mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-12 01:40:10 +08:00
Merge remote-tracking branch 'LCTT/master'
This commit is contained in:
commit
fb75db2d41
@ -3,35 +3,36 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
公共服务最重要的一点就是守时,但是很多人并没有意识到这一点。大多数公共时间服务器都是由志愿者管理,以满足不断增长的需求。学习如何运行你自己的时间服务器,为基本的公共利益做贡献。(查看 [在 Linux 上使用 NTP 保持精确时间][1] 去学习如何设置一台局域网时间服务器)
|
||||
最重要的公共服务之一就是<ruby>报时<rt>timekeeping</rt></ruby>,但是很多人并没有意识到这一点。大多数公共时间服务器都是由志愿者管理,以满足不断增长的需求。这里学习一下如何运行你自己的时间服务器,为基础公共利益做贡献。(查看 [在 Linux 上使用 NTP 保持精确时间][1] 去学习如何设置一台局域网时间服务器)
|
||||
|
||||
### 著名的时间服务器滥用事件
|
||||
|
||||
就像现实生活中任何一件事情一样,即便是像时间服务器这样的公益项目,也会遭受不称职的或者恶意的滥用。
|
||||
|
||||
消费类网络设备的供应商因制造了大混乱而臭名昭著。我回想起的第一件事发生在 2003 年,那时,Netgear 在它们的路由器中硬编码了 University of Wisconsin-Madison 的 NTP 时间服务器地址。使得时间服务器的查询请求突然增加,随着 NetGear 卖出越来越多的路由器,这种情况越发严重。更有意思的是,路由器的程序设置是每秒钟发送一次请求,这将使服务器难堪重负。后来 Netgear 发布了升级固件,但是,升级他们的设备的用户很少,并且他们的其中一些用户的设备,到今天为止,还在不停地每秒钟查询一次 University of Wisconsin-Madison 的 NTP 服务器。Netgear 给 University of Wisconsin-Madison 捐献了一些钱,以帮助弥补他们带来的成本增加,直到这些路由器全部淘汰。类似的事件还有 D-Link、Snapchat、TP-Link 等等。
|
||||
消费类网络设备的供应商因制造了大混乱而臭名昭著。我回想起的第一件事发生在 2003 年,那时,NetGear 在它们的路由器中硬编码了威斯康星大学的 NTP 时间服务器地址。使得时间服务器的查询请求突然增加,随着 NetGear 卖出越来越多的路由器,这种情况越发严重。更有意思的是,路由器的程序设置是每秒钟发送一次请求,这将使服务器难堪重负。后来 Netgear 发布了升级固件,但是,升级他们的设备的用户很少,并且他们的其中一些用户的设备,到今天为止,还在不停地每秒钟查询一次威斯康星大学的 NTP 服务器。Netgear 给威斯康星大学捐献了一些钱,以帮助弥补他们带来的成本增加,直到这些路由器全部淘汰。类似的事件还有 D-Link、Snapchat、TP-Link 等等。
|
||||
|
||||
对 NTP 协议进行反射和放大,已经成为发起 DDoS 攻击的一个选择。当攻击者使用一个伪造的源地址向目标受害者发送请求,称为反射;攻击者发送请求到多个服务器,这些服务器将回复请求,这样就使伪造的地址受到轰炸。放大是指一个很小的请求收到大量的回复信息。例如,在 Linux 上,`ntpq` 命令是一个查询你的 NTP 服务器并验证它们的系统时间是否正确的很有用的工具。一些回复,比如,对端列表,是非常大的。组合使用反射和放大,攻击者可以将 10 倍甚至更多带宽的数据量发送到被攻击者。
|
||||
对 NTP 协议进行反射和放大,已经成为发起 DDoS 攻击的一个选择。当攻击者使用一个伪造的目标受害者的源地址向时间服务器发送请求,称为反射攻击;攻击者发送请求到多个服务器,这些服务器将回复请求,这样就使伪造的源地址受到轰炸。放大攻击是指一个很小的请求收到大量的回复信息。例如,在 Linux 上,`ntpq` 命令是一个查询你的 NTP 服务器并验证它们的系统时间是否正确的很有用的工具。一些回复,比如,对端列表,是非常大的。组合使用反射和放大,攻击者可以将 10 倍甚至更多带宽的数据量发送到被攻击者。
|
||||
|
||||
那么,如何保护提供公益服务的公共 NTP 服务器呢?从使用 NTP 4.2.7p26 或者更新的版本开始,它们可以帮助你的 Linux 发行版不会发生前面所说的这种问题,因为它们都是在 2010 年以后发布的。这个发行版都默认禁用了最常见的滥用攻击。目前,[最新版本是 4.2.8p10][2],它发布于 2017 年。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以采用的另一个措施是,在你的网络上启用入站和出站过滤器。阻塞进入你的网络的数据包,以及拦截发送到伪造地址的出站数据包。入站过滤器帮助你,而出站过滤器则帮助你和其他人。阅读 [BCP38.info][3] 了解更多信息。
|
||||
你可以采用的另一个措施是,在你的网络上启用入站和出站过滤器。阻塞宣称来自你的网络的数据包进入你的网络,以及拦截发送到伪造返回地址的出站数据包。入站过滤器可以帮助你,而出站过滤器则帮助你和其他人。阅读 [BCP38.info][3] 了解更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 层级为 0、1、2 的时间服务器
|
||||
|
||||
NTP 有超过 30 年的历史了,它是至今还在使用的最老的因特网协议之一。它的用途是保持计算机与协调世界时间(UTC)的同步。NTP 网络是分层组织的,并且同层的设备是对等的。层次 0 包含主守时设备,比如,原子钟。层级 1 的时间服务器与层级 0 的设备同步。层级 2 的设备与层级 1 的设备同步,层级 3 的设备与层级 2 的设备同步。NTP 协议支持 16 个层级,现实中并没有使用那么多的层级。同一个层级的服务器是相互对等的。
|
||||
NTP 有超过 30 年的历史了,它是至今还在使用的最老的因特网协议之一。它的用途是保持计算机与世界标准时间(UTC)的同步。NTP 网络是分层组织的,并且同层的设备是对等的。<ruby>层次<rt>Stratum</rt></ruby> 0 包含主报时设备,比如,原子钟。层级 1 的时间服务器与层级 0 的设备同步。层级 2 的设备与层级 1 的设备同步,层级 3 的设备与层级 2 的设备同步。NTP 协议支持 16 个层级,现实中并没有使用那么多的层级。同一个层级的服务器是相互对等的。
|
||||
|
||||
过去很长一段时间内,我们都为客户端选择配置单一的 NTP 服务器,而现在更好的做法是使用 [NTP 服务器地址池][4],它使用往返的 DNS 信息去共享负载。池地址只是为客户端服务的,比如单一的 PC 和你的本地局域网 NTP 服务器。当你运行一台自己的公共服务器时,你不能使用这些池中的地址。
|
||||
过去很长一段时间内,我们都为客户端选择配置单一的 NTP 服务器,而现在更好的做法是使用 [NTP 服务器地址池][4],它使用轮询的 DNS 信息去共享负载。池地址只是为客户端服务的,比如单一的 PC 和你的本地局域网 NTP 服务器。当你运行一台自己的公共服务器时,你不用使用这些池地址。
|
||||
|
||||
### 公共 NTP 服务器配置
|
||||
|
||||
运行一台公共 NTP 服务器只有两步:设置你的服务器,然后加入到 NTP 服务器池。运行一台公共的 NTP 服务器是一种很高尚的行为,但是你得先知道如何加入到 NTP 服务器池中。加入 NTP 服务器池是一种长期责任,因为即使你加入服务器池后,运行了很短的时间马上退出,然后接下来的很多年你仍然会接收到请求。
|
||||
运行一台公共 NTP 服务器只有两步:设置你的服务器,然后申请加入到 NTP 服务器池。运行一台公共的 NTP 服务器是一种很高尚的行为,但是你得先知道这意味着什么。加入 NTP 服务器池是一种长期责任,因为即使你加入服务器池后,运行了很短的时间马上退出,然后接下来的很多年你仍然会接收到请求。
|
||||
|
||||
你需要一个静态的公共 IP 地址,一个至少 512Kb/s 带宽的、可靠的、持久的因特网连接。NTP 使用的是 UDP 的 123 端口。它对机器本身要求并不高,很多管理员在其它的面向公共的服务器(比如,Web 服务器)上顺带架设了 NTP 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
配置一台公共的 NTP 服务器与配置一台用于局域网的 NTP 服务器是一样的,只需要几个配置。我们从阅读 [协议规则][5] 开始。遵守规则并注意你的行为;几乎每个时间服务器的维护者都是像你这样的志愿者。然后,从 [StratumTwoTimeServers][6] 中选择 2 台层级为 4-7 的上游服务器。选择的时候,选取地理位置上靠近(小于 300 英里的)你的因特网服务提供商的上游服务器,阅读他们的访问规则,然后,使用 `ping` 和 `mtr` 去找到延迟和跳数最小的服务器。
|
||||
配置一台公共的 NTP 服务器与配置一台用于局域网的 NTP 服务器是一样的,只需要几个配置。我们从阅读 [协议规则][5] 开始。遵守规则并注意你的行为;几乎每个时间服务器的维护者都是像你这样的志愿者。然后,从 [StratumTwoTimeServers][6] 中选择 4 到 7 个层级 2 的上游服务器。选择的时候,选取地理位置上靠近(小于 300 英里的)你的因特网服务提供商的上游服务器,阅读他们的访问规则,然后,使用 `ping` 和 `mtr` 去找到延迟和跳数最小的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
以下的 `/etc/ntp.conf` 配置示例文件,包括了 IPv4 和 IPv6,以及基本的安全防护:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# stratum 2 server list
|
||||
server servername_1 iburst
|
||||
@ -47,10 +48,10 @@ restrict -6 default kod noquery nomodify notrap nopeer limited
|
||||
# Allow ntpq and ntpdc queries only from localhost
|
||||
restrict 127.0.0.1
|
||||
restrict ::1
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动你的 NTP 服务器,让它运行几分钟,然后测试它对远程服务器的查询:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ntpq -p
|
||||
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
|
||||
@ -63,21 +64,21 @@ $ ntpq -p
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
目前表现很好。现在从另一台 PC 上使用你的 NTP 服务器名字进行测试。以下的示例是一个正确的输出。如果有不正确的地方,你将看到一些错误信息。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ntpdate -q _yourservername_
|
||||
$ ntpdate -q yourservername
|
||||
server 66.96.99.10, stratum 2, offset 0.017690, delay 0.12794
|
||||
server 98.191.213.2, stratum 1, offset 0.014798, delay 0.22887
|
||||
server 173.49.198.27, stratum 2, offset 0.020665, delay 0.15012
|
||||
server 129.6.15.28, stratum 1, offset -0.018846, delay 0.20966
|
||||
26 Jan 11:13:54 ntpdate[17293]: adjust time server 98.191.213.2 offset 0.014798 sec
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你的服务器运行的很好,你就可以向 [manage.ntppool.org][7] 申请加入池中。
|
||||
|
||||
查看官方的手册 [分布式网络时间服务器(NTP)][8] 学习所有的命令、配置选项、以及高级特性,比如,管理、查询、和验证。访问以下的站点学习关于运行一台时间服务器所需要的一切东西。
|
||||
查看官方的手册 [分布式网络时间服务器(NTP)][8] 学习所有的命令、配置选项、以及高级特性,比如,管理、查询、和验证。访问以下的站点学习关于运行一台时间服务器所需要的一切东西。
|
||||
|
||||
通过来自 Linux 基金会和 edX 的免费课程 ["Linux 入门" ][9] 学习更多 Linux 的知识。
|
||||
通过来自 Linux 基金会和 edX 的免费课程 [“Linux 入门”][9] 学习更多 Linux 的知识。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,12 +86,12 @@ via: https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-to-linux/2018/2/how-run-your-own-public-t
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[CARLA SCHRODER][a]
|
||||
译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/cschroder
|
||||
[1]:https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-to-linux/2018/1/keep-accurate-time-linux-ntp
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-9462-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.ntp.org/downloads.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.bcp38.info/index.php/Main_Page
|
||||
[4]:http://www.pool.ntp.org/en/use.html
|
||||
@ -1,43 +1,41 @@
|
||||
一个仅下载文件新的部分的传输工具
|
||||
Zsync:一个仅下载文件新的部分的传输工具
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
仅仅因为网费每天变得越来越便宜,你也不应该重复下载相同的东西来浪费你的流量。一个很好的例子就是下载 Ubuntu 或任何 Linux 镜像的开发版本。如你所知,Ubuntu 开发人员每隔几个月就会发布一次日常构建、alpha、beta 版 ISO 镜像以供测试。在过去,一旦发布我就会下载这些镜像,并审查每个版本。现在不用了!感谢 **Zsync** 文件传输程序。现在可以仅下载 ISO 镜像新的部分。这将为你节省大量时间和 Internet 带宽。不仅时间和带宽,它将为你节省服务端和客户端的资源。
|
||||
就算是网费每天变得越来越便宜,你也不应该重复下载相同的东西来浪费你的流量。一个很好的例子就是下载 Ubuntu 或任何 Linux 镜像的开发版本。如你所知,Ubuntu 开发人员每隔几个月就会发布一次日常构建、alpha、beta 版 ISO 镜像以供测试。在过去,一旦发布我就会下载这些镜像,并审查每个版本。现在不用了!感谢 Zsync 文件传输程序。现在可以仅下载 ISO 镜像新的部分。这将为你节省大量时间和 Internet 带宽。不仅时间和带宽,它将为你节省服务端和客户端的资源。
|
||||
|
||||
Zsync 使用与 **Rsync** 相同的算法,但它只下载文件的新部分,你会得到一份已有文件旧版本的副本。 Rsync 主要用于在计算机之间同步数据,而 Zsync 则用于分发数据。简单地说,可以使用 Zsync 将中心的一个文件分发给数千个下载者。它在 Artistic License V2 许可证下发布,完全免费且开源。
|
||||
Zsync 使用与 Rsync 相同的算法,如果你会得到一份已有文件旧版本,它只下载该文件新的部分。 Rsync 主要用于在计算机之间同步数据,而 Zsync 则用于分发数据。简单地说,可以使用 Zsync 将中心的一个文件分发给数千个下载者。它在 Artistic License V2 许可证下发布,完全免费且开源。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 Zsync
|
||||
|
||||
Zsync 在大多数 Linux 发行版的默认仓库中有。
|
||||
|
||||
在 **Arch Linux** 及其衍生版上,使用命令安装它:
|
||||
在 Arch Linux 及其衍生版上,使用命令安装它:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S zsync
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **Fedora** 上:
|
||||
在 Fedora 上,启用 Zsync 仓库:
|
||||
|
||||
启用 Zsync 仓库:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf copr enable ngompa/zsync
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
并使用命令安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install zsync
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint** 上:
|
||||
在 Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint 上:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install zsync
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于其他发行版,你可以从 [**Zsync 下载页面**][1]下载二进制文件,并手动编译安装它,如下所示。
|
||||
对于其他发行版,你可以从 [Zsync 下载页面][1]下载二进制打包文件,并手动编译安装它,如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ wget http://zsync.moria.org.uk/download/zsync-0.6.2.tar.bz2
|
||||
$ tar xjf zsync-0.6.2.tar.bz2
|
||||
@ -45,44 +43,41 @@ $ cd zsync-0.6.2/
|
||||
$ configure
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 用法
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,**只有当人们提供 zsync 下载时,zsync 才有用**。目前,Debian、Ubuntu(所有版本)的 ISO 镜像都可以用 .zsync 下载。例如,请访问以下链接。
|
||||
请注意,只有当人们提供 zsync 下载方式时,zsync 才有用。目前,Debian、Ubuntu(所有版本)的 ISO 镜像都有 .zsync 下载链接。例如,请访问以下链接。
|
||||
|
||||
你可能注意到,Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 每日构建版有直接的 ISO 和 .zsync 文件。如果你下载 .ISO 文件,则必须在 ISO 更新时下载完整的 ISO 文件。但是,如果你下载的是 .zsync 文件,那么 Zsync 将在未来仅下载新的更改。你不需要每次都下载整个 ISO 映像。
|
||||
你可能注意到,Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 每日构建版有直接的 ISO 和 .zsync 文件。如果你下载 .ISO 文件,则必须在 ISO 更新时下载完整的 ISO 文件。但是,如果你下载的是 .zsync 文件,那么 Zsync 以后仅会下载新的更改。你不需要每次都下载整个 ISO 映像。
|
||||
|
||||
.zsync 文件包含 zsync 程序所需的元数据。该文件包含 rsync 算法的预先计算的校验和。它在服务器上生成一次,然后由任意数量的下载器使用。要使用 Zsync 客户端程序下载 .zsync 文件,你只需执行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ zsync <.zsync-file-URL>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ zsync http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/daily-live/current/bionic-desktop-amd64.iso.zsync
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的系统中已有以前的镜像文件,那么 Zsync 将计算远程服务器中旧文件和新文件之间的差异,并仅下载新的部分。你将在终端看见计算过程一系列的点或星星。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你下载的文件的旧版本存在于当前工作目录,那么 Zsync 将只下载新的部分。下载完成后,你将看到两个镜像,一个你刚下载的镜像和以 **.iso.zs-old** 为扩展名的旧镜像。
|
||||
如果你下载的文件的旧版本存在于当前工作目录,那么 Zsync 将只下载新的部分。下载完成后,你将看到两个镜像,一个你刚下载的镜像和以 .iso.zs-old 为扩展名的旧镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
如果没有找到相关的本地数据,Zsync 会下载整个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
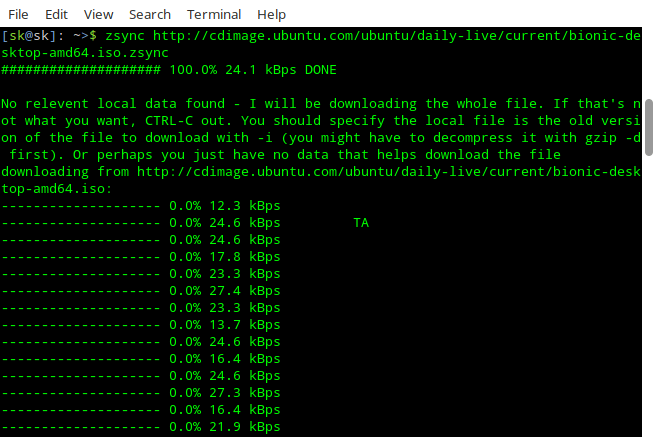
|
||||
|
||||
你可以随时按 **CTRL-C** 取消下载过程。
|
||||
你可以随时按 `CTRL-C` 取消下载过程。
|
||||
|
||||
试想一下,如果你直接下载 .ISO 文件或使用 torrent,每当你下载新镜像时,你将损失约 1.4GB 流量。因此,Zsync 不会下载整个 Alpha、beta 和日常构建映像,而只是在你的系统上下载了 ISO 文件的新部分,并在系统中有一个旧版本的拷贝。
|
||||
|
||||
今天就到这里。希望对你有帮助。我将很快另外写一篇有用的指南。在此之前,请继续关注 OSTechNix!
|
||||
|
||||
干杯!
|
||||
|
||||
今天就到这里。希望对你有帮助。我将很快另外写一篇有用的指南。在此之前,请保持关注!
|
||||
|
||||
干杯!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -90,7 +85,7 @@ via: https://www.ostechnix.com/zsync-file-transfer-utility-download-new-parts-fi
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上检查您的网络连接
|
||||
解读 ip 命令展示的网络连接信息
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**ip**命令有很多可以告诉你网络连接配置和状态的信息,但是所有这些词和数字意味着什么? 让我们深入了解一下,看看所有显示的值都试图告诉你什么。
|
||||
`ip` 命令可以告诉你很多网络连接配置和状态的信息,但是所有这些词和数字意味着什么? 让我们深入了解一下,看看所有显示的值都试图告诉你什么。
|
||||
|
||||
当您使用`ip a`(或`ip addr`)命令获取系统上所有网络接口的信息时,您将看到如下所示的内容:
|
||||
当您使用 `ip a`(或 `ip addr`)命令获取系统上所有网络接口的信息时,您将看到如下所示的内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ip a
|
||||
@ -23,46 +23,46 @@ $ ip a
|
||||
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这个系统上的两个接口 - 环回(lo)和网络(enp0s25)——显示了很多统计数据。 “lo”接口显然是环回地址。 我们可以在列表中看到环回IPv4地址(127.0.0.1)和环回IPv6( **::1**)。 正常的网络接口更有趣。
|
||||
这个系统上的两个接口 - 环回(`lo`)和网络(`enp0s25`)——显示了很多统计数据。 `lo` 接口显然是<ruby>环回地址<rt>loolback</rt></ruby>。 我们可以在列表中看到环回 IPv4 地址(`127.0.0.1`)和环回 IPv6(`::1`)。 而普通的网络接口更有趣。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么是enp0s25而不是eth0
|
||||
### 为什么是 enp0s25 而不是 eth0
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想知道为什么它在这个系统上被称为**enp0s25**,而不是可能更熟悉的**eth0**,那我们可以稍微解释一下。
|
||||
如果你想知道为什么它在这个系统上被称为 `enp0s25`,而不是可能更熟悉的 `eth0`,那我们可以稍微解释一下。
|
||||
|
||||
新的命名方案被称为“可预测的网络接口”。 它已经在基于systemd的Linux系统上使用了一段时间了。 接口名称取决于硬件的物理位置。 “**en**”仅仅就是“ethernet”的意思就像“eth”用于对于eth0,一样。 “**p**”是以太网卡的总线编号,“**s**”是插槽编号。 所以“enp0s25”告诉我们很多我们正在使用的硬件的信息。
|
||||
新的命名方案被称为“<ruby>可预测的网络接口<rt>Predictable Network Interface</rt></ruby>”。 它已经在基于systemd 的 Linux 系统上使用了一段时间了。 接口名称取决于硬件的物理位置。 `en` 仅仅就是 “ethernet” 的意思,就像 “eth” 用于对应 `eth0`,一样。 `p` 是以太网卡的总线编号,`s` 是插槽编号。 所以 `enp0s25` 告诉我们很多我们正在使用的硬件的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
`<BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP>` 这个配置串告诉我们:
|
||||
|
||||
<BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> 这个配置串告诉我们:
|
||||
```
|
||||
BROADCAST 该接口支持广播
|
||||
MULTICAST 该接口支持多播
|
||||
UP 网络接口已启用
|
||||
LOWER_UP 网络电缆已插入,设备已连接至网络
|
||||
mtu 1500 最大传输单位(数据包大小)为1,500字节
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
列出的其他值也告诉了我们很多关于接口的知识,但我们需要知道“brd”和“qlen”这些词代表什么意思。 所以,这里显示的是上面展示的**ip**信息的其余部分的翻译。
|
||||
列出的其他值也告诉了我们很多关于接口的知识,但我们需要知道 `brd` 和 `qlen` 这些词代表什么意思。 所以,这里显示的是上面展示的 `ip` 信息的其余部分的翻译。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mtu 最大传输单位(数据包大小)为1,500字节
|
||||
mtu 1500 最大传输单位(数据包大小)为1,500字节
|
||||
qdisc pfifo_fast 用于数据包排队
|
||||
state UP 网络接口已启用
|
||||
group default 接口组
|
||||
qlen 1000 传输队列长度
|
||||
link/ether 00:1e:4f:c8:43:fc 接口的MAC(硬件)地址
|
||||
link/ether 00:1e:4f:c8:43:fc 接口的 MAC(硬件)地址
|
||||
brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff 广播地址
|
||||
inet 192.168.0.24/24 IPv4地址
|
||||
inet 192.168.0.24/24 IPv4 地址
|
||||
brd 192.168.0.255 广播地址
|
||||
scope global 全局有效
|
||||
dynamic enp0s25 地址是动态分配的
|
||||
valid_lft 80866sec IPv4地址的有效使用期限
|
||||
preferred_lft 80866sec IPv4地址的首选生存期
|
||||
inet6 fe80::2c8e:1de0:a862:14fd/64 IPv6地址
|
||||
valid_lft 80866sec IPv4 地址的有效使用期限
|
||||
preferred_lft 80866sec IPv4 地址的首选生存期
|
||||
inet6 fe80::2c8e:1de0:a862:14fd/64 IPv6 地址
|
||||
scope link 仅在此设备上有效
|
||||
valid_lft forever IPv6地址的有效使用期限
|
||||
preferred_lft forever IPv6地址的首选生存期
|
||||
valid_lft forever IPv6 地址的有效使用期限
|
||||
preferred_lft forever IPv6 地址的首选生存期
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您可能已经注意到,ifconfig命令提供的一些信息未包含在**ip a** 命令的输出中 —— 例如传输数据包的统计信息。 如果您想查看发送和接收的数据包数量以及冲突数量的列表,可以使用以下ip命令:
|
||||
您可能已经注意到,`ifconfig` 命令提供的一些信息未包含在 `ip a` 命令的输出中 —— 例如传输数据包的统计信息。 如果您想查看发送和接收的数据包数量以及冲突数量的列表,可以使用以下 `ip` 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ip -s link show enp0s25
|
||||
@ -74,7 +74,8 @@ $ ip -s link show enp0s25
|
||||
6131373 78152 0 0 0 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
另一个**ip**命令提供有关系统路由表的信息。
|
||||
另一个 `ip` 命令提供有关系统路由表的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ip route show
|
||||
default via 192.168.0.1 dev enp0s25 proto static metric 100
|
||||
@ -82,7 +83,7 @@ default via 192.168.0.1 dev enp0s25 proto static metric 100
|
||||
192.168.0.0/24 dev enp0s25 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.0.24 metric 100
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**ip**命令是非常通用的。 您可以从**ip**命令及其来自[Red Hat][1]的选项获得有用的备忘单。
|
||||
`ip` 命令是非常通用的。 您可以从 `ip` 命令及其来自[Red Hat][1]的选项获得有用的备忘单。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -90,7 +91,7 @@ via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3262045/linux/checking-your-network-co
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
|
||||
译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by yizhuoyan
|
||||
|
||||
How To Set Readonly File Permissions On Linux / Unix Web Server DocumentRoot
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
How do I set a read-only permission for all of my files stored in /var/www/html/ directory?
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the chmod command to set read-only permission for all files on a Linux / Unix / macOS / Apple OS X / *BSD operating systems. This page explains how to setup read only file permission on Linux or Unix web server such as Nginx, Lighttpd, Apache and more.
|
||||
|
||||
[![Proper read-only permissions for Linux/Unix Nginx/Apache web server's directory][1]][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### How to set files in read-only mode
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax is:
|
||||
```
|
||||
### use only for files ##
|
||||
chmod 0444 /var/www/html/*
|
||||
chmod 0444 /var/www/html/*.php
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to to set directories in read-only mode
|
||||
|
||||
TO set directories in read-only mode, enter:
|
||||
```
|
||||
### use only for dirs ##
|
||||
chmod 0444 /var/www/html/
|
||||
chmod 0444 /path/to/your/dir/
|
||||
# ***************************************************************************
|
||||
# Say webserver user/group is www-data, and file-owned by ftp-data user/group
|
||||
# ***************************************************************************
|
||||
# All files/dirs are read-only
|
||||
chmod -R 0444 /var/www/html/
|
||||
# All files/dir owned by ftp-data
|
||||
chown -R ftp-data:ftp-data /var/www/html/
|
||||
# All directories and sub-dirs has 0445 permission (so that webserver user www-data can read our files)
|
||||
find /var/www/html/ -type d -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} chmod 0445 "{}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
To find all files (including sub-directories in /var/www/html) and set read-only permission, enter:
|
||||
```
|
||||
### works on files only ##
|
||||
find /var/www/html -type f -iname "*" -print0 | xargs -I {} -0 chmod 0444 {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
However, you need to set set read-only and execute permission on /var/www/html and all sub-directories so that web server can enter into your DocumentRoot, enter:
|
||||
```
|
||||
### works on dirs only ##
|
||||
find /var/www/html -type d -iname "*" -print0 | xargs -I {} -0 chmod 0544 {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### A warning about write permission
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that write access on a directory /var/www/html/ allows anyone to remove or add new files. In other words, you may need to set a read-only permission for /var/www/html/ directory itself:
|
||||
```
|
||||
### read-only web-root but web server allowed to read files ##
|
||||
chmod 0555 /var/www/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases you can change file owner and group to set tight permissions as per your setup:
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Say /var/www/html is owned by normal user, you can set it to root:root or httpd:httpd (recommended) ###
|
||||
chown -R root:root /var/www/html/
|
||||
|
||||
### Make sure apache user owns /var/www/html/ ##
|
||||
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### A note about NFS exported directories
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify whether the directory should have [read-only or read/write permissions using /etc/exports][2] file. This file defines the various shares on the NFS server and their permissions. A few examples:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Read-only access to anyone
|
||||
/var/www/html *(ro,sync)
|
||||
|
||||
# Read-write access to a client on 192.168.1.10 (upload.example.com)
|
||||
/var/www/html 192.168.1.10(rw,sync)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### A note about read-only Samba (CIFS) share for MS-Windows clients
|
||||
|
||||
To share sales as read-only, update smb.conf as follows:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[sales]
|
||||
comment = Sales Data
|
||||
path = /export/cifs/sales
|
||||
read only = Yes
|
||||
guest ok = Yes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### A note about file systems table
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the /etc/fstab file on Unix or Linux to configure to mount certain files in read-only mode. You need to have a dedicated partition. Do not set / or other system partitions in read-only mode. In this example /srv/html is set to read-only mode using /etc/fstab file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/dev/sda6 /srv/html ext4 ro 1 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the mount command to [remount partition in read-only mode][3] (run it as the root user):
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount -o remount,ro /dev/sda6 /srv/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
OR
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount -o remount,ro /srv/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
The above command will try to attempt to remount an already-mounted filesystem at /srv/html. This is commonly used to change the mount flags for a filesystem, especially to make a readonly filesystem writeable. It does not change device or mount point. To make file system writable again, enter:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount -o remount,rw /dev/sda6 /srv/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
OR
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount -o remount,rw /srv/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux: chattr Command
|
||||
|
||||
You can change file [attributes on a Linux file system to read-only][4] using the chattr command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
chattr +i /path/to/file.php
|
||||
chattr +i /var/www/html/
|
||||
|
||||
# find everything in /var/www/html and set to read-only #
|
||||
find /var/www/html -iname "*" -print0 | xargs -I {} -0 chattr +i {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To remove read-only attribute pass the -i option:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# chattr -i /path/to/file.php
|
||||
```
|
||||
FreeBSD, Mac OS X and other BSD unix user can use the [chflags command][5]:
|
||||
```
|
||||
### set read-only ##
|
||||
chflags schg /path/to/file.php
|
||||
|
||||
# remove read-only ##
|
||||
chflags noschg /path/to/file.php
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-set-readonly-file-permission-in-linux-unix/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Vivek Gite][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.cyberciti.biz
|
||||
[1]:https://www.cyberciti.biz/media/new/faq/2012/04/linux-unix-set-read-only-file-system-permission-for-apache-nginx.jpg
|
||||
[2]:https://www.cyberciti.biz//www.cyberciti.biz/faq/centos-fedora-rhel-nfs-v4-configuration/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-freebsd-remount-partition/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-password-trick.html
|
||||
[5]:https://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-write-protect-file-with-immutable-bit.html
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
translating by yizhuoyan
|
||||
|
||||
Prevent Files And Folders From Accidental Deletion Or Modification In Linux
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
hankchow translating
|
||||
|
||||
Check Linux Distribution Name and Version
|
||||
======
|
||||
You have joined new company and want to install some software’s which is requested by DevApp team, also want to restart few of the service after installation. What to do?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
|
||||
leemeans translating
|
||||
How to block local spoofed addresses using the Linux firewall
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Attackers are finding sophisticated ways to penetrate even remote networks that are protected by intrusion detection and prevention systems. No IDS/IPS can halt or minimize attacks by hackers who are determined to take over your network. Improper configuration allows attackers to bypass all implemented network security measures.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, I will explain how security engineers or system administrators can prevent these attacks.
|
||||
|
||||
Almost all Linux distributions come with a built-in firewall to secure processes and applications running on the Linux host. Most firewalls are designed as IDS/IPS solutions, whose primary purpose is to detect and prevent malicious packets from gaining access to a network.
|
||||
|
||||
A Linux firewall usually comes with two interfaces: iptables and ipchains. Most people refer to these interfaces as the "iptables firewall" or the "ipchains firewall." Both interfaces are designed as packet filters. Iptables acts as a stateful firewall, making decisions based on previous packets. Ipchains does not make decisions based on previous packets; hence, it is designed as a stateless firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we will focus on the iptables firewall, which comes with kernel version 2.4 and beyond.
|
||||
|
||||
With the iptables firewall, you can create policies, or ordered sets of rules, which communicate to the kernel how it should treat specific classes of packets. Inside the kernel is the Netfilter framework. Netfilter is both a framework and the project name for the iptables firewall. As a framework, Netfilter allows iptables to hook functions designed to perform operations on packets. In a nutshell, iptables relies on the Netfilter framework to build firewall functionality such as filtering packet data.
|
||||
|
||||
Each iptables rule is applied to a chain within a table. An iptables chain is a collection of rules that are compared against packets with similar characteristics, while a table (such as nat or mangle) describes diverse categories of functionality. For instance, a mangle table alters packet data. Thus, specialized rules that alter packet data are applied to it, and filtering rules are applied to the filter table because the filter table filters packet data.
|
||||
|
||||
Iptables rules have a set of matches, along with a target, such as `Drop` or `Deny`, that instructs iptables what to do with a packet that conforms to the rule. Thus, without a target and a set of matches, iptables can’t effectively process packets. A target simply refers to a specific action to be taken if a packet matches a rule. Matches, on the other hand, must be met by every packet in order for iptables to process them.
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we understand how the iptables firewall operates, let's look at how to use iptables firewall to detect and reject or drop spoofed addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
### Turning on source address verification
|
||||
|
||||
The first step I, as a security engineer, take when I deal with spoofed addresses from remote hosts is to turn on source address verification in the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Source address verification is a kernel-level feature that drops packets pretending to come from your network. It uses the reverse path filter method to check whether the source of the received packet is reachable through the interface it came in.
|
||||
|
||||
To turn source address verification, utilize the simple shell script below instead of doing it manually:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
#author’s name: Michael K Aboagye
|
||||
|
||||
#purpose of program: to enable reverse path filtering
|
||||
|
||||
#date: 7/02/18
|
||||
|
||||
#displays “enabling source address verification” on the screen
|
||||
|
||||
echo -n "Enabling source address verification…"
|
||||
|
||||
#Overwrites the value 0 to 1 to enable source address verification
|
||||
|
||||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/default/rp_filter
|
||||
|
||||
echo "completed"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The preceding script, when executed, displays the message `Enabling source address verification` without appending a new line. The default value of the reverse path filter is 0.0, which means no source validation. Thus, the second line simply overwrites the default value 0 to 1. 1 means that the kernel will validate the source by confirming the reverse path.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you can use the following command to drop or reject spoofed addresses from remote hosts by choosing either one of these targets: `DROP` or `REJECT`. However, I recommend using `DROP` for security reasons.
|
||||
|
||||
Replace the “IP-address” placeholder with your own IP address, as shown below. Also, you must choose to use either `REJECT` or `DROP`; the two targets don’t work together.
|
||||
```
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -i internal_interface -s IP_address -j REJECT / DROP
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -i internal_interface -s 192.168.0.0/16 -j REJECT/ DROP
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This article provides only the basics of how to prevent spoofing attacks from remote hosts using the iptables firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/2/block-local-spoofed-addresses-using-linux-firewall
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Michael Kwaku Aboagye][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/revoks
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
leemeans translating
|
||||
A Command Line Productivity Tool For Tracking Work Hours
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by amwps290
|
||||
chkservice – A Tool For Managing Systemd Units From Linux Terminal
|
||||
======
|
||||
systemd stand for system daemon is a new init system and system manager which is become very popular and widely adapted new standard init system by most of Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
Systemctl is a systemd utility which is help us to manage systemd daemons. It control system startup and services, uses parallelization, socket and D-Bus activation for starting services, offers on-demand starting of daemons, keeps track of processes using Linux control groups, maintains mount and automount points.
|
||||
|
||||
Also it offers logging daemon, utilities to control basic system configuration like the hostname, date, locale, maintain a list of logged-in users and running containers and virtual machines, system accounts, runtime directories and settings, and daemons to manage simple network configuration, network time synchronization, log forwarding, and name resolution.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Is chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
[chkservice][1] is an ncurses-based tool for managing systemd units from the terminal. It provides the user with a comprehensive view of all systemd services and allows them to be changed easily.
|
||||
|
||||
It requires super user privileges to make changes into unit states or sysv scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Install chkservice In Linux
|
||||
|
||||
We can install chkservice in two ways, either package or manual method.
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Debian/Ubuntu`** , use [APT-GET Command][2] or [APT Command][3]to install chkservice.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linuxenko/chkservice
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Arch Linux`** based systems, use [Yaourt Command][4] or [Packer Command][5] to install chkservice from AUR repository.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ yaourt -S chkservice
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ packer -S chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Fedora`** , use [DNF Command][6] to install chkservice.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf copr enable srakitnican/default
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Debian Based Systems`** , use [DPKG Command][7] to install chkservice.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ wget https://github.com/linuxenko/chkservice/releases/download/0.1/chkservice_0.1.0-amd64.deb
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i chkservice_0.1.0-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`RPM Based Systems`** , use [DNF Command][8] to install chkservice.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum install https://github.com/linuxenko/chkservice/releases/download/0.1/chkservice_0.1.0-amd64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Use chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
Just fire the following command to launch the chkservice tool. The output is split to four parts.
|
||||
|
||||
* **`First Part:`** This part shows about daemons status like, enabled [X] or disabled [] or static [s] or masked -m-
|
||||
* **`Second Part:`** This part shows daemons status like, started [ >] or stopped [=]
|
||||
* **`Third Part:`** This part shows the unit name
|
||||
* **`Fourth Part:`** This part showing the unit short description
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![][10]
|
||||
|
||||
To view help page, hit `?` button. This will shows you available options to manage the systemd services.
|
||||
![][11]
|
||||
|
||||
Select the units, which you want to enable or disable then hit `Space Bar` button.
|
||||
![][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Select the units, which you want to start or stop then hit `s` button.
|
||||
![][13]
|
||||
|
||||
Select the units, which you want to reload then hit `r` button. After hit `r` key, you can see the `updated` message at the top.
|
||||
![][14]
|
||||
|
||||
Hit `q` button to quit the utility.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.2daygeek.com/chkservice-a-tool-for-managing-systemd-units-from-linux-terminal/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ramya Nuvvula][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.2daygeek.com/author/ramya/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/linuxenko/chkservice
|
||||
[2]:https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-get-apt-cache-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.2daygeek.com/install-yaourt-aur-helper-on-arch-linux/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.2daygeek.com/install-packer-aur-helper-on-arch-linux/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.2daygeek.com/dnf-command-examples-manage-packages-fedora-system/
|
||||
[7]:https://www.2daygeek.com/dpkg-command-to-manage-packages-on-debian-ubuntu-linux-mint-systems/
|
||||
[8]:https://www.2daygeek.com/rpm-command-examples/
|
||||
[9]:data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
|
||||
[10]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-1.png
|
||||
[11]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-2.png
|
||||
[12]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-3.png
|
||||
[13]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-4.png
|
||||
[14]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-5.png
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如何在Linux/Unix中的Web服务根文档目录(DocumentRoot)上设置只读文件权限
|
||||
======
|
||||
我是如何对存放在/var/www/html/目录中的所有我的文件设置只读权限的?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用`chmod`命令对Linux / Unix / macOS / Apple OS X / *BSD操作系统上的所有文件来设置只读权限。这篇文章介绍如何在Linux/Unix的web服务器(如 Nginx, Lighttpd, Apache等)上来设置只读文件权限。
|
||||
[![Proper read-only permissions for Linux/Unix Nginx/Apache web server's directory][1]][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何设置文件为只读模式
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
语法为:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
### 仅针对文件 ##
|
||||
chmod 0444 /var/www/html/*
|
||||
chmod 0444 /var/www/html/*.php
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何设置目录为只读模式
|
||||
|
||||
语法为:
|
||||
```
|
||||
### 仅针对目录##
|
||||
chmod 0444 /var/www/html/
|
||||
chmod 0444 /path/to/your/dir/
|
||||
# ***************************************************************************
|
||||
# Say webserver user/group is www-data, and file-owned by ftp-data user/group
|
||||
# 假如webserver用户/用户组是www-data ,文件拥有者是ftp-data用户/用户组
|
||||
# ***************************************************************************
|
||||
# 设置目录所有文件为只读
|
||||
chmod -R 0444 /var/www/html/
|
||||
#设置文件/目录拥有者为ftp-data
|
||||
chown -R ftp-data:ftp-data /var/www/html/
|
||||
# 所有目录和子目录的权限为0445 (这样webserver用户或用户组就可以读取我们的文件)
|
||||
find /var/www/html/ -type d -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} chmod 0445 "{}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
找到所有/var/www/html下的所有文件(包括子目录),键入:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
### 仅对文件有效##
|
||||
find /var/www/html -type f -iname "*" -print0 | xargs -I {} -0 chmod 0444 {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
然而,你需要在/var/www/html目录及其子目录上设置只读和执行权限,如此才能让web server能够访问根目录,键入:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
### 仅对目录有效 ##
|
||||
find /var/www/html -type d -iname "*" -print0 | xargs -I {} -0 chmod 0544 {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 警惕写权限
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
请注意在/var/www/html/目录上的写权限会允许任何人删除文件或添加新文件。也就是说,你可能需要设置一个只读权限给/var/www/html/目录本身。
|
||||
```
|
||||
### web根目录只读##
|
||||
chmod 0555 /var/www/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
在某些情况下,根据你的设置要求,你可以改变文件的属主和属组来设置严格的权限。
|
||||
```
|
||||
### 如果/var/www/html目录的拥有人是普通用户,你可以设置拥有人为: root:root 或 httpd:httpd (推荐) ###
|
||||
chown -R root:root /var/www/html/
|
||||
|
||||
### 确保apache拥有/var/www/html/ ##
|
||||
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 关于NFS导出目录
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在/etc/exports文件中指定哪个目录应该拥有[只读或者读写权限 ][2] . 这个文件定义各种各样的共享在NFS服务器和他们的权限。如:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 对任何人只读权限
|
||||
/var/www/html *(ro,sync)
|
||||
|
||||
# 对192.168.1.10(upload.example.com)客户端读写权限访问
|
||||
/var/www/html 192.168.1.10(rw,sync)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 关于Samba (CIFS)只读共享对MS-Windows客户端
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
共享sales为只读,更新smb.conf,如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[sales]
|
||||
comment = Sales Data
|
||||
path = /export/cifs/sales
|
||||
read only = Yes
|
||||
guest ok = Yes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 关于文件系统表(file systems table)
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在Unix/Linux上的/etc/fstab文件中配置挂载某些文件为只读模式。
|
||||
你需要有专用分区,不要设置其他系统分区为只读模式。
|
||||
|
||||
如下在/etc/fstab文件中设置/srv/html为只读模式。
|
||||
```
|
||||
/dev/sda6 /srv/html ext4 ro 1 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
你可以使用`mount`命令[重新挂载分区为只读模式][3](使用root用户)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount -o remount,ro /dev/sda6 /srv/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
或者
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount -o remount,ro /srv/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会尝试重新挂载已挂载的文件系统在/srv/html上。这是改变文件系统挂载标志的常用方法,特别是让只读文件改为可写的。这种方式不会改变设备或者挂载点。让文件变得再次可写,键入:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount -o remount,rw /dev/sda6 /srv/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
或
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount -o remount,rw /srv/html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux: chattr 命令
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在Linux文件系统上使用`chattr`命令[改变文件属性为只读][4],如:
|
||||
```
|
||||
chattr +i /path/to/file.php
|
||||
chattr +i /var/www/html/
|
||||
|
||||
# 查找任何在/var/www/html下的文件并设置为只读#
|
||||
find /var/www/html -iname "*" -print0 | xargs -I {} -0 chattr +i {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
通过提供`-i`选项可删除只读属性
|
||||
```
|
||||
chattr -i /path/to/file.php
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
FreeBSD, Mac OS X 和其他BSD Unix用户可使用[`chflags`命令][5]:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
### 设置只读 ##
|
||||
chflags schg /path/to/file.php
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除只读 ##
|
||||
chflags noschg /path/to/file.php
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
来源: https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-set-readonly-file-permission-in-linux-unix/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Vivek Gite][a]
|
||||
译者:[yizhuoyan](https://github.com/yizhuoyan)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.cyberciti.biz
|
||||
[1]:https://www.cyberciti.biz/media/new/faq/2012/04/linux-unix-set-read-only-file-system-permission-for-apache-nginx.jpg
|
||||
[2]:https://www.cyberciti.biz//www.cyberciti.biz/faq/centos-fedora-rhel-nfs-v4-configuration/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-freebsd-remount-partition/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-password-trick.html
|
||||
[5]:https://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-write-protect-file-with-immutable-bit.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
如何使用Linux防火墙隔离局域网受欺骗地址
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
即便是被入侵检测和隔离系统保护的远程网络,黑客们也在寻找精致的方法入侵。IDS/IPS是不能停止或者减少那些想要接管你的网络的黑客的攻击的。不恰当的配置允许攻击者绕过所有部署的安全措施。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我将会解释安全工程师或者系统管理员怎样可以避免这些攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
几乎所有的Linux发行版都带着一个内建的防火墙来保护运行在Linux宿主机上的进程和应用程序。大多数都按照IDS/IPS解决方案设计,这样的设计的主要目的是检测和避免恶意包获取网络的进入权。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux防火墙通常带有两个接口:iptable和ipchain程序。大多数人将这些接口称作iptables防火墙或者ipchains防火墙。这两个接口都被设计成包过滤器。iptables是有状态防火墙,基于先前的包做出决定。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我们将会专注于内核2.4之后出现的iptables防火墙。
|
||||
|
||||
有了iptables防火墙,你可以创建策略或者有序的规则集,规则集可以告诉内核如何对待特定的数据包。在内核中的是Netfilter框架。Netfilter既是框架也是iptables防火墙的工程名。作为一个框架,Netfilter允许iptables勾取被设计来操作数据包的函数。概括地说,iptables依靠Netfilter框架构筑诸如过滤数据包数据的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
每个iptables规则都被应用到一个含表的链中。一个iptables链就是一个比较包中相似字符的规则的集合。而表(例如nat或者mangle)则描述不同的功能目录。例如,一个mangle表转化包数据。因此,特定的改变包数据的规则被应用到这里,而过滤规则被应用到filter表,因为filter表过滤包数据。
|
||||
|
||||
iptables规则有一系列匹配,伴随着一个诸如`Drop`或者`Deny`的目标,这可以告诉iptables对一个包做什么符合规则。因此,没有一个目标和一系列匹配,iptables就不能有效地处理包。如果一个包匹配一条规则,一个目标简单地指向一个将要采取的特定措施。另一方面,为了让iptables处理,匹配必须被每个包满足吗。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们已经知道iptables防火墙如何工作,开始着眼于如何使用iptables防火墙检测并拒绝或丢弃被欺骗的地址吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 打开源地址验证
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个安全工程师,在处理远程主机被欺骗地址的时候,我采取的第一步是在内核打开源地址验证。
|
||||
|
||||
源地址验证是一种内核层级的特性,这种特性丢弃那些伪装成来自你的网络的包。这种特性使用反向路径过滤器方法来检查收到的包的源地址是否可以通过包到达的接口可以到达。(译注:到达的包的源地址应该可以从它到达的网络接口反向到达,只需反转源地址和目的地址就可以达到这样的效果)
|
||||
|
||||
利用下面简单的脚本可以打开源地址验证而不用手工操作:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
#作者: Michael K Aboagye
|
||||
|
||||
#程序目标: 打开反向路径过滤
|
||||
|
||||
#日期: 7/02/18
|
||||
|
||||
#在屏幕上显示 “enabling source address verification”
|
||||
|
||||
echo -n "Enabling source address verification…"
|
||||
|
||||
#将值0覆盖为1来打开源地址验证
|
||||
|
||||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/default/rp_filter
|
||||
|
||||
echo "completed"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
先前的脚本在执行的时候只显示了`Enabling source address verification`这条信息而没有添加新行。默认的反向路径过滤的值是0,0表示没有源验证。因此,第二行简单地将默认值0覆盖为1。1表示内核将会通过确认反向路径来验证源(地址)。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,你可以使用下面的命令通过选择`DROP`或者`REJECT`目标中的一个来丢弃或者拒绝来自远端主机的被欺骗地址。但是,处于安全原因的考虑,我建议使用`DROP`目标。
|
||||
|
||||
像下面这样,用你自己的IP地址代替“IP-address” 占位符。另外,你必须选择使用`REJECT`或者`DROP`中的一个,这两个目标不能同时使用。
|
||||
```
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -i internal_interface -s IP_address -j REJECT / DROP
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -i internal_interface -s 192.168.0.0/16 -j REJECT/ DROP
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章只提供了如何使用iptables防火墙来避免远端欺骗攻击的基础(知识)。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/2/block-local-spoofed-addresses-using-linux-firewall
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Michael Kwaku Aboagye][a]
|
||||
译者:[leemeans](https://github.com/leemeans)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/revoks
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
||||
# chkservice -Linux终端管理系统单元的工具
|
||||
|
||||
systemd 即系统守护进程是一个新的初始化系统和系统管理工具,这个 systemd 非常流行,大部分的 Linux 发行版开始使用这种新的初始化系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Systemctl 是一个 systemd 的工具,它可以帮助我们管理 systemd 守护进程。 它控制系统启动和服务,使用并行化方式,套接字和 D-Bus 激活启动服务,提供按需启动守护进程,使用 Linux 控制组跟踪进程,维护挂载和自动挂载点。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,它还提供了守护进程日志、用于控制基本系统配置如主机名、日期、地区、维护登录用户列表和运行容器和虚拟机、系统帐户、运行时目录和设置,以及守护进程来管理简单的网络配置、网络时间同步、日志转发和名称解析。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
[chkservice][1] 是一个基于 ncurses 的在终端中管理系统资源的工具。它提供了一个非常全面的系统资源视图,可以使它们非常容易修改。
|
||||
|
||||
只有拥有超级管理权限才能够改变系统资源状态和系统启动脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 安装 chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以通过两种方式安装 chkservice,通过包安装或者手动安装。
|
||||
|
||||
对于 `Debian/Ubuntu`,使用 [APT-GET Command][2] 或 [APT Command][3] 安装 chkservice.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linuxenko/chkservice
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于 `Arch Linux` 系的系统,使用 [Yaourt Command][4] 或 [Packer Command][5] 从 AUR 库安装 chkservice。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ yaourt -S chkservice
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ packer -S chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于 **`Fedora`** , 使用 [DNF Command][6] 安装 chkservice。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf copr enable srakitnican/default
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于 `Debian` 系系统,使用 [DPKG Command][7] 安装 chkservice。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ wget https://github.com/linuxenko/chkservice/releases/download/0.1/chkservice_0.1.0-amd64.deb
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i chkservice_0.1.0-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于 `RPM` 系的系统,使用 [DNF Command][8] 安装 chkservice。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum install https://github.com/linuxenko/chkservice/releases/download/0.1/chkservice_0.1.0-amd64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用 chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
只需输入以下命令即可启动 chkservice 工具。 输出分为四部分。
|
||||
|
||||
* **`第一部分:`** 这一部分显示了守护进程的状态,比如可用的 [X] 或者不可用的 [] 或者静态的 [s] 或者被掩藏的 -m-
|
||||
* **`第二部分:`** 这一部分显示守护进程的状态例如开始 [ >] 或者停止 [=]
|
||||
* **`第三部分:`** 这一部分显示单元的名称
|
||||
* **`第四部分:`** 这一部分简短地显示了守护进程的一些信息
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo chkservice
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![][10]
|
||||
|
||||
要查看帮助页面,点击 `?` 按钮。 这将向您显示管理 systemd 服务的可用选项。
|
||||
|
||||
![][11]
|
||||
|
||||
选择要启用或禁用的守护进程,然后点击`空格键`按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
![][12]
|
||||
|
||||
选择你想开始或停止的守护进程,然后点击 `s` 按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
![][13]
|
||||
|
||||
选择要重新启动的守护进程,然后按 `r` 按钮。 点击 `r` 键后,您可以在顶部看到更新的提示。
|
||||
|
||||
![][14]
|
||||
|
||||
按 `q` 按钮退出。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.2daygeek.com/chkservice-a-tool-for-managing-systemd-units-from-linux-terminal/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ramya Nuvvula][a]
|
||||
译者:[amwps290](https://github.com/amwps290)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.2daygeek.com/author/ramya/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/linuxenko/chkservice
|
||||
[2]:https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-get-apt-cache-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.2daygeek.com/install-yaourt-aur-helper-on-arch-linux/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.2daygeek.com/install-packer-aur-helper-on-arch-linux/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.2daygeek.com/dnf-command-examples-manage-packages-fedora-system/
|
||||
[7]:https://www.2daygeek.com/dpkg-command-to-manage-packages-on-debian-ubuntu-linux-mint-systems/
|
||||
[8]:https://www.2daygeek.com/rpm-command-examples/
|
||||
[9]:data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
|
||||
[10]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-1.png
|
||||
[11]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-2.png
|
||||
[12]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-3.png
|
||||
[13]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-4.png
|
||||
[14]:https://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/chkservice-to-manage-systemd-units-5.png
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user