4.4 KiB
translation by strugglingyouth Linux and Unix Port Scanning With netcat [nc] Command
How do I find out which ports are opened on my own server? How do I run port scanning using the nc command instead of the nmap command on a Linux or Unix-like systems?
The nmap (“Network Mapper”) is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing. If nmap is not installed and you do not wish to use all of nmap options you can use netcat/nc command for scanning ports. This may useful to know which ports are open and running services on a target machine. You can use nmap command for port scanning too.
How do I use nc to scan Linux, UNIX and Windows server port scanning?
If nmap is not installed try nc / netcat command as follow. The -z flag can be used to tell nc to report open ports, rather than initiate a connection. Run nc command with -z flag. You need to specify host name / ip along with the port range to limit and speedup operation:
## syntax ##
nc -z -v {host-name-here} {port-range-here}
nc -z -v host-name-here ssh
nc -z -v host-name-here 22
nc -w 1 -z -v server-name-here port-Number-her
## scan 1 to 1023 ports ##
nc -zv vip-1.vsnl.nixcraft.in 1-1023
Sample outputs:
Connection to localhost 25 port [tcp/smtp] succeeded!
Connection to vip-1.vsnl.nixcraft.in 25 port [tcp/smtp] succeeded!
Connection to vip-1.vsnl.nixcraft.in 80 port [tcp/http] succeeded!
Connection to vip-1.vsnl.nixcraft.in 143 port [tcp/imap] succeeded!
Connection to vip-1.vsnl.nixcraft.in 199 port [tcp/smux] succeeded!
Connection to vip-1.vsnl.nixcraft.in 783 port [tcp/*] succeeded!
Connection to vip-1.vsnl.nixcraft.in 904 port [tcp/vmware-authd] succeeded!
Connection to vip-1.vsnl.nixcraft.in 993 port [tcp/imaps] succeeded!
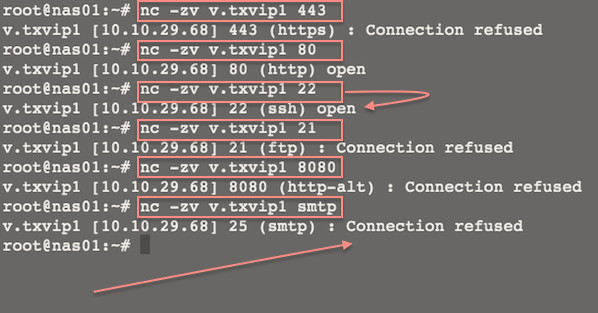
You can scan individual port too:
nc -zv v.txvip1 443
nc -zv v.txvip1 80
nc -zv v.txvip1 22
nc -zv v.txvip1 21
nc -zv v.txvip1 smtp
nc -zvn v.txvip1 ftp
## really fast scanner with 1 timeout value ##
netcat -v -z -n -w 1 v.txvip1 1-1023
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Linux/Unix: Use Netcat to Establish and Test TCP and UDP Connections on a Server
Where,
- -z : Port scanning mode i.e. zero I/O mode.
- -v : Be verbose [use twice -vv to be more verbose].
- -n : Use numeric-only IP addresses i.e. do not use DNS to resolve ip addresses.
- -w 1 : Set time out value to 1.
More examples:
$ netcat -z -vv www.cyberciti.biz http
www.cyberciti.biz [75.126.153.206] 80 (http) open
sent 0, rcvd 0
$ netcat -z -vv google.com https
DNS fwd/rev mismatch: google.com != maa03s16-in-f2.1e100.net
DNS fwd/rev mismatch: google.com != maa03s16-in-f6.1e100.net
DNS fwd/rev mismatch: google.com != maa03s16-in-f5.1e100.net
DNS fwd/rev mismatch: google.com != maa03s16-in-f3.1e100.net
DNS fwd/rev mismatch: google.com != maa03s16-in-f8.1e100.net
DNS fwd/rev mismatch: google.com != maa03s16-in-f0.1e100.net
DNS fwd/rev mismatch: google.com != maa03s16-in-f7.1e100.net
DNS fwd/rev mismatch: google.com != maa03s16-in-f4.1e100.net
google.com [74.125.236.162] 443 (https) open
sent 0, rcvd 0
$ netcat -v -z -n -w 1 192.168.1.254 1-1023
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.254] 989 (ftps-data) open
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.254] 443 (https) open
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.254] 53 (domain) open
See also
- Scanning network for open ports with the nmap command for more info.
- Man pages - nc(1), nmap(1)
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-port-scanning/