7.5 KiB
15 Interview Questions on Linux “ls” Command – Part 1
The listing command in UNIX and UNIX like operating System ‘ls‘ is one of the most basic and widely used utility in command-line. It is POSIX compliant utility available for GNU coreutils and BSD variants. The ‘ls’ command can be used with a variety of options to get desired results. This article aims at deep insight of file listing command in Linux with relevant examples.
1. How will you List files from a directory?
Ans: The Linux file listing command ‘ls‘ comes to rescue here.
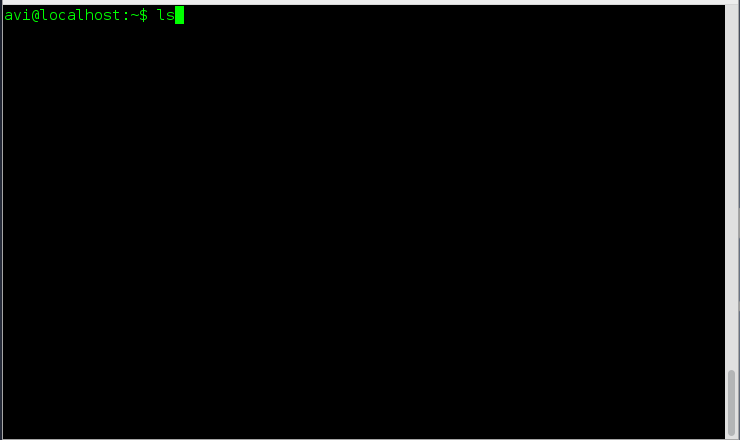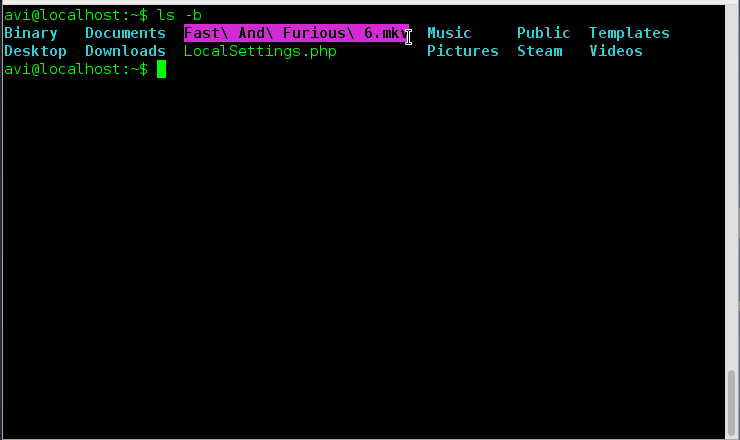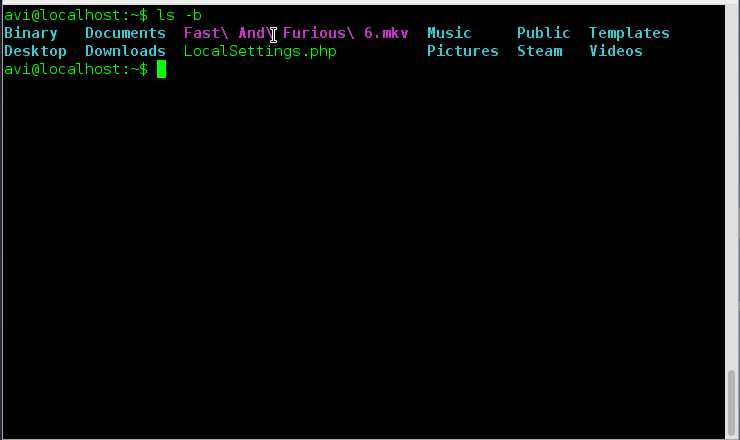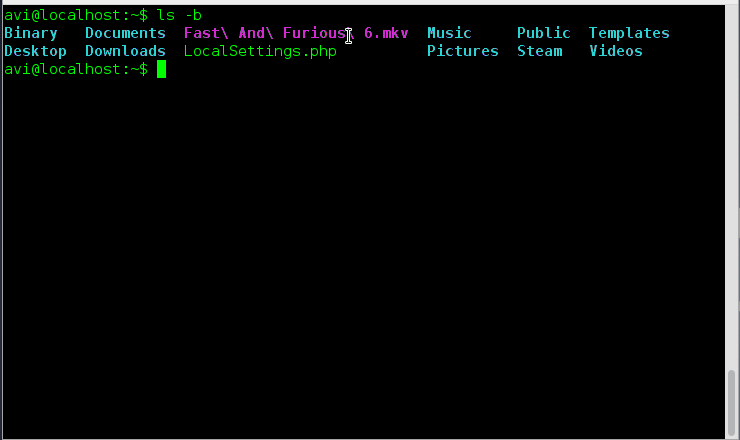
# ls
Alternatively, we can use ‘echo‘ command to list files within a directory in association with wildcard (*).
# echo *
2. How will you list all the directories only using echo command?
# echo */
3. How will you list all the files within a directory including hidden files aka (.) dot files?
Ans: We need to use option ‘-a‘ (list hidden files) with command ‘ls‘.
# ls -a
4. How do you list all the files within a directory including hidden files, but do not list implied ‘.’ and ‘..’?
Ans: We need to use option ‘-A‘ (do not list implied . and ..) with command ‘ls‘.
# ls -A
5. How will you print the content of a directory in long format listing?
Ans: We need to use option ‘l‘ (long format) with command ‘ls‘.
# ls -l
In the above example, the output seems like.
drwxr-xr-x 5 avi tecmint 4096 Sep 30 11:31 Binary
Here, drwxr-xr-x is file permission for owner, group and world. Owner has Read(r), Write(w) and Execute(x) permission. The group to which this file belongs has Read(r) and Execute(x) permission but not Write(w) permission, same permission implies for the world that have access to this file.
- The Initial ‘d‘ means its a Directory.
- Number ‘5‘ represents Symbolic Link.
- The File Binary belongs to user avi and group tecmint.
- Sep 30 11:31 represents the date and time it was last modified.
6. You are supposed to print the content of directory in long format listing, showing hidden/dot files. How will you achieve this?
Ans: We need to use option ‘-a‘ (list hidden files) and ‘-l‘ (long listing) together with command ‘ls‘.
# ls -la
Alternatively We can use option ‘-A‘ and ‘-l‘ with ‘ls‘ command, if we do not want to list implied ‘.’ and ‘..’.
# ls -lA
7. How will you figure out the author of each file?
Ans: We need to use option ‘–author‘ along with option ‘-l‘ to print the author name of each file.
# ls --author -l
8. How will you print escape for non-graphic character?
Ans: We just need to use option ‘-b‘ to print escape for non-graphic character.
# ls -b
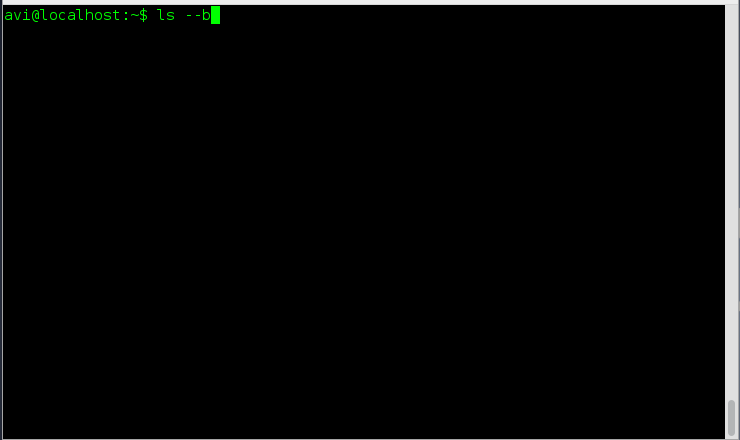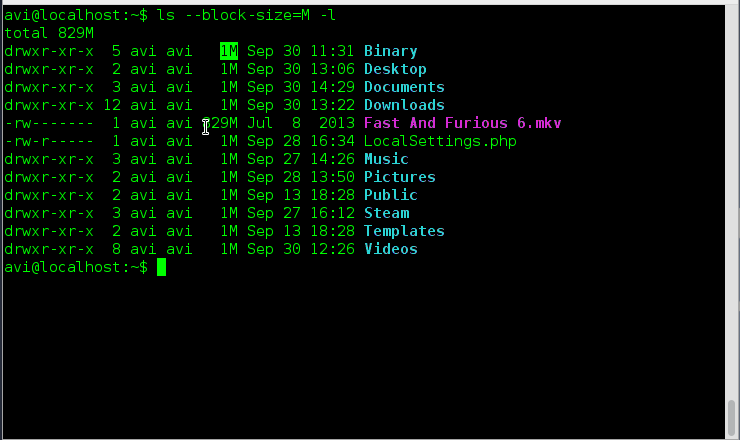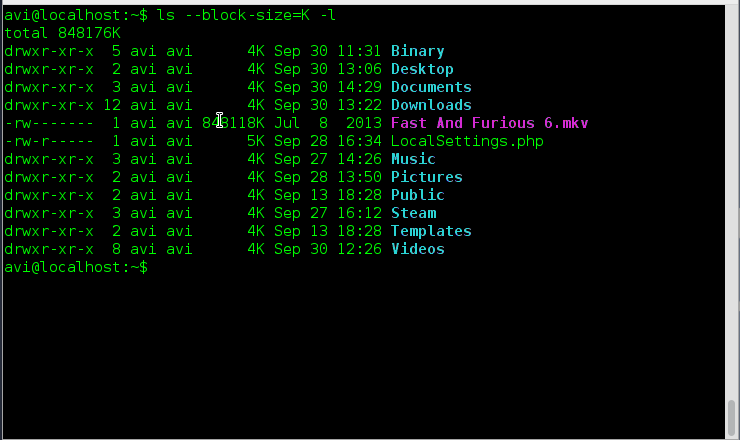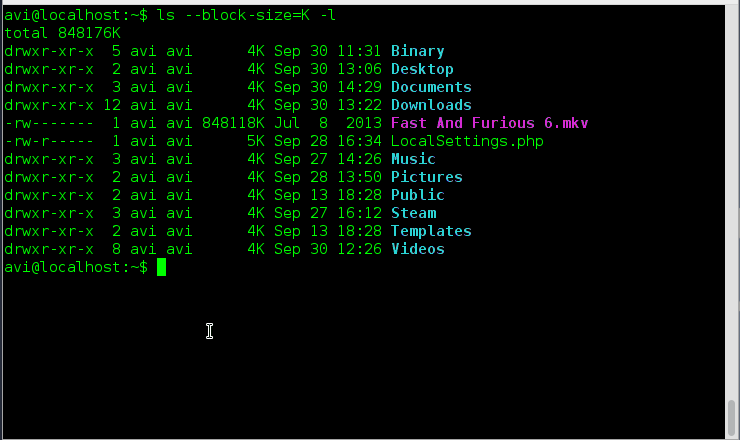
9. List the size of files and folders in desired scale format. How will you achieve this?
Ans: Here option ‘–block-size=scale‘ along with option ‘-l‘ needs to be used. We need to remove ‘scale’ in the example with the desired scale viz M, K, etc.
# ls --block-size=M -l
# ls --block-size=K -l
10. List the files within a directory, but don’t show the backup files, i.e., those files that end with ~.
Ans: Here option ‘-B‘ (do not list implied entries ending with ~) comes to rescue.
# ls -B
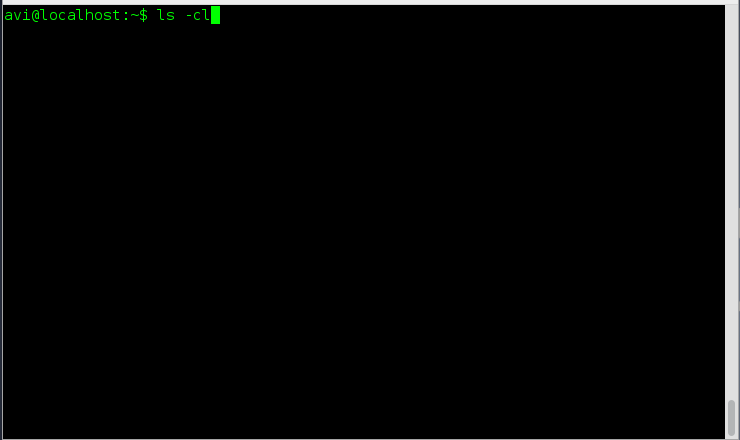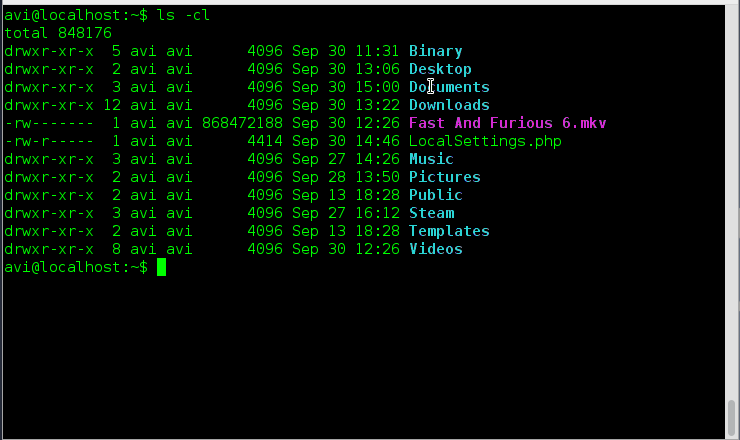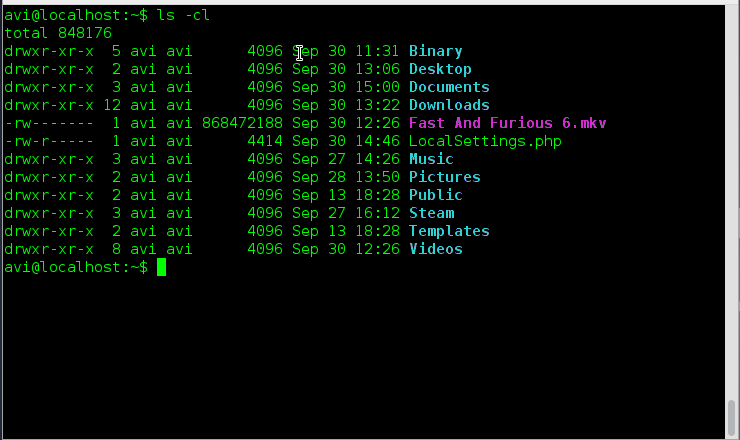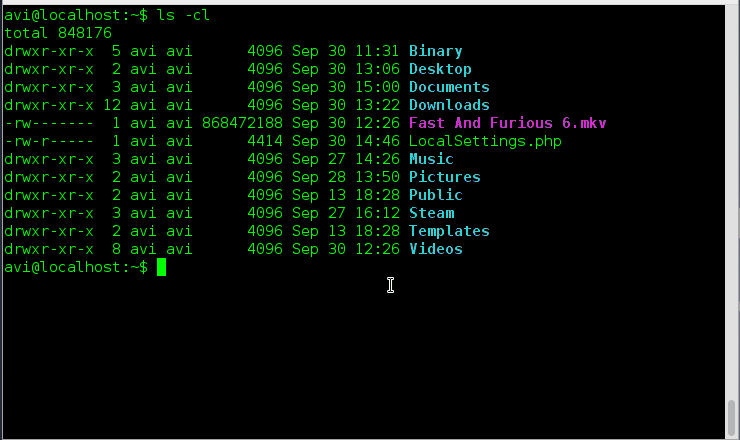
11. Sort all the files within a directory by name and show associated last modification information.
Ans: We need to use option ‘-c‘ and option ‘-l‘ with command ls to fulfil the need as suggested above.
# ls -cl
12. Sort all the files within a directory by modification time and show associated information.
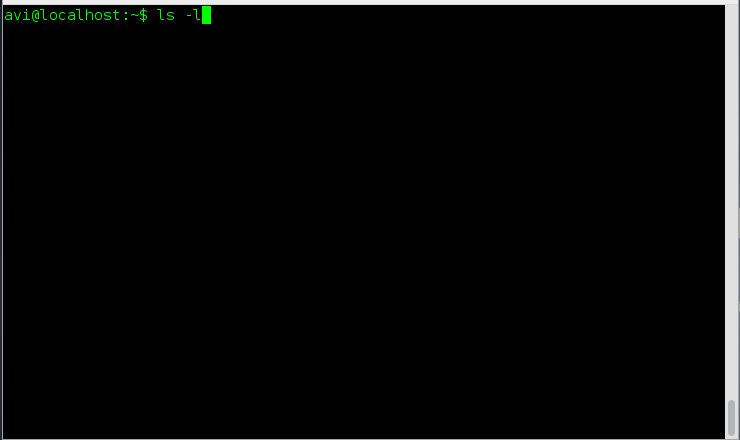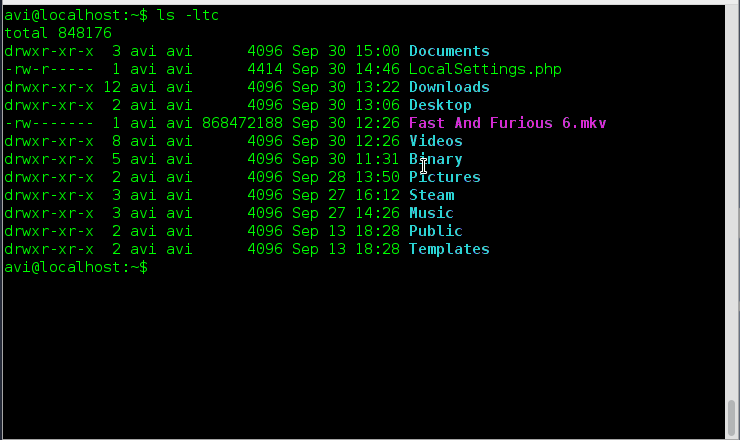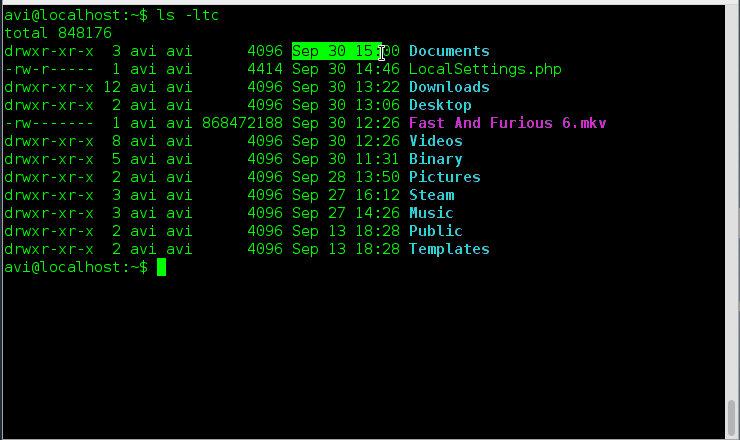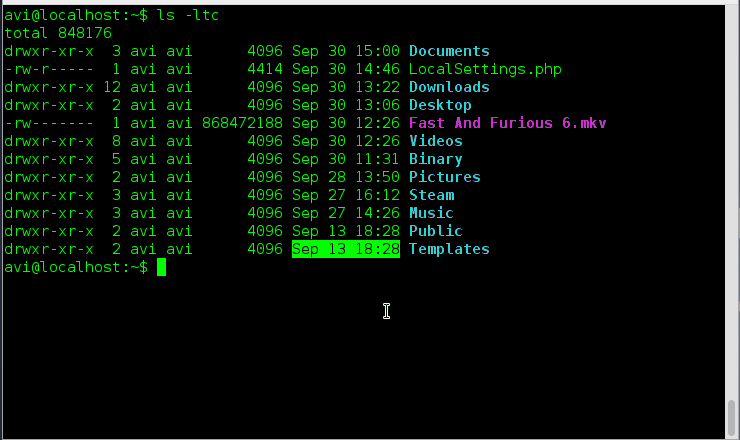
Ans: We need to use three options together i.e., ‘-l‘, ‘-t‘ and ‘-c‘ with command ls to sort files by modification time, newest first.
# ls -ltc
13. How will you control the output of ‘ls’ command to be colorful or no-color?
Ans: We need to use option ‘–color=parameter‘. The parameter to be used with color option are ‘auto’, ‘always’ and ‘never’ which are self explanatory.
# ls --color=never
# ls --color=auto
# ls --color=always
14. You are supposed to list directory entries themselves, not their contents. What will you do?
Ans: Here the option ‘-d‘ comes handy.
# ls -d
15. Create an alias for long format listing “ls -l” as “ll” and output the result to a file and not standard output.
Ans: Here in the above scenario, we need to add alias to .bashrc file and then use redirect operator to write the output to file and not standard output. We will be using editor nano.
# ls -a
# nano .bashrc
# ll >> ll.txt
# nano ll.txt
That’s all for now. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. I’ll be here again with another interesting article soon. Till then stay tuned and connected.
Real Also:
via: http://www.tecmint.com/ls-command-interview-questions/
作者:Avishek Kumar 译者:译者ID 校对:校对者ID