微软爱上 Linux:当 PowerShell 来到 Linux 时 ============================================================ 在微软爱上 Linux 之后,**PowerShell** 这个原本只是 Windows 才能使用的组件,于 2016 年 8 月 18 日开源并且成为跨平台软件,登陆了 Linux 和 macOS。 **PowerShell** 是一个微软开发的自动化任务和配置管理系统。它基于 .NET 框架,由命令行语言解释器(shell)和脚本语言组成。 PowerShell 提供对 **COM** (<ruby>组件对象模型<rt>Component Object Model</rt></ruby>) 和 **WMI** (<ruby>Windows 管理规范<rt>Windows Management Instrumentation</rt></ruby>) 的完全访问,从而允许系统管理员在本地或远程 Windows 系统中 [执行管理任务][1],以及对 WS-Management 和 CIM(<ruby>公共信息模型<rt>Common Information Model</rt></ruby>)的访问,实现对远程 Linux 系统和网络设备的管理。 通过这个框架,管理任务基本上由称为 **cmdlets**(发音 command-lets)的 **.NET** 类执行。就像 Linux 的 shell 脚本一样,用户可以通过按照一定的规则将一组 **cmdlets** 写入文件来制作脚本或可执行文件。这些脚本可以用作独立的[命令行程序或工具][2]。 ### 在 Linux 系统中安装 PowerShell Core 6.0 要在 Linux 中安装 **PowerShell Core 6.0**,我们将会用到微软软件仓库,它允许我们通过最流行的 Linux 包管理器工具,如 [apt-get][3]、[yum][4] 等来安装。 #### 在 Ubuntu 16.04 中安装 首先,导入该公共仓库的 **GPG** 密钥,然后将 **Microsoft Ubuntu** 仓库注册到 **APT** 的源中来安装 **PowerShell**: ``` $ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add - $ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install -y powershell ``` #### 在 Ubuntu 14.04 中安裝 ``` $ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add - $ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/14.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install -y powershell ``` #### 在 CentOS 7 中安裝 首先,将 **Microsoft RedHat** 仓库注册到 **YUM** 包管理器仓库列表中,然后安装 **PowerShell**: ``` $ sudo curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/7/prod.repo > /etc/yum.repos.d/microsoft.repo $ sudo yum install -y powershell ``` ### 如何在 Linux 中使用 PowerShell Core 6.0 在这一节中,我们将会简单介绍下 **PowerShell**;我们将会看到如何启动 PowerShell,运行一些基础命令,操作文件、目录和进程。然后学习怎样列出所有可用的命令、显示命令帮助和别名。 输入以下命令来启动 PowerShell: ``` $ powershell ``` [  ][5] *在 Linux 中启动 PowerShell* 你可以通过以下命令来查看 PowerShell 版本: ``` $PSVersionTable ``` [  ][6] *查看 PowerShell 版本* 在 Linux 中运行基本的 PowerShell 命令。 ``` get-date [# 显示当前日期] get-uptime [# 显示开机时间] get-location [# 显示当前工作目录] ``` #### 在 PowerShell 中操作文件和目录 1、 可以通过两种方法创建空文件: ``` new-item tecmint.tex 或者 "">tecmint.tex ``` 然后往里面添加内容并查看文件内容。 ``` set-content tecmint.tex -value "TecMint Linux How Tos Guides" get-content tecmint.tex ``` [ 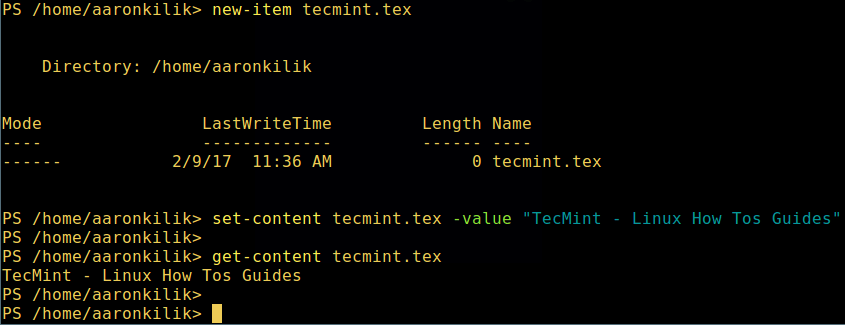 ][7] *在 PowerShell 中创建新文件* 2、 在 PowerShell 中删除一个文件 ``` remove-item tecmint.tex get-content tecmint.tex ``` [ 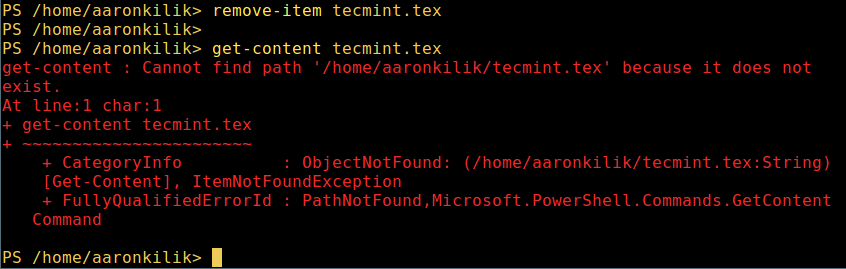 ][8] *在 PowerShell 中删除一个文件* 3、 创建目录 ``` mkdir tecmint-files cd tecmint-files “”>domains.list ls ``` [ 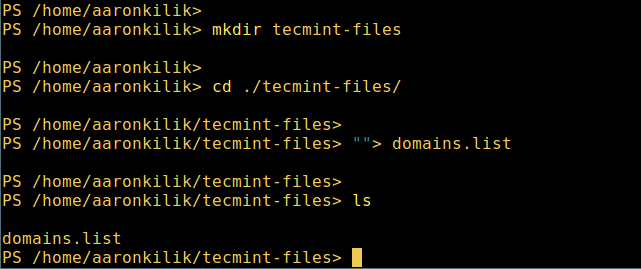 ][9] *在 PowerShell 中创建目录* 4、 执行长格式的列表操作,列出文件/目录详细情况,包括模式(文件类型)、最后修改时间等,使用以下命令: ``` dir ``` [ 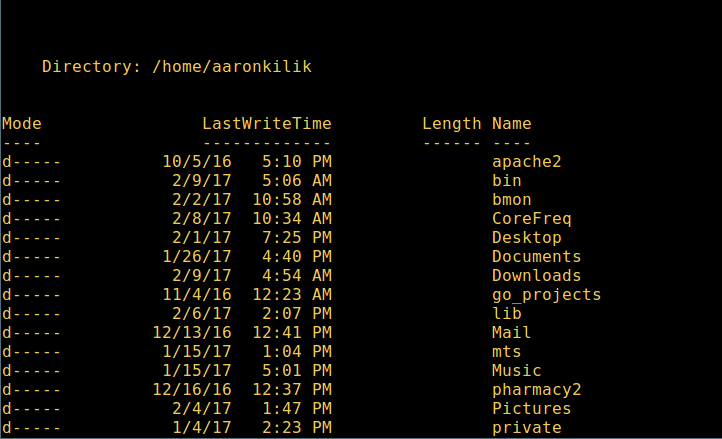 ][10] *Powershell 中列出目录长列表* 5、 显示系统中所有的进程: ``` get-process ``` [ 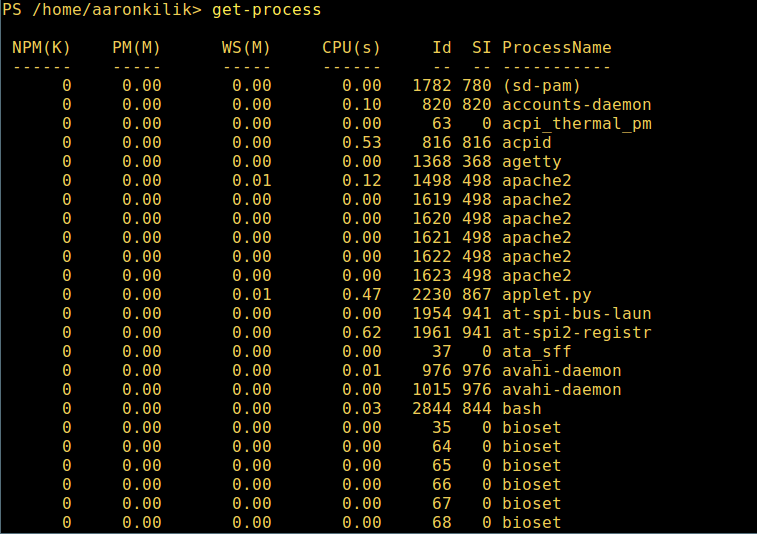 ][11] *在 PowerShell 中显示运行中的进程* 6、 通过给定的名称查看正在运行的进程/进程组细节,将进程名作为参数传给上面的命令,如下: ``` get-process apache2 ``` [ 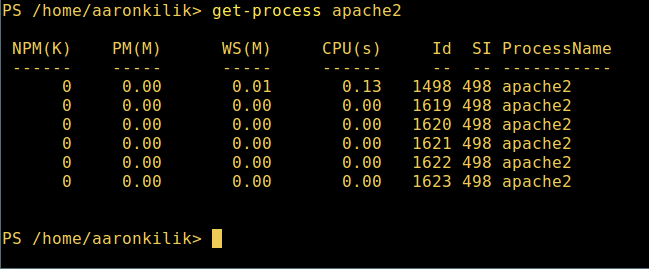 ][12] *在 PowerShell 中查看指定的进程* 输出中各部分的含义: * NPM(K) – 进程使用的非分页内存,单位:Kb。 * PM(K) – 进程使用的可分页内存,单位:Kb。 * WS(K) – 进程的工作集大小,单位:Kb,工作集由进程所引用到的内存页组成。 * CPU(s) – 进程在所有处理器上所占用的处理器时间,单位:秒。 * ID – 进程 ID (PID). * ProcessName – 进程名称。 7、 想要了解更多,获取 PowerShell 命令列表: ``` get-command ``` [ 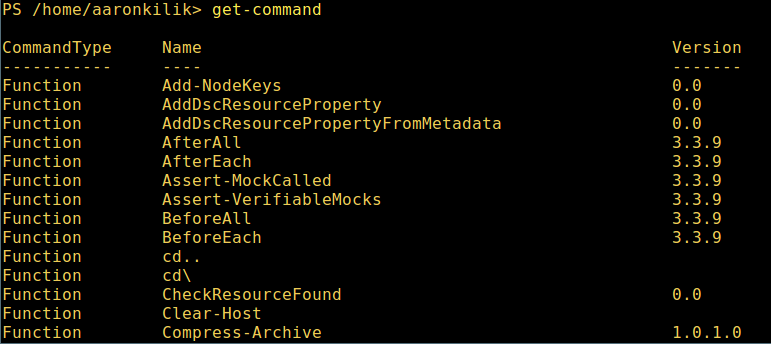 ][13] *列出 PowerShell 的命令* 8、 想知道如何使用一个命令,查看它的帮助(类似于 Unix/Linux 中的 man);举个例子,你可以这样获取命令 **Describe** 的帮助: ``` get-help Describe ``` [ 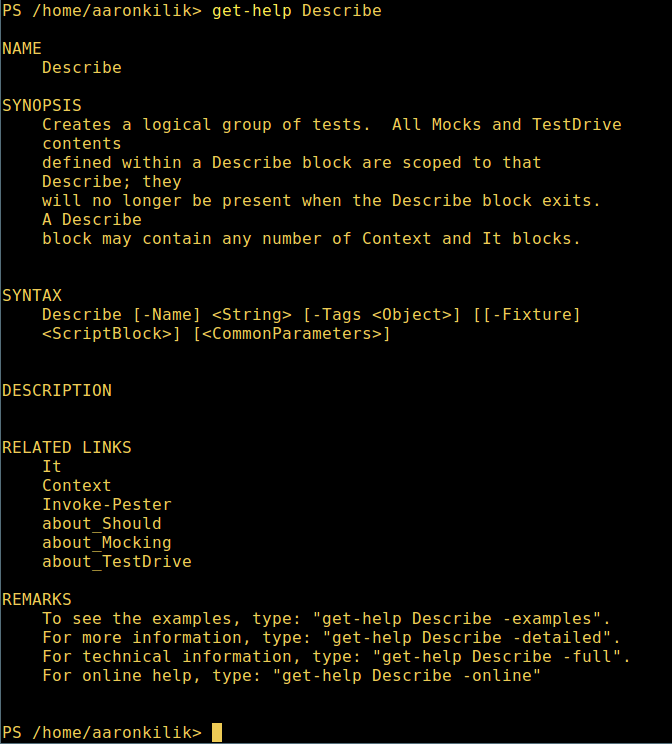 ][14] *PowerShell 帮助手册* 9、 显示所有命令的别名,輸入: ``` get-alias ``` [ 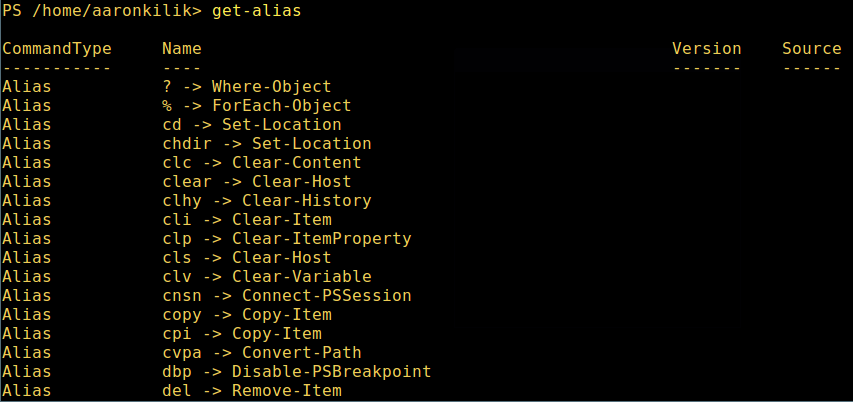 ][15] *列出 PowerShell 命令别名* 10、 最后,不过也很重要,显示命令历史记录(曾运行过的命令的列表): ``` history ``` [ 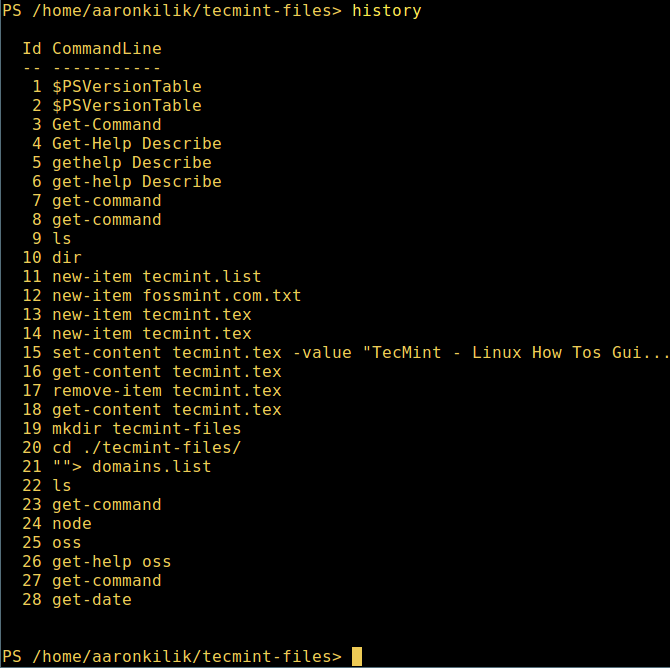 ][16] *显示 PowerShell 命令历史记录* 就是这些了!在这篇文章里,我们展示了如何在 Linux 中安装**微软的 PowerShell Core 6.0**。在我看来,与传统 Unix/Linux 的 shell 相比,PowerShell 还有很长的路要走。目前看来,PowerShell 还需要在命令行操作机器,更重要的是,编程(写脚本)等方面,提供更好、更多令人激动和富有成效的特性。 查看 PowerShell 的 GitHub 仓库:[https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell][17]。 请在评论中分享你的观点。 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 作者简介: Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 狂热爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发者,目前是 TecMint 的内容编辑,是一个热爱研究计算机与坚定的分享知识的人。 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-powershell-in-linux/ 作者:[Aaron Kili][a] 译者:[zijung](https://github.com/zijung) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng) 本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出 [a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/ [1]:http://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintenance-tasks/ [2]:http://www.tecmint.com/tag/commandline-tools/ [3]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/ [4]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/ [5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/start-powershell.png [6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/check-powershell-version.png [7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Create-New-File-in-Powershell.png [8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Delete-File-in-Powershell.png [9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/create-new-directory-in-Powershell.png [10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Directory-Long-Listing-in-Powershell.png [11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/View-Running-Processes-in-Powershell.png [12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/View-Specific-Process-in-Powershell.png [13]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Commands.png [14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Powershell-Help-Manual.png [15]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Command-Aliases.png [16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Command-History.png [17]:https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell [18]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/ [19]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/ [20]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/