mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-23 21:20:42 +08:00
200 lines
8.0 KiB
Markdown
200 lines
8.0 KiB
Markdown
Linux日志文件总管——logrotate
|
||
================================================================================
|
||
日志文件包含了关于系统中发生的事件的有用信息,在排障过程中或者系统性能分析时经常被用到。对于忙碌的服务器,日志文件大小会增长极快,服务器会很快消耗磁盘空间,这成了个问题。除此之外,处理一个单个的庞大日志文件也常常是件十分棘手的事。
|
||
|
||
logrotate是个十分有用的工具,它可以自动对日志进行截断(或轮循)、压缩以及删除旧的日志文件。例如,你可以设置logrotate,让/var/log/foo日志文件每30天轮循,并删除超过6个月的日志。配置完后,logrotate的运作完全自动化,不必进行任何进一步的人为干预。另外,旧日志也可以通过电子邮件发送,不过该选项超出了本教程的讨论范围。
|
||
|
||
主流Linux发行版上都默认安装有logrotate包,如果出于某种原因,logrotate没有出现在里头,你可以使用apt-get或yum命令来安装。
|
||
|
||
在Debian或Ubuntu上:
|
||
|
||
# apt-get install logrotate cron
|
||
|
||
在Fedora,CentOS或RHEL上:
|
||
|
||
# yum install logrotate crontabs
|
||
|
||
logrotate的配置文件是/etc/logrotate.conf,通常不需要对它进行修改。日志文件的轮循设置在独立的配置文件中,它(们)放在/etc/logrotate.d/目录下。
|
||
|
||
### 样例一 ###
|
||
|
||
在第一个样例中,我们将创建一个10MB的日志文件/var/log/log-file。我们将展示怎样使用logrotate来管理该日志文件。
|
||
|
||
我们从创建一个日志文件开始吧,然后在其中填入一个10MB的随机比特流数据。
|
||
|
||
# touch /var/log/log-file
|
||
# head -c 10M < /dev/urandom > /var/log/log-file
|
||
|
||
由于现在日志文件已经准备好,我们将配置logrotate来轮循该日志文件。让我们为该文件创建一个配置文件。
|
||
|
||
# vim /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
/var/log/log-file {
|
||
monthly
|
||
rotate 5
|
||
compress
|
||
delaycompress
|
||
missingok
|
||
notifempty
|
||
create 644 root root
|
||
postrotate
|
||
/usr/bin/killall -HUP rsyslogd
|
||
endscript
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
这里:
|
||
|
||
- **monthly**: 日志文件将按月轮循。其它可用值为‘daily’,‘weekly’或者‘yearly’。
|
||
- **rotate 5**: 一次将存储5个归档日志。对于第六个归档,时间最久的归档将被删除。
|
||
- **compress**: 在轮循任务完成后,已轮循的归档将使用gzip进行压缩。
|
||
- **delaycompress**: 总是与compress选项一起用,delaycompress选项指示logrotate不要将最近的归档压缩,压缩将在下一次轮循周期进行。这在你或任何软件仍然需要读取最新归档时很有用。
|
||
- **missingok**: 在日志轮循期间,任何错误将被忽略,例如“文件无法找到”之类的错误。
|
||
- **notifempty**: 如果日志文件为空,轮循不会进行。
|
||
- **create 644 root root**: 以指定的权限创建全新的日志文件,同时logrotate也会重命名原始日志文件。
|
||
- **postrotate/endscript**: 在所有其它指令完成后,postrotate和endscript里面指定的命令将被执行。在这种情况下,rsyslogd 进程将立即再次读取其配置并继续运行。
|
||
|
||
上面的模板是通用的,而配置参数则根据你的需求进行调整,不是所有的参数都是必要的。
|
||
|
||
### 样例二 ###
|
||
|
||
在本例中,我们只想要轮循一个日志文件,然而日志文件大小可以增长到50MB。
|
||
|
||
# vim /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
/var/log/log-file {
|
||
size=50M
|
||
rotate 5
|
||
create 644 root root
|
||
postrotate
|
||
/usr/bin/killall -HUP rsyslogd
|
||
endscript
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
### 样例三 ###
|
||
|
||
我们想要让旧日志文件以创建日期命名,这可以通过添加dateext常熟实现。
|
||
|
||
# vim /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
/var/log/log-file {
|
||
monthly
|
||
rotate 5
|
||
dateext
|
||
create 644 root root
|
||
postrotate
|
||
/usr/bin/killall -HUP rsyslogd
|
||
endscript
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
这将让归档文件在它们的文件名中包含日期信息。
|
||
|
||
### 排障 ###
|
||
|
||
这里提供了一些logrotate设置的排障提示。
|
||
|
||
#### 1. 手动运行logrotate ####
|
||
|
||
**logrotate**可以在任何时候从命令行手动调用。
|
||
|
||
要调用为/etc/lograte.d/下配置的所有日志调用**logrotate**:
|
||
|
||
# logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf
|
||
|
||
要为某个特定的配置调用logrotate:
|
||
|
||
# logrotate /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||
|
||
#### 2. 演练 ####
|
||
|
||
排障过程中的最佳选择是使用‘-d’选项以预演方式运行logrotate。要进行验证,不用实际轮循任何日志文件,可以模拟演练日志轮循并显示其输出。
|
||
|
||
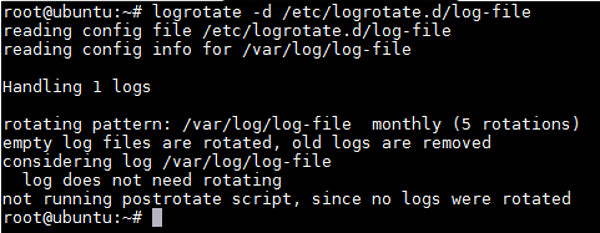
# logrotate -d /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
正如我们从上面的输出结果可以看到的,logrotate判断该轮循是不必要的。如果文件的时间小于一天,这就会发生了。
|
||
|
||
#### 3. 强制轮循 ####
|
||
|
||
即使轮循条件没有满足,我们也可以通过使用‘-f’选项来强制logrotate轮循日志文件,‘-v’参数提供了详细的输出。
|
||
|
||
# logrotate -vf /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
reading config file /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||
reading config info for /var/log/log-file
|
||
|
||
Handling 1 logs
|
||
|
||
rotating pattern: /var/log/log-file forced from command line (5 rotations)
|
||
empty log files are rotated, old logs are removed
|
||
considering log /var/log/log-file
|
||
log needs rotating
|
||
rotating log /var/log/log-file, log->rotateCount is 5
|
||
dateext suffix '-20140916'
|
||
glob pattern '-[0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9]'
|
||
renaming /var/log/log-file.5.gz to /var/log/log-file.6.gz (rotatecount 5, logstart 1, i 5),
|
||
old log /var/log/log-file.5.gz does not exist
|
||
renaming /var/log/log-file.4.gz to /var/log/log-file.5.gz (rotatecount 5, logstart 1, i 4),
|
||
old log /var/log/log-file.4.gz does not exist
|
||
. . .
|
||
renaming /var/log/log-file.0.gz to /var/log/log-file.1.gz (rotatecount 5, logstart 1, i 0),
|
||
old log /var/log/log-file.0.gz does not exist
|
||
log /var/log/log-file.6.gz doesn't exist -- won't try to dispose of it
|
||
renaming /var/log/log-file to /var/log/log-file.1
|
||
creating new /var/log/log-file mode = 0644 uid = 0 gid = 0
|
||
running postrotate script
|
||
compressing log with: /bin/gzip
|
||
|
||
#### 4. Logrotate的记录日志 ####
|
||
|
||
logrotate自身的日志通常存放于/var/lib/logrotate/status目录。如果处于排障目的,我们想要logrotate记录到任何指定的文件,我们可以指定像下面这样从命令行指定。
|
||
|
||
# logrotate -vf –s /var/log/logrotate-status /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||
|
||
#### 5. Logrotate定时任务 ####
|
||
|
||
logrotate需要的**cron**任务应该在安装时就自动创建了,我把cron文件的内容贴出来,以供大家参考。
|
||
|
||
# cat /etc/cron.daily/logrotate
|
||
|
||
----------
|
||
|
||
#!/bin/sh
|
||
|
||
# Clean non existent log file entries from status file
|
||
cd /var/lib/logrotate
|
||
test -e status || touch status
|
||
head -1 status > status.clean
|
||
sed 's/"//g' status | while read logfile date
|
||
do
|
||
[ -e "$logfile" ] && echo "\"$logfile\" $date"
|
||
done >> status.clean
|
||
mv status.clean status
|
||
|
||
test -x /usr/sbin/logrotate || exit 0
|
||
/usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf
|
||
|
||
小结一下,logrotate工具对于防止因庞大的日志文件而耗尽存储空间是十分有用的。配置完毕后,进程是全自动的,可以长时间在不需要人为干预下运行。本教程重点关注几个使用logrotate的几个基本样例,你也可以定制它以满足你的需求。
|
||
|
||
希望本文对你有所帮助。
|
||
|
||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||
|
||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/logrotate-manage-log-files-linux.html
|
||
|
||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||
|
||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||
|
||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|