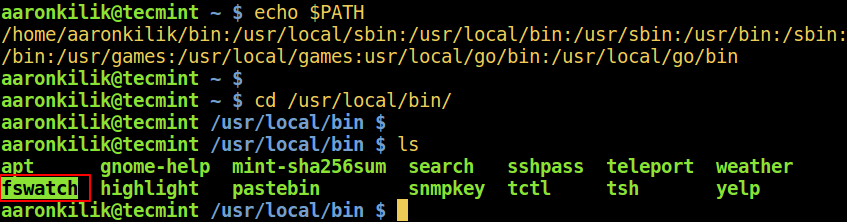
Assuming you have echoed the values of PATH and moved into the directory /usr/local/bin and noticed a new command called [fswatch (monitors file modification changes)][3]:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ echo $PATH
|
||
$ cd /usr/local/bin
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][4]
|
||
|
||
Find New Commands in Linux
|
||
|
||
Now let’s find out the description and location of the fswatch command using following different ways in Linux.
|
||
|
||
### 1\. whatis Command
|
||
|
||
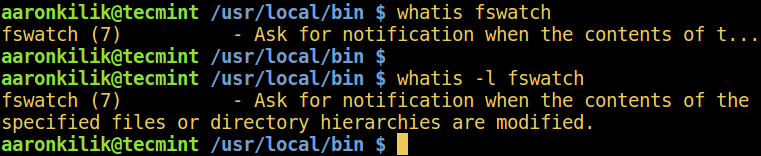
whatis is used to display one-line manual page descriptions of the command name (such as fswatch in the command below) you enter as an argument.
|
||
|
||
If the description is too long some parts are trimmed of by default, use the `-l` flag to show a complete description.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ whatis fswatch
|
||
$ whatis -l fswatch
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][5]
|
||
|
||
Linux whatis Command Example
|
||
|
||
### 2\. apropos Command
|
||
|
||
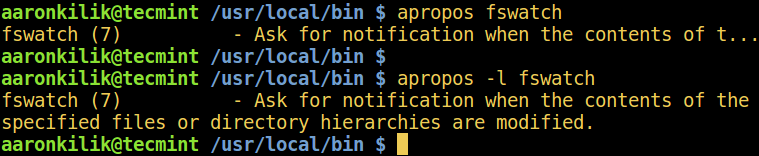
apropos searches for the manual page names and descriptions of the keyword (considered a regex, which is the command name) provided.
|
||
|
||
The `-l` option enables showing of the compete description.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ apropos fswatch
|
||
$ apropos -l fswatch
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][6]
|
||
|
||
Linux apropos Command Example
|
||
|
||
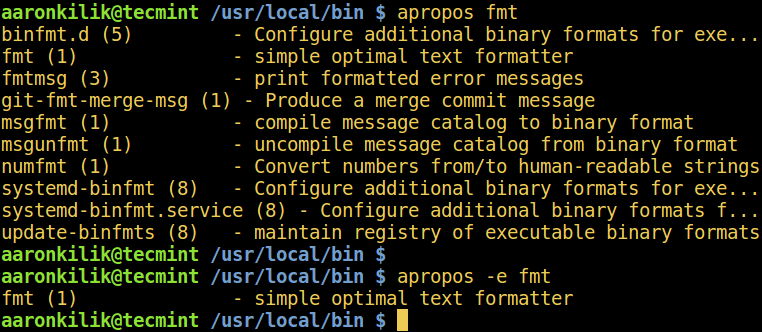
By default, apropos may show an output of all matched lines, as in the example below. You can only match the exact keyword using the `-e` switch:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ apropos fmt
|
||
$ apropos -e fmt
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][7]
|
||
|
||
Linux apropos Command Show by Keyword
|
||
|
||
### 3\. type Command
|
||
|
||
type tells you the full pathname of a given command, additionally, in case the command name entered is not a program that exists as a separate disk file, type also tells you the command classification:
|
||
|
||
1. Shell built-in command or
|
||
2. Shell keyword or reserved word or
|
||
3. An alias
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ type fswatch
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][8]
|
||
|
||
Linux type Command Example
|
||
|
||
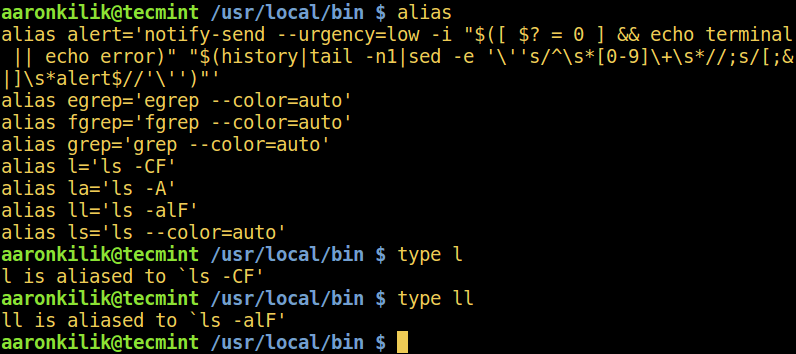
When the command is an alias for another command, type shows the command executed when the alias is run. Use the alias command to view all aliases created on your system:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ alias
|
||
$ type l
|
||
$ type ll
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][9]
|
||
|
||
Show All Aliases in Linux
|
||
|
||
### 4\. which Command
|
||
|
||
which helps to locate a command, it prints the absolute command path as below:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ which fswatch
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||

|
||
][10]
|
||
|
||
Find Linux Command Location
|
||
|
||
Some binaries can be stored in more than one directory under the PATH, use the `-a` flag to show all matching pathnames.
|
||
|
||
### 5\. whereis Command
|
||
|
||
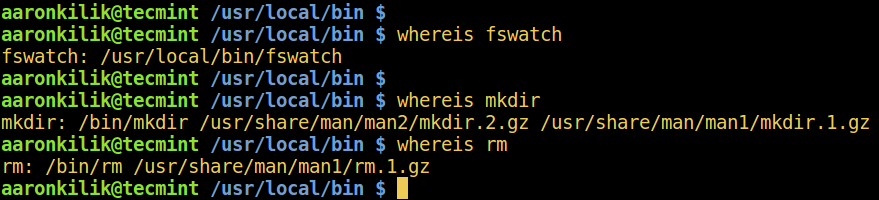
whereis command locates the binary, source, and manual page files for the command name provided as follows:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ whereis fswatch
|
||
$ whereis mkdir
|
||
$ whereis rm
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][11]
|
||
|
||
Linux whereis Command Example
|
||
|
||
Although the commands above may be vital in finding some quick info about a command/program, opening and reading through its manual page always provides a full documentation, including a list of other related programs:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
$ man fswatch
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
In this article, we reviewed five simple commands used to display short manual page descriptions and location of a command. You can make a contribution to this post or ask a question via the feedback section below.
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
作者简介:
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-command-description-and-location/
|
||
|
||
作者:[Aaron Kili ][a]
|
||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/category/top-tools/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/tag/linux-tricks/
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/fswatch-monitors-files-and-directory-changes-modifications-in-linux/
|
||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Find-New-Commands-in-Linux.png
|
||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Whatis-Command-Example.png
|
||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Linux-apropos-Command-Example.png
|
||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Linux-apropos-Command-Keyword-Example.png
|
||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Linux-type-Command-Example.png
|
||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Show-All-Aliases-in-Linux.png
|
||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Find-Linux-Command-Location.png
|
||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Linux-whereis-Command-Example.png
|