mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
110 lines
8.0 KiB
Markdown
110 lines
8.0 KiB
Markdown
How to block network traffic by country on Linux
|
|
================================================================================
|
|
As a system admin who maintains production Linux servers, there are circumstances where you need to **selectively block or allow network traffic based on geographic locations**. For example, you are experiencing denial-of-service attacks mostly originating from IP addresses registered with a particular country. You want to block SSH logins from unknown foreign countries for security reasons. Your company has a distribution right to online videos, which requires it to legally stream to particular countries only. You need to prevent any local host from uploading documents to any non-US remote cloud storage due to geo-restriction company policies.
|
|
|
|
All these scenarios require an ability to set up a firewall which does **country-based traffic filtering**. There are a couple of ways to do that. For one, you can use TCP wrappers to set up conditional blocking for individual applications (e.g., SSH, NFS, httpd). The downside is that the application you want to protect must be built with TCP wrappers support. Besides, TCP wrappers are not universally available across different platforms (e.g., Arch Linux [dropped][2] its support). An alternative approach is to set up [ipset][3] with country-based GeoIP information and apply it to iptables rules. The latter approach is more promising as the iptables-based filtering is application-agnostic and easy to set up.
|
|
|
|
In this tutorial, I am going to present **another iptables-based GeoIP filtering which is implemented with xtables-addons**. For those unfamiliar with it, xtables-addons is a suite of extensions for netfilter/iptables. Included in xtables-addons is a module called xt_geoip which extends the netfilter/iptables to filter, NAT or mangle packets based on source/destination countries. For you to use xt_geoip, you don't need to recompile the kernel or iptables, but only need to build xtables-addons as modules, using the current kernel build environment (/lib/modules/`uname -r`/build). Reboot is not required either. As soon as you build and install xtables-addons, xt_geoip is immediately usable with iptables.
|
|
|
|
As for the comparison between xt_geoip and ipset, the [official source][3] mentions that xt_geoip is superior to ipset in terms of memory foot print. But in terms of matching speed, hash-based ipset might have an edge.
|
|
|
|
In the rest of the tutorial, I am going to show **how to use iptables/xt_geoip to block network traffic based on its source/destination countries**.
|
|
|
|
### Install Xtables-addons on Linux ###
|
|
|
|
Here is how you can compile and install xtables-addons on various Linux platforms.
|
|
|
|
To build xtables-addons, you need to install a couple of dependent packages first.
|
|
|
|
#### Install Dependencies on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ####
|
|
|
|
$ sudo apt-get install iptables-dev xtables-addons-common libtext-csv-xs-perl pkg-config
|
|
|
|
#### Install Dependencies on CentOS, RHEL or Fedora ####
|
|
|
|
CentOS/RHEL 6 requires EPEL repository being set up first (for perl-Text-CSV_XS).
|
|
|
|
$ sudo yum install gcc-c++ make automake kernel-devel-`uname -r` wget unzip iptables-devel perl-Text-CSV_XS
|
|
|
|
#### Compile and Install Xtables-addons ####
|
|
|
|
Download the latest `xtables-addons` source code from the [official site][4], and build/install it as follows.
|
|
|
|
$ wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/xtables-addons/Xtables-addons/xtables-addons-2.10.tar.xz
|
|
$ tar xf xtables-addons-2.10.tar.xz
|
|
$ cd xtables-addons-2.10
|
|
$ ./configure
|
|
$ make
|
|
$ sudo make install
|
|
|
|
Note that for Red Hat based systems (CentOS, RHEL, Fedora) which have SELinux enabled by default, it is necessary to adjust SELinux policy as follows. Otherwise, SELinux will prevent iptables from loading xt_geoip module.
|
|
|
|
$ sudo chcon -vR --user=system_u /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/extra/*.ko
|
|
$ sudo chcon -vR --type=lib_t /lib64/xtables/*.so
|
|
|
|
### Install GeoIP Database for Xtables-addons ###
|
|
|
|
The next step is to install GeoIP database which will be used by xt_geoip for IP-to-country mapping. Conveniently, the xtables-addons source package comes with two helper scripts for downloading GeoIP database from MaxMind and converting it into a binary form recognized by xt_geoip. These scripts are found in geoip folder inside the source package. Follow the instructions below to build and install GeoIP database on your system.
|
|
|
|
$ cd geoip
|
|
$ ./xt_geoip_dl
|
|
$ ./xt_geoip_build GeoIPCountryWhois.csv
|
|
$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/share/xt_geoip
|
|
$ sudo cp -r {BE,LE} /usr/share/xt_geoip
|
|
|
|
According to [MaxMind][5], their GeoIP database is 99.8% accurate on a country-level, and the database is updated every month. To keep the locally installed GeoIP database up-to-date, you want to set up a monthly [cron job][6] to refresh the local GeoIP database as often.
|
|
|
|
### Block Network Traffic Originating from or Destined to a Country ###
|
|
|
|
Once xt_geoip module and GeoIP database are installed, you can immediately use the geoip match options in iptables command.
|
|
|
|
$ sudo iptables -m geoip --src-cc country[,country...] --dst-cc country[,country...]
|
|
|
|
Countries you want to block are specified using [two-letter ISO3166 code][7] (e.g., US (United States), CN (China), IN (India), FR (France)).
|
|
|
|
For example, if you want to block incoming traffic from Yemen (YE) and Zambia (ZM), the following iptables command will do.
|
|
|
|
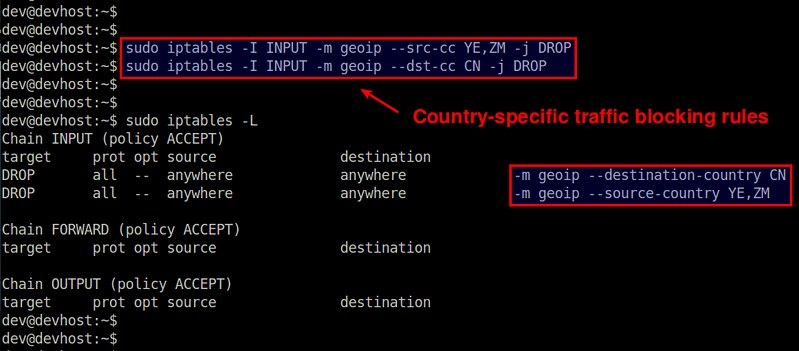
$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m geoip --src-cc YE,ZM -j DROP
|
|
|
|
If you want to block outgoing traffic destined to China (CN), run the following command.
|
|
|
|
$ sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -m geoip --dst-cc CN -j DROP
|
|
|
|
The matching condition can also be "negated" by prepending "!" to "--src-cc" or "--dst-cc". For example:
|
|
|
|
If you want to block all incoming non-US traffic on your server, run this:
|
|
|
|
$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m geoip ! --src-cc US -j DROP
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### For Firewall-cmd Users ####
|
|
|
|
Some distros such as CentOS/RHEL 7 or Fedora have replaced iptables with firewalld as the default firewall service. On such systems, you can use firewall-cmd to block traffic using xt_geoip similarly. The above three examples can be rewritten with firewall-cmd as follows.
|
|
|
|
$ sudo firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 0 -m geoip --src-cc YE,ZM -j DROP
|
|
$ sudo firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter OUTPUT 0 -m geoip --dst-cc CN -j DROP
|
|
$ sudo firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 0 -m geoip ! --src-cc US -j DROP
|
|
|
|
### Conclusion ###
|
|
|
|
In this tutorial, I presented iptables/xt_geoip which is an easy way to filter network packets based on their source/destination countries. This can be a useful arsenal to deploy in your firewall system if needed. As a final word of caution, I should mention that GeoIP-based traffic filtering is not a foolproof way to ban certain countries on your server. GeoIP database is by nature inaccurate/incomplete, and source/destination geography can easily be spoofed using VPN, Tor or any compromised relay hosts. Geography-based filtering can even block legitimate traffic that should not be banned. Understand this limitation before you decide to deploy it in your production environment.
|
|
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
|
via: http://xmodulo.com/block-network-traffic-by-country-linux.html
|
|
|
|
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
|
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
|
|
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
|
[1]:https://www.archlinux.org/news/dropping-tcp_wrappers-support/
|
|
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/block-unwanted-ip-addresses-linux.html
|
|
[3]:http://xtables-addons.sourceforge.net/geoip.php
|
|
[4]:http://xtables-addons.sourceforge.net/
|
|
[5]:https://support.maxmind.com/geoip-faq/geoip2-and-geoip-legacy-databases/how-accurate-are-your-geoip2-and-geoip-legacy-databases/
|
|
[6]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/add-cron-job-linux.html
|
|
[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_3166-1 |