mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-23 21:20:42 +08:00
157 lines
7.0 KiB
Markdown
157 lines
7.0 KiB
Markdown
Linux 下清空或删除大文件内容的 5 种方法
|
||
============================================================
|
||
|
||
在 Linux 终端下处理文件时,有时我们想直接清空文件的内容但又不必使用任何 [**Linux 命令行编辑器**][1] 去打开这些文件。那怎样才能达到这个目的呢?在这篇文章中,我们将介绍几种借助一些实用的命令来清空文件内容的方法。
|
||
|
||
**注意:**在我们进一步深入了解这些方法之前,请记住: 由于[**在 Linux 中一切皆文件**][2],你需要时刻注意,确保你将要清空的文件不是重要的用户文件或者系统文件。清空重要的系统文件或者配置文件可能会引发严重的应用失败或者系统错误。
|
||
|
||
前面已经说道,下面的这些方法都是从命令行中达到清空文件的目的。
|
||
|
||
**提示:**在下面的示例中,我们将使用名为 `access.log` 的文件来作为示例样本。
|
||
|
||
### 1. 通过重定向到 Null 来清空文件内容
|
||
|
||
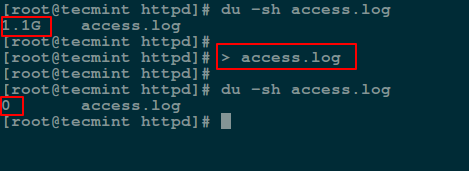
清空或者让一个文件成为空白的最简单方式,是像下面那样,通过 shell 重定向 `null` (不存在的事物)到该文件:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# > access.log
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][3]
|
||
|
||
*在 Linux 下使用 Null 重定向来清空大文件*
|
||
|
||
### 2. 使用 ‘true’ 命令重定向来清空文件
|
||
|
||
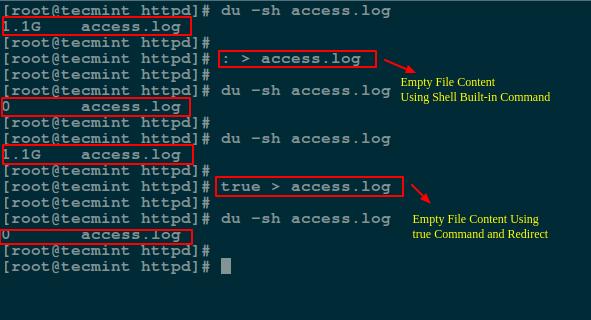
下面我们将使用 `:` 符号,它是 shell 的一个内置命令,等同于 `true` 命令,它可被用来作为一个 no-op(即不进行任何操作)。
|
||
|
||
另一种清空文件的方法是将 `:` 或者 `true` 内置命令的输出重定向到文件中,具体如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# : > access.log
|
||
或
|
||
# true > access.log
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][4]
|
||
|
||
*使用 Linux 命令清空大文件*
|
||
|
||
### 3. 使用 `cat`/`cp`/`dd` 实用工具及 `/dev/null` 设备来清空文件
|
||
|
||
在 Linux 中, `null` 设备基本上被用来丢弃某个进程不再需要的输出流,或者作为某个输入流的空白文件,这些通常可以利用重定向机制来达到。
|
||
|
||
所以 `/dev/null` 设备文件是一个特殊的文件,它将清空送到它这里来的所有输入,而它的输出则可被视为一个空文件。
|
||
|
||
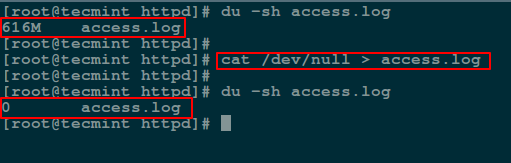
另外,你可以通过使用 [**cat 命令**][5] 显示 `/dev/null` 的内容然后重定向输出到某个文件,以此来达到清空该文件的目的。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# cat /dev/null > access.log
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][6]
|
||
|
||
*使用 cat 命令来清空文件*
|
||
|
||
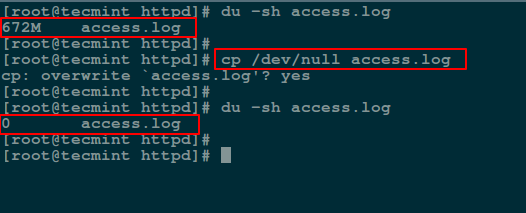
下面,我们将使用 [**cp 命令**][7] 复制 `/dev/null` 的内容到某个文件来达到清空该文件的目的,具体如下所示:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# cp /dev/null access.log
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][8]
|
||
|
||
*使用 cp 命令来清空文件*
|
||
|
||
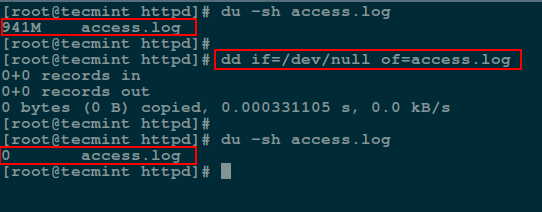
而下面的命令中, `if` 代表输入文件,`of` 代表输出文件。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# dd if=/dev/null of=access.log
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][9]
|
||
|
||
*使用 dd 命令来清空文件内容*
|
||
|
||
### 4. 使用 echo 命令清空文件
|
||
|
||
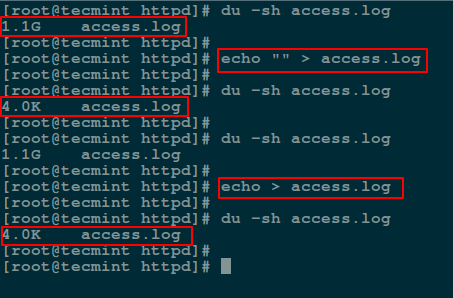
在这里,你可以使用 [**echo 命令**][10] 将空字符串的内容重定向到文件中,具体如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# echo "" > access.log
|
||
或者
|
||
# echo > access.log
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][11]
|
||
|
||
*使用 echo 命令来清空文件*
|
||
|
||
**注意:**你应该记住空字符串并不等同于 `null` 。字符串表明它是一个具体的事物,只不过它的内容可能是空的,但 `null` 则意味着某个事物并不存在。
|
||
|
||
基于这个原因,当你将 [echo 命令][12] 的输出作为输入重定向到文件后,使用 [cat 命令][13] 来查看该文件的内容时,你将看到一个空白行(即一个空字符串)。
|
||
|
||
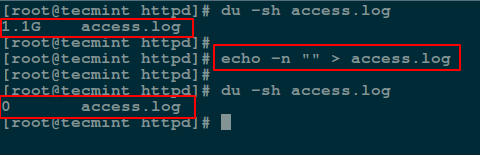
要将 null 做为输出输入到文件中,你应该使用 `-n` 选项,这个选项将告诉 echo 不再像上面的那个命令那样输出结尾的那个新行。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# echo -n "" > access.log
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][14]
|
||
|
||
*使用 Null 重定向来清空文件*
|
||
|
||
### 5. 使用 truncate 命令来清空文件内容
|
||
|
||
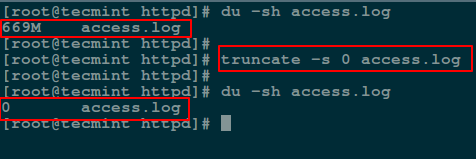
`truncate` 可被用来[**将一个文件缩小或者扩展到某个给定的大小**][15]。
|
||
|
||
你可以利用它和 `-s` 参数来特别指定文件的大小。要清空文件的内容,则在下面的命令中将文件的大小设定为 0:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# truncate -s 0 access.log
|
||
```
|
||
[
|
||
|
||
][16]
|
||
|
||
*在 Linux 中截断文件内容*
|
||
|
||
我要介绍的就是这么多了。在本文中,我们介绍了几种通过使用一些简单的命令行工具和 shell 重定向机制来清除或清空文件内容的方法。
|
||
|
||
上面介绍的这些可能并不是达到清空文件内容这个目的的所有可行的实践方法,所以你也可以通过下面的评论栏告诉我们本文中尚未提及的其他方法。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/empty-delete-file-content-linux/
|
||
|
||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||
校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-editors/
|
||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/explanation-of-everything-is-a-file-and-types-of-files-in-linux/
|
||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-Large-File-in-Linux.png
|
||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-Large-File-Using-Linux-Commands.png
|
||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-cat-Command.png
|
||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/progress-monitor-check-progress-of-linux-commands/
|
||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Content-Using-cp-Command.png
|
||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Content-Using-dd-Command.png
|
||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-echo-Command.png
|
||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-Null-Redirect.png
|
||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/parted-command-to-create-resize-rescue-linux-disk-partitions/
|
||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Truncate-File-Content-in-Linux.png
|