mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-09 01:30:10 +08:00
commit
fe4bb1d292
@ -1,89 +1,90 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中创建 RAID 5(条带化与分布式奇偶校验) - 第4部分
|
||||
在 Linux 下使用 RAID(四):创建 RAID 5(条带化与分布式奇偶校验)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在 RAID 5 中,条带化数据跨多个驱磁盘使用分布式奇偶校验。分布式奇偶校验的条带化意味着它将奇偶校验信息和条带中的数据分布在多个磁盘上,它将有很好的数据冗余。
|
||||
|
||||
在 RAID 5 中,数据条带化后存储在分布式奇偶校验的多个磁盘上。分布式奇偶校验的条带化意味着它将奇偶校验信息和条带化数据分布在多个磁盘上,这样会有很好的数据冗余。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中配置 RAID 5
|
||||
*在 Linux 中配置 RAID 5*
|
||||
|
||||
对于此 RAID 级别它至少应该有三个或更多个磁盘。RAID 5 通常被用于大规模生产环境中花费更多的成本来提供更好的数据冗余性能。
|
||||
对于此 RAID 级别它至少应该有三个或更多个磁盘。RAID 5 通常被用于大规模生产环境中,以花费更多的成本来提供更好的数据冗余性能。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 什么是奇偶校验? ####
|
||||
|
||||
奇偶校验是在数据存储中检测错误最简单的一个方法。奇偶校验信息存储在每个磁盘中,比如说,我们有4个磁盘,其中一个磁盘空间被分割去存储所有磁盘的奇偶校验信息。如果任何一个磁盘出现故障,我们可以通过更换故障磁盘后,从奇偶校验信息重建得到原来的数据。
|
||||
奇偶校验是在数据存储中检测错误最简单的常见方式。奇偶校验信息存储在每个磁盘中,比如说,我们有4个磁盘,其中相当于一个磁盘大小的空间被分割去存储所有磁盘的奇偶校验信息。如果任何一个磁盘出现故障,我们可以通过更换故障磁盘后,从奇偶校验信息重建得到原来的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
#### RAID 5 的优点和缺点 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 提供更好的性能
|
||||
- 提供更好的性能。
|
||||
- 支持冗余和容错。
|
||||
- 支持热备份。
|
||||
- 将失去一个磁盘的容量存储奇偶校验信息。
|
||||
- 将用掉一个磁盘的容量存储奇偶校验信息。
|
||||
- 单个磁盘发生故障后不会丢失数据。我们可以更换故障硬盘后从奇偶校验信息中重建数据。
|
||||
- 事务处理读操作会更快。
|
||||
- 由于奇偶校验占用资源,写操作将是缓慢的。
|
||||
- 适合于面向事务处理的环境,读操作会更快。
|
||||
- 由于奇偶校验占用资源,写操作会慢一些。
|
||||
- 重建需要很长的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 要求 ####
|
||||
|
||||
创建 RAID 5 最少需要3个磁盘,你也可以添加更多的磁盘,前提是你要有多端口的专用硬件 RAID 控制器。在这里,我们使用“mdadm”包来创建软件 RAID。
|
||||
|
||||
mdadm 是一个允许我们在 Linux 下配置和管理 RAID 设备的包。默认情况下 RAID 没有可用的配置文件,我们在创建和配置 RAID 后必须将配置文件保存在一个单独的文件中,例如:mdadm.conf。
|
||||
mdadm 是一个允许我们在 Linux 下配置和管理 RAID 设备的包。默认情况下没有 RAID 的配置文件,我们在创建和配置 RAID 后必须将配置文件保存在一个单独的文件 mdadm.conf 中。
|
||||
|
||||
在进一步学习之前,我建议你通过下面的文章去了解 Linux 中 RAID 的基础知识。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Basic Concepts of RAID in Linux – Part 1][1]
|
||||
- [Creating RAID 0 (Stripe) in Linux – Part 2][2]
|
||||
- [Setting up RAID 1 (Mirroring) in Linux – Part 3][3]
|
||||
- [介绍 RAID 的级别和概念][1]
|
||||
- [使用 mdadm 工具创建软件 RAID 0 (条带化)][2]
|
||||
- [用两块磁盘创建 RAID 1(镜像)][3]
|
||||
|
||||
#### 我的服务器设置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Operating System : CentOS 6.5 Final
|
||||
IP Address : 192.168.0.227
|
||||
Hostname : rd5.tecmintlocal.com
|
||||
Disk 1 [20GB] : /dev/sdb
|
||||
Disk 2 [20GB] : /dev/sdc
|
||||
Disk 3 [20GB] : /dev/sdd
|
||||
操作系统 : CentOS 6.5 Final
|
||||
IP 地址 : 192.168.0.227
|
||||
主机名 : rd5.tecmintlocal.com
|
||||
磁盘 1 [20GB] : /dev/sdb
|
||||
磁盘 2 [20GB] : /dev/sdc
|
||||
磁盘 3 [20GB] : /dev/sdd
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章是 RAID 系列9教程的第4部分,在这里我们要建立一个软件 RAID 5(分布式奇偶校验)使用三个20GB(名为/dev/sdb, /dev/sdc 和 /dev/sdd)的磁盘在 Linux 系统或服务器中上。
|
||||
这是9篇系列教程的第4部分,在这里我们要在 Linux 系统或服务器上使用三个20GB(名为/dev/sdb, /dev/sdc 和 /dev/sdd)的磁盘建立带有分布式奇偶校验的软件 RAID 5。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第1步:安装 mdadm 并检验磁盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1.正如我们前面所说,我们使用 CentOS 6.5 Final 版本来创建 RAID 设置,但同样的做法也适用于其他 Linux 发行版。
|
||||
1、 正如我们前面所说,我们使用 CentOS 6.5 Final 版本来创建 RAID 设置,但同样的做法也适用于其他 Linux 发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
# lsb_release -a
|
||||
# ifconfig | grep inet
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 6.5 摘要
|
||||
*CentOS 6.5 摘要*
|
||||
|
||||
2. 如果你按照我们的 RAID 系列去配置的,我们假设你已经安装了“mdadm”包,如果没有,根据你的 Linux 发行版使用下面的命令安装。
|
||||
2、 如果你按照我们的 RAID 系列去配置的,我们假设你已经安装了“mdadm”包,如果没有,根据你的 Linux 发行版使用下面的命令安装。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install mdadm [on RedHat systems]
|
||||
# apt-get install mdadm [on Debain systems]
|
||||
# yum install mdadm [在 RedHat 系统]
|
||||
# apt-get install mdadm [在 Debain 系统]
|
||||
|
||||
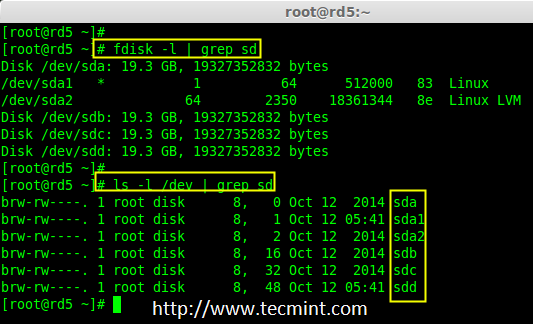
3. “mdadm”包安装后,先使用‘fdisk‘命令列出我们在系统上增加的三个20GB的硬盘。
|
||||
3、 “mdadm”包安装后,先使用`fdisk`命令列出我们在系统上增加的三个20GB的硬盘。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk -l | grep sd
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
安装 mdadm 工具
|
||||
*安装 mdadm 工具*
|
||||
|
||||
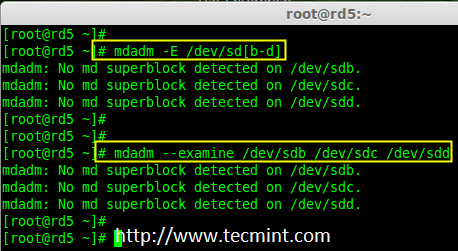
4. 现在该检查这三个磁盘是否存在 RAID 块,使用下面的命令来检查。
|
||||
4、 现在该检查这三个磁盘是否存在 RAID 块,使用下面的命令来检查。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -E /dev/sd[b-d]
|
||||
# mdadm --examine /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd
|
||||
# mdadm --examine /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd # 或
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
检查 Raid 磁盘
|
||||
*检查 Raid 磁盘*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 上面的图片说明,没有检测到任何超级块。所以,这三个磁盘中没有定义 RAID。让我们现在开始创建一个吧!
|
||||
|
||||
### 第2步:为磁盘创建 RAID 分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
5. 首先,在创建 RAID 前我们要为磁盘分区(/dev/sdb, /dev/sdc 和 /dev/sdd),在进行下一步之前,先使用‘fdisk’命令进行分区。
|
||||
5、 首先,在创建 RAID 前磁盘(/dev/sdb, /dev/sdc 和 /dev/sdd)必须有分区,因此,在进行下一步之前,先使用`fdisk`命令进行分区。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/sdc
|
||||
@ -93,20 +94,20 @@ CentOS 6.5 摘要
|
||||
|
||||
请按照下面的说明在 /dev/sdb 硬盘上创建分区。
|
||||
|
||||
- 按 ‘n’ 创建新的分区。
|
||||
- 然后按 ‘P’ 选择主分区。选择主分区是因为还没有定义过分区。
|
||||
- 接下来选择分区号为1。默认就是1.
|
||||
- 按 `n` 创建新的分区。
|
||||
- 然后按 `P` 选择主分区。选择主分区是因为还没有定义过分区。
|
||||
- 接下来选择分区号为1。默认就是1。
|
||||
- 这里是选择柱面大小,我们没必要选择指定的大小,因为我们需要为 RAID 使用整个分区,所以只需按两次 Enter 键默认将整个容量分配给它。
|
||||
- 然后,按 ‘P’ 来打印创建好的分区。
|
||||
- 改变分区类型,按 ‘L’可以列出所有可用的类型。
|
||||
- 按 ‘t’ 修改分区类型。
|
||||
- 这里使用‘fd’设置为 RAID 的类型。
|
||||
- 然后再次使用‘p’查看我们所做的更改。
|
||||
- 使用‘w’保存更改。
|
||||
- 然后,按 `P` 来打印创建好的分区。
|
||||
- 改变分区类型,按 `L`可以列出所有可用的类型。
|
||||
- 按 `t` 修改分区类型。
|
||||
- 这里使用`fd`设置为 RAID 的类型。
|
||||
- 然后再次使用`p`查看我们所做的更改。
|
||||
- 使用`w`保存更改。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建 sdb 分区
|
||||
*创建 sdb 分区*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 我们仍要按照上面的步骤来创建 sdc 和 sdd 的分区。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -118,7 +119,7 @@ CentOS 6.5 摘要
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建 sdc 分区
|
||||
*创建 sdc 分区*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建 /dev/sdd 分区 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -126,93 +127,87 @@ CentOS 6.5 摘要
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建 sdd 分区
|
||||
*创建 sdd 分区*
|
||||
|
||||
6. 创建分区后,检查三个磁盘 sdb, sdc, sdd 的变化。
|
||||
6、 创建分区后,检查三个磁盘 sdb, sdc, sdd 的变化。
|
||||
|
||||
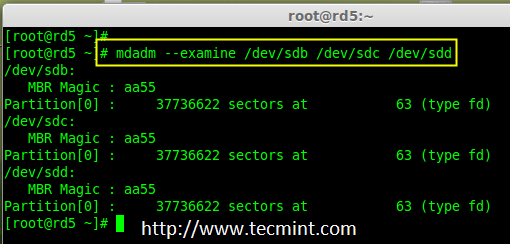
# mdadm --examine /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -E /dev/sd[b-c]
|
||||
# mdadm -E /dev/sd[b-c] # 或
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
检查磁盘变化
|
||||
*检查磁盘变化*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 在上面的图片中,磁盘的类型是 fd。
|
||||
|
||||
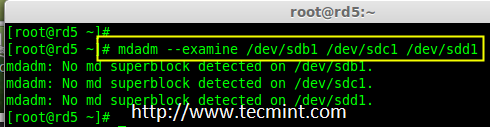
7.现在在新创建的分区检查 RAID 块。如果没有检测到超级块,我们就能够继续下一步,创建一个新的 RAID 5 的设置在这些磁盘中。
|
||||
7、 现在在新创建的分区检查 RAID 块。如果没有检测到超级块,我们就能够继续下一步,在这些磁盘中创建一个新的 RAID 5 配置。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在分区中检查 Raid
|
||||
*在分区中检查 RAID *
|
||||
|
||||
### 第3步:创建 md 设备 md0 ###
|
||||
|
||||
8. 现在创建一个 RAID 设备“md0”(即 /dev/md0)使用所有新创建的分区(sdb1, sdc1 and sdd1) ,使用以下命令。
|
||||
8、 现在使用所有新创建的分区(sdb1, sdc1 和 sdd1)创建一个 RAID 设备“md0”(即 /dev/md0),使用以下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --create /dev/md0 --level=5 --raid-devices=3 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1 /dev/sdd1
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -C /dev/md0 -l=5 -n=3 /dev/sd[b-d]1
|
||||
# mdadm -C /dev/md0 -l=5 -n=3 /dev/sd[b-d]1 # 或
|
||||
|
||||
9. 创建 RAID 设备后,检查并确认 RAID,包括设备和从 mdstat 中输出的 RAID 级别。
|
||||
9、 创建 RAID 设备后,检查并确认 RAID,从 mdstat 中输出中可以看到包括的设备的 RAID 级别。
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证 Raid 设备
|
||||
*验证 Raid 设备*
|
||||
|
||||
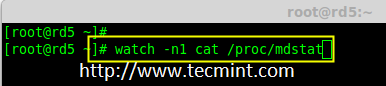
如果你想监视当前的创建过程,你可以使用‘watch‘命令,使用 watch ‘cat /proc/mdstat‘,它会在屏幕上显示且每隔1秒刷新一次。
|
||||
如果你想监视当前的创建过程,你可以使用`watch`命令,将 `cat /proc/mdstat` 传递给它,它会在屏幕上显示且每隔1秒刷新一次。
|
||||
|
||||
# watch -n1 cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
监控 Raid 5 过程
|
||||
*监控 RAID 5 构建过程*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Raid 5 过程概要
|
||||
*Raid 5 过程概要*
|
||||
|
||||
10. 创建 RAID 后,使用以下命令验证 RAID 设备
|
||||
10、 创建 RAID 后,使用以下命令验证 RAID 设备
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -E /dev/sd[b-d]1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证 Raid 级别
|
||||
*验证 Raid 级别*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 因为它显示三个磁盘的信息,上述命令的输出会有点长。
|
||||
|
||||
11. 接下来,验证 RAID 阵列的假设,这包含正在运行 RAID 的设备,并开始重新同步。
|
||||
11、 接下来,验证 RAID 阵列,假定包含 RAID 的设备正在运行并已经开始了重新同步。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --detail /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证 Raid 阵列
|
||||
*验证 RAID 阵列*
|
||||
|
||||
### 第4步:为 md0 创建文件系统###
|
||||
|
||||
12. 在挂载前为“md0”设备创建 ext4 文件系统。
|
||||
12、 在挂载前为“md0”设备创建 ext4 文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建 md0 文件系统
|
||||
*创建 md0 文件系统*
|
||||
|
||||
13.现在,在‘/mnt‘下创建目录 raid5,然后挂载文件系统到 /mnt/raid5/ 下并检查下挂载点的文件,你会看到 lost+found 目录。
|
||||
13、 现在,在`/mnt`下创建目录 raid5,然后挂载文件系统到 /mnt/raid5/ 下,并检查挂载点下的文件,你会看到 lost+found 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/raid5
|
||||
# mount /dev/md0 /mnt/raid5/
|
||||
# ls -l /mnt/raid5/
|
||||
|
||||
14. 在挂载点 /mnt/raid5 下创建几个文件,并在其中一个文件中添加一些内容然后去验证。
|
||||
14、 在挂载点 /mnt/raid5 下创建几个文件,并在其中一个文件中添加一些内容然后去验证。
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /mnt/raid5/raid5_tecmint_{1..5}
|
||||
# ls -l /mnt/raid5/
|
||||
@ -222,9 +217,9 @@ Raid 5 过程概要
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
挂载 Raid 设备
|
||||
*挂载 RAID 设备*
|
||||
|
||||
15. 我们需要在 fstab 中添加条目,否则系统重启后将不会显示我们的挂载点。然后编辑 fstab 文件添加条目,在文件尾追加以下行,如下图所示。挂载点会根据你环境的不同而不同。
|
||||
15、 我们需要在 fstab 中添加条目,否则系统重启后将不会显示我们的挂载点。编辑 fstab 文件添加条目,在文件尾追加以下行。挂载点会根据你环境的不同而不同。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/fstab
|
||||
|
||||
@ -232,19 +227,19 @@ Raid 5 过程概要
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
自动挂载 Raid 5
|
||||
*自动挂载 RAID 5*
|
||||
|
||||
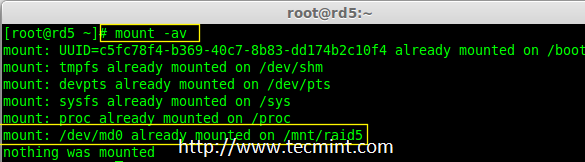
16. 接下来,运行‘mount -av‘命令检查 fstab 条目中是否有错误。
|
||||
16、 接下来,运行`mount -av`命令检查 fstab 条目中是否有错误。
|
||||
|
||||
# mount -av
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
检查 Fstab 错误
|
||||
*检查 Fstab 错误*
|
||||
|
||||
### 第5步:保存 Raid 5 的配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
17. 在前面章节已经说过,默认情况下 RAID 没有配置文件。我们必须手动保存。如果此步不跟 RAID 设备将不会存在 md0,它将会跟一些其他数子。
|
||||
17、 在前面章节已经说过,默认情况下 RAID 没有配置文件。我们必须手动保存。如果此步中没有跟随不属于 md0 的 RAID 设备,它会是一些其他随机数字。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,我们必须要在系统重新启动之前保存配置。如果配置保存它在系统重新启动时会被加载到内核中然后 RAID 也将被加载。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -252,17 +247,17 @@ Raid 5 过程概要
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
保存 Raid 5 配置
|
||||
*保存 RAID 5 配置*
|
||||
|
||||
注意:保存配置将保持 RAID 级别的稳定性在 md0 设备中。
|
||||
注意:保存配置将保持 md0 设备的 RAID 级别稳定不变。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第6步:添加备用磁盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||
18.备用磁盘有什么用?它是非常有用的,如果我们有一个备用磁盘,当我们阵列中的任何一个磁盘发生故障后,这个备用磁盘会主动添加并重建进程,并从其他磁盘上同步数据,所以我们可以在这里看到冗余。
|
||||
18、 备用磁盘有什么用?它是非常有用的,如果我们有一个备用磁盘,当我们阵列中的任何一个磁盘发生故障后,这个备用磁盘会进入激活重建过程,并从其他磁盘上同步数据,这样就有了冗余。
|
||||
|
||||
更多关于添加备用磁盘和检查 RAID 5 容错的指令,请阅读下面文章中的第6步和第7步。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Add Spare Drive to Raid 5 Setup][4]
|
||||
- [在 RAID 5 中添加备用磁盘][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -274,12 +269,12 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-raid-5-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/understanding-raid-setup-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-raid0-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-raid1-in-linux/
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-6085-1.html
|
||||
[2]:https://linux.cn/article-6087-1.html
|
||||
[3]:https://linux.cn/article-6093-1.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-raid-6-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
Xtreme Download Manager Updated With Fresh GUI
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Xtreme Download Manager][1], unarguably one of the [best download managers for Linux][2], has a new version named XDM 2015 which brings a fresh new look to it.
|
||||
|
||||
Xtreme Download Manager, also known as XDM or XDMAN, is a popular cross-platform download manager available for Linux, Windows and Mac OS X. It is also compatible with all major web browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari enabling you to download directly from XDM when you try to download something in your web browser.
|
||||
|
||||
Applications such as XDM are particularly useful when you have slow/limited network connectivity and you need to manage your downloads. Imagine downloading a huge file from internet on a slow network. What if you could pause and resume the download at will? XDM helps you in such situations.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the main features of XDM are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Pause and resume download
|
||||
- [Download videos from YouTube][3] and other video sites
|
||||
- Force assemble
|
||||
- Download speed acceleration
|
||||
- Schedule downloads
|
||||
- Limit download speed
|
||||
- Web browser integration
|
||||
- Support for proxy servers
|
||||
|
||||
Here you can see the difference between the old and new XDM.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Old XDM
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
New XDM
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Xtreme Download Manager in Ubuntu based Linux distros ###
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to the PPA by Noobslab, you can easily install Xtreme Download Manager using the commands below. XDM requires Java but thanks to the PPA, you don’t need to bother with installing dependencies separately.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install xdman
|
||||
|
||||
The above PPA should be available for Ubuntu and other Ubuntu based Linux distributions such as Linux Mint, elementary OS, Linux Lite etc.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Remove XDM ####
|
||||
|
||||
To remove XDM (installed using the PPA), use the commands below:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove xdman
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
|
||||
For other Linux distributions, you can download it from the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Xtreme Download Manager][4]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/xtreme-download-manager-install/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://xdman.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/4-best-download-managers-for-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/download-youtube-videos-ubuntu/
|
||||
[4]:http://xdman.sourceforge.net/download.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
The Strangest, Most Unique Linux Distros
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
From the most consumer focused distros like Ubuntu, Fedora, Mint or elementary OS to the more obscure, minimal and enterprise focused ones such as Slackware, Arch Linux or RHEL, I thought I've seen them all. Couldn't have been any further from the truth. Linux eco-system is very diverse. There's one for everyone. Let's discuss the weird and wacky world of niche Linux distros that represents the true diversity of open platforms.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Puppy Linux**: An operating system which is about 1/10th the size of an average DVD quality movie rip, that's Puppy Linux for you. The OS is just 100 MB in size! And it can run from RAM making it unusually fast even in older PCs. You can even remove the boot medium after the operating system has started! Can it get any better than that? System requirements are bare minimum, most hardware are automatically detected, and it comes loaded with software catering to your basic needs. [Experience Puppy Linux][1].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Suicide Linux**: Did the name scare you? Well it should. 'Any time - any time - you type any remotely incorrect command, the interpreter creatively resolves it into rm -rf / and wipes your hard drive'. Simple as that. I really want to know the ones who are confident enough to risk their production machines with [Suicide Linux][2]. **Warning: DO NOT try this on production machines!** The whole thing is available in a neat [DEB package][3] if you're interested.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**PapyrOS**: "Strange" in a good way. PapyrOS is trying to adapt the material design language of Android into their brand new Linux distribution. Though the project is in early stages, it already looks very promising. The project page says the OS is 80% complete and one can expect the first Alpha release anytime soon. We did a small write up on [PapyrOS][4] when it was announced and by the looks of it, PapyrOS might even become a trend-setter of sorts. Follow the project on [Google+][5] and contribute via [BountySource][6] if you're interested.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Qubes OS**: Qubes is an open-source operating system designed to provide strong security using a Security by Compartmentalization approach. The assumption is that there can be no perfect, bug-free desktop environment. And by implementing a 'Security by Isolation' approach, [Qubes Linux][7] intends to remedy that. Qubes is based on Xen, the X Window System, and Linux, and can run most Linux applications and supports most Linux drivers. Qubes was selected as a finalist of Access Innovation Prize 2014 for Endpoint Security Solution.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Satanic Edition**: Ubuntu SE is a Linux distribution based on Ubuntu. "It brings together the best of free software and free metal music" in one comprehensive package consisting of themes, wallpapers, and even some heavy-metal music sourced from talented new artists. Though the project doesn't look actively developed anymore, Ubuntu Satanic Edition is strange in every sense of that word. [Ubuntu SE (Slightly NSFW)][8].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Tiny Core Linux**: Puppy Linux not small enough? Try this. Tiny Core Linux is a 12 MB graphical Linux desktop! Yep, you read it right. One major caveat: It is not a complete desktop nor is all hardware completely supported. It represents only the core needed to boot into a very minimal X desktop typically with wired internet access. There is even a version without the GUI called Micro Core Linux which is just 9MB in size. [Tiny Core Linux][9] folks.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**NixOS**: A very experienced-user focused Linux distribution with a unique approach to package and configuration management. In other distributions, actions such as upgrades can be dangerous. Upgrading a package can cause other packages to break, upgrading an entire system is much less reliable than reinstalling from scratch. And top of all that you can't safely test what the results of a configuration change will be, there's no "Undo" so to speak. In NixOS, the entire operating system is built by the Nix package manager from a description in a purely functional build language. This means that building a new configuration cannot overwrite previous configurations. Most of the other features follow this pattern. Nix stores all packages in isolation from each other. [More about NixOS][10].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**GoboLinux**: This is another very unique Linux distro. What makes GoboLinux so different from the rest is its unique re-arrangement of the filesystem. It has its own subdirectory tree, where all of its files and programs are stored. GoboLinux does not have a package database because the filesystem is its database. In some ways, this sort of arrangement is similar to that seen in OS X. [Get GoboLinux][11].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Hannah Montana Linux**: Here is a Linux distro based on Kubuntu with a Hannah Montana themed boot screen, KDM, icon set, ksplash, plasma, color scheme, and wallpapers (I'm so sorry). [Link][12]. Project not active anymore.
|
||||
|
||||
**RLSD Linux**: An extremely minimalistic, small, lightweight and security-hardened, text-based operating system built on Linux. "It's a unique distribution that provides a selection of console applications and home-grown security features which might appeal to hackers," developers claim. [RLSD Linux][13].
|
||||
|
||||
Did we miss anything even stranger? Let us know.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techdrivein.com/2015/08/the-strangest-most-unique-linux-distros.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Manuel Jose
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://puppylinux.org/main/Overview%20and%20Getting%20Started.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://qntm.org/suicide
|
||||
[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/suicide-linux/files/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.techdrivein.com/2015/02/papyros-material-design-linux-coming-soon.html
|
||||
[5]:https://plus.google.com/communities/109966288908859324845/stream/3262a3d3-0797-4344-bbe0-56c3adaacb69
|
||||
[6]:https://www.bountysource.com/teams/papyros
|
||||
[7]:https://www.qubes-os.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://ubuntusatanic.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://tinycorelinux.net/
|
||||
[10]:https://nixos.org/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.gobolinux.org/
|
||||
[12]:http://hannahmontana.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[13]:http://rlsd2.dimakrasner.com/
|
||||
@ -1,114 +0,0 @@
|
||||
wyangsun translating
|
||||
Install Strongswan - A Tool to Setup IPsec Based VPN in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
IPsec is a standard which provides the security at network layer. It consist of authentication header (AH) and encapsulating security payload (ESP) components. AH provides the packet Integrity and confidentiality is provided by ESP component . IPsec ensures the following security features at network layer.
|
||||
|
||||
- Confidentiality
|
||||
- Integrity of packet
|
||||
- Source Non. Repudiation
|
||||
- Replay attack protection
|
||||
|
||||
[Strongswan][1] is an open source implementation of IPsec protocol and Strongswan stands for Strong Secure WAN (StrongS/WAN). It supports the both version of automatic keying exchange in IPsec VPN (Internet keying Exchange (IKE) V1 & V2).
|
||||
|
||||
Strongswan basically provides the automatic keying sharing between two nodes/gateway of the VPN and after that it uses the Linux Kernel implementation of IPsec (AH & ESP). Key shared using IKE mechanism is further used in the ESP for the encryption of data. In IKE phase, strongswan uses the encryption algorithms (AES,SHA etc) of OpenSSL and other crypto libraries. However, ESP component of IPsec uses the security algorithm which are implemented in the Linux Kernel. The main features of Strongswan are given below.
|
||||
|
||||
- 509 certificates or pre-shared keys based Authentication
|
||||
- Support of IKEv1 and IKEv2 key exchange protocols
|
||||
- Optional built-in integrity and crypto tests for plugins and libraries
|
||||
- Support of elliptic curve DH groups and ECDSA certificates
|
||||
- Storage of RSA private keys and certificates on a smartcard.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be used in the client / server (road warrior) and gateway to gateway scenarios.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install ###
|
||||
|
||||
Almost all Linux distro’s, supports the binary package of Strongswan. In this tutorial, we will install the strongswan from binary package and also the compilation of strongswan source code with desirable features.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using binary package ###
|
||||
|
||||
Strongswan can be installed using following command on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS .
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo aptitude install strongswan
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The global configuration (strongswan.conf) file and ipsec configuration (ipsec.conf/ipsec.secrets) files of strongswan are under /etc/ directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pre-requisite for strongswan source compilation & installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
- GMP (Mathematical/Precision Library used by strongswan)
|
||||
- OpenSSL (Crypto Algorithms from this library)
|
||||
- PKCS (1,7,8,11,12)(Certificate encoding and smart card integration with Strongswan )
|
||||
|
||||
#### Procedure ####
|
||||
|
||||
**1)** Go to /usr/src/ directory using following command in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$cd /usr/src
|
||||
|
||||
**2)** Download the source code from strongswan site suing following command
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo wget http://download.strongswan.org/strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
(strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz is the latest version.)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**3)** Extract the downloaded software and go inside it using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo tar –xvzf strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz; cd strongswan-5.2.1
|
||||
|
||||
**4)** Configure the strongswan as per desired options using configure command.
|
||||
|
||||
./configure --prefix=/usr/local -–enable-pkcs11 -–enable-openssl
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If GMP library is not installed, then configure script will generate following error.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, first of all, install the GMP library using following command and then run the configure script.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
However, if GMP is already installed and still above error exists then create soft link of libgmp.so library at /usr/lib , /lib/, /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ paths in Ubuntu using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so.10.1.3 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the creation of libgmp.so softlink, again run the ./configure script and it may find the gmp library. However, it may generate another error of gmp header file which is shown the following figure.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install the libgmp-dev package using following command for the solution of above error.
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo aptitude install libgmp-dev
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After installation of development package of gmp library, again run the configure script and if it does not produce any error, then the following output will be displayed.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Type the following commands for the compilation and installation of strongswan.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make ; sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
After the installation of strongswan , the Global configuration (strongswan.conf) and ipsec policy/secret configuration files (ipsec.conf/ipsec.secretes) are placed in **/usr/local/etc** directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Strongswan can be used as tunnel or transport mode depends on our security need. It provides well known site-2-site and road warrior VPNs. It can be use easily with Cisco,Juniper devices.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/security/install-strongswan/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nido][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/naveeda/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.strongswan.org/
|
||||
@ -1,187 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by GOLinux!
|
||||
Mhddfs – Combine Several Smaller Partition into One Large Virtual Storage
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Let’s assume that you have 30GB of movies and you have 3 drives each 20 GB in size. So how will you store?
|
||||
|
||||
Obviously you can split your videos in two or three different volumes and store them on the drive manually. This certainly is not a good idea, it is an exhaustive work which requires manual intervention and a lots of your time.
|
||||
|
||||
Another solution is to create a [RAID array of disk][1]. The RAID has always remained notorious for loss of storage reliability and usable disk space. Another solution is mhddfs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mhddfs – Combine Multiple Partitions in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs is a driver for Linux that combines several mount points into one virtual disk. It is a fuse based driver, which provides a easy solution for large data storage. It combines all small file systems to create a single big virtual filesystem which contains every particle of its member filesystem including files and free spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Why you need Mhddfs? ####
|
||||
|
||||
All your storage devices creates a single virtual pool and it can be mounted right at the boot. This small utility takes care of, which drive is full and which is empty and to write data to what drive, intelligently. Once you create virtual drives successfully, you can share your virtual filesystem using [SAMBA][2]. Your client will always see a huge drive and lots of free space.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features of Mhddfs ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Get attributes of the file system and system information.
|
||||
- Set attributes of the file system.
|
||||
- Create, Read, Remove and write Directories and files.
|
||||
- Support for file locks and Hardlinks on single device.
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="472"></colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="491"></colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="29" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">Pros of mhddfs</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">Cons of mhddfs</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Perfect for home users.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;">mhddfs driver is not built in the Linux Kernel</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Simple to run.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Required lots of processing power during runtime</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> No evidence of Data loss</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> No redundancy solution.</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Do not split the file.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Hardlinks moving not supported</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Add new files to the combined virtual filesystem.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Manage the location where these files are saved.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Extended file attributes</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation of Mhddfs in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian and portable to alike systems, you can install mhddfs package using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install Mhddfs on Debian based Systems
|
||||
|
||||
On RHEL/CentOS Linux systems, you need to turn on [epel-repository][3] and then execute the below command to install mhddfs package.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora 22+ systems, you may get it by dnf package manger as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# dnf install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install Mhddfs on Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
If incase, mhddfs package isn’t available from epel repository, then you need to resolve following dependencies to install and compile it from source as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
- FUSE header files
|
||||
- GCC
|
||||
- libc6 header files
|
||||
- uthash header files
|
||||
- libattr1 header files (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
Next, download the latest source package simply as suggested below and compile it.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://mhddfs.uvw.ru/downloads/mhddfs_0.1.39.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar -zxvf mhddfs*.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd mhddfs-0.1.39/
|
||||
# make
|
||||
|
||||
You should be able to see binary mhddfs in the current directory. Move it to /usr/bin/ and /usr/local/bin/ as root.
|
||||
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/bin/
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
All set, mhddfs is ready to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I use Mhddfs? ###
|
||||
|
||||
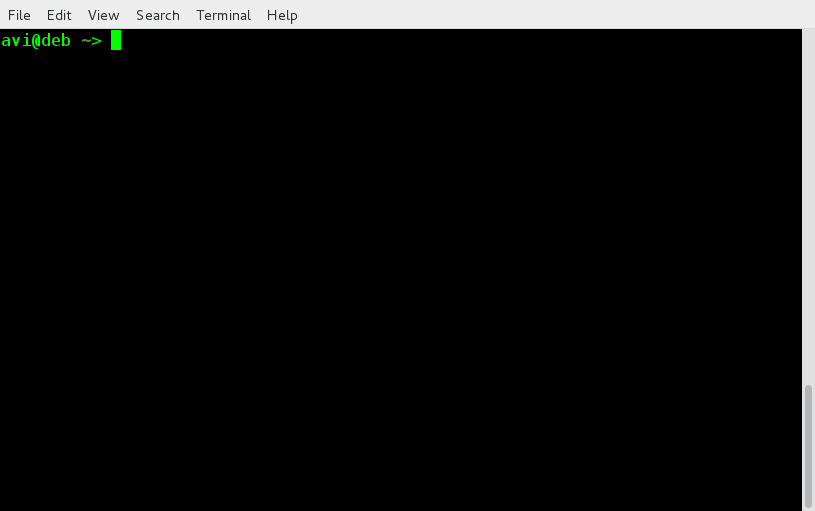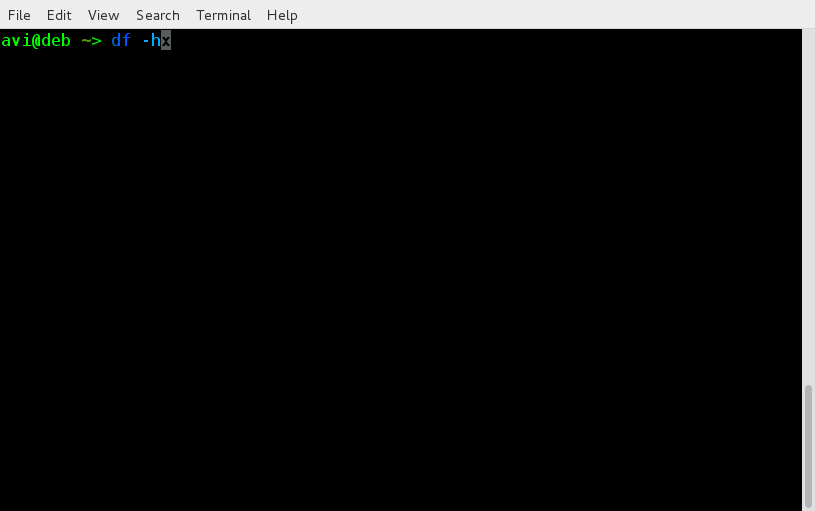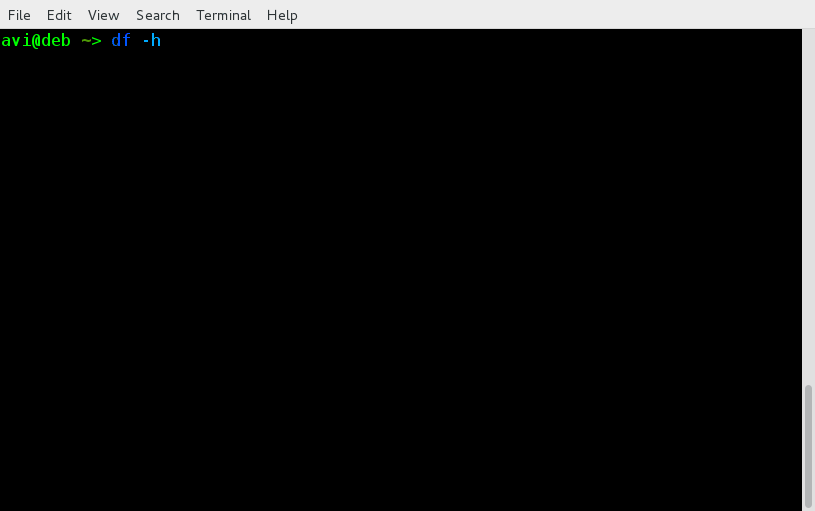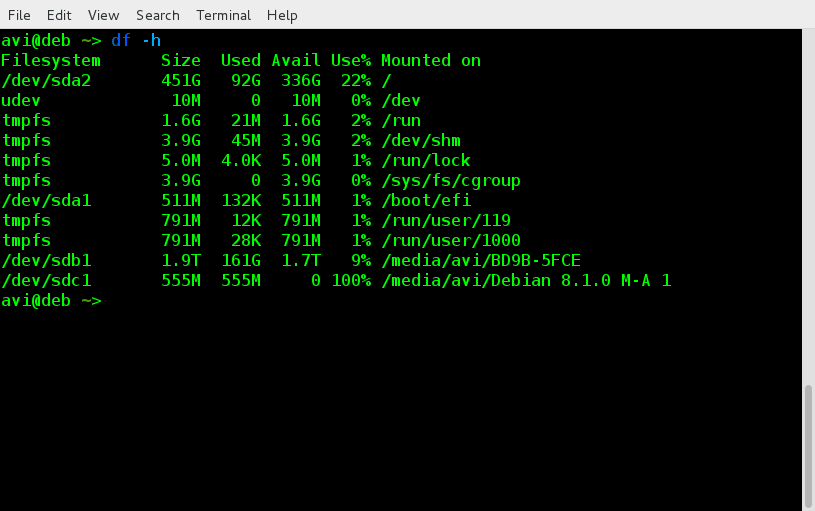
1. Lets see all the HDD mounted to my system currently.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample Output**
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/sda1 511M 132K 511M 1% /boot/efi
|
||||
/dev/sda2 451G 92G 336G 22% /
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 1.9T 161G 1.7T 9% /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE
|
||||
/dev/sdc1 555M 555M 0 100% /media/avi/Debian 8.1.0 M-A 1
|
||||
|
||||
Notice the ‘Mount Point‘ name here, which we will be using later.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Create a directory `/mnt/virtual_hdd` where all these all file system will be grouped together as,
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
3. And then mount all the file-systems. Either as root or as a user who is a member of FUSE group.
|
||||
|
||||
# mhddfs /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd -o allow_other
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mount All File System in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: We are used mount Point names here of all the HDDs. Obviously the mount point in your case will be different. Also notice “-o allow_other” option makes this Virtual file system visible to all others and not only the person who created it.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Now run “df -h” see all the filesystems. It should contain the one you created just now.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Verify Virtual File System Mount
|
||||
|
||||
You can perform all the option to the Virtual File System you created as you would have done to a Mounted Drive.
|
||||
|
||||
5. To create this Virtual File system on every system boot, you should add the below line of code (in your case it should be different, depending upon your mount point), at the end of /etc/fstab file as root.
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs# /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd fuse defaults,allow_other 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
6. If at any point of time you want to add/remove a new drive to Virtual_hdd, you may mount a new drive, copy the contents of mount point /mnt/virtual_hdd, un-mount the volume, Eject the Drive you want to remove and/or mount the new drive you want to include, Mount the overall filesystem under Virtual_hdd using mhddfs command and you should be done.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How do I Un-Mount Virtual_hdd? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Unmounting virtual_hdd is as easy as,
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Unmount Virtual Filesystem
|
||||
|
||||
Notice it is umount and not unmount. A lot of user type it wrong.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I am working on another post you people will love to read. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-partitions-into-one-in-linux-using-mhddfs/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/understanding-raid-setup-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/mount-filesystem-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Run Kali Linux 2.0 In Docker Container
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Introduction ###
|
||||
|
||||
Kali Linux is a well known operating system for security testers and ethical hackers. It comes bundled with a large list of security related applications and make it easy to perform penetration testing. Recently, [Kali Linux 2.0][1] is out and it is being considered as one of the most important release for this operating system. On the other hand, Docker technology is getting massive popularity due to its scalability and ease of use. Dockers make it super easy to ship your software applications to your users. Breaking news is that you can now run Kali Linux via Dockers; let’s see how :)
|
||||
|
||||
### Running Kali Linux 2.0 In Docker ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Related Notes**
|
||||
|
||||
If you don’t have docker installed on your system, you can do it by using the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
**For Ubuntu/Linux Mint/Debian:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install docker
|
||||
|
||||
**For Fedora/RHEL/CentOS:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install docker
|
||||
|
||||
**For Fedora 22:**
|
||||
|
||||
dnf install docker
|
||||
|
||||
You can start docker service by running:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo docker start
|
||||
|
||||
First of all make sure that docker service is running fine by using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo docker status
|
||||
|
||||
Kali Linux docker image has been uploaded online by Kali Linux development team, simply run following command to download this image to your system.
|
||||
|
||||
docker pull kalilinux/kali-linux-docker
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once download is complete, run following command to find out the Image ID for your downloaded Kali Linux docker image file.
|
||||
|
||||
docker images
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now run following command to start your kali Linux docker container from image file (Here replace Image ID with correct one).
|
||||
|
||||
docker run -i -t 198cd6df71ab3 /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
It will immediately start the container and will log you into the operating system, you can start working on Kali Linux here.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can verify that container is started/running fine, by using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
docker ps
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Dockers are the smartest way to deploy and distribute your packages. Kali Linux docker image is pretty handy, does not consume any high amount of space on the disk and it is pretty easy to test this wonderful distro on any docker installed operating system now.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxpitstop.com/run-kali-linux-2-0-in-docker-container/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aun][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linuxpitstop.com/author/aun/
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxpitstop.com/install-kali-linux-2-0/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
|
||||
How to Convert From RPM to DEB and DEB to RPM Package Using Alien
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
As I’m sure you already know, there are plenty of ways to install software in Linux: using the package management system provided by your distribution ([aptitude, yum, or zypper][1], to name a few examples), compiling from source (though somewhat rare these days, it was the only method available during the early days of Linux), or utilizing a low level tool such as dpkg or rpm with .deb and .rpm standalone, precompiled packages, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Convert RPM to DEB and DEB to RPM Package Using Alien
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we will introduce you to alien, a tool that converts between different Linux package formats, with .rpm to .deb (and vice versa) being the most common usage.
|
||||
|
||||
This tool, even when its author is no longer maintaining it and states in his website that alien will always probably remain in experimental status, can come in handy if you need a certain type of package but can only find that program in another package format.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, alien saved my day once when I was looking for a .deb driver for a inkjet printer and couldn’t find any – the manufacturer only provided a .rpm package. I installed alien, converted the package, and before long I was able to use my printer without issues.
|
||||
|
||||
That said, we must clarify that this utility should not be used to replace important system files and libraries since they are set up differently across distributions. Only use alien as a last resort if the suggested installation methods at the beginning of this article are out of the question for the required program.
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, we must note that even though we will use CentOS and Debian in this article, alien is also known to work in Slackware and even in Solaris, besides the first two distributions and their respective families.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Installing Alien and Dependencies ###
|
||||
|
||||
To install alien in CentOS/RHEL 7, you will need to enable the EPEL and the Nux Dextop (yes, it’s Dextop – not Desktop) repositories, in that order:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install epel-release
|
||||
# rpm --import http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/RPM-GPG-KEY-nux.ro
|
||||
|
||||
The latest version of the package that enables this repository is currently 0.5 (published on Aug. 10, 2015). You should check [http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/dextop/el7/x86_64/][2] to see whether there’s a newer version before proceeding further:
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/dextop/el7/x86_64/nux-dextop-release-0-5.el7.nux.noarch.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
then do,
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install alien
|
||||
|
||||
In Fedora, you will only need to run the last command.
|
||||
|
||||
In Debian and derivatives, simply do:
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install alien
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Converting from .deb to .rpm Package ###
|
||||
|
||||
For this test we have chosen dateutils, which provides a set of date and time utilities to deal with large amounts of financial data. We will download the .deb package to our CentOS 7 box, convert it to .rpm and install it:
|
||||
|
||||
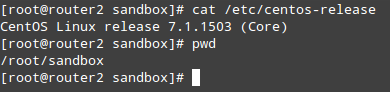
|
||||
|
||||
Check CentOS Version
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /etc/centos-release
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.us.debian.org/debian/pool/main/d/dateutils/dateutils_0.3.1-1.1_amd64.deb
|
||||
# alien --to-rpm --scripts dateutils_0.3.1-1.1_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Convert .deb to .rpm package in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**Important**: (Please note how, by default, alien increases the version minor number of the target package. If you want to override this behavior, add the –keep-version flag).
|
||||
|
||||
If we try to install the package right away, we will run into a slight issue:
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh dateutils-0.3.1-2.1.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install RPM Package
|
||||
|
||||
To solve this issue, we will enable the epel-testing repository and install the rpmrebuild utility to edit the settings of the package to be rebuilt:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum --enablerepo=epel-testing install rpmrebuild
|
||||
|
||||
Then run,
|
||||
|
||||
# rpmrebuild -pe dateutils-0.3.1-2.1.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Which will open up your default text editor. Go to the `%files` section and delete the lines that refer to the directories mentioned in the error message, then save the file and exit:
|
||||
|
||||
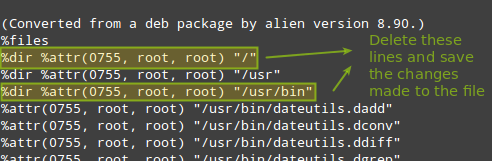
|
||||
|
||||
Convert .deb to Alien Version
|
||||
|
||||
When you exit the file you will be prompted to continue with the rebuild. If you choose Y, the file will be rebuilt into the specified directory (different than the current working directory):
|
||||
|
||||
# rpmrebuild –pe dateutils-0.3.1-2.1.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
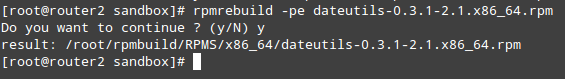
|
||||
|
||||
Build RPM Package
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can proceed to install the package and verify as usual:
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/dateutils-0.3.1-2.1.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
# rpm -qa | grep dateutils
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install Build RPM Package
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you can list the individual tools that were included with dateutils and alternatively check their respective man pages:
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l /usr/bin | grep dateutils
|
||||
|
||||
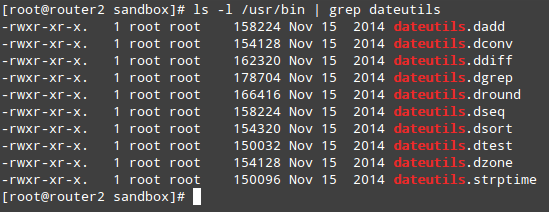
|
||||
|
||||
Verify Installed RPM Package
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Converting from .rpm to .deb Package ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this section we will illustrate how to convert from .rpm to .deb. In a 32-bit Debian Wheezy box, let’s download the .rpm package for the zsh shell from the CentOS 6 OS repository. Note that this shell is not available by default in Debian and derivatives.
|
||||
|
||||
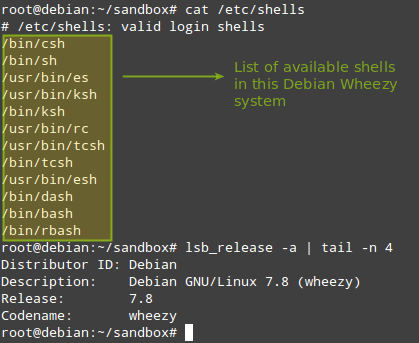
# cat /etc/shells
|
||||
# lsb_release -a | tail -n 4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check Shell and Debian OS Version
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6/os/i386/Packages/zsh-4.3.11-4.el6.centos.i686.rpm
|
||||
# alien --to-deb --scripts zsh-4.3.11-4.el6.centos.i686.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
You can safely disregard the messages about a missing signature:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Convert .rpm to .deb Package
|
||||
|
||||
After a few moments, the .deb file should have been generated and be ready to install:
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i zsh_4.3.11-5_i386.deb
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install RPM Converted Deb Package
|
||||
|
||||
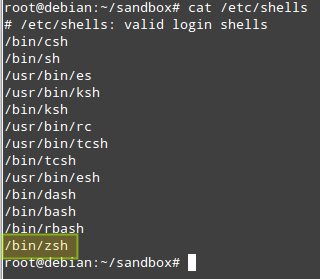
After the installation, you can verify that zsh is added to the list of valid shells:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /etc/shells
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Confirm Installed Zsh Package
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have explained how to convert from .rpm to .deb and vice versa to install packages as a last resort when such programs are not available in the repositories or as distributable source code. You will want to bookmark this article because all of us will need alien at one time or another.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to share your thoughts about this article using the form below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/convert-from-rpm-to-deb-and-deb-to-rpm-package-using-alien/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-package-management/
|
||||
[2]:http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/dextop/el7/x86_64/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
Linux/UNIX: Bash Read a File Line By Line
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
How do I read a file line by line under a Linux or UNIX-like system using KSH or BASH shell?
|
||||
|
||||
You can use while..do..done bash loop to read file line by line on a Linux, OSX, *BSD, or Unix-like system.
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax to read file line by line on a Bash Unix & Linux shell:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. The syntax is as follows for bash, ksh, zsh, and all other shells -
|
||||
1. while read -r line; do COMMAND; done < input.file
|
||||
1. The -r option passed to red command prevents backslash escapes from being interpreted.
|
||||
1. Add IFS= option before read command to prevent leading/trailing whitespace from being trimmed -
|
||||
1. while IFS= read -r line; do COMMAND_on $line; done < input.file
|
||||
|
||||
Here is more human readable syntax for you:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
input="/path/to/txt/file"
|
||||
while IFS= read -r var
|
||||
do
|
||||
echo "$var"
|
||||
done < "$input"
|
||||
|
||||
**Examples**
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some examples:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/ksh
|
||||
file="/home/vivek/data.txt"
|
||||
while IFS= read line
|
||||
do
|
||||
# display $line or do somthing with $line
|
||||
echo "$line"
|
||||
done <"$file"
|
||||
|
||||
The same example using bash shell:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
file="/home/vivek/data.txt"
|
||||
while IFS= read -r line
|
||||
do
|
||||
# display $line or do somthing with $line
|
||||
printf '%s\n' "$line"
|
||||
done <"$file"
|
||||
|
||||
You can also read field wise:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
file="/etc/passwd"
|
||||
while IFS=: read -r f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 f6 f7
|
||||
do
|
||||
# display fields using f1, f2,..,f7
|
||||
printf 'Username: %s, Shell: %s, Home Dir: %s\n' "$f1" "$f7" "$f6"
|
||||
done <"$file"
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
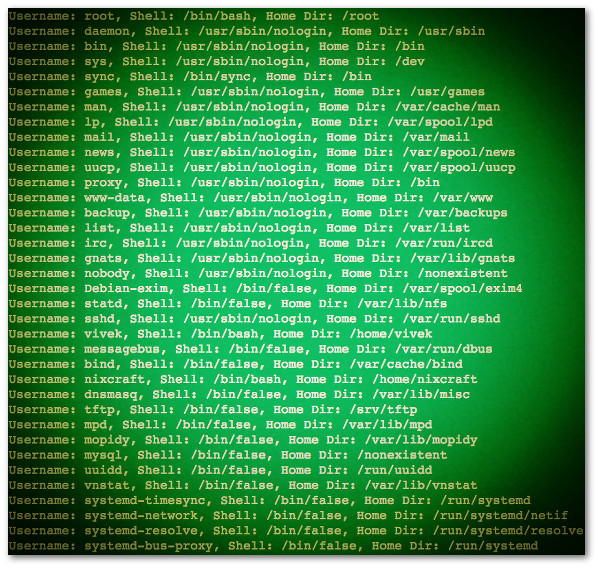
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.01: Bash shell scripting- read file line by line demo outputs
|
||||
|
||||
**Bash Scripting: Read text file line-by-line to create pdf files**
|
||||
|
||||
My input file is as follows (faq.txt):
|
||||
|
||||
4|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/mysql-user-creation/|Mysql User Creation: Setting Up a New MySQL User Account
|
||||
4096|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/ksh-korn-shell/|What is UNIX / Linux Korn Shell?
|
||||
4101|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/what-is-posix-shell/|What Is POSIX Shell?
|
||||
17267|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-check-battery-status/|Linux: Check Battery Status Command
|
||||
17245|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/restarting-ntp-service-on-linux/|Linux Restart NTPD Service Command
|
||||
17183|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/ubuntu-linux-determine-your-ip-address/|Ubuntu Linux: Determine Your IP Address
|
||||
17172|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/determine-ip-address-of-linux-server/|HowTo: Determine an IP Address My Linux Server
|
||||
16510|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/unix-linux-restart-php-service-command/|Linux / Unix: Restart PHP Service Command
|
||||
8292|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/mounting-harddisks-in-freebsd-with-mount-command/|FreeBSD: Mount Hard Drive / Disk Command
|
||||
8190|http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rebooting-solaris-unix-server/|Reboot a Solaris UNIX System
|
||||
|
||||
My bash script:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# Usage: Create pdf files from input (wrapper script)
|
||||
# Author: Vivek Gite <Www.cyberciti.biz> under GPL v2.x+
|
||||
#---------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
#Input file
|
||||
_db="/tmp/wordpress/faq.txt"
|
||||
|
||||
#Output location
|
||||
o="/var/www/prviate/pdf/faq"
|
||||
|
||||
_writer="~/bin/py/pdfwriter.py"
|
||||
|
||||
# If file exists
|
||||
if [[ -f "$_db" ]]
|
||||
then
|
||||
# read it
|
||||
while IFS='|' read -r pdfid pdfurl pdftitle
|
||||
do
|
||||
local pdf="$o/$pdfid.pdf"
|
||||
echo "Creating $pdf file ..."
|
||||
#Genrate pdf file
|
||||
$_writer --quiet --footer-spacing 2 \
|
||||
--footer-left "nixCraft is GIT UL++++ W+++ C++++ M+ e+++ d-" \
|
||||
--footer-right "Page [page] of [toPage]" --footer-line \
|
||||
--footer-font-size 7 --print-media-type "$pdfurl" "$pdf"
|
||||
done <"$_db"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
**Tip: Read from bash variable**
|
||||
|
||||
Let us say you want a list of all installed php packages on a Debian or Ubuntu Linux, enter:
|
||||
|
||||
# My input source is the contents of a variable called $list #
|
||||
list=$(dpkg --list php\* | awk '/ii/{print $2}')
|
||||
printf '%s\n' "$list"
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
php-pear
|
||||
php5-cli
|
||||
php5-common
|
||||
php5-fpm
|
||||
php5-gd
|
||||
php5-json
|
||||
php5-memcache
|
||||
php5-mysql
|
||||
php5-readline
|
||||
php5-suhosin-extension
|
||||
|
||||
You can now read from $list and install the package:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# BASH can iterate over $list variable using a "here string" #
|
||||
while IFS= read -r pkg
|
||||
do
|
||||
printf 'Installing php package %s...\n' "$pkg"
|
||||
/usr/bin/apt-get -qq install $pkg
|
||||
done <<< "$list"
|
||||
printf '*** Do not forget to run php5enmod and restart the server (httpd or php5-fpm) ***\n'
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
Installing php package php-pear...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-cli...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-common...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-fpm...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-gd...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-json...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-memcache...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-mysql...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-readline...
|
||||
Installing php package php5-suhosin-extension...
|
||||
*** Do not forget to run php5enmod and restart the server (httpd or php5-fpm) ***
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/unix-howto-read-line-by-line-from-file/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[作者名][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,217 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA Series: Securing SSH, Setting Hostname and Enabling Network Services – Part 8
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
As a system administrator you will often have to log on to remote systems to perform a variety of administration tasks using a terminal emulator. You will rarely sit in front of a real (physical) terminal, so you need to set up a way to log on remotely to the machines that you will be asked to manage.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, that may be the last thing that you will have to do in front of a physical terminal. For security reasons, using Telnet for this purpose is not a good idea, as all traffic goes through the wire in unencrypted, plain text.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, in this article we will also review how to configure network services to start automatically at boot and learn how to set up network and hostname resolution statically or dynamically.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA: Secure SSH and Enable Network Services – Part 8
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing and Securing SSH Communication ###
|
||||
|
||||
For you to be able to log on remotely to a RHEL 7 box using SSH, you will have to install the openssh, openssh-clients and openssh-servers packages. The following command not only will install the remote login program, but also the secure file transfer tool, as well as the remote file copy utility:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install openssh openssh-clients openssh-servers
|
||||
|
||||
Note that it’s a good idea to install the server counterparts as you may want to use the same machine as both client and server at some point or another.
|
||||
|
||||
After installation, there is a couple of basic things that you need to take into account if you want to secure remote access to your SSH server. The following settings should be present in the `/etc/ssh/sshd_config` file.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change the port where the sshd daemon will listen on from 22 (the default value) to a high port (2000 or greater), but first make sure the chosen port is not being used.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let’s suppose you choose port 2500. Use [netstat][1] in order to check whether the chosen port is being used or not:
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -npltu | grep 2500
|
||||
|
||||
If netstat does not return anything, you can safely use port 2500 for sshd, and you should change the Port setting in the configuration file as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
Port 2500
|
||||
|
||||
2. Only allow protocol 2:
|
||||
|
||||
Protocol 2
|
||||
|
||||
3. Configure the authentication timeout to 2 minutes, do not allow root logins, and restrict to a minimum the list of users which are allowed to login via ssh:
|
||||
|
||||
LoginGraceTime 2m
|
||||
PermitRootLogin no
|
||||
AllowUsers gacanepa
|
||||
|
||||
4. If possible, use key-based instead of password authentication:
|
||||
|
||||
PasswordAuthentication no
|
||||
RSAAuthentication yes
|
||||
PubkeyAuthentication yes
|
||||
|
||||
This assumes that you have already created a key pair with your user name on your client machine and copied it to your server as explained here.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Enable SSH Passwordless Login][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring Networking and Name Resolution ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. Every system administrator should be well acquainted with the following system-wide configuration files:
|
||||
|
||||
- /etc/hosts is used to resolve names <---> IPs in small networks.
|
||||
|
||||
Every line in the `/etc/hosts` file has the following structure:
|
||||
|
||||
IP address - Hostname - FQDN
|
||||
|
||||
For example,
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.0.10 laptop laptop.gabrielcanepa.com.ar
|
||||
|
||||
2. `/etc/resolv.conf` specifies the IP addresses of DNS servers and the search domain, which is used for completing a given query name to a fully qualified domain name when no domain suffix is supplied.
|
||||
|
||||
Under normal circumstances, you don’t need to edit this file as it is managed by the system. However, should you want to change DNS servers, be advised that you need to stick to the following structure in each line:
|
||||
|
||||
nameserver - IP address
|
||||
|
||||
For example,
|
||||
|
||||
nameserver 8.8.8.8
|
||||
|
||||
3. 3. `/etc/host.conf` specifies the methods and the order by which hostnames are resolved within a network. In other words, tells the name resolver which services to use, and in what order.
|
||||
|
||||
Although this file has several options, the most common and basic setup includes a line as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
order bind,hosts
|
||||
|
||||
Which indicates that the resolver should first look in the nameservers specified in `resolv.conf` and then to the `/etc/hosts` file for name resolution.
|
||||
|
||||
4. `/etc/sysconfig/network` contains routing and global host information for all network interfaces. The following values may be used:
|
||||
|
||||
NETWORKING=yes|no
|
||||
HOSTNAME=value
|
||||
|
||||
Where value should be the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
|
||||
|
||||
GATEWAY=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
|
||||
|
||||
Where XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX is the IP address of the network’s gateway.
|
||||
|
||||
GATEWAYDEV=value
|
||||
|
||||
In a machine with multiple NICs, value is the gateway device, such as enp0s3.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Files inside `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts` (network adapters configuration files).
|
||||
|
||||
Inside the directory mentioned previously, you will find several plain text files named.
|
||||
|
||||
ifcfg-name
|
||||
|
||||
Where name is the name of the NIC as returned by ip link show:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Check Network Link Status
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Network Files
|
||||
|
||||
Other than for the loopback interface, you can expect a similar configuration for your NICs. Note that some variables, if set, will override those present in `/etc/sysconfig/network` for this particular interface. Each line is commented for clarification in this article but in the actual file you should avoid comments:
|
||||
|
||||
HWADDR=08:00:27:4E:59:37 # The MAC address of the NIC
|
||||
TYPE=Ethernet # Type of connection
|
||||
BOOTPROTO=static # This indicates that this NIC has been assigned a static IP. If this variable was set to dhcp, the NIC will be assigned an IP address by a DHCP server and thus the next two lines should not be present in that case.
|
||||
IPADDR=192.168.0.18
|
||||
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
|
||||
GATEWAY=192.168.0.1
|
||||
NM_CONTROLLED=no # Should be added to the Ethernet interface to prevent NetworkManager from changing the file.
|
||||
NAME=enp0s3
|
||||
UUID=14033805-98ef-4049-bc7b-d4bea76ed2eb
|
||||
ONBOOT=yes # The operating system should bring up this NIC during boot
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting Hostnames ###
|
||||
|
||||
In Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, the hostnamectl command is used to both query and set the system’s hostname.
|
||||
|
||||
To display the current hostname, type:
|
||||
|
||||
# hostnamectl status
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check System Hostname
|
||||
|
||||
To change the hostname, use
|
||||
|
||||
# hostnamectl set-hostname [new hostname]
|
||||
|
||||
For example,
|
||||
|
||||
# hostnamectl set-hostname cinderella
|
||||
|
||||
For the changes to take effect you will need to restart the hostnamed daemon (that way you will not have to log off and on again in order to apply the change):
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart systemd-hostnamed
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Set System Hostname
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, RHEL 7 also includes the nmcli utility that can be used for the same purpose. To display the hostname, run:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli general hostname
|
||||
|
||||
and to change it:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli general hostname [new hostname]
|
||||
|
||||
For example,
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli general hostname rhel7
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Set Hostname Using nmcli Command
|
||||
|
||||
### Starting Network Services on Boot ###
|
||||
|
||||
To wrap up, let us see how we can ensure that network services are started automatically on boot. In simple terms, this is done by creating symlinks to certain files specified in the [Install] section of the service configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
In the case of firewalld (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service):
|
||||
|
||||
[Install]
|
||||
WantedBy=basic.target
|
||||
Alias=dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service
|
||||
|
||||
To enable the service:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable firewalld
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, disabling firewalld entitles removing the symlinks:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl disable firewalld
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enable Service at System Boot
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have summarized how to install and secure connections via SSH to a RHEL server, how to change its name, and finally how to ensure that network services are started on boot. If you notice that a certain service has failed to start properly, you can use systemctl status -l [service] and journalctl -xn to troubleshoot it.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to let us know what you think about this article using the comment form below. Questions are also welcome. We look forward to hearing from you!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-series-secure-ssh-set-hostname-enable-network-services-in-rhel-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ssh-passwordless-login-using-ssh-keygen-in-5-easy-steps/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
FSSlc Translating
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA Series: Installing, Configuring and Securing a Web and FTP Server – Part 9
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A web server (also known as a HTTP server) is a service that handles content (most commonly web pages, but other types of documents as well) over to a client in a network.
|
||||
@ -173,4 +175,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-series-install-and-secure-apache-web-server-an
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.google.com/cse?cx=partner-pub-2601749019656699:2173448976&ie=UTF-8&q=virtual+hosts&sa=Search&gws_rd=cr&ei=Dy9EVbb0IdHisASnroG4Bw#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=apache
|
||||
[3]:http://www.google.com/cse?cx=partner-pub-2601749019656699:2173448976&ie=UTF-8&q=virtual+hosts&sa=Search&gws_rd=cr&ei=Dy9EVbb0IdHisASnroG4Bw#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=apache
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
安装Strongswan - Linux上一个基于IPsec的vpn工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
IPsec是一个提供网络层安全的标准。它包含认证头(AH)和安全负载封装(ESP)组件。AH提供包的完整性,ESP组件提供包的保密性。IPsec确保了在网络层的安全特性。
|
||||
|
||||
- 保密性
|
||||
- 数据包完整性
|
||||
- 来源不可抵赖性
|
||||
- 重放攻击防护
|
||||
|
||||
[Strongswan][1]是一个IPsec协议实现的开源代码,Strongswan代表强壮开源广域网(StrongS/WAN)。它支持IPsec的VPN两个版本的密钥自动交换(网络密钥交换(IKE)V1和V2)。
|
||||
|
||||
Strongswan基本上提供了自动交换密钥共享VPN两个节点或网络,然后它使用Linux内核的IPsec(AH和ESP)实现。密钥共享使用了IKE机制的特性使用ESP编码数据。在IKE阶段,strongswan使用OpenSSL加密算法(AES,SHA等等)和其他加密类库。无论如何,ESP组成IPsec使用的安全算法,它是Linux内核实现的。Strongswan的主要特性是下面这些。
|
||||
|
||||
- x.509证书或基于预共享密钥认证
|
||||
- 支持IKEv1和IKEv2密钥交换协议
|
||||
- 可选内置插件和库的完整性和加密测试
|
||||
- 支持椭圆曲线DH群体和ECDSA证书
|
||||
- 在智能卡上存储RSA私钥和证书
|
||||
|
||||
它能被使用在客户端或服务器(road warrior模式)和网关到网关的情景。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
几乎所有的Linux发行版都支持Strongswan的二进制包。在这个教程,我们将从二进制包安装strongswan也编译strongswan合适的特性的源代码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用二进制包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用以下命令安装Strongswan到Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo aptitude install strongswan
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
strongswan的全局配置(strongswan.conf)文件和ipsec配置(ipsec.conf/ipsec.secrets)文件都在/etc/目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
### strongswan源码编译安装的依赖包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- GMP(strongswan使用的Mathematical/Precision 库)
|
||||
- OpenSSL(加密算法在这个库里)
|
||||
- PKCS(1,7,8,11,12)(证书编码和智能卡与Strongswan集成)
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 ####
|
||||
|
||||
**1)** 在终端使用下面命令到/usr/src/目录
|
||||
|
||||
$cd /usr/src
|
||||
|
||||
**2)** 用下面命令从strongswan网站下载源代码
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo wget http://download.strongswan.org/strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
(strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz 是最新版。)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**3)** 用下面命令提取下载软件,然后进入目录。
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo tar –xvzf strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz; cd strongswan-5.2.1
|
||||
|
||||
**4)** 使用configure命令配置strongswan每个想要的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
./configure --prefix=/usr/local -–enable-pkcs11 -–enable-openssl
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果GMP库没有安装,然后配置脚本将会发生下面的错误。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
因此,首先,使用下面命令安装GMP库然后执行配置脚本。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
无论如何,如果GMP已经安装而且还一致报错,然后在Ubuntu上使用下面命令创建libgmp.so库的软连到/usr/lib,/lib/,/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/路径下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so.10.1.3 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建libgmp.so软连后,再执行./configure脚本也许就找到gmp库了。无论如何,gmp头文件也许发生其他错误,像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
为解决上面的错误,使用下面命令安装libgmp-dev包
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo aptitude install libgmp-dev
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装gmp的开发库后,在运行一遍配置脚本,如果没有发生错误,则将看见下面的这些输出。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令编译安装strongswan。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make ; sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
安装strongswan后,全局配置(strongswan.conf)和ipsec策略/密码配置文件(ipsec.conf/ipsec.secretes)被放在**/usr/local/etc**目录。
|
||||
|
||||
根据我们的安全需要Strongswan可以用作隧道或者传输模式。它提供众所周知的site-2-site模式和road warrior模式的VPN。它很容易使用在Cisco,Juniper设备上。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/security/install-strongswan/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nido][a]
|
||||
译者:[wyangsun](https://github.com/wyangsun)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/naveeda/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.strongswan.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,183 @@
|
||||
Mhddfs——将多个小分区合并成一个大的虚拟存储
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
让我们假定你有30GB的电影,并且你有3个驱动器,每个的大小为20GB。那么,你会怎么来存放东西呢?
|
||||
|
||||
很明显,你可以将你的视频分割成2个或者3个不同的卷,并将它们手工存储到驱动器上。这当然不是一个好主意,它成了一项费力的工作,它需要你手工干预,而且花费你大量时间。
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个解决方案是创建一个[RAID磁盘阵列][1]。然而,RAID在缺乏存储可靠性,磁盘空间可用性差等方面声名狼藉。另外一个解决方案,就是mhddfs。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Mhddfs——在Linux中合并多个分区
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs是一个用于Linux的驱动,它可以将多个挂载点合并到一个虚拟磁盘中。它是一个基于FUSE的驱动,提供了一个用于大数据存储的简单解决方案。它将所有小文件系统合并,以创建一个单一的大虚拟文件系统,该文件系统包含其成员文件系统的所有颗粒,包括文件和空闲空间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你为什么需要Mhddfs? ####
|
||||
|
||||
你所有存储设备创建了一个单一的虚拟池,它可以在启动时被挂载。这个小工具可以智能地照看并处理哪个驱动器满了,哪个驱动器空着,将数据写到哪个驱动器中。当你成功创建虚拟驱动器后,你可以使用[SAMBA][2]来共享你的虚拟文件系统。你的客户端将在任何时候都看到一个巨大的驱动器和大量的空闲空间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Mhddfs特性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 获取文件系统属性和系统信息。
|
||||
- 设置文件系统属性。
|
||||
- 创建、读取、移除和写入目录和文件。
|
||||
- 支持文件锁和单一设备上的硬链接。
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="472"></colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="491"></colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="29" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">mhddfs的优点</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">mhddfs的缺点</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 适合家庭用户</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;">mhddfs驱动没有内建在Linux内核中 </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 运行简单</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 运行时需要大量处理能力</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 没有明显的数据丢失</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 没有冗余解决方案</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 不分割文件</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 不支持移动硬链接</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 添加新文件到合并的虚拟文件系统</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 管理文件保存的位置</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 扩展文件属性</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux中安装Mhddfs ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Debian及其类似的移植系统中,你可以使用下面的命令来安装mhddfs包。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装Mhddfs到基于Debian的系统中
|
||||
|
||||
在RHEL/CentOS Linux系统中,你需要开启[epel仓库][3],然后执行下面的命令来安装mhddfs包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora 22及以上系统中,你可以通过dnf包管理来获得它,就像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||
# dnf install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装Mhddfs到Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
如果万一mhddfs包不能从epel仓库获取到,那么你需要解决下面的依赖,然后像下面这样来编译源码并安装。
|
||||
|
||||
- FUSE头文件
|
||||
- GCC
|
||||
- libc6头文件
|
||||
- uthash头文件
|
||||
- libattr1头文件(可选)
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,只需从下面建议的地址下载最新的源码包,然后编译。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://mhddfs.uvw.ru/downloads/mhddfs_0.1.39.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar -zxvf mhddfs*.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd mhddfs-0.1.39/
|
||||
# make
|
||||
|
||||
你应该可以在当前目录中看到mhddfs的二进制文件,以root身份将它移动到/usr/bin/和/usr/local/bin/中。
|
||||
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/bin/
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
一切搞定,mhddfs已经可以用了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 我怎么使用Mhddfs? ###
|
||||
|
||||
1.让我们看看当前所有挂载到我们系统中的硬盘。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
**样例输出**
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/sda1 511M 132K 511M 1% /boot/efi
|
||||
/dev/sda2 451G 92G 336G 22% /
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 1.9T 161G 1.7T 9% /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE
|
||||
/dev/sdc1 555M 555M 0 100% /media/avi/Debian 8.1.0 M-A 1
|
||||
|
||||
注意这里的‘挂载点’名称,我们后面会使用到它们。
|
||||
|
||||
2.创建目录‘/mnt/virtual_hdd’,在这里,所有这些文件系统将被组成组。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
3.然后,挂载所有文件系统。你可以通过root或者FUSE组中的某个成员来完成。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# mhddfs /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd -o allow_other
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在Linux中挂载所有文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:这里我们使用了所有硬盘的挂载点名称,很明显,你的挂载点名称会有所不同。也请注意“-o allow_other”选项可以让这个虚拟文件系统让其它所有人可见,而不仅仅是创建它的人。
|
||||
|
||||
4.现在,运行“df -h”来看看所有文件系统。它应该包含了你刚才创建的那个。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
验证虚拟文件系统挂载
|
||||
|
||||
你可以像对已挂在的驱动器那样给虚拟文件系统部署所有的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
5.要在每次系统启动创建这个虚拟文件系统,你应该以root身份添加下面的这行代码(在你那里会有点不同,取决于你的挂载点)到/etc/fstab文件的末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs# /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd fuse defaults,allow_other 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
6.如果在任何时候你想要添加/移除一个新的驱动器到/从虚拟硬盘,你可以挂载一个新的驱动器,拷贝/mnt/vritual_hdd的内容,卸载卷,弹出你要移除的的驱动器并/或挂载你要包含的新驱动器。使用mhddfs命令挂载全部文件系统到Virtual_hdd下,这样就全部搞定了。
|
||||
#### 我怎么卸载Virtual_hdd? ####
|
||||
|
||||
卸载virtual_hdd相当简单,就像下面这样
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
卸载虚拟文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
注意,是umount,而不是unmount,很多用户都输错了。
|
||||
|
||||
到现在为止全部结束了。我正在写另外一篇文章,你们一定喜欢读的。到那时,请保持连线到Tecmint。请在下面的评论中给我们提供有用的反馈吧。请为我们点赞并分享,帮助我们扩散。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-partitions-into-one-in-linux-using-mhddfs/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/understanding-raid-setup-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/mount-filesystem-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
如何在Docker容器中运行Kali Linux 2.0
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### 介绍 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Kali Linux是一个对于安全测试人员和白帽的一个知名的操作系统。它带有大量安全相关的程序,这让它很容易用于渗透测试。最近,[Kali Linux 2.0][1]发布了,并且它被认为是这个操作系统最重要的一次发布。另一方面,Docker技术由于它的可扩展性和易用性让它变得很流行。Dokcer让你非常容易地将你的程序带给你的用户。好消息是你可以通过Docker运行Kali Linux了,让我们看看该怎么做:)
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Docker中运行Kali Linux 2.0 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**相关提示**
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还没有在系统中安装docker,你可以运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Ubuntu/Linux Mint/Debian:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install docker
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Fedora/RHEL/CentOS:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install docker
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Fedora 22:**
|
||||
|
||||
dnf install docker
|
||||
|
||||
你可以运行下面的命令来启动docker:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo docker start
|
||||
|
||||
首先运行下面的命令确保服务正在运行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo docker status
|
||||
|
||||
Kali Linux的开发团队已将Kali Linux的docker镜像上传了,只需要输入下面的命令来下载镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
docker pull kalilinux/kali-linux-docker
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下载完成后,运行下面的命令来找出你下载的docker镜像的ID。
|
||||
|
||||
docker images
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在运行下面的命令来从镜像文件启动kali linux docker容器(这里用正确的镜像ID替换)。
|
||||
|
||||
docker run -i -t 198cd6df71ab3 /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
它会立刻启动容器并且会登录操作系统,你现在可以在Kaili Linux中工作了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过下面的命令来验证通气已经启动/运行中了:
|
||||
|
||||
docker ps
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker是一种最聪明的用来部署和分发包的方式。Kali Linux docker镜像非常容易上手,也不会消耗很大的硬盘空间,这样也容易地在任何安装了docker的操作系统上测试这个很棒的发行版了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxpitstop.com/run-kali-linux-2-0-in-docker-container/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aun][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linuxpitstop.com/author/aun/
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxpitstop.com/install-kali-linux-2-0/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,215 @@
|
||||
RHCSA 系列:安全 SSH,设定主机名及开启网络服务 – Part 8
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
作为一名系统管理员,你将经常使用一个终端模拟器来登陆到一个远程的系统中,执行一系列的管理任务。你将很少有机会坐在一个真实的(物理)终端前,所以你需要设定好一种方法来使得你可以登陆到你被要求去管理的那台远程主机上。
|
||||
|
||||
事实上,当你必须坐在一台物理终端前的时候,就可能是你登陆到该主机的最后一种方法。基于安全原因,使用 Telnet 来达到以上目的并不是一个好主意,因为穿行在线缆上的流量并没有被加密,它们以文本方式在传送。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,在这篇文章中,我们也将复习如何配置网络服务来使得它在开机时被自动开启,并学习如何设置网络和静态或动态地解析主机名。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA: 安全 SSH 和开启网络服务 – Part 8
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装并确保 SSH 通信安全 ###
|
||||
|
||||
对于你来说,要能够使用 SSH 远程登陆到一个 RHEL 7 机子,你必须安装 `openssh`,`openssh-clients` 和 `openssh-servers` 软件包。下面的命令不仅将安装远程登陆程序,也会安装安全的文件传输工具以及远程文件复制程序:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install openssh openssh-clients openssh-servers
|
||||
|
||||
注意,安装上服务器所需的相应软件包是一个不错的主意,因为或许在某个时刻,你想使用同一个机子来作为客户端和服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
在安装完成后,如若你想安全地访问你的 SSH 服务器,你还需要考虑一些基本的事情。下面的设定应该在文件 `/etc/ssh/sshd_config` 中得以呈现。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 更改 sshd 守护进程的监听端口,从 22(默认的端口值)改为一个更高的端口值(2000 或更大),但首先要确保所选的端口没有被占用。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,让我们假设你选择了端口 2500 。使用 [netstat][1] 来检查所选的端口是否被占用:
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -npltu | grep 2500
|
||||
|
||||
假如 netstat 没有返回任何信息,则你可以安全地为 sshd 使用端口 2500,并且你应该在上面的配置文件中更改端口的设定,具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
Port 2500
|
||||
|
||||
2. 只允许协议 2:
|
||||
|
||||
Protocol 2
|
||||
|
||||
3. 配置验证超时的时间为 2 分钟,不允许以 root 身份登陆,并将允许通过 ssh 登陆的人数限制到最小:
|
||||
|
||||
LoginGraceTime 2m
|
||||
PermitRootLogin no
|
||||
AllowUsers gacanepa
|
||||
|
||||
4. 假如可能,使用基于公钥的验证方式而不是使用密码:
|
||||
|
||||
PasswordAuthentication no
|
||||
RSAAuthentication yes
|
||||
PubkeyAuthentication yes
|
||||
|
||||
这假设了你已经在你的客户端机子上创建了带有你的用户名的一个密钥对,并将公钥复制到了你的服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
- [开启 SSH 无密码登陆][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置网络和名称的解析 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 每个系统管理员应该对下面这个系统配置文件非常熟悉:
|
||||
|
||||
- /etc/hosts 被用来在小型网络中解析名称 <---> IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
文件 `/etc/hosts` 中的每一行拥有如下的结构:
|
||||
|
||||
IP address - Hostname - FQDN
|
||||
|
||||
例如,
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.0.10 laptop laptop.gabrielcanepa.com.ar
|
||||
|
||||
2. `/etc/resolv.conf` 特别指定 DNS 服务器的 IP 地址和搜索域,它被用来在没有提供域名后缀时,将一个给定的查询名称对应为一个全称域名。
|
||||
|
||||
在正常情况下,你不必编辑这个文件,因为它是由系统管理的。然而,若你非要改变 DNS 服务器的 IP 地址,建议你在该文件的每一行中,都应该遵循下面的结构:
|
||||
|
||||
nameserver - IP address
|
||||
|
||||
例如,
|
||||
|
||||
nameserver 8.8.8.8
|
||||
|
||||
3. `/etc/host.conf` 特别指定在一个网络中主机名被解析的方法和顺序。换句话说,告诉名称解析器使用哪个服务,并以什么顺序来使用。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管这个文件由几个选项,但最为常见和基本的设置包含如下的一行:
|
||||
|
||||
order bind,hosts
|
||||
|
||||
它意味着解析器应该首先查看 `resolv.conf` 中特别指定的域名服务器,然后到 `/etc/hosts` 文件中查找解析的名称。
|
||||
|
||||
4. `/etc/sysconfig/network` 包含了所有网络接口的路由和全局主机信息。下面的值可能会被使用:
|
||||
|
||||
NETWORKING=yes|no
|
||||
HOSTNAME=value
|
||||
|
||||
其中的 value 应该是全称域名(FQDN)。
|
||||
|
||||
GATEWAY=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
|
||||
|
||||
其中的 XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX 是网关的 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
GATEWAYDEV=value
|
||||
|
||||
在一个带有多个网卡的机器中, value 为网关设备名,例如 enp0s3。
|
||||
|
||||
5. 位于 `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts` 中的文件(网络适配器配置文件)。
|
||||
|
||||
在上面提到的目录中,你将找到几个被命名为如下格式的文本文件。
|
||||
|
||||
ifcfg-name
|
||||
|
||||
其中 name 为网卡的名称,由 `ip link show` 返回:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查网络连接状态
|
||||
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
网络文件
|
||||
|
||||
除了环回接口,你还可以为你的网卡进行一个相似的配置。注意,假如设定了某些变量,它们将为这个特别的接口,覆盖掉 `/etc/sysconfig/network` 中定义的值。在这篇文章中,为了能够解释清楚,每行都被加上了注释,但在实际的文件中,你应该避免加上注释:
|
||||
|
||||
HWADDR=08:00:27:4E:59:37 # The MAC address of the NIC
|
||||
TYPE=Ethernet # Type of connection
|
||||
BOOTPROTO=static # This indicates that this NIC has been assigned a static IP. If this variable was set to dhcp, the NIC will be assigned an IP address by a DHCP server and thus the next two lines should not be present in that case.
|
||||
IPADDR=192.168.0.18
|
||||
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
|
||||
GATEWAY=192.168.0.1
|
||||
NM_CONTROLLED=no # Should be added to the Ethernet interface to prevent NetworkManager from changing the file.
|
||||
NAME=enp0s3
|
||||
UUID=14033805-98ef-4049-bc7b-d4bea76ed2eb
|
||||
ONBOOT=yes # The operating system should bring up this NIC during boot
|
||||
|
||||
### 设定主机名 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 RHEL 7 中, `hostnamectl` 命令被同时用来查询和设定系统的主机名。
|
||||
|
||||
要展示当前的主机名,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
# hostnamectl status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查系统的主机名
|
||||
|
||||
要更改主机名,使用
|
||||
|
||||
# hostnamectl set-hostname [new hostname]
|
||||
|
||||
例如,
|
||||
|
||||
# hostnamectl set-hostname cinderella
|
||||
|
||||
要想使得更改生效,你需要重启 hostnamed 守护进程(这样你就不必因为要应用更改而登出系统并再登陆系统):
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart systemd-hostnamed
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
设定系统主机名
|
||||
|
||||
另外, RHEL 7 还包含 `nmcli` 工具,它可被用来达到相同的目的。要展示主机名,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli general hostname
|
||||
|
||||
且要改变主机名,则运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli general hostname [new hostname]
|
||||
|
||||
例如,
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli general hostname rhel7
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用 nmcli 命令来设定主机名
|
||||
|
||||
### 在开机时开启网络服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
作为本文的最后部分,就让我们看看如何确保网络服务在开机时被自动开启。简单来说,这个可通过创建符号链接到某些由服务的配置文件中的 [Install] 小节中指定的文件来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
以 firewalld(/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service) 为例:
|
||||
|
||||
[Install]
|
||||
WantedBy=basic.target
|
||||
Alias=dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service
|
||||
|
||||
要开启该服务,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable firewalld
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,要禁用 firewalld,则需要移除符号链接:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl disable firewalld
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在开机时开启服务
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我们总结了如何安装 SSH 及使用它安全地连接到一个 RHEL 服务器,如何改变主机名,并在最后如何确保在系统启动时开启服务。假如你注意到某个服务启动失败,你可以使用 `systemctl status -l [service]` 和 `journalctl -xn` 来进行排错。
|
||||
|
||||
请随意使用下面的评论框来让我们知晓你对本文的看法。提问也同样欢迎。我们期待着你的反馈!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-series-secure-ssh-set-hostname-enable-network-services-in-rhel-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ssh-passwordless-login-using-ssh-keygen-in-5-easy-steps/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user