菜鸟教程:全面学习 pwd 命令
================================================================================
对于那些使用Linux命令行的人来说,‘**pwd**‘命令是非常有用的,它告诉你你现在在那个目录,从根目录(**/**)如何到达。特别是对于或许会在目录的切换间容易糊涂的Linux新手而言,‘**pwd**‘ 可以拯救他们。

*15个 pwd 命令示例*
### 什么是pwd? ###
‘**pwd**‘ 代表的是‘**Print Working Directory**’(打印当前目录)。如它的名字那样,‘**pwd**’会打印出当前工作目录,或简单的来说就是当前用户所位于的目录。它会打印出以根目录 (**/**)为起点的完整目录名(绝对目录)。这条命令是一条shell内建命令,并且在大多数shell中都可以使用,如bash、Bourne shell,ksh、zsh等等。
#### pwd的基本语法: ####
# pwd [OPTION]
#### pwd的选项 ####
| 选项 |
描述 |
| -L (即逻辑路径logical ) |
使用环境中的路径,即使包含了符号链接 |
| -P (即物理路径physical) |
避免所有的符号链接 |
| –help |
显示帮助并退出 |
| –version |
输出版本信息并退出 |
如果同时使用了‘**-L**‘和‘**-P**‘,‘**-L**‘会有更高的优先级。如果没有指定参数,pwd会避开所有的软链接,也就是说会使用‘**-P**‘参数。
pwd的退出状态:
本篇的目的是采用例子让你对‘**pwd**‘有更深入的领悟。
**1.** 打印当前工作目录.
avi@tecmint:~$ /bin/pwd
/home/avi

*打印工作目录*
**2.** 为文件夹创建一个符号链接(比如说在home目录下创建一个**htm**链接指向**/var/www/html**)。进入新创建的目录并打印出含有以及不含符号链接的目录。
在home目录下创建一个htm链接指向/var/www/html,并进入。
avi@tecmint:~$ ln -s /var/www/html/ htm
avi@tecmint:~$ cd htm

*创建符号链接*
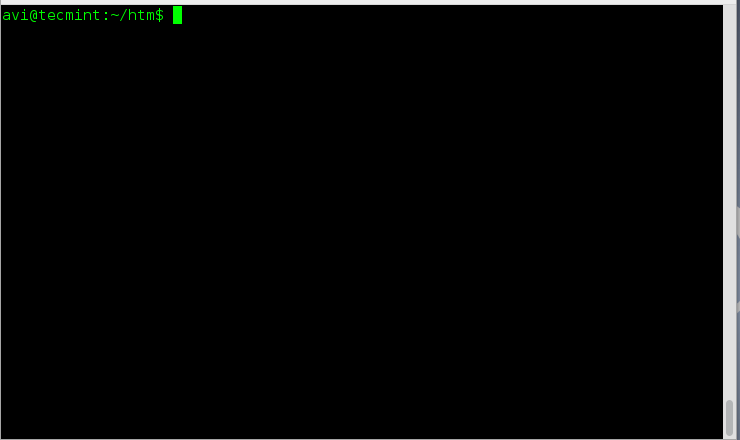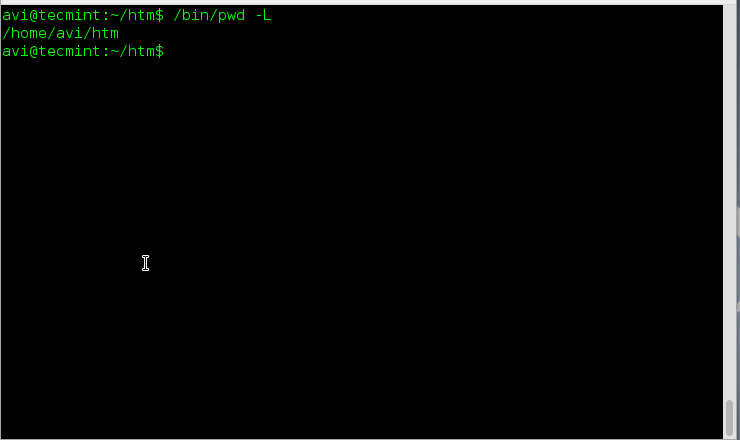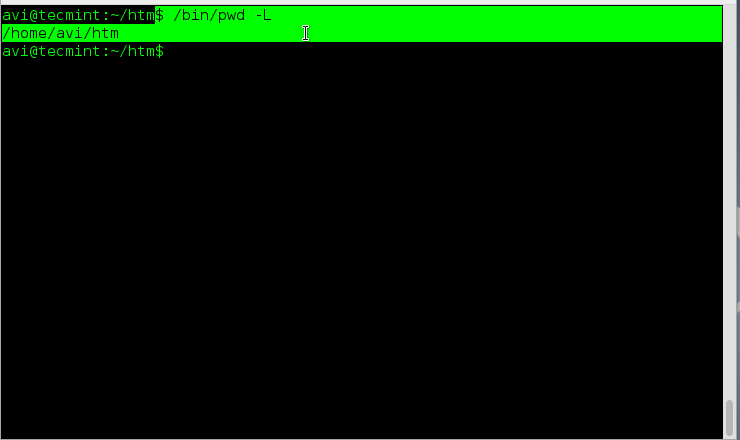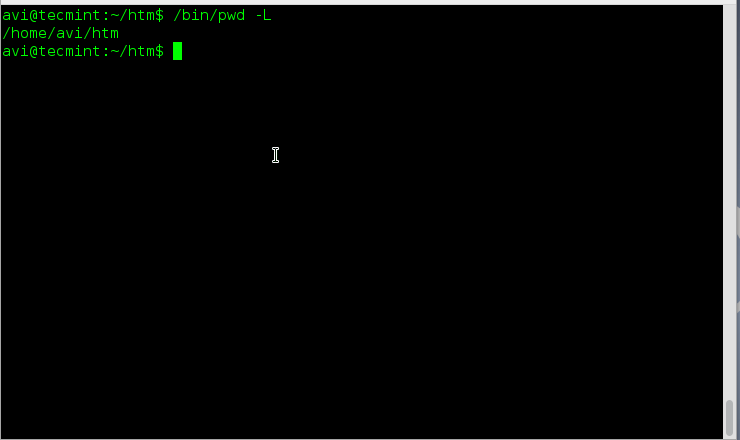
**3.** 从当前环境中打印目录即使它含有符号链接。
avi@tecmint:~$ /bin/pwd -L
/home/avi/htm
*打印工作目录*
**4.** 解析符号链接并打印出物理目录。
avi@tecmint:~$ /bin/pwd -P
/var/www/html

*打印物理工作目录*
**5.** 查看一下“**pwd**”和“**pwd -P**”的输出是否一致,也就是说,如果没有跟上选项,“**pwd**”时候会自动采用**-P**选项。
avi@tecmint:~$ /bin/pwd
/var/www/html
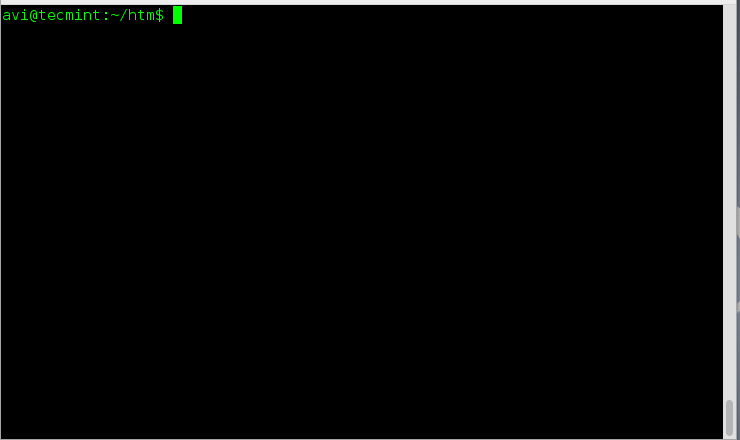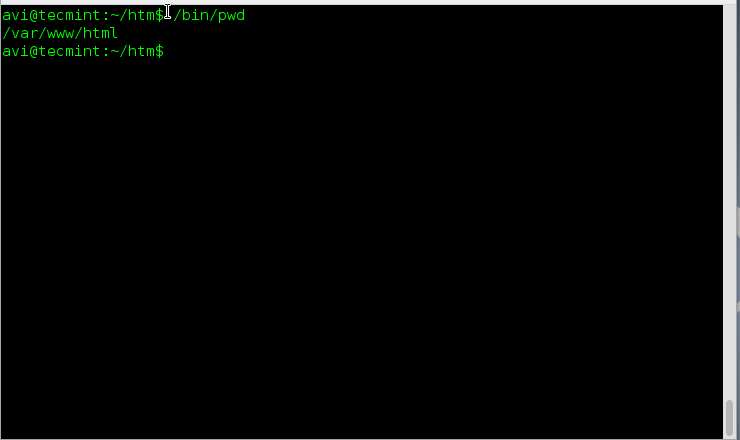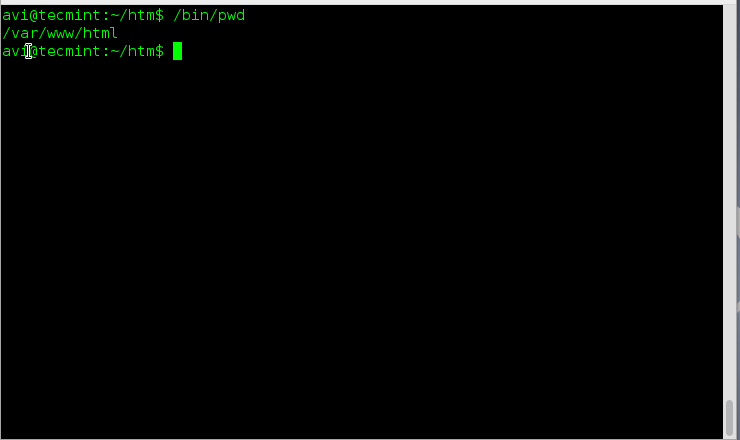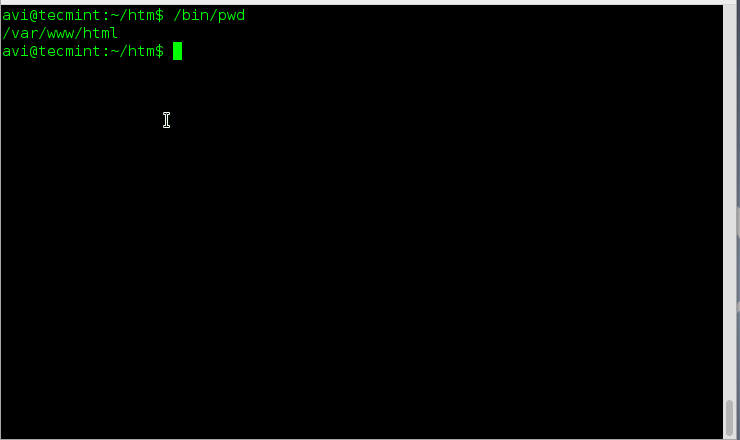
*检查pwd输出*
**结论:** 上面例子4和5的输出很明显(结果相同),当你“**pwd**”后面不带参数时,pwd会使用“**-P**”选项。
**6.** 打印pwd命令的版本。
avi@tecmint:~$ /bin/pwd --version
pwd (GNU coreutils) 8.23
Copyright (C) 2014 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later .
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Written by Jim Meyering.

*检查pwd命令版本*
**注意:** ‘pwd’ 通常不带选项运行,且没有任何参数
**重要:** 你可能注意到我们刚才运行的都是 “**/bin/pwd**” 而不是 “**pwd**”。
这有什么区别呢?直接使用“**pwd**”意味着使用shell内置的pwd。你的shell可能有不同版本的pwd。具体请参考手册。当你使用的是**/bin/pwd**时,我们调用的是二进制版本的命令。虽然二进制的版本有更多的选项,但是它们两者都能打印当前的目录。
**7.** 打印所有含有可执行pwd的路径
avi@tecmint:~$ type -a pwd
pwd is a shell builtin
pwd is /bin/pwd

*打印可执行文件路径*
**8.** 存储“**pwd**”命令的值到变量中(比如说:**a** ),并从中打印变量的值(对于观察shell脚本很重要)。
avi@tecmint:~$ a=$(pwd)
avi@tecmint:~$ echo "Current working directory is : $a"
Current working directory is : /home/avi

*存储pwd的值到变量中*
下面的例子中也可以用**printf**来替代。
**9.** 将工作路径切换到其他地方(比如说 **/home**),并在命令行中显示。通过执行命令(比如说 ‘**ls**‘)来验证一切**OK**。
avi@tecmint:~$ cd /home
avi@tecmint:~$ PS1='$pwd> ' [注意例子中的单引号]
> ls

*改变当前工作路径*
**10.** 设置多行显示 (就像下面这样),
/home
123#Hello#!
接着执行命令(比如说 **ls**)来检验一切**OK**。
avi@tecmint:~$ PS1='
> $PWD
$ 123#Hello#!
$ '
/home
123#Hello#!

*设置多行显示*
**11.** 一下子检查当前工作路径以及先前的工作路径。
avi@tecmint:~$ echo “$PWD $OLDPWD”
/home /home/avi

*检查当前工作路径*
**12.** pwd文件的绝对路径(以**/**开始)。
/bin/pwd
**13.** pwd源文件文件的绝对路径(以**/**开始)。
/usr/include/pwd.h
**13.** pwd手册的绝对路径(以**/**开始)。
/usr/share/man/man1/pwd.1.gz
**15.** 写一个shell脚本分析home目录下的一个目录(比如**tecmint**)。如果当前目录是**tecmint**就输出“**Well! You are in tecmint directory**”接着输出“**Good Bye**”,不然就在**tecmint**下面创建一个目录并提示你cd进入它。
让我们首先创建一个‘tecmint’目录,在下面创建一个名为‘pwd.sh’的脚本文件。
avi@tecmint:~$ mkdir tecmint
avi@tecmint:~$ cd tecmint
avi@tecmint:~$ nano pwd.sh
接下来在pwd.sh中加入下面的脚本。
#!/bin/bash
x="$(pwd)"
if [ "$x" == "/home/$USER/tecmint" ]
then
{
echo "Well you are in tecmint directory"
echo "Good Bye"
}
else
{
mkdir /home/$USER/tecmint
echo "Created Directory tecmint you may now cd to it"
}
fi
给予执行权限并运行。
avi@tecmint:~$ chmod 755 pwd.sh
avi@tecmint:~$ ./pwd.sh
Well you are in tecmint directory
Good Bye
#### 总结 ####
**pwd**是一个最简单且会广泛用到的命令。掌握好pwd是使用Linux终端的基础。就是这些了。我很快会再带来另外有趣的文章,请不要走开继续关注我们。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://www.tecmint.com/pwd-command-examples/
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/